
Enhanced Coagulation for Landfill Leachate Pretreatment
W K Bai
1
, F Liu
2
and H You
1, 2,*
1
Environmental school,Harbin Institute of Technology,Harbin 150090, P. R. China
2
School of Marine Science and Technology,Harbin Institute of Technology
(Weihai),Weihai 264209, P. R. China
Corresponding author and e-mail: H You, youhong@hit.edu.cn
Abstract. Coagulation was used in this paper to pretreat the waste incineration plant leachate
to reduce the subsequent processing load. This work strengthened the traditional coagulation
by compound coagulant and two-time coagulation. Results showed that the coagulation effect
of poly aluminum chloride and polymeric ferric sulfate compound coagulant is better than
that of polymeric aluminum chloride alone. The turbidity decreased from 74.0 NTU to 21.2
NTU, and the COD removal rate increased from 29.7% to 33%. In the case of the same
dosage, the effect of two-time coagulation is stronger than that of one-time coagulation.
1. Introduction
A large amount of high concentration leachate was produced in the waste incineration plant, which is
mostly produced by garbage stacking 5~7d [1]. The leachate of waste incineration plant is
characterized by high COD concentration, high metal content, large variation of water quality and
quantity, imbalance of nutrient proportion and low pH [2]. Because there are a lot of refractory
organic matter in leachate, the traditional biological treatment methods are limited [3], which is more
difficult for the high concentration leachate in the waste incineration plant. Physical and chemical
methods have been used by more and more researchers to deal with landfill leachate, such as
photocatalytic oxidation [4], electrolysis Fenton [5], membrane treatment method [6] and so on.
Coagulation is one of the most commonly-used physical and chemical methods [7]. Pretreatment of
landfill leachate by coagulation could flocculate and precipitate part of the refractory organic matter
and remove toxic substances from leachate, and provide a good operation environment for biological
treatment.
The traditional coagulant treatment of landfill leachate need a large dosage of coagulant and have
poor coagulation effect. In order to solve these problems, compound coagulant [8] and two-time
coagulation are used to treat landfill leachate. The combination of coagulants is polyaluminum
chloride (PAC) and polyferric sulfate (PFS). The two-time coagulation is after one coagulation,
coagulant is added to the effluent again.
Bai, W., Liu, F. and You, H.
Enhanced Coagulation for Landfill Leachate Pretreatment.
In Proceedings of the International Workshop on Environmental Management, Science and Engineering (IWEMSE 2018), pages 431-436
ISBN: 978-989-758-344-5
Copyright © 2018 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
431

2. Materials and methods
2.1. Leachate
The landfill leachate was obtained from Weihai municipal solid waste incineration plant. The raw
water data of leachate are shown in Table 1.
Table 1. Water quality of leachate.
COD(mg/L)
NH
4
+
-N(mg/L)
pH
turbidity(NTU)
PO
4
3-
(mg/L)
67550
2310
5.98
1718
479.51
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Traditional coagulation. PAC and PFS were separately added to the leachate with different
dosage and pH. Stirring conditions are 300 r/min for 30 s, 120 r/min for 60 s, 40 r/min for 10 min.
The supernatant was measured after the static precipitation of 10 min.
2.2.2. Compound coagulant. PAC and PFS composite coagulant was separately added to the leachate
with different PAC/PFS ratio, pH and dosage. Stirring conditions are 300 r/min for 30 s, 120 r/min
for 60 s, 40 r/min for 10 min. The supernatant was measured after the static precipitation of 10 min.
2.2.3. Two-time coagulation. After first coagulation, coagulant was added to the supernatant and then
the leachate was coagulated again. PAC and PFS composite coagulant was added to the leachate wirh
different respective dosage of two times coagulation. Stirring conditions of two times coagulation are
300 r/min for 30 s, 120 r/min for 60 s, 40 r/min for 10 min. The supernatant was measured after the
static precipitation of 10 min.
