
Correlation between Parasite Density with Plasma Levels of TNF-α
and IL-10 in Malaria Mix Infection in East Sumba District, East Nusa
Tenggara Province
Meka Faizal Farabi
1
, Heny Arwati
2
Yoes Prijatna Dachlan
2
1
Sekolah Pascasarjana, Universitas Airlangga, Surabaya, Indonesia
2
Department of Parasitology, Universitas Airlangga, Surabaya, Indonesia
Keywords: Mix Malaria, Parasite Density, TNF-α, IL-10
Abstract: East Nusa Tenggara Province is a malaria endemic area located in Eastern part of Indonesia with Annual
Parasite Incidence of 7.04% including falciparum malaria, vivax malaria and mix malaria. The information
on parasite density and plasma levels of TNF- α and IL-10 in mix malaria infection is rarely found. This
research is conducted to collect the information mentioned above. Methods: Diagnosis of malaria infection in
subjects was done by Rapid Diagnostic Test (RDT) as well as microscopy examination. Parasite density was
calculated based on number of parasite per 200 leukocytes on the Giemsa-stained thick blood films. Levels
of TNF-α and IL-10 in plasma were measured using Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA).
Results: Five patiensts were diagnosed as mix malaria infection, with average of parasite density was 4341
paracite/µL. Average level of TNF-α and IL-10 was 207.31 pg/mL and = 15.91 pg/mL, respectively. Ratio of
TNF-α : IL-10 was 13 : 1. This research concludes, increased levels of TNF-α will decrease the parasite
density based on the time of infection, while the increase in parasite density is directly proportional to elevate
levels of IL-10 (p= 0,032).
1 INTRODUCTION
Malaria is a long-standing disease that still threatens
the lives of children, pregnant women and many
others in East Nusa Tenggara (ENT). Indonesian
malaria reports show that the population of ENT,
which accounts for 2% of Indonesia's population,
contributes to 25% of the total incidence of malaria in
Indonesia. On the island of Sumba itself the Annual
Parasite Incidence is high (Pusdatin, 2016).
Indonesia is located in a tropical which is the
endemic area of P. falciparum and P. vivax and high
transmission rate of malaria through mosquito bites
makes it possible for repeating inoculation by both
Plasmodium and causing mixed infection (Imwong,
2011).
Clinical conditions of people infected with mixed
malaria differ from those infected with single malaria,
this is due to the interaction between Plasmodium in
human hosts. The P. falciparum parasite has a faster
life cycle than P. vivax. The temperature of fever with
mixed infection is higher than single infection
(McKenzie, 2006).
The aim of this research is to determine the
relationship between parasite density with plasma
levels of TNF-α and IL-10 in patients with P. vivax
and P. falciparum mixed infections in East Sumba
Distric, East Nusa Tenggara.
2 IMMUNE RESPONSE DURING
MALARIA INFECTION
2.1 Innate Immune Response
Innate immune system is the first step in the immune
response to pathogens. The system includes a variety
of nonspecific responses such as recruitment of
immune cells to the site of infection, complement
cascade activation, destruction of foreign objects by
specific leukocytes and activation of the adaptive
immune system through antigen presentation (Clark,
2010). The main function of innate immunity is to
limit the parasitic density of the initial infection and
to modulate the specific immune response necessary
to eliminate parasites (Stevenson, 2004).
418
Farabi, M., Arwati, H. and Dachlan, Y.
Correlation between Parasite Density with Plasma Levels of TNF-Î
´
s and IL-10 in Malaria Mix Infection in East Sumba District, East Nusa Tenggara Province.
DOI: 10.5220/0007544104180421
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference Postgraduate School (ICPS 2018), pages 418-421
ISBN: 978-989-758-348-3
Copyright
c
2018 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

Non-specific immune responses are represented
by multiple cells and intercellular components. One
of the innate immune systems that will respond
during a malaria infection is the mononuclear
phagocyte system (MPS), which includes monocytes,
macrophages, and dendritic cells (Mac-Daniel, 2015).
2.2 Adaptive Immune Response
2.2.1 Cellular
In the cellular immune response, T lymphocytes are a
major component of the immune system that serves
to recognize and destroy antigens through cytotoxic
activity and cytotoxic activation and activation of
various cell types and cytokine production (Abbas,
2012).
