
The Analysis of Victim Wound Quality and Quantity in Assuming
The Perpetrator’s Psychological Condition to Determine The
Perpetrator’s Legal Liability
Ignatius N.S.
1
, Mieke Sylvia Margaretha
2
and Ahmad Yudianto
3
1
Department of Forensic Science, Postgraduate School, Universitas Airlangga, Jl. Airlangga no. 4-6, Surabaya, Indonesia
2
Department of Forensic Odontology, Faculty of Dentistry, Universitas Airlangga, Surabaya, Indonesia
3
Department of Forensic Medicine, Faculty of Medicine, Universitas Airlangga, Surabaya, Indonesia
Keywords: Forensic Science, Forensic Psychology, Wound Examination, Insanity
Abstract: In the law enforcement process, cases are often found where the perpetrator/defendant has a psychological
condition that positions them as mentally unstable subjects; or known in the famous plea of “innocent due to
insanity”. Procedurally, the examination to determine one’s mental condition must meet several
requirements as described in Article 44 of the Criminal Code (KUHP) and also Health Act No. 18 of 2014
on Mental Health Article 71; but these conditions tend to be inflexible to the dynamics of Indonesian
society, especially due to the vast plurality and the legal system in Indonesia that are different from other
countries. In addition, these conditions are vulnerable to exploitation as a method of avoiding legal liability
in some cases that have occurred lately because the verification process tends to be held in the court, which
gives the perpetrator some advantages. Therefore, other methods are needed in order to provide additional
data that can raise the objectivity and reliability analysis of law enforcers, such as wound analysis. In this
study, we will compare some medical examination reports with various properties that revolve around
wounds. The conclusion is that there is a correlation between the number of injuries and the victim's manner
of death which, when traced, can provide additional data that can be used to describe the emotional
condition of the perpetrator at the time of the incident. It still needs to be retested with a larger sample to
gain a more valid and reliable result considering the sample used is a coroner's report, and often the reports
are (a) missing or (b) incomplete as attached to them are letters stating ‘not willing to go through autopsy’.
1 INTRODUCTION
Today, in the law enforcement process there are
often cases where the perpetrator/defendant has a
psychological condition that positions the defendant
as a mentally ill subject; in Indonesia it is legally
known as ODMK/ODGJ. Some of the most common
examples are shooting cases in the United States
where the culprit after being captured/identified
tends to be classified as ODMK/ODGJ. Indeed this
does not very often appear in Indonesia, but with
socio-economic conditions that tend to fluctuate this
can be an exploited gap in order to keep the
perpetrators/defendants from prosecution or
punishment.
Globally, the handling of criminal acts involving
actors as ODMK/ODGJ follows and is adapted by
the World Health Organization (WHO) "Guidelines
for the Promotion of Persons with Mental Disorder"
under the UN resolution in Geneva. Locally, in the
process of law enforcement in Indonesia, if the
perpetrator is found with conditions that meet the
criteria already mentioned, the procedure will be
handled under the protection of the Criminal Code
Article 44 and also endorsed by Health Act No. 18
of 2014 on the Mental Health Article 71. Both
regulations are based on the definition of psychology
and psychopathology of insanity, which can be
described as a behavioural or mental pattern that
causes significant distress or impairment (D.F.L.,
2008; Heffner, 2018; Hockenbury & Hockenbury,
2010) of personal functioning such as the cognitive
process of the mind (Hastie & Dawes, 2010).
In addition, based on some experience shared by
fellow Indonesian forensic colleagues, a unique fact
was revealed that the presence of forensic
psychologists in Indonesia tends to be scarce and the
N.S., I., Margaretha, M. and Yudianto, A.
The Analysis of Victim Wound Quality and Quantity in Assuming The Perpetratorâ
˘
A
´
Zs Psychological Condition to Determine The Perpetratorâ
˘
A
´
Zs Legal Liability.
DOI: 10.5220/0007542003170320
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference Postgraduate School (ICPS 2018), pages 317-320
ISBN: 978-989-758-348-3
Copyright
c
2018 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
317

use of psychological services tends to call in the help
of psychologists from outside the region. Moreover,
if the psychologist is not available then the one
called by the police is a psychiatrist; which also
makes the handling biased and cases more
complicated due to different professional
backgrounds and job focuses, where psychologists
are more concerned with subject detection and
history, while psychiatrists are more in the direction
of medical treatment and drug delivery.
