
Experiment Study on Water Diversion and Sediment Control
of North Canal Expansion Project
H H Hu
*
, A J Deng, Z D Dong, W D Wang and M Ye
China Institute of Water Resources and Hydropower Research, Beijing, China
Corresponding author and e-mail: H H Hu, sowaco@iwhr.com
Abstract. This paper mainly analyses the evolution trend of river bed before and after the
construction of water intake project, and optimizes the layout of water intake project and
sluice by comparing the difference through physical model experiment study. Meanwhile, it
examines the limit scour ability and protective measures for energy dissipation of sluice by
using theoretical analysis and experimental research and verifies the diversion capacity of the
channel after the construction of water intake project and put forward the corresponding
sediment control measures. The experiment results show that the layout of water intake
project and sluice is reasonable, and it is less affected the flow characteristics of the river
channel and changes in scouring and silting of the bed surface; it is met the requirements of
the design that the amount of water for design sluice can reach 149m
3
/s; it is reco mmended to
appropriately increase the design size of stiller and apron for the actual needs; the measure of
sediment control is proposed that scouring sediment by using sluice can reduce the bed
surface elevation near Fish Mouth in order to reduce the coarse sediment into the diversion
channel. This research provides the scientific basis and technical support for the optimizat ion
design of North Canal expansion project.
1. Introduction
1.1. Project overview
The headwork of Northern Nen River Diversion Project is located in the mainstream of Nen River
about 6 km away from the northwest of Laha Town, Nehe County, of which the control basin area is
96,211 km
2
. The control area of Nierji Reservoir in the mainstream of Nen River is 66,382 km
2
,
accounting for 69% of total headword. Since the headwork of Northern Nen River Diversion Project
was completed in 1976, great economic and social benefits have been brought to the downstream
industrial and agricultural development. In recent years, with the development of downstream
industrial and agricultural production and the increase of urban residential living water, the diversion
scale of original headwork (no-dam diversion) has become increasingly inadequate and needs to be
expanded. On the other hand, the upstream Nierji Reservoir has been completed to be put into use,
which will guarantee to provide favorable conditions for the safety and diversion expansion of the
headwork of Northern Nen River Diversion Project. However, due to the headwork of Northern Nen
River Diversion Project located in the midstream of Nen River, this segment of river channel is flat
and braided with slow drop gradient and small swale difference. Although renovation has been
Hu, H., Deng, A., Dong, Z., Wang, W. and Ye, M.
Experiment Study on Water Diversion and Sediment Control of North Canal Expansion Project.
In Proceedings of the International Workshop on Environmental Management, Science and Engineering (IWEMSE 2018), pages 207-216
ISBN: 978-989-758-344-5
Copyright © 2018 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
207

carried out for many years, the current big regime has been under control, but local erosion and
deposition has still occurred. In particular, after the use of Nierji Reservoir and the barrage
construction of headwork with backwater, the conditions of inflow water and sediment as well as
water flow before the gate have changed greatly.
1.2. Basic characteristics of water and sediment in Nen River
Nen River originates from the south slope of Yilehuli Mountain in the Greater Khingan Mountains
with a total channel length of 1,370 km and a basin area of 29.70×10
4
km
2
. This basin belongs to the
mid-temperate continental monsoon climate zone, and the average precipitation in the middle and
lower reaches is 400~460 mm. The inter-annual precipitation is relatively large, and the intra-annual
precipitation is unevenly distributed. Precipitation is mainly concentrated in July - September,
accounting for about 70% of annual total. Heavy rains mainly occur in July and August, accounting
for 83.7% of annual total, of which July presents the most rainstorms, accounting for 60%. Torrential
rain is the main factor for the formation of flood in Nen River Basin, and the flood in Nen River
Basin is consistent with the characteristics of rainstorm, i.e., the floods of Nen River Basin are
mainly induced by several rainstorms [1].