2.2.2 Humoral
The main characteristic of the Plasmodium parasite
that infects the erythrocytes is increasing the
production of Tumor Necrosis Factor alpha (TNF-α)
cytokines from macrophages, malaria pigments and
glycolipids such as Glycosil Phosphatidyl Inositol
(GPI). TNF is a major cytokine in acute inflammatory
responses. Severe infections can trigger the
production of TNF in large quantities that lead to
systemic reactions. TNF-α is produced by
neutrophils, activated lymphocytes, macrophages,
Natural Killer (NK) cells and some non-lymphoid
cells such as astrocytes, endothelial cells and smooth
muscle cells (Dietrick, 2008).
TNF-α plays a role in regulating Interleukin 12
(IL-12) production by macrophages and shows that
TNF-α is important as a co-factor for IL-12 in
increasing Interferon (IFN) production by NK cells.
TNF-α concentrations in plasma are associated with
changes in fever and parasite clearance
(Malaguarnera, 2002).
IL-10 that produced by monocytes is found in
plasma of patients with acute malaria. Th2 cells and
B cells, inhibiting cytokine production in Th1 and
CD8+ cells. IL-10 increases cell proliferation and
immunoglobulin production necessary for the
development and maturation of anti-malarial
antibodies. IL-10 also serves as a down regulator in
macrophages, reduces antigen presentation, plays an
important role in neutralizing the pathology of
macrophages in cerebral malaria by inhibiting IFN-γ
and TNF-α secretions (Malaguarnera, 2002).
3 METHOD
3.1 Location
This research was done in East Sumba district of the
Province of ENT. This province is located in Eastern
part of Indonesia that contain 7 islands. East Sumba
distric also contains several small islands. Easter
Sumba district bordered by the Sumba strait on the
north, Hindia ocean to the south, Sabu sea to the east
and Central Sumba district to the west. This district
that located in tropical region has rainy during
January-April and the rest was dry season, causing
this region classified as dry area (BPS Sumba Timur,
2016).
3.2 Blood Samples Collection
Blood sample colletcion was done by active and
passive malaria case detections. Active case was
performed by visitsing malaria suspected patient in
high transmission areas. Passive case detection was
carried out by collecting the blood samples of patients
who visiting Public Health Centers (PHC) and
Lindimara Christian Hospital. Prior to blood colletion
the characteristics of patients were recorded including
name, gender, age and address. All individuals aged
from four to seventy years old of both sexes included
in the study. Three millilitres of blood were collected
by vena punctured after the patient signed the
informed consent to prepare thick and thin blood film
and plasma collection. Inclusion critera were people
who diagnosed positive mixed malaria infection
containing P. falciparum and P. vivax by Rapid
Diagnostic Test (RDT) and microscopy examination.
3.3 Microscopy Examination and
Parasite Density Count
Microcopy examination was done on Giemsa-stained
thick and thin blood film using light microscop under
1000x magnification with oil immersion to detect
and identify the species of malaria parasites.
Detection by RDT was conducted by the staff of
PHC. Parasite density were counted per 500
leucocyte based on the following formula:
(1)
Correlation between Parasite Density with Plasma Levels of TNF-Î
´
s and IL-10 in Malaria Mix Infection in East Sumba District, East Nusa
Tenggara Province
419
3.4 Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent
Assay (ELISA)
Plasma levels of TNF-α and IL-10 were measured by
using ELISA according to the manufacturer’s
protocol (Elabscience, USA), with all samples
running in a single assay. The ELISA was performed
andnd analysed by a single operator, and standard
curves were derived from cytokine standards.
3.5 Data Analysis
A total of 110 individuals enrolled in this study, 64
were diagnosed negative malaria, 22 diagnosed as
positive P. falciparum, 19 diagnosed as positive P.
vivax and 5 diagnosed as positive mixed malaria.
4 RESULT AND DISCUSSION
4.1 Thick Blood Smear Examination
Subject diagnosed as positive mixed malaria have 2
types of Plasmodium that is P. falciparum and P.
vivax can be seen under microscope. The result of
thick blood film examination as follow:
Figure 1. Microfotography of mixed malaria thick blood
smear
Seen in Figure 1. the difference between the two
species of the ring and the trofoocytic nucleus P.