Moreover, the evaluation of a perpetrator’s
psychological condition is imperative for the
criminal investigation (Heillburn, 1992; Klein-
Benheim & Jacobs, 1995) and the advancement of
the scientific scope which can also improve the
value of an expert witness testimony (Solomon,
2017). Based on the explanations that have been
described, it takes a method that could provide
additional examination data that can improve the
objectivity and reliability of the investigator's
analysis in law enforcement. That method is in the
form of wound analysis.
The wound is defined as the breakdown or loss
of some body tissues (Kumar et al., 2007; Potter &
Perry, 2017; Sjamsuhidayat & Jong, 2004;
Budiyanto, 1997; Dorland, 2002). Injury can result
from sharp stabs/blows, blunt objects, accidents,
shots, animal bites, chemicals, hot water, water
vapour, exposure to fire, electricity and lightning
(Murtutik & Marjiyanto, 2013). In some case
development, it is often found that when the victim
is injured with severe damage or with a large
number of injuries, the offender is often the person
diagnosed as ODMK/ODGJ. By pattern, a wound
itself is differentiated into four patterns (Knight,
2002) such as: a) Abrasion like grazes or scratches;
b) Contusion like bruises; c) Laceration like a cut or
tear; and d) Incised Wound like cuts, slashes, stabs,
etc.
So far, the number and pattern of injuries
inflicted by violence/crime in which the offender is
implied as ODGJ/ODMK has not been widely
studied; the wound analysis is often used but only as
a variable to support the analysis of medical
treatment methods and is rarely used in forensic and
law enforcement aspects (Mustafa, 2007). As a past
study concludes, there are factors that can be
described from the condition of the wound regarding
the perpetrator’s mental health condition (Turvey,
2007). Thus, practically, judgment based on this
wound analysis can provide concise, valid and
reliable decisions without the aid of psychological
tests on the psychiatric condition of the offender.
In this study, we will compare some medical
reports that include some of the following criteria:
(1) unnatural death, (2) deaths due to the actions of
others, (3) victims with severe injuries, (4) victims
with a large number of wounds. Researchers also do
not eliminate the possibility of emergence of
interference/restriction that hinders maximum data
retrieval. The interruptions include, among other
things, missing reports and incomplete reports that
do not meet the criteria.
2 MATERIALS AND METHOD
This research method used paralleled literature
reviews on available studies of wounds and the
psychological condition based on DSM-V
guidelines. The data collection process was
conducted at the Department of Forensic Medicine,
RSUD Dr. Soetomo, Surabaya. The methodology of
this research is described as follows;
Figure 1: Methodology of the research
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Based on the data collected, there are approximately
170 cases with the properties that match the criteria
for the studies. But after further inspection, there are
only 40 cases that can be used as data for this study;
which is described in the tables below.
Table 1: Number of reports used in the study.
Year
Number of Cases
2011
1
2012
5
2013
6
2014
1
2015
4
2016
6
2017
14
Phase 1
• Collecting of data from mortality reports
with time frame of the past 5 years.
Phase 2
• Sorting the data based on the criteria of
the quantity and quality of the wounds
and the cause of death.
Phase 3
• Analyzing and recording the data.
ICPS 2018 - 2nd International Conference Postgraduate School
318
Year
Number of Cases
2018
3
TOTAL
40
Table 2: CoD and MoD comparison of reports used
Table 3: Classification of wounds from the report data
under study.