Nen River has less sediment with a small number of sediment observation data. According to
statistics, the multi-year average suspended sediment discharge rate of Ayanqian Station is 13.54 kg/s,
multi-year average suspended sediment discharge is 42.7 x 10
4
t, multi-year average suspended
sediment content is 0.041 kg/m
3
, and the measured maximum suspended sediment content is 0.323
kg/m
3
. There are no observation data of bed load in Nen River Basin, and the bed-load sediment
discharge is calculated as 4.27 x 10
4
t according to the suspended load ratio of 10%, the multi-year
average total sediment discharge of Ayanqian Station is 47 x 10
4
t, and that at the headword of
Northern Nen River Diversion Project is calculated as 69 x 10
4
t according to the area [2].
2. Model design and validation
2.1. Model design
This model test is mainly to study the erosion and deposition evolution of the channel in the
mainstream of Nen River after building the sluice gate as well as the water intake and sediment
control situations of diversion channel. Due to Nen River with large water flow and small sediment
content, the channel evolution is mainly dominated by bed load. Therefore, during model designing,
in addition to consider the similar motion of water flow, it is mainly required to guarantee similar
motion of bed load with the consideration of similar motion of suspended sediment. Based on the
comprehensive consideration of model test requirements, test technical conditions, sediment grain
size, test simulation range and other factors, normal model is used in this local model test. According
to the gravity similarity criterion for design, model geometry scale is set as 80, and natural sediment
is used for model sediment. Due to no measured bed load data of this channel, the empirical formulas
such as the Sharmov Formula are adopted to estimate the bed-load sediment discharge rate and the
bed-load gradation under different flow levels. The results are shown in Figure 1.
IWEMSE 2018 - International Workshop on Environmental Management, Science and Engineering
208

Figure 1. Bed-load gradation under different flow levels.
2.2. Model validation
The channel segment simulated by this model test is short in lack of validation data, but in order to
ensure the reliability and accuracy of test results, based on the collected measured data and
theoretical analysis, this model test is mainly to validate several aspects such as water level, channel
erosion and deposition as well as the current diversion quantity of diversion channel.
For water level validation, except the local point with small water flow, the prototype under other
conditions accords well with model level, showing that model roughness and resistance are similar,
thus satisfying the precision requirement of model test. With the increase of river flow, the water
level error between the prototype and model is gradually decreasing, which is mainly due to the large
influence of channel morphology resistance in the case of small flow. For the validation of channel
erosion and deposition, the prototype and the model are consistent in the on-way erosion and
deposition trend, and the erosion and deposition places basically coincide. Moreover, the lateral
distribution of bed surface erosion and deposition has the basically consistent trend, showing that the
model is basically similar in the location and amplitude of erosion and deposition. For the calibration
of channel diversion quantity, when the great river flow is 126.00 ~ 445.00 m3/s, actual natural
diversion quantity is basically 8.02 ~ 40.00 m3/s, and the measured diversion quantity of the model is
basically 8.70 ~ 40.53 m3/s. The absolute error of the two values is nearly less than 0.70 m3 /s.
Except for the minimum level with larger relative error, other flow levels have the relative error
below 3%. Therefore, model measurement value is basically close to natural measurement value,
indicating that the accuracy of model production can meet the test requirements.
Experiment Study on Water Diversion and Sediment Control of North Canal Expansion Project
209

3. Analysis on river channel evolution before and after the construction of diversion junction
3.1. Water level changes of river channel before and after the construction of diversion junction
Test observation is carried out on the changes of channel water level at different flow levels of 500,
1500 and 2500 m
3
/s under four conditions, i.e., before the gate construction of diversion junction and
the constructions of 8-hole, 11-hole and 12-hole sluice gates. The results show that in the case of
small flow level, the backwater of small flow level has a large amplitude, which is about 100 cm. But
in the case of large inflow, the channel water level of normal inflow has exceeded control-application
water level, so the discharge gate is open to use, when the backwater at corresponding flow level has
a smaller amplitude, basic under 20 cm. In addition, under three arrangement schemes of 8-hole, 11-
hole and 12-hole sluice gates, the backwater amplitudes are basically approaching, and those of 11-
hole and 12-hole sluice gates are slightly smaller than 8-hole sluice gate.