vivax is thicker and larger (blue arrow) than the ring
and nucleus of the thin and small P. falciparum
trophosoit (red arrow)
4.2 Parasite Density
Five samples were examied with ELISA and found
the Parasite Density as follow:
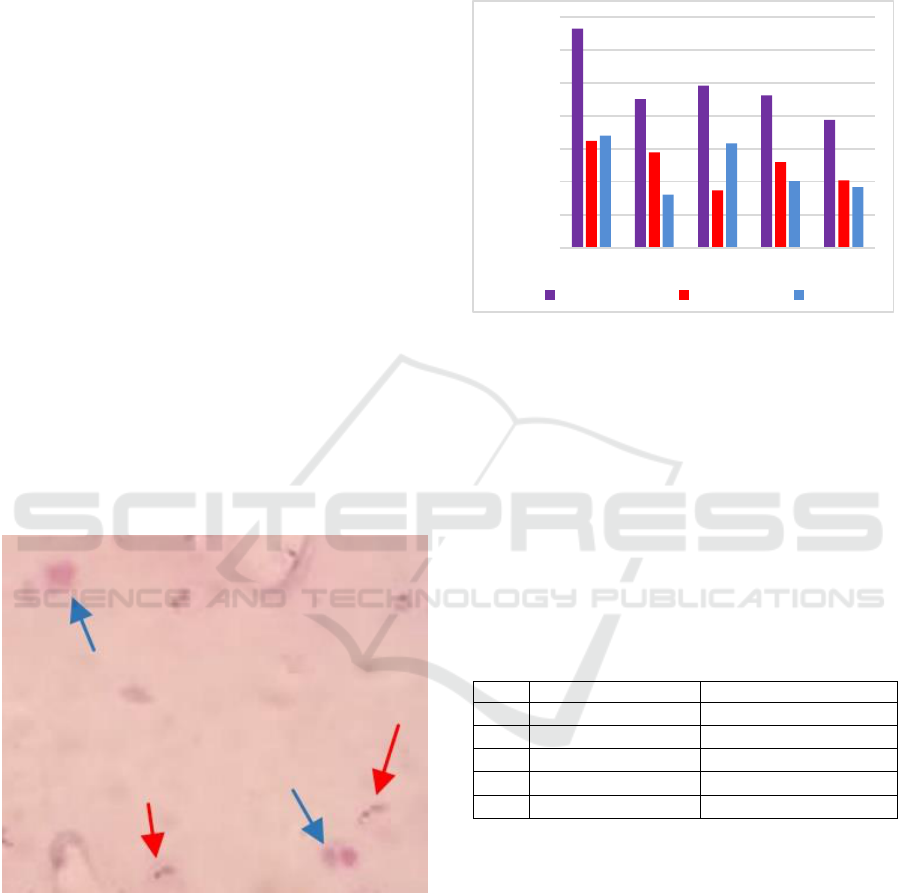
Figure 2. Parasite density of subject with mixed malaria
The highest parasitic density was 6,656
parasites/μL while the lowest parasitic density was
3,888 parasites/μL. From Figure 2. the mean ratio
between P. falciparum and P. vivax is 1.04: 1
indicating no dominant Plasmodium in mixed
infections found.
4.3 Plasma Cytokine Level
Five samples were examined with ELISA and found
the level of of TNF-α and IL-10 as follow:
Table 1. Plasma cytokine level of mixed malaria
No.
TNF- α
IL-10
1.
0
10,523
2.
94,861
35,559
3.
0
0
4.
101,085
0,807
5.
425,983
11,369
Subjects 1 and 3 have very low levels of TNF-α
and can not be detected with ELISA. Subjects with
low TNF-α levels were subjects 2 and 4 of 94.861
pg/mL and 101.085 pg/mL respectively, whereas
highest TNF-α levels were in sample 5 of 425.983
pg/mL. Subjects 1 and 5 had relatively low IL-10
levels of 10.523 pg/mL and 11.369 pg/mL while the
highest IL-10 levels were in sample 2 of 35.559
pg/mL. Subject 4 had a very low IL-10 level of 0.807
pg/mL and subject 3 was very low and undetectable
at ELISA. From Figure 2. can be determined the ratio
of TNF-α and IL-10 for each subject. Subject 1 has
ratio TNF-α : IL-10 of 0, subjet 2 ratio 2,67:1, subject
0
1000
2000
3000
4000
5000
6000
7000
1 2 3 4 5
Parasite Density
Total Parasite Falciparum Vivax
ICPS 2018 - 2nd International Conference Postgraduate School
420

3 ratio 0, subject ratio 125,15:1 and subject 5 ratio
37,47:1.
4.4 Statistical Analysis
Statistical analysis were conducted to data from 5
subjects. Kolgorov-Smirnov test were used to
describe the distribution of samples. The results of
these tests show the distribution of the sample is
normal with p > 0,05.