Year
Type of Wound
Bruise
Abrasion
Stab
Bite mark
2011
24
16
15
2012
25
20
17
2013
27
19
18
2014
30
18
18
2015
31
22
19
2016
26
23
25
2017
30
19
17
2018
29
20
19
1
TOTAL
Figure 2: The 1
st
bite mark on the body
Figure 2: The 2
st
bite mark on the body
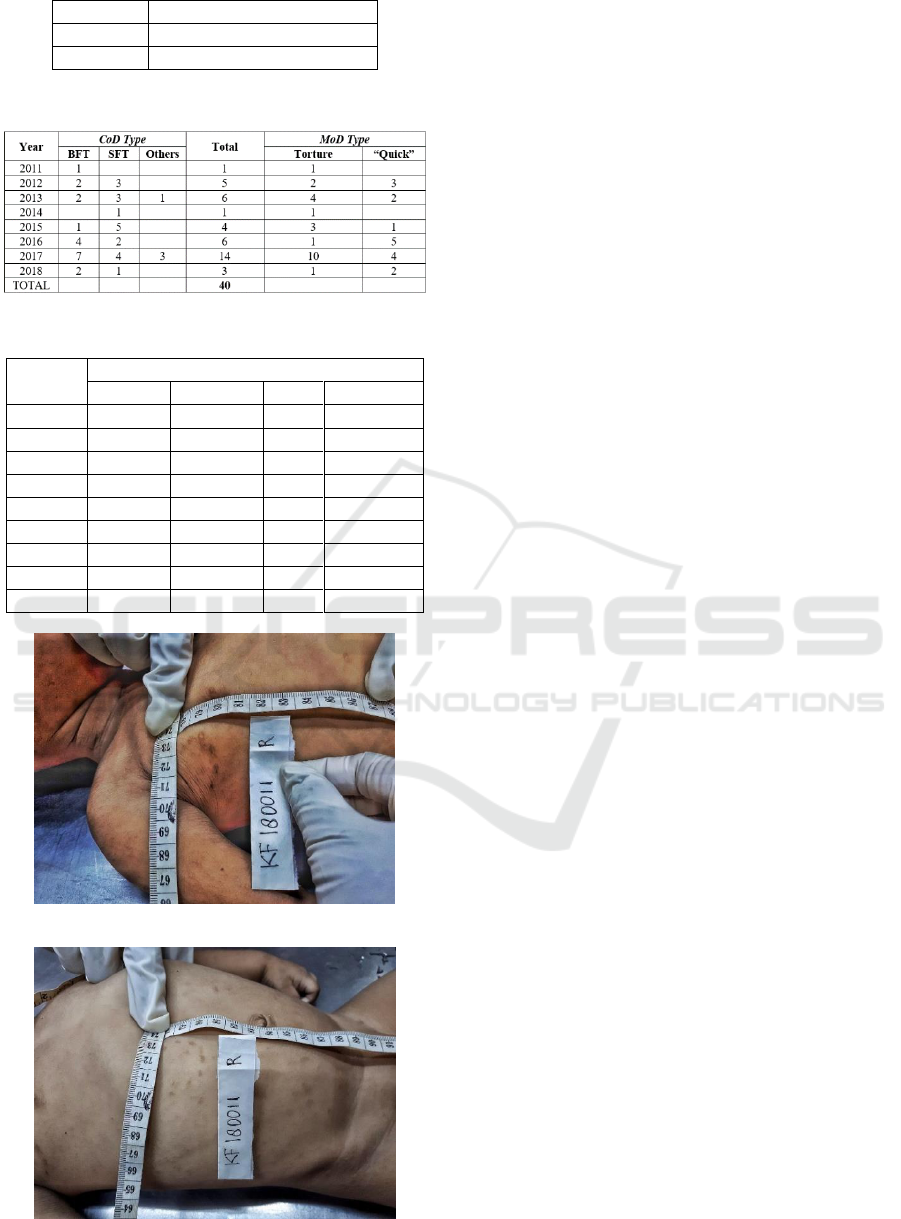
In one particular case, there is a wound that can
be described as a bite mark (photos below). As per
further research indicates, the perpetrator of the
corresponding case is regarded as mentally ill.
The obstacle in this study is that the sample used
is strictly evidence-based on the report from the
morgue. The researcher cannot determine the exact
validity from the perpetrator’s side due to the fear of
contaminating ongoing investigation. Furthermore,
the pool of the data has reduced from 170 reports to
40 reports due to the impartiality of the reports. The
impartiality is caused by the existence of the letter
for “not undergoing normal autopsy”, which
happens in Indonesia due to the social norms that the
body must not be tampered with and must be quickly
buried.
4 CONCLUSIONS
In this research, it is found that bite marks are more
likely to occur in cases that indicate the victim and
the offender have a kinship/emotional relationship.
