
DEA-based Ecological Efficiency Evaluation during the
Process of Industrial Transformation in the Pearl River Delta
Urban Cluster
M R Su
1,*
, D Z Li
2
, C Ma
1
, L L Liao
2
and L R Yu
1
1
Research Center for Eco-Environmental Engineering, Dongguan University of
Technology, Dongguan 523808, China.
2
School of Environment and Civil Engineering, Dongguan University of Technology,
Dongguan 523808, China.
Corresponding author and e-mail: M R Su, sumr@dgut.edu.cn
Abstract. In order to comprehensively evaluate the effect of industrial transformation, the
concept of ecological efficiency was introduced in this paper due to its merit of integrating
social, economic, and environmental factors. The indicator system and model of ecological
efficiency evaluation was subsequently established, while the model based on data
envelopment analysis is hopeful to reduce the subjectivity of evaluation. The case study on the
Pearl River Delta Urban Cluster shows the generally increased ecological efficiency during the
process of industrial transformation. However, the declined returns to scale implies the lack of
satisfactory harmony among different cities in the Pearl River Delta Urban Cluster. Certain
suggestions to improve ecological efficiency was put forward based on the results.
1. Introduction
Industrial transformation is undoubtedly a hopeful option of socio-economic development especially
in the regions where the traditional economy has caused certain eco-environmental problems. In the
past decades, many cities and regions in China has experienced the industrial transformation, the
remained question is that whether the industrial transformation is effective, i.e., realizes the desired
goal of harmonious socio-economic and eco-environmental development.
In order to comprehensively evaluate the effect of industrial transformation, the concept of
ecological efficiency is introduced in this paper regarding its integration and linkage among social,
economic, and environmental factors [1]. Although ecological efficiency has been widely studied on
such scales as nation, region, and enterprise [2–6], there is few attempt from the viewpoint of
industrial transformation. And more effective evaluation method is still necessary to resolve the
existent problems, e.g., reducing the subjectivity of the evaluation.
Focusing on these demands, the evaluation method of ecological efficiency based on data
envelopment analysis is constructed in this paper, attempting to evaluate the overall effect of
industrial transformation. The case study is conducted for the Pearl River Delta Urban Cluster, the
representative of industrial transformation in China with relatively long history and remarkable
Su, M., Li, D., Ma, C., Liao, L. and Yu, L.
DEA-based Ecological Efficiency Evaluation During the Process of Industrial Transformation in the Pearl River Delta Urban Cluster.
In Proceedings of the International Workshop on Environmental Management, Science and Engineering (IWEMSE 2018), pages 301-307
ISBN: 978-989-758-344-5
Copyright © 2018 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
301

outcome. Certain suggestions to improve ecological efficiency is finally proposed based on the
results.
2. Methodology
2.1. Concept of ecological efficiency
Although there are various understandings of ecological efficiency among different organizations and
scholars [2, 4, 6–8], its essential point is always the efficiency, i.e., the ratio of the output to input for
a system. Differing from the general efficiency, ecological efficiency also considers the resource and
environmental factors besides the traditional economic factor, e.g., it investigates such undesired
output as waste gas and wastewater besides economic output along with the resource and
environmental input.
2.2. Evaluation indicators of ecological efficiency
According to the essential point of ecological efficiency, the evaluation indicator system were
confirmed, when referring to indicators established in the traditional German economic account [1],
the data availability and the correlation among different indicators. As indicated in Table 1, it mainly
includes three aspects, i.e., resource, environment, and economy, in which the first two aspects
mainly reflect the input dimension while the last one represents the output dimension. And it should
be pointed out that the undesired output (i.e., environmental discharge) was regarded as the input
indicator rather than output in this paper, when considering the following two facts. The first one is
that it is difficult to collect accurate data of investment for dispose of undesired output, while the
undesired output is an alternative. Another one is that the undesired output can be regarded as a kind
of input per se for the environment since it needs absorption and dispose by the environment.
Table 1. The evaluation indicator system of ecological efficiency.
Dimension
Aspect
Item
Indicator
Input
Resource
Labor
Amount of employment at the end of
the year
Land
Area of cultivated land at the end of
the year
Area of built-up parts
Water resource
Amount of non-residential water
consumption
Energy
Amount of non-residential electricity
consumption
Environment
Water environment
Amount of industrial wastewater
discharge
Atmospheric environment
Amount of industrial waste gas
emission
Output
Economy
Gross domestic product
2.3. Evaluation model of ecological efficiency based on data envelopment analysis
The weights of different indicators are always an open question which may influence the results of
comprehensive assessment. With the ability of conducting assessment without confirming weights of
indicators, the method named as data envelopment analysis was selected to implement evaluation of
ecological efficiency. To better satisfy the demand of dynamic evaluation of ecological efficiency
IWEMSE 2018 - International Workshop on Environmental Management, Science and Engineering
302

during the process of industrial transformation, the BCC (Banker, Charnes, Cooper) model was
applied in which the returns to scale is variable.
