
Hydro Chemical Assessment of Edipsos Geothermal Area,
Greece
G
Diamantopoulos
1,*
, D
Poutoukis
2
, B
Raco
3
, A Arvanitis
4
and E
Dotsika
1
1
Stable Isotopes Unit, N.C.S.R. “Demokritos”, Institute of Nanoscience and
Nanotechnology, 15310, Ag. Paraskevi Attikis, Greece
2
General Secretariat for Research and Technology, Mesogion 14-18, 11510, Athens,
Greece
3
Institute of Geosciences and Earth Resources, Via G. Moruzzi 1, 56124 Pisa, Italy
4
Institute of Geology and Mineral Exploration, (I.G.M.E.), S. Loui 1, 3rd entrance of
Olympic Village, 13677, Athens, Greece
Corresponding author and e-mail: G
Diamantopoulos,
g.diamantopoulos@inn.demokritos.gr
Abstract. A geochemical survey on the thermal flu ids of Ed ipsos area was undertaken. In
order to investigate the mineralization process, a geochemical and isotopic analysis (major
ions,
18
O,
2
H) was conducted for thermal waters of springs and boreholes. The Edipsos area is
found in the north part of Euboea, south-east of Athens, and is characterized by high salinity
waters. The evaluation of the geochemical data of the thermal waters of Ed ipsos suggests that
they are fed by thermal water mixed with local groundwater and seawater. The most adequate
geothermometers were applied on selected samples for the determination of the deep aquifer
temperature.
1. Introduction
The thermal springs of Edipsos located in North Euboea are well known since ancient times as
“Pausanias”, and were reported by Aristotle and others for their healing attributes. Despite that these
springs were known from antiquity, the origin of the thermal water remains poorly documented.
Dotsika [1] compared different geothermometers to assess the temperature of reservoirs concluded
that Edipsos thermal field are high-enthalpy hydrothermal system.
2. Geology
The geology of northern Euboea (Figure 1) includes at the lower series a Permian–Triassic
volcanoclastic complex. Its basement consists of metamorphic rocks of pre-middle to middle
Carboniferous age, which are overlain by shallow marine clastic and carbonate rocks of middle
Triassic age [2, 3]. The sedimentary rocks are intercalated with volcanic rocks that are overlain by
Jurassic limestones. An ophiolitic corps, Late Jurassic–Early Cretaceous, is found above the
limestones [2]. The volcanic rocks are best developed at the southeast part of Edipsos. The lithology
is bedded tuff, fine grained agglomerate and rare ignimbrite. Fluvio-lacustrine deposits (Lower
Miocene to Upper Pliocene) were formed during the earlier neotectonic phases of the region [4, 5].
Diamantopoulos, G., Poutoukis, D., Raco, B., Arvanitis, A. and Dotsika, E.
Hydro Chemical Assessment of Edipsos Geothermal Area, Greece.
In Proceedings of the International Workshop on Environmental Management, Science and Engineering (IWEMSE 2018), pages 253-259
ISBN: 978-989-758-344-5
Copyright © 2018 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
253