3.2. River regime changes of river channel before and after the construction of diversion junction
In this test, the changes of river regime under the three flow levels of 500, 1500 and 2500 m
3
/s are
observed. When the flow is 500 m
3
/s, the mainstream bending is obvious. However, the mainstream
bending degrees at the two flow levels of 1500 and 2500 m
3
/s are reduced to a certain extent, but
artificial groin has more significant control on the mainstream than the natural change of river
channel. Through comparing the running trajectory of mainstream line before and after the gate
construction at three flow levels, it can be seen that there are no obvious changes in river regime
before and after the gate construction at the flow levels of 500, 1500 and 2500 m
3
/s. Therefore, after
the construction of diversion junction, whether the combination of 8-hole or 11-hole gates is used or
the scheme of total 12-hole gate is applied, the three arrangement schemes have basically not
changed the current running trend of original channel.
3.3. Flow velocity changes before and after the construction of diversion junction
As viewed from the test results of mean vertical velocity at three flow levels of 500, 1500 and 2500
m3/s before and after the construction of diversion junction, the location of maximum vertical
velocity at different flow levels on different cross sections basically corresponds to the lowest point
of river section, and the basic rule of velocity distribution is almost consistent with water depth
changes. The greater the water depth is, the larger the mean vertical velocity will be. Therefore,
before and after the construction of diversion junction, when the big river inflow is small, the control
of sluice gate is applied, resulting in sharp decrease of flow velocity in backwater segment. For the
flow of 500 m3 / s, flow velocity decreases by about 50%. When the big river inflow is large, the
floodgate is open to use, when the water intake junction has less effect on river velocity, and the
change rule of flow velocity and water level change correspond to each other.
3.4. Changes in riverbed erosion and deposition of river channel before and after the construction of
diversion junction
In order to increase comparability, the inlet water and sediment, outlet water level, initial topography
and other conditions of this erosion and deposition test scheme are identical. The on-way changes in
channel erosion and deposition before and after the construction of diversion junction are shown in
Figure 2. As viewed from the overall change trend, the on-way riverbed erosion quantity from test
inlet to fish-mouth river segment shows a gradual increase trend, while that from fish-mouth segment
to outlet segment presents a gradual decrease trend, and the on-way erosion and deposition changes
of the entire test river segment is basically “V-shaped”. The construction of water intake junction has
not changed the overall trend of the changes in river channel erosion and deposition, but it still has
some impacts on the changes in river channel erosion and deposition. Thus, it can be seen that after
the construction of water intake junction, the riverbed surface erosion ability of test river segment has
IWEMSE 2018 - International Workshop on Environmental Management, Science and Engineering
210

a tendency to decrease, i.e., the riverbed surface deposition in the deposition segment before
construction will increase to a certain extent, and the riverbed surface erosion degree in the erosion
segment before construction will be reduced, but the reduced amplitude is relatively small. Therefore,
it can be considered the construction of water intake junction has little impacts on the erosion and
deposition changes on the test river segment.
Figure 2. On-way changes of river channel erosion and deposition before and after the construction
of diversion junction.
Experiment Study on Water Diversion and Sediment Control of North Canal Expansion Project
211

4. Comparison in the layout of diversion junction and different arrangement patterns of sluice
gate
According to the preliminary design scheme requirements of this diversion junction project, the water
intake junction of this test will be arranged in two layout patterns, i.e., the dam-gate combination and
the total gate. In the test combination scheme, three layout patterns are included, i.e., 8-hole sluice
gate + overflow weir (hereinafter referred to as 8-hole + weir), 11-hole sluice gate + overflow dam
(hereinafter referred to as 11-hole dam gate) and 12-hole sluice gate (hereinafter referred to 12-hole
total gate). The three design schemes have basically the same layout positions, and the gate hole size
of sluice gate and bottom elevation are all the same.