In the BCC model, it is assumed that there are n decision making unit and each unit has s input and
t output. When x
j
represents the input of the jth decision making unit, and y
j
means the output of the jth
decision making unit, then the efficiency of the jth unit can be converted into a problem of linear
programming solution, when θ means the efficiency.
min θ
(1)
(2)
(3)
Concretely speaking, the decision making unit is the Pearl River Delta Urban Cluster and the nine
typical cities, the input is that from resource and environment, while the output is the economic
outcome.
In order to analyze the change of ecological efficiency during the process of industrial
transformation, the Malmquist index was combined with the merit of time series analysis. The
calculation is given in Eq. (4):
(4)
where
and
is the single stage distance function with fixed returns to
scale, while
and
is the inter-temporal distance function with fixed
returns to scale.
The result parameter obtained from data envelopment analysis and Malmquist index can be mainly
divided into three types, including the overall efficiency, the input slackness degree, and the change of
efficiency.
(1) The overall efficiency
Pure technological efficiency: the efficiency influenced by management and technology,
Scale efficiency: the efficiency influenced by industrial scale,
Comprehensive efficiency: the integrated efficiency influenced by both technology and industrial
scale.
(2) The input slackness degree
The input is redundant when the value of input slackness degree > 0, and the input is insufficient
when the value < 0, and the input is suitable when the value = 0.
(3) The change of efficiency
Change of technological efficiency: the technological efficiency increases when the value ≥ 1, and
the efficiency decreases when the value < 1,
Change of technological progress: the technological level improves when the value ≥ 1, and the
technological level declines when the value < 1,
Change of pure technological efficiency: the pure technological efficiency increases when the value
≥ 1, and the efficiency decreases when the value < 1,
s.t.
j
y
j
jn
x
0
j
y
j
jn
y
0
j
= 1
j
0 j n
M
X
t+1
Y
t+1
X
t
Y
t
= [
D
t+1
X
t+1
Y
t+1
CRS
D
t+1
X
t
Y
t
CRS
D
t
X
t+1
Y
t+1
CRS
D
t
X
t
Y
t
CRS
]
1
2
DEA-based Ecological Efficiency Evaluation During the Process of Industrial Transformation in the Pearl River Delta Urban Cluster
303

Change of scale efficiency: the scale efficiency increases when the value ≥ 1, and the efficiency
decreases when the value < 1,
Change of total factor productivity: it means the ratio of total production to total factor input. The
total factor productivity increases when the value ≥ 1, and the efficiency decreases when the value < 1.
2.4. Data sources
Required data during 1997–2015 were mainly collected from various statistical yearbook, e.g.,
Guangdong Statistical Yearbook, China City Statistical Yearbook, Yangtze River Delta & Pearl
River Delta and Hong Kong & Macao SAR & Tai Wan Statistical Yearbook, as well as the statistical
yearbooks of the nine typical cities in the Pearl River Delta. Moreover, some data were acquired from
the online resources, e.g., the website of municipal water authority and Guangdong statistical
information.
3. Results and discussion
3.1. Overall ecological efficiency of the Pearl River Delta Urban Cluster
Based on the BCC model, the overall ecological efficiency of the Pearl River Delta Urban Cluster
and nine cities were obtained, as shown in Table 2. Three findings are investigated from the results.
(1) Except for Dongguan and Zhongshan, the comprehensive efficiency of other seven cities was
higher than that of the Pearl River Delta Urban Cluster during the study period. It means that the
usage of input was efficient in these seven cities when using that of the Pearl River Delta Urban
Cluster as the baseline. (2) Although with relatively low comprehensive efficiency, Dongguan and
Zhongshan had increased returns to scale during the study period, which implies that the ecological
efficiency was gradually improved during the process of industrial transformation. (3) The Pearl
River Delta Urban Cluster showed decreased returns to scale, although none city showed the same
trend during the study period. It reflects that the coordination among different cities in the Pearl
River Delta Urban Cluster was unsatisfactory.
Table 2. The ecological efficiency obtained from BCC model.
Area
Comprehensive
efficiency
Pure
technological
efficiency
Scale
efficiency
Change of scale
efficiency
Guangzhou
1.000
1.000
1.000
-
Shenzhen
1.000
1.000
1.000
-
Zhuhai
1.000
1.000
1.000
-
Huizhou
1.000
1.000
1.000
-
Dongguan
0.749
0.861
0.870
irs
Zhongshan
0.848
1.000
0.848
irs
Jiangmen
1.000
1.000
1.000
-
Foshan
1.000
1.000
1.000
-
Zhaoqing
1.000
1.000
1.000
-
The Pearl River Delta
0.897
1.000
0.897
drs
Note: ‘irs’ means the returns to scale increase, ‘drs’ means the returns to scale decrease, and ‘-’ means
the returns to scale remain unchanged.