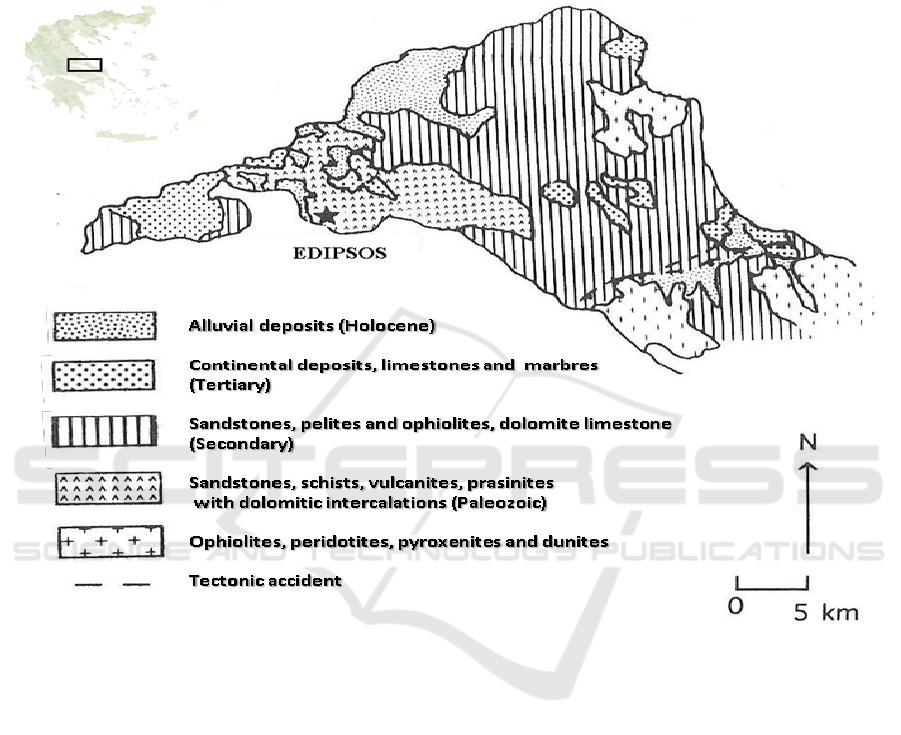
The grabben of north Euboic gulf was formed during the last geological periods by NW–SE to
WNW–ESE normal fault zones (Mettos et al. 1992). The study area is highly faulted due to
extensional tectonics. A system of N.NE-S.SW and W.NW–E.SE to NW–SE normal fault zones
prevails. The fault zones are associated with the Northern Euboea graben, due to most recent
(Quaternary) phase of the long-lasting extension established in the broader back-arc area of the
Hellenic arc. In Edipsos, thermogenic travertine deposits exist created by the local hot-springs.
Figure 1. Simplified geological map of Edipsos area, according to the geological map of I.G.M.E.
(1983).
3. Sampling and analysis
Sampling of waters was carried out in the Edipsos area. Thermal (a1,a2,a3,a4,a5,a6) and cold water
were sampled with cold waters temperature ranging from 14.7
o
C to 18
o
C and thermal waters
temperature ranging from 29.1 to 83
o
C. Temperature, pH, conductivity and alkalinity were measured
directly in the field. Filtered (0.45 µm), acidified (with HNO
3
1:1) water samples were collected for
determination of cations and SiO
2
. Untreated samples were collected for analyses of anions. The
major chemical constituents were analysed according to the standard methods. Na
+
, K
+
, Ca
2+
, Mg
2+
and SiO
2
contents were determined by atomic absorption. Anions were analysed by ion
chromatography. The B
+
content was determined photometrically using the curcumin method (Hayes
and Metcalfe 1962). Chemical analyses were conducted at the Institute of Geosciences and Earth
Resource, C.N.R, Pisa. The isotopic composition of the waters was conducted according to the
isotopic methods for the
18
O [6] and
2
H analysis [7]. The results are expressed in delta (δ) ‰ vs
SMOW (Standard Mean Ocean Water). The error for δ
18
O is ± 0.2 ‰ and for δ
2
H ± 2‰. Isotopic
analyses were carried out at the Stable Isotopes Unit, N.C.S.R. “Demokritos”.
IWEMSE 2018 - International Workshop on Environmental Management, Science and Engineering
254

4. Hydrochemical and isotopic characteristics of the waters
In the studied area two prevalent water types are presented: Ca-HCO
3
and Na-Cl groundwater
(Figure2). The group of water chemical type Ca-HCO
3
is comprised by cold waters. This chemical
type usually refers to meteoric origin which also is confirmed by concentrations of TDS that range
from 307.2 mg/L to 464.6 mg/L, less than 1000 mg/L, belonging to fresh water.
Figure 2. Piper diagram.
Figure 3. Graph of B
+
versus Cl
-
for cold and thermal waters of Edipsos.
Hydro Chemical Assessment of Edipsos Geothermal Area, Greece
255

The Na-Cl group includes the thermal springs and well together with the seawater. Their
temperature ranges from 29.1 to 83
o
C with pH values indicating a slightly acid environment, (from
5.8 to 7.2). The thermal waters of Edipsos exhibit high values of B and Li in relation to sea water.