4.1. Comparison in the flow characteristics of three layout patterns
In terms of the water level changes in three different layout schemes, the backwater amplitudes of the
three schemes are basically the same, and those of 11-hole dam gate and 12-hole total gate are
slightly less than the combination scheme of 8-hole dam gate. For regime changes under different
layout schemes, three kinds of layout schemes have basically the same mainstream lines. Only in the
river segment near water intake junction, the mainstream lines of 11-hole dam gate or 12-hole total
gate are slightly towards the right bank over 8-hole + weir, but the deviation is small, which can be
negligible relative to the whole test river segment. For velocity variation under different layout
schemes, the influences of three layout schemes on flow velocity are mainly concentrated near the
sluice gate, where the two schemes of 11-hole dam date and 12-hole total gate have almost the same
maximum velocity, but the positions of maximum velocity of the two schemes are slightly towards
right bank, while the three kinds of layout schemes have basically approaching maximum velocity
value. Therefore, it can be considered that the three layout mechanisms have a certain effect on
velocity distribution, but have little impact on flow velocity.
4.2. The effect of three layout patterns on the change of river channel erosion and deposition
As known from the foregoing analysis, after the construction of water intake junction, the erosion
and deposition evolutionary trend of the test river segment has not changed, but the change amplitude
is reduced to a certain extent, and the influence degrees of three layout patterns are different. Test
results show that the erosion and deposition change amplitudes of 11-hole dam gate and 12-hole total
gate are slightly bigger than that of 8-hole + weir, and such change characteristics are more obvious
in the case of lager flow. However, the erosion and deposition change amplitudes of 11-hole dam
gate and 12-hole total gate are basically approaching with no obvious difference.
4.3. Comparison in different layout patterns of sluice gate
By comparing the changes in mainstream regime, flow velocity, main-channel erosion and deposition
as well as other indexes of river channel before the construction of sluice gate, it can be seen that the
influences of total gate scheme or gate dam scheme on current river channel are slightly less than that
of 8-hole + weir. As viewed from flood and sediment discharge, the total gate scheme or the gate
dam scheme is superior to the 8-hole + weir scheme. Therefore, it is recommended to use the total
gate scheme or the gate dam scheme. For eventual adoption of 11-hole dam gate scheme or 12-hole
total gate scheme, due to a small difference of the two schemes, as viewed from model test results,
two kinds of schemes can be used either. But in the comprehensive considerations of various factors
such as hydraulic design technique and economic benefit, this design is suggested to use 11-hole dam
gate scheme.
IWEMSE 2018 - International Workshop on Environmental Management, Science and Engineering
212

5. Ultimate scour ability under sluice gate and its energy dissipation protection measures
5.1. Ultimate scour ability under sluice gate
Table 1. Ultimate scour depth table under sluice gate in different working conditions.
working condition
1 2
3
4
Water Level before sluice /m
174.50 176.50
174.50
176.50
Elevation below sluice /m
169.00 169.00
169.00
169.00
Water level after sluice
Free flow Free low
Free flow
Free flow
Number of sluice holes
1 1
4
4
Length of scour pit (measured) /m
82.00 129.00
73.00
120.00
Maximum scour depth (measured) /m
3.71 14.25
3.42
12.77
Minimum starting velocity (calculated)
/(m·s-
1
)
1.32 1.43
1.32
1.43
Minimum coarsening particle
size(calculated) /(mm)
20.00 21.00
20.00
21.00
Maximum scour depth(calculated)/m
3.96 14.80
3.70
13.87
After the construction of river sluice in natural channel, due to the change of flow boundary
condition, riverbed scouring will occur to the channel in the lower reaches of sluice, so that riverbed
sediment compositions become coarse. For the riverbed with pebble and sediment, the fine particles
of riverbed will be rushed away by flow, or migrated towards downstream in the form of sediment
waves. Coarser particles are gradually gathered to eventually form an anti-rushing coarsening layer.