3.2. The input slackness degree of ecological efficiency for the Pearl River Delta Urban Cluster
The input slackness degree of ecological efficiency for the Pearl River Delta Urban Cluster were also
calculated based on the BCC model. It is denoted in Table 3 that the input of employment and
IWEMSE 2018 - International Workshop on Environmental Management, Science and Engineering
304
non-residential water were non-redundant, whereas that of industrial waste gas, non-residential
electricity, cultivated land, and built-up area showed obvious redundancy during the study period. It
implies that the ecological efficiency during the process of industrial transformation is closely related
with resource and environmental input, and the influence of industrial transformation on resource and
environment should be paid attention to.
Table 3. The input slackness degree based on BCC model.
Aspect
Indicator
Input slackness
degree
Resource
Amount of employment at the end of the year
0
Area of cultivated land at the end of the year
1.365
Area of built-up parts
0.718
Amount of non-residential water consumption
0
Amount of non-residential electricity consumption
3.124
Environment
Amount of industrial wastewater discharge
0.053
Amount of industrial waste gas emission
49.376
3.3. The dynamic analysis of ecological efficiency for the Pearl River Delta Urban Cluster
The dynamics of ecological efficiency for the Pearl River Delta Urban Cluster was analyzed based on
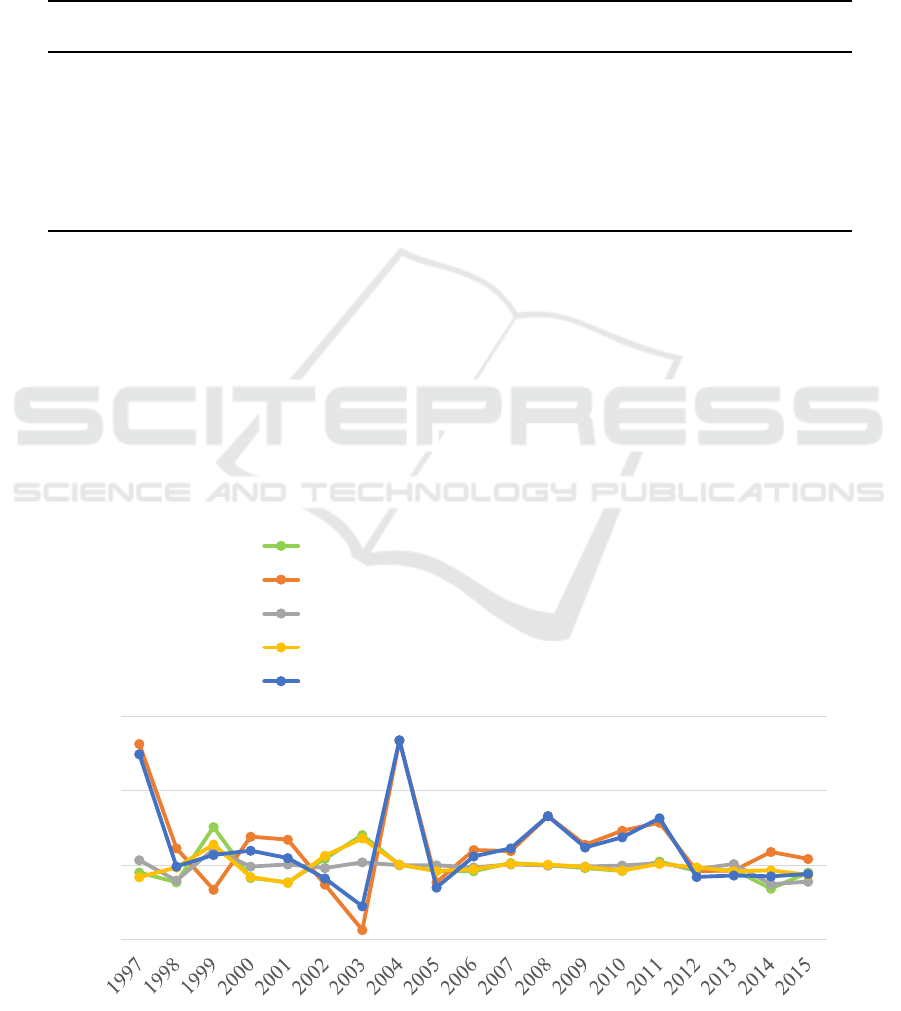
the Malmquist index method. As shown in Figure 1, the change value of total factor productivity was
bigger than one in most of years during 1997–2015, representing the ecological efficiency of the
Pearl River Delta Urban Cluster generally improved during the process of industrial transformation.