With normal distribution sample, next analysis is
using Pearson corellation test to determine the
correlation between parasite density, TNF-α, IL-10
and the ratio of both cytokines. Correlation is
significant at the p < 0,05. The result shows that no
significant correlation between parasite density and
TNF-α with p= 0,213 also no significant correlation
between parasite density and cytokine ratio with p=
0,130. But there is a significant correlation between
parasite density and IL-10 with p= 0,032.
4.5 Discussion
Increased levels of IL-10 correlate with increased
parasitemia. Exemplified by the highest parasite
density in subjects No. 1 compared to 4 other
subjects. The increase in IL-10 accompanied by very
low levels of TNF-α shows IL-10 anti-inflammatory
cytokines suppress the performance of TNF-α as a
pro-inflammatory cytokine in eliminating parasites
(Othoro, 1999). Subjects No. 2 showed an imbalance
of pro and anti-inflammatory cytokines responses
because with parasite densities that were still 4,512
parasites / μL the levels of IL-10 had increased to
reduce the TNF-α: IL-10 ratio of 2.67: 1, if IL-10
levels were continues to increase whilst TNF-α level
were decreased, the correlation was parasite density
in subject No.2 would not decrease. Plasma level of
IL-10 subjects No.4 need to be re-examined to see the
direction of change, if IL-10 remains in a low state
then TNF-α levels will be uncontrolled and at risk of
causing malaria complications. If IL-10 levels
increase optimally, there will be a regulatory balance
between pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory
cytokines. Subjects No.3 has no detectable plasma
cytokine level, this correlates with the parasite
density that still considerably high because no
cytokines response from the subject. Subject No.5 has
a clinical manifestation of high body temperature, this
indicates that level of TNF-α were increased thus
inhibiting the growth of parasite. This correlation can
be seen by the Parasite Density of Subject No.5 was
the lowest among other subjects.
5 CONCLUSIONS
Increased levels of TNF-α will decrease the parasite
density based on the time of infection but an
excessive increase will lead to complications of
malaria. While the increase in parasite density is
directly proportional to elevate levels of IL-10 is
evidenced by statistically significant correlation
between parasite density and IL-10 (p = 0,032).
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The author would like to thank all community health
centers’ staff in East Sumba that help us to collect
samples especially Nikson and Luluk which provide
us a lot of information.
REFERENCES
Imwong M1, Nakeesathit S, Day NP, White NJ. A Review
Of Mixed Malaria Species Infections In Anopheline
Mosquitoes. Malar J. 2011 Aug 31;10:253. doi:
10.1186/1475-2875-10-253.
Pusat Data dan Informasi Kementrian Kesehatan RI.
InfoDATIN Malaria 2016. ISSN 2442-7659
McKenzie, F. Ellis. et al. Fever in Patients with Mixed-
Species Malaria. Clinical Infectious Diseases 2006;
42:1713–8
Stevenson M.M. & Riley E.M. 2004. Innate Immunity to
Malaria. Nat Rev Immunol. 4(3): 169-180
Mac-Daniel L. & Menard R. 2015. Plasmodium and
Mononuclear Phagocytes. Mikrob Pathog. 78: 43-51
Abbas A.K., Litchman A.H., Pillai S. 2012. Properties and
Overview of Immune Responses; Cell and tissues of
Immune System. Cellular and Molecular Immunology,
seventh ed. Philladelphia: Elsevier Sunders; p. 1-36.
Detrick B, Nagineni CN, Hooks J. Cytokines: Regulators of
Immune Responses and Key Therapeutic Targets. IN:
Gorman MRG ,Donnenberg AD. (Eds). Handbook of
Human Imunology. 2nd ed. CRC Press, 2008.
Malaguarnera, L., Musumeci, S. The immune response to
Plasmodium falciparum malaria. Lancet Infect Dis.
2002; 2: 472 – 8.
Bruno B Andrade et al. Severe Plasmodium Vivax Malaria
Exhibits Marked Inflammatory Imbalance. Malaria
Journal 2010, 9:13
Ju¨ rgen May et al. Plasma Interleukin-10:Tumor Necrosis
Factor (TNF)-α Ratio Is Associated with TNF Promoter
Variants and Predicts Malarial Complications. The
Journal of Infectious Diseases 2000;182:1570–3
Caroline Othoro et al. A Low Interleukin-10 Tumor
Necrosis Factor-a Ratio Is Associated with Malaria
Anemia in Children Residing in a Holoendemic Malaria
Region in Western Kenya. The Journal of Infectious
Diseases 1999;179:279–82
Correlation between Parasite Density with Plasma Levels of TNF-Î
´
s and IL-10 in Malaria Mix Infection in East Sumba District, East Nusa
Tenggara Province
421