In order to ensure the safety operation of diversion junction, this study is based on the ultimate scour
experiment under the most unfavorable working conditions, using the riverbed surface coarsening
theory proposed by the Academician Han of the China Institute of Water Resources and Hydropower
Research[3]
to calculate the ultimate scour depth of riverbed in the lower reaches of sluice in
diversion junction under the corresponding working conditions. Meanwhile, the calculated results are
compared with experimental results for analysis (see Table 1). It can be seen from Table 1 that the
calculation results are slightly larger than the experimental results, but both are basically close to
each other. In addition, it can be seen from the test results that the maximum impact distance of
ultimate scour pit can reach about 120 m in the downstream of sluice gate.
5.2. Energy dissipation protection measures under sluice gate
As viewed from the model test and theoretical analysis results of ultimate scour depth, the ultimate
scour depth of sluice gate can be up to about 15 m, and the influence scope of scour pit is up to 120
m. Therefore, hydraulic energy dissipation facilities must be built in the downstream of sluice gate.
In the feasibility study report of water intake junction, the stilling basin is used for energy dissipation
after sluice gate. The stilling basin is designed with a length of 20 m and a depth of 2 m, and the
apron is designed with a length of 40 m. In order to test the energy dissipation effect of designed
stilling basin, through analyzing all operation conditions of sluice gate, it is believed in this
experiment that when the water level in front of sluice gate is 176.2 m and the downstream discharge
is ecological water demand, the operation condition of sluice gate suddenly open for flood discharge
is the most unfavorable. The experimental results show that in the above-mentioned most
unfavorable conditions, the design dimension of sluice-gate stilling basin is slightly small, and the
current design dimension of stilling basin can meet the requirement of energy dispassion for the
single-hole discharge of about 35 m
3
/s. Therefore, it is suggested to increase the design dimensions
of sluice-gate stilling basin and apron. If the dimension of existing stilling basin is kept unchanged, it
is suggested to operate in the dry season of sluice gate. If the discharge amount is larger, it should be
Experiment Study on Water Diversion and Sediment Control of North Canal Expansion Project
213

to adopt the pattern of multi-hole operation. The single-hole discharge at the early stage of opening is
advised to be no more than 35 m
3
/ s. With the increase of water level in the downstream of sluice
gate, single-hole discharge can be increased gradually.
6. Analysis on diversion capacity and sediment control measures of water diversion channel
after the construction of water intake junction
6.1. Diversion capacity analysis of water diversion channel
After the expansion of diversion sluice, whether the diversion capacity can meet the design
requirement is a key point of this study. According to the design requirements, when the water levels
above and under diversion sluice are 176.2 m and 176.0 m after the expansion respectively, the
diversion capacity of diversion sluice should reach the requirement of 145 m
3
/s. Test results about the
flow coefficients of diversion sluice design scheme are shown in Table 2. It can be seen from Table 2
that under the combination of such working conditions, the diversion flow of model test is about 149
m
3
/ s. Therefore, the expanded diversion sluice can basically meet the design requirements. However,
regarding the outflow of this sluice gate with high submergence degree, the accuracy of test results is
reduced to a certain extent, so it is suggested to be considered in the design.
Table 2. Flow coefficient table of diversion sluice design scheme.
Group
Water Level
before sluice /m
Water level
after sluice/m
Water level
difference /m
Weir measurement
flow/(m3·s-1)
Discharge
coefficient/m
c
1
176.51
176.30
0.21
156
0.328
2
176.51
176.01
0.50
224
0.332
3
176.52
175.00
1.52
246
0.334
4
176.23
176.01
0.22
147
0.333
5
176.22
175.82
0.40
194
0.341
6
176.22
174.87
1.35
221
0.336
6.2. Sediment control measures of diversion channel and their effect analysis
As viewed from the existing layout of water intake junction, the main factors influencing the
sediment into diversion channel are the elevation difference between diversion channel bottom and
riverbed surface and the diversion quantity. After determining the diversion quantity and the
elevation of diversion channel bottom, the riverbed surface elevation near fish-mouth plays a decisive
role in the coarse sediment quantity into the diversion channel[4-6]. As viewed from previous
analysis and the results of this test, after the construction of diversion junction, cumulative deposition
is not generally produced in the river segment near fish-mouth, so that it is beneficial to reduce the
coarse sediment into diversion channel. But in order to study the sediment situation into diversion
channel under the most adverse circumstances, this experimental study is assumed under the riverbed
surface elevation of 172 m near fish-mouth for the sediment flushing of sluice gate and sediment
intake test of diversion channel in two working conditions with inlet flow of 500 m
3
/s and 2500 m
3
/s.