3. Results and discussion
3.1. Influence of coagulation conditions on traditional coagulation
PAC and PFS were separately added with different dosage and pH. Figure 1 showed the removal
effect of these two coagulants on turbidity and COD under different conditions. As can be seen from
Figure 1a and 1b, the removal efficiency of turbidity and COD by PAC is significantly better than
that of PFS. The turbidity and the COD of the supernatant gradually decrease with the increasing of
coagulant dosage. It is not completely in line with the conventional coagulation for the composition
of the leachate is too complicated and the turbidity is too high. There is no case that the particle is
stable again with increasing dosage of coagulant, resulting in a poor coagulation effect. The decrease
rate of turbidity turned slowly with a dosage of 4 g/L. So the dosage was fixed as 4 g/L, and change
the pH. Figure 1c and 1d showed that the turbidity value gradually decreased with the increasing of
pH value. The best coagulation effect was achieved with PAC addition and pH=9. The turbidity of
the supernatant was 74 NTU and the turbidity removal rate was 95.7%. The COD was 47517 mg/L
and the COD removal rate was 29.7%.
IWEMSE 2018 - International Workshop on Environmental Management, Science and Engineering
432
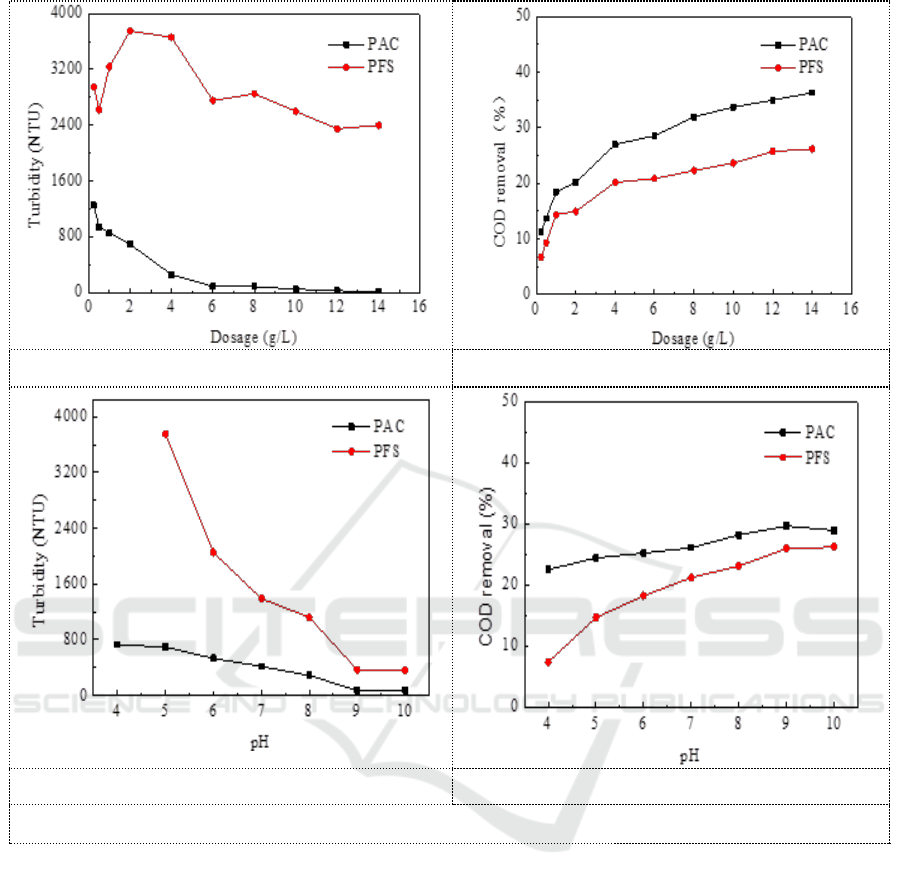
a. Effect of coagulant dosage on turbidity
b. Effect of coagulant dosage on COD removal
c. Effect of pH on turbidity
d. Effect of pH on COD removal
Figure 1. Comparison of coagulation effect of PAC and PFS under different conditions.