The high concentration of B and Li can be explained by water-rock interactions processes. In order to
clarify the mechanism of water-rock interaction B
+
concentrations were plotted with respect to Cl
-
(Figure 3) as they constitute conserved elements [8]. In this diagram we observe that the excess of B
is not associated with a relevant excess in Cl in respect to seawater (the chlorine values remain
stable).
Independent confirmation of the B+ transfer from the rock to the thermal waters may be possible
to obtain through Li+, another conservative species also derived from the rock. Although B+ should
be rather easily removed from sediments, the transfer of Li+ from rock requires intense water–rock
interaction at high temperatures. Edipsos present also notable Li+ contents. The concentration of Li+
and B of thermal waters ranges from 1 to 1.6 mg/l and from 7 to 9 mg/l respectively. The high Li/B
ratio of these waters also exhibits wide variability from 0.14 to 0.18 respectively, typical of water
discharged „arc-type‟ systems [9].
Apart from the water-rock interaction process that controls the Li
+
and B
+
contents, the Na
+
, Br
-
,
Cl
-
and most of SO
4
2-
in thermal spring waters derive from sea water, which are more or less diluted
by fresh, bicarbonate water and the supply of these ions by rock leaching is negligible. In fact the
positive correlation between Cl
-
and Na
+
(and K
+
) indicates that high Cl
-
contents of thermal waters
arise from the contribution of seawater and/or a sodium-chloride geothermal liquid.
But Bromine, in
contrast to Na
+
, is considered to be conservative ion, even in geothermal environments, because its
contents are not affected by interactions with rocks [10]. The Cl/Br ratio ranges from 283 to 340
values close to that of seawater. Assuming that chlorides in these samples have marine origin, we
calculated that sea water at Edipsos seems to be involved in rate of 90-94%. Moreover, the thermal
spring waters exhibit not only Br/Cl lower but also higher B/Cl and Li/Cl ratios than those of
seawater, as stated above, indicating that the high-salinity end member cannot be actual marine water.
It could be either marine water modified through water–rock interaction at high (or relatively high)
temperature or a seawater-magmatic water mixture.
The isotopic values of the region‟s waters are plotted in the diagram of Figure 4 with the Global
Meteoric Water Line [11] and the Eastern Mediterranean Water Line [12, 13]. The isotopic data of
Edipsos thermal waters exhibit δ
18
O values similar to that of seawater, but differing δ
2
H. In
particular, the δ
18
O values of Edipsos samples (δ18O values from −0.2‰ to 1‰) are close to that
of seawater (δ
18
O ≈ 1‰) reflecting a seawater origin. However, this doesn't seem to apply for δ
2
H
values which range from −11.7‰ to −3‰ (δ
2
H ≈ 6‰ for seawater). This observed vertical
distribution of δ
2
H values suggests the above explanation (participation of magmatic water in the
deep geothermal aquifer).