During the experiment, two cases of existing fixed bed and no fixed bed are considered. Under
different working conditions, the on-way distribution of maximum scour depth of river channel is
shown in Figure 3. When the riverbed surface elevation is 172 m, the sediment flushing effect of
sluice gate is more obvious. For the two cases of existing fixed bed and no fixed bed, the maximum
scour depth of typical section in the case of no fixed bed is generally larger than that of existing fixed
bed. It can be seen that the existing fixed bed has a certain influence on the sediment block effect of
sluice gate. In addition, as viewed from the experimental results of different working conditions, the
sediment intake of diversion channel accounts for about 1%-3% of river sediment intake.
IWEMSE 2018 - International Workshop on Environmental Management, Science and Engineering
214
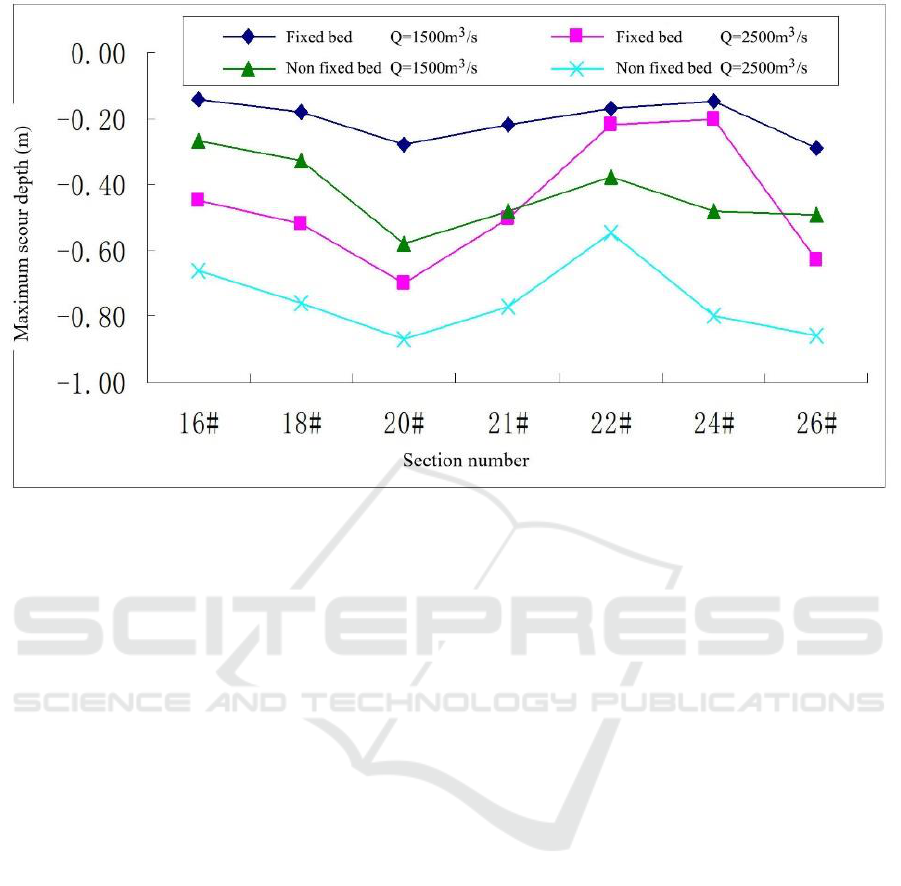
Figure 3. On-way distribution map of maximum scour depth of river channel under different
working conditions.