However, it is also found out that the change value of total factor productivity was smaller than one
during 2012–2015, showing the declined trend of ecological efficiency in recent years which was
mainly caused by the decrease of scale efficiency. Due to the big industrial scale in the Pearl River
Delta Urban Cluster, the harmony among various aspects of different industries and cities has not
been achieved, thus affects the ecological efficiency.
Figure 1. The change of ecological efficiency for the Pearl River Delta Urban Cluster.
0.75
1
1.25
1.5
Change of technological efficiency
Change of technological progress
Change of pure technological efficiency
Change of scale efficiency
Change of total factor productivity
DEA-based Ecological Efficiency Evaluation During the Process of Industrial Transformation in the Pearl River Delta Urban Cluster
305

3.4. Suggestions for improving ecological efficiency in the Pearl River Delta Urban Cluster
Based on the above-mentioned results, the suggestions for improving ecological efficiency in the
Pearl River Delta Urban Cluster was put forward from three aspect. First, some input needs to be
reduced when considering the redundancy, which mainly includes non-residential electricity,
cultivated land, and built-up area. In order to reduce the non-residential electricity consumption, the
industry should transfers into that of low energy consumption, and the energy-saving awareness of
employees should be improved. The productive cultivation technique needs to be studied and
developed to decrease the redundancy of the cultivated land. In terms of the input of built-up area, a
more rational planning are necessary combining with the urban development ability and orientation.
Second, undesired output needs to be reduced, which mainly includes the waste gas and wastewater.
The industry is required transferred from high emission to low emission. Third, the urban network in
the Pearl River Delta Urban Cluster needs to be optimized, which requires a more holistic industrial
planning in the whole urban cluster where different cities develop advantageous complementary
industry.
4. Conclusions
In order to check the effect of industrial transformation, the concept of ecological efficiency was
introduced in this paper regarding its integration of economy, resource, and environment. The
evaluation indicator system of ecological efficiency was established. The evaluation model based on
data envelopment analysis and the Malmquist index was also developed, which is hopeful to reduce
the evaluation subjectivity without confirming the weights of different indicators. The Pearl River
Delta Urban Cluster-the representative of industrial transformation in China-was selected as the case
to demonstrate the application of the established evaluation indicators and mathematical model. It is
indicated that the ecological efficiency of the Pearl River Delta Urban Cluster generally increased
during the process of industrial transformation but with declined returns to scale, which implies the
lack of satisfactory coordination among different cities. Such suggestions to improve ecological
efficiency is finally proposed as reduce certain input and undesired output, and strength the holistic
industrial planning in the Pearl River Delta Urban Cluster.
Acknowledgments
This research was financially supported by the National Key R & D Program of China (No.
2016YFC0502800, 2017YFC0405900), the National Natural Science Foundation of China
(No.71673027), the Natural Science Foundation for Distinguished Young Scholars of Guangdong
Province (No.2017A030306032), GDUPS (2017), and the Scientific Research Foundation for
High-level Talents and Innovation Team in Dongguan University of Technology (No.
KCYKYQD2016001).
References
[1] Hoh H, Scoer K and Seibel S 2001 Eco-efficiency indicators in German
environmental-economic accounting (Federal Statistical Office, Germany)
[2] Zhang Z, Zhu D J, Shi Q H and Cheng M W 2018 Which countries are more ecologically
efficient in improving human well-being? An application of the index of ecological
well-being performance Resou. Conserv. Recy. 129 pp 112–119
[3] Yue S J, Yang Y and Pu Z N 2017 Total-factor ecology efficiency of regions in China Ecol.
Indic. 73 pp 284–292
[4] Silveira J L, Lamas W de Q, Tuna C E, Villela I A de C and Miro L S 2012 Ecological efficiency
and thermoeconomic analysis of a cogeneration system at a hospital Renew.Sust. Energ. Rev.
16 pp 2894–2906
IWEMSE 2018 - International Workshop on Environmental Management, Science and Engineering
306

[5] Sun L Y, Miao C L and Yang L 2017 Ecological-economic efficiency evaluation of green
technology innovation in strategic emerging industries based on entropy weighted TOPSIS
method Ecol. Indic. 73 pp 554–558
[6] Coronado C R, Villela A de C and Silveira J L 2010 Ecological efficiency in CHP: Biodiesel
case Appl. Therm. Eng. 30 pp 458–463
[7] Jollands N 2006 Concepts of efficiency in ecological economics: Sisyphus and the decision
maker Ecol. Econ. 56 pp 359–372
[8] Katsaros G, Stichler P, Subirats J and Guitart J 2016 Estimation and forecasting of ecological
efficiency of virtual machines Future Gener. Comp. Sy. 55 pp 480–494
DEA-based Ecological Efficiency Evaluation During the Process of Industrial Transformation in the Pearl River Delta Urban Cluster
307