IWEMSE 2018 - International Workshop on Environmental Management, Science and Engineering
256
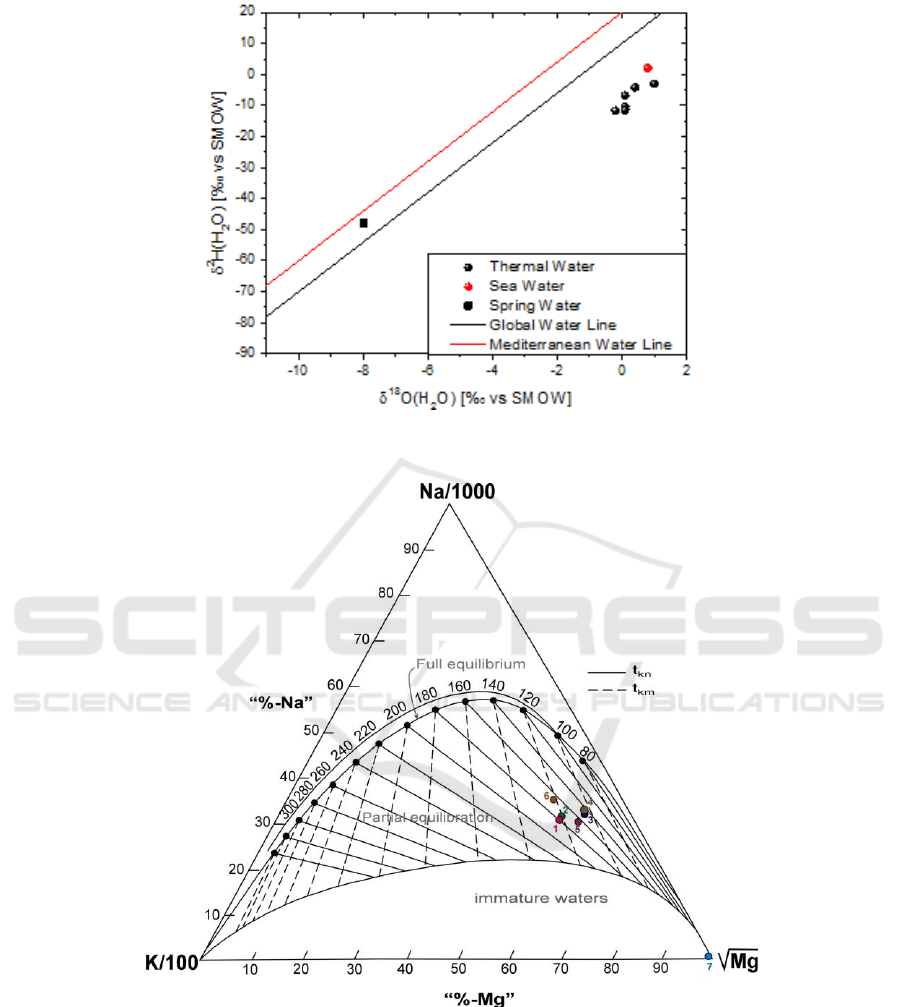
Figure 4. Diagram δ
18
Ο vs δ
2
Η.
Figure 5. Giggenbach diagram.
34
S contents of the samples are compared to those of marine sulfate, which is very constant over
the world (δ
34
S = 20‰ CD and δ
18
O = 9.5‰ SMOW; [14]). All the samples present δ
34
S similar to
that of seawater (20.5 to 19.4‰) but the δ
18
O of the thermal spring water is very diminished in
relation (6.8 to 7.2‰) to that of seawater. All the samples presented identical values of δ
34
S–(SO
4
)
with respect to the value of seawater (20‰ ±1‰ δ
34
S) while they were differentiated with respect to
δ
18
O–(H
2
O). The diminished δ
18
O value of the SO
4
2−
in the water of the springs in comparison to the
Hydro Chemical Assessment of Edipsos Geothermal Area, Greece
257

one of the SO
2
4−
of sea water origin (9.5 ± 0.2‰) could be attributed to isotopic equilibration
between δ
18
O–(H
2
O) and δ
18
O–(SO
4
).
5. Geothermometres
Geothemometres also contribute to the estimation of the subsurface reservoir temperatures in
geothermal system (Table 1, fig 5). The operating principle of geothermometers is the representation
of equilibrium of temperature-dependent reactions between minerals and the circulating fluids (for eg.
[15]). Different geothermometers, chemical and isotopic, were applied to the thermal waters of
Edipsos (Table 1). The isotopic geothermometer, (
18
O(SO
4
2-
- H
2
O), that we use is based on the
equilibrium exchange of oxygen isotopes between aqueous sulfate and water [16].
The resulting temperature is different for each chemical geothermometer with moderate to large
variation. A possible cause could be sea water contribution, that possible disturbs the water – mineral
equilibrium that the chemical geothermometers rely on. Furthermore, the only chemical
geothermometer which would not be affected by the marine contribution is the quartz
geothermometer that suggests a lower temperature. Regarding the isotopic geothermometers, if the
δ
18
O content of aqueous sulfate is only controlled by equilibration with water, and if isotopic
equilibrium is reached (as the isotope of sulfate demonstrated), the temperature of geothermal fluid
would be close to 234 °C.