7. Conclusions
1) The construction of water intake junction will not have a great impact on current water sediment
characteristics and riverbed evolution of Nen River. The layout of sluice gate in water intake
junction is basically reasonable, which has less influence on the river flow characteristics and
the change of riverbed surface erosion and deposition. For three kinds of layout schemes, the
influences of 11-hole dam gate and 12-hole total gate schemes are slightly less than that of 8-
hole + weir design scheme. In comprehensive consideration of economy and design technology,
this design is recommended to adopt the layout scheme of 11-hole dam gate.
2) When the water level in front of sluice gate is 176.2 m and the downstream discharge is
ecological water demand, the stilling-basin design dimension of sluice gate is slightly small, and
the existing design dimension can only meet the energy dissipation requirement for single-hole
discharge of about 35 m
3
/s. Therefore, it is suggested to appropriately increase the design
dimensions of stilling basin and apron in sluice gate. If the current dimension of stilling basin is
maintained, it is recommended to use the pattern of multi-hole operation, and the initial single-
hole discharge should be appropriate without exceeding 35 m
3
/s.
3) Under the water and sediment conditions of model test, the riverbed surface in the river segment
near the fish-mouth of water intake junction is dominated by scour with no cumulative sediment
deposition. However, sediment deposition will occur in the diversion channel, and the channel
sediment intake is about 1% ~ 3% of big river sediment intake. In terms of sediment control
measures, the changes in the open position of sluice gate have little influence on the reduction of
sediment intake in diversion channel. However, in the case of cumulative deposition on channel
riverbed surface, the sediment flushing of sluice gate can reduce the riverbed surface elevation
near the fish-mouth, thus beneficial to reduce coarse sediment into the diversion channel.
4) In the case of sluice gate expanded to 3 holes with each hole width of 7 m for the working
conditions of water level above and under gate as 176.2 m and 176.0 m respectively, the water
diversion of sluice gate can reach 149 m
3
/s, basically meeting the design requirement for water
diversion of 145 m
3
/s.
Experiment Study on Water Diversion and Sediment Control of North Canal Expansion Project
215

Acknowledgement
This research was supported by “13th Five-Year Plan” to Support National key R & D project (Grant
No.2017YFC0405201) and IWHR Special Project (Grant NO. SC0145B172017) respectively.
References
[1] Gao J R Gao, Chen D F Chen, Liu Y F Liu and etc 2004 Planning Report of Nen River
Diversion Expansion Key Project in Heilongjiang Province as A Supporting Project of
Nierji Water Complex R. Haerbin: Heilongjiang Water Conservancy and Hydropower
Survey and Design Institute (in Chinese)
[2] Cao W H, Jiang N S, Chen D and etc 1998 Experimental Study on River Engineering Model
of River Channel Treatment Project at the Headwork of Northern Nen River Diversion
Project R. Beijing: Scientific Research Report of China Water Conservancy and
Hydropower Research Institute (in Chinese)
[3] Han Q W, Xiang X L, Wang Y C and etc 1983 Riverbed Sediment Coarsening C.
Proceedings of the Second International Symposium on River Sediment. Beijing: Water
Conservancy and Hydropower Press (in Chinese)
[4] Fan L J 2013Study on the causes and control measures of channel deformation in North
diversion main canal J. Haerbin: Heilongjiang Science and Technology of Water
Conservancy (8): 91-93 (in Chinese)
[5] Zhao F Z, Wang S W and Li X D 2007 Preliminary analysis on effect of river regulation works
in North diversion canal head J. Haerbin: Heilongjiang Science and Technology of Water
Conservancy (6): 147-148 (in Chinese)
[6] Wang S W, Zhao F Z and Liu D W 2008 Influence of the evolution of the upper reaches of the
diversion channel upstream to the diversion J. Haerbin: Heilongjiang Science and
Technology of Water Conservancy (1):45. (in Chinese)
IWEMSE 2018 - International Workshop on Environmental Management, Science and Engineering
216