This conclusion still needs to be reconfirmed by
increasing the number of samples because cases with
bite marks found in this study account for only one
and the overall types of bite mark lesions tend to be
rare and not even categorized as an individual type
of wound. From the cases, there is a correlation
between the number of injuries and the manner of
death in which in the further search and the manner
of death can provide a partial picture for the
emotional state of the perpetrator. The emotional
picture also needs to be confirmed because this
research did not study the perpetrator’s end for
fearing disturbing ongoing police investigation. By
these results and circumstances, it is concluded that
the psychological measurement of a perpetrator can
not be seen based on the form of his crime, but the
consequences of the offender's offense can be used
to look at the emotional state of the offender at the
time of his/her conduct for further examination if
there is a strong allegation that person is
ODMK/ODGJ.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The author conveys gratitude to the staff of the
Department of Forensic Medicine, which also
includes the medical examiners for helping
categorize the reports. The author also conveys
The Analysis of Victim Wound Quality and Quantity in Assuming The Perpetratorâ
˘
A
´
Zs Psychological Condition to Determine The
Perpetratorâ
˘
A
´
Zs Legal Liability
319

gratitude to Mr. Pudji Hardjanto for giving expert
opinions based on his experience in law enforcement
for this research.
REFERENCES
Budiyanto A, e. a. (1997). In Ilmu Kedokteran Forensik
(pp. 3-11, 15-16, 26-33, 55-57, 64-70.). Jakarta:
Bagian Kedokteran Forensik FKUI.
Carter, R. T., & Forsyth, J. M. (2007). Examining race and
culture in psychology journals: The case of forensic
psychology. Professional Psychology: Research and
Practice, XXXVIII(2), 133-142.
D, F. L. (2008). Psychology: Six perspectives (pp. 12–15).
Thousand Oaks: Sage Publications.
Hastie, R., & Dawes, R. M. (2010). Rational Choice in an
Uncertain World: The Psychology of Judgment and
Decsision Making. London: Sage.
Heffner, C. (2018). Chapter 9: Section 1:
Psychopathology. Retrieved from http://allpsych.com:
http://allpsych.com/psychology101/psychopathology/#
.VOUVvvnF-VJ
Heilbrun, K. (1992, June). The Role of Psychological
Testing in Forensic Assessment. Law and Human
Behavior, 16(3), 257-272.
Hockenbury, & Hockenbury. (2010). Psychology. Worth
Publishers.
Kamus Kedokteran Dorland. (2002). Jakarta : EGC
MEdical Publisher.
Klein-Benheim, M., & Jacobs, D. (1995). The
Psychological Autopsy: A Useful Tool for
Determining Proximate Causation in Suicide Cases.
Bull Am Acad Psychiatry Law, 23(2), 165-182.
Kumar, V., Abbas, A. K., Fausto, N., & Mitchell, R. N.
(2007). Robbins Basic Pathology. Philadelphia:
Elsevier.
Murtutik, L., & Marjiyanto. (2013). Hubungan Kadar
Albumin Dengan Penyembuhan Luka Pada Pasien
Post Operasi Laparatomy Di Ruang Mawar Rumah
Sakit Slamet Riyadi Surakarta. Jurnal Ilmu
Keperawatan Indonesia, VI, 3.
Mustafa, M. (2007). Kriminologi. Depok: FISIP UI
PRESS.
Nasional, B. P. (n.d.). Kitab Undang-Undang Hukum
Pidana. Jakarta.
Oshima, T. (2000). Forensic Wound Examination.
Forensic Science International, 153-164.
Potter, P. A., & Perry, A. G. (2017). Buku Ajar
Fundamental Keperawatan : Konsep,. Amsterdam:
Elsevier.
Saukko, P., & Knight, B. (2004). Knight's Forensic
Pathology. London: Edward Arnold.
Sjamsuhidayat, R., & Jong, W. d. (2004). 2004. Buku Ajar
Ilmu Bedah, Edisi 2,. Jakarta: EGC.
Solomon, N. (2017). Redefining the psychological
autopsy: A proposal for collaboration between
forensic pathology and investigative psychology.
Journal of Investigative Psychology and Offender
Profiling, 46-50.
Turvey, B. E. (2016). Criminal Profiling: An Introduction
to Behavioral Evidence Analysis (Vol. IV). Ann
Arbor, Michigan, USA: Academic Press.
UNDANG-UNDANG REPUBLIK INDONESIA
NOMOR 18 TAHUN 2014 TENTANG
KESEHATAN JIWA. (2014, August 7). Lembaran
Negara Republik Indonesia.
APPENDIX
ODGJ: Orang Dengan Gangguan Jiwa (person with
mental disorder)
ODMK: Orang Dengan Masalah Kejiwaan (person
with psychiatric problems)
ICPS 2018 - 2nd International Conference Postgraduate School
320