Table 1. Temperatures (ºC) calculated using different Geothermometer.
EDIPSOS
(
18
O(SO
4
2-
-H
2
O)
[16]
Quarz
(no steam loss) [17]
Na-K [18]
Na-K [15]
Na-K-Ca (TNKC)
t
o
C (t>100
o
C) [15]
a1
230
104,3
147,54
127,56
147,25
a2
235
105,0
143,28
123,15
144,18
a3
230
100,6
162,12
142,72
157,16
a4
230
104,3
163,70
144,36
163,61
a5
-
-
131,05
110,52
83,69
6. Conclusions
The high B and Li
+
contents measured in these thermal waters show that the supply of these ions by
rock leaching is significant. Especially the transfer of Li
+
from rock requires intense water-rock
interaction at high temperatures. The use of isotopic geothermometer attributes a temperature greater
than 200°C to the deep geothermal field.
References
[1] Dotsika E 1991Utilisation du geothermometre isotopique sulfate-eau en milieux de haute
temperature sous influence marine potentielle: Les systemes geothermaux de Grece Thesis
Paris 11
[2] Katsikatsos G and et al 1986 Geological structure of internal Hellenides (E. Thessaly–SW
Macedonia–Euboea–Attica–Northern Cyclades islands and Lesvos) Geological and
Geophysical Research, Special Issue p 191-212
[3] Katsikatsos G, M Vidakis and G Migiros 1981 Platycampos sheet, Geological map of Greece
1: 50,000 Athens IGME
[4] Guernet C 1971 Études géologiques en Eubée et dans les régions voisines:(Grèce) 91
résidence Bois des Godeaux
[5] Ioakim C and et al 1992 Evolution geodynamique et reconstruction paleoenvironmentale des
basins neogènès-quaternaires de la Gréce centrale. Paleontologia I evolució (24): p 393-
IWEMSE 2018 - International Workshop on Environmental Management, Science and Engineering
258

402
[6] Epstein S and T M 1953 Variation of 18O content of water from natural sources Geochim.
Cosmochim Acta 4: p 213–224
[7] Coleman M L and et al 1982 Reduction of water with zinc for hydrogen isotope analysis.
Analytical chemistry 54(6): p 993-995
[8] Giggenbach W 1992 Isotopic shifts in waters from geothermal and volcanic systems along
convergent plate boundaries and their origin Earth and planetary science letters 113(4): p
495-510
[9] Giggenbach W and et al 1995 Isotopic and chemical composition of waters and gases from the
East Coast accretionary prism, New Zealand
[10] Henley R W and Ellis A J 1983 Geothermal systems ancient and modern: a geochemical
review Earth-science reviews 19(1): p 1-50
[11] Craig H 1961 Isotopic variations in meteoric waters. Science 133(3465): p 1702-1703
[12] Aouad A and et al 2004 Etude isotopique de la pluie et de la neige sur le Mont Liban:
premiers résultats/Isotope study of snow and rain on Mount Lebanon: preliminary results
Hydrological Sciences Journal 49(3)
[13] Bowen G J and Wilkinson B 2002 Spatial distribution of δ18O in meteoric precipitation
Geology 30(4): p 315-318
[14] Longinelli A 1989 Oxygen-18 and sulphur-34 in dissolved oceanic sulphate and phosphate the
marine environment p 219-255
[15] Fournier R and Truesdell A 1973 An empirical Na-K-Cageothermometer for natural waters
Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta 37(5): p 1255-1275
[16] Lloyd R 1968 Oxygen isotope behavior in the sulfate
‐
water system. Journal of Geophysical
Research 73(18): p 6099-6110
[17] Fournier R 1977 Chemical geothermometers and mixing models for geothermal systems.
Geothermics 5(1-4): p 41-50
[18] Giggenbach W F 1988 Geothermal solute equilibria. derivation of Na-K-Mg-Ca geoindicators.
Geochimica et cosmochimica acta 52(12): p 2749-2765
Hydro Chemical Assessment of Edipsos Geothermal Area, Greece
259