3.2. Influence of coagulation conditions on compound coagulant
Figure 2 showed the coagulation efficiency of compound coagulants under different conditions by
changing PAC and PFS coagulation ratio, dosage and pH respectively. It can be seen from Figure 2a
that the turbidity of the supernatant is the lowest when PAC: PFS is 2:1. The PAC/PFS ratio of the
compound coagulant used in the next experiment is 2:1. It can be seen from Figure 2b that the
turbidity of the supernatant decreases with the increasing of coagulant dosage. As the dosage of
coagulant continues to increase, there was no re-stabilization of the particles. It can be seen from
Figure 2c that the turbidity of the supernatant decreases with the increasing of the pH value.
Turbidity reaches minimum (37 NTU) when pH= 9.
Enhanced Coagulation for Landfill Leachate Pretreatment
433
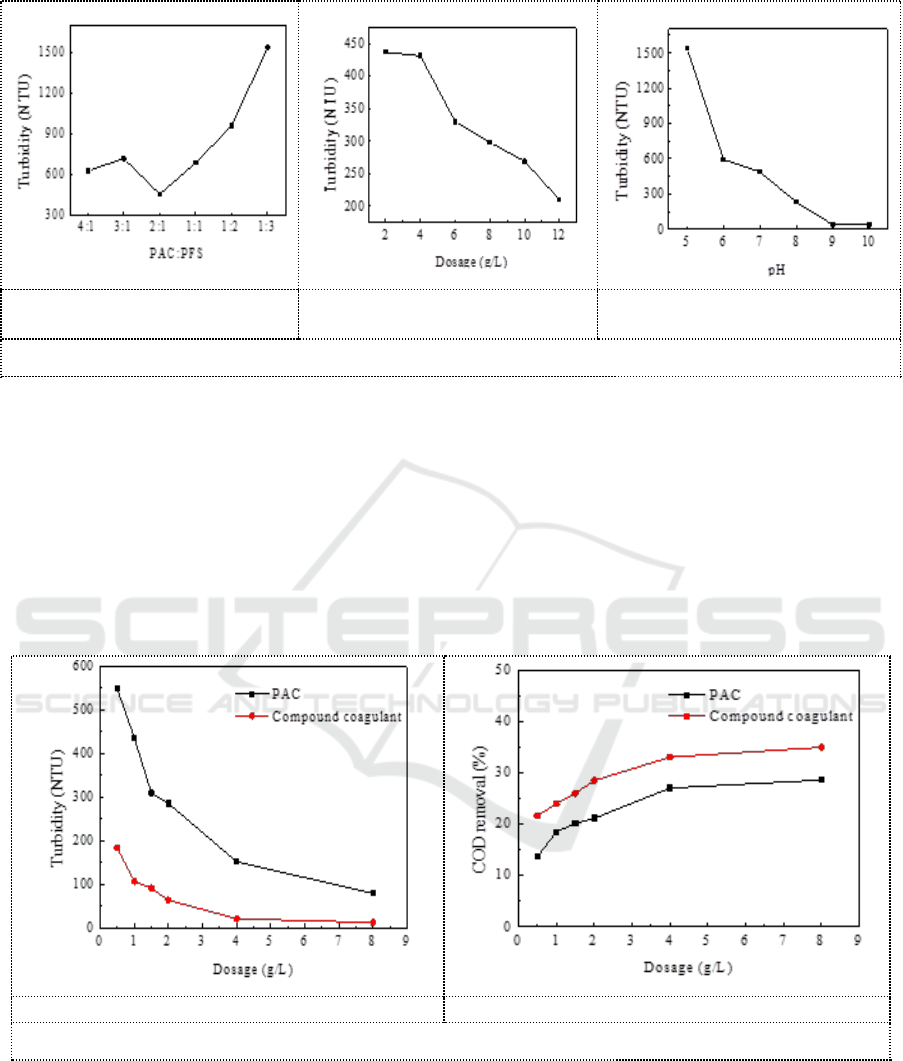
a. Influence of PAC/PFS ratio
on turbidity.
b .Effect of compound coagulant
dosage on turbidity.
c .The effect of pH on turbidity.
Figure 2. Effect of coagulation conditions on PAC/PFS coagulation.
3.3. Comparison of compound coagulation and traditional coagulation effect
When pH =9, compound coagulants (PAC: PFS =2:1) and PAC are separately added to the leachate.
Figure 3 showed the coagulation effect of the compound coagulant and the PAC under the same
conditions with the increasing of coagulant dosage. The COD and turbidity removal efficiency of the
compound coagulant is obviously stronger than that of PAC. Taking 4g/L as a reference, when the
dosage of compound coagulant was 4 g/L, the turbidity was 21.2 NTU and the turbidity removal rate
was 98.8%, the COD was 45233 mg/L and the COD removal rate was 33.0%. When PAC was added,
the turbidity was 74.0 NTU, the turbidity removal rate was 95.7%, the COD was 47517 mg/L and the
COD removal rate was 29.7% under the same conditions.
a .Comparison of turbidity.
b. Comparison of COD removal.
Figure 3. Comparison of coagulation effect between PAC coagulant and compound coagulant.
3.4. Comparison of two-time coagulation and one-time coagulation
When pH = 9, recoagulate on the basis of first coagulant with compound coagulant dosage of 0.5 g/L,
1 g/L, 2 g/L, 4 g/L, 8 g/L. Figure 4 showed the effect of the total compound coagulant dosage of two-
time coagulation on turbidity and COD removal. It can be seen that the effect of two-time
coagulation on the removal of turbidity and COD is significantly better than that of one-time
coagulation and the secondary coagulation is more likely to reach the optimal dosage of coagulant.
IWEMSE 2018 - International Workshop on Environmental Management, Science and Engineering
434
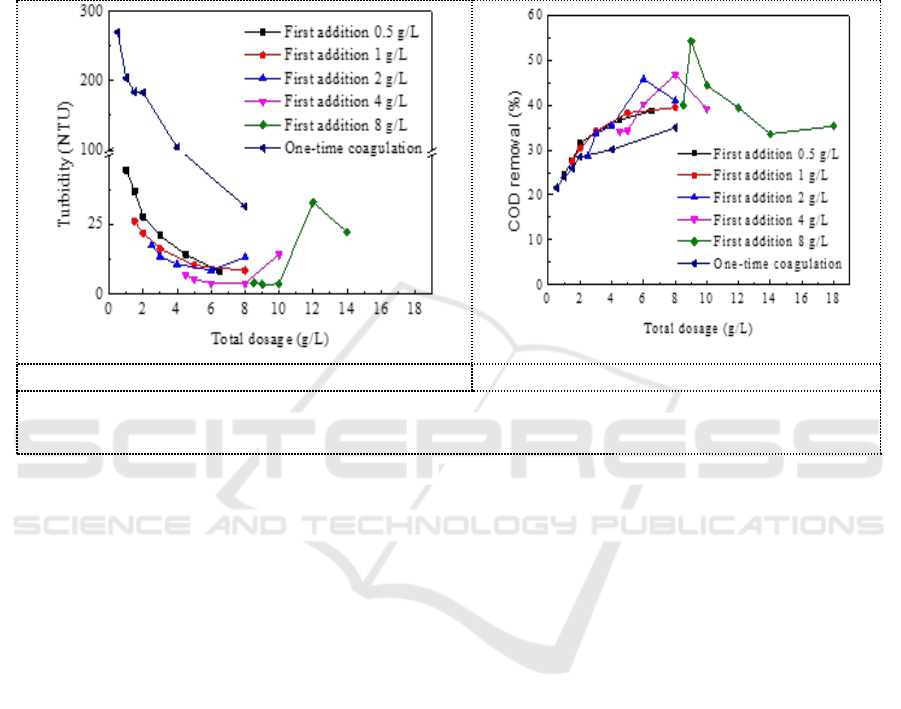
When the first coagulation dosage was 4 g/L, the second dosage was 0.5 g/L with a total dosage of
4.5 g/L, the turbidity of the two-time coagulation supernatant was 6.8 NTU. While the turbidity of
the supernatant is 95.0 NTU with one-time coagulation (4.5g/L). When the first coagulation dosage
was 8 g/L, and the second dosage was 1 g/L with a total dosage was 9g/L, the COD removal rate of
two-time coagulation was 54.3%. While the COD removal rate was 35% with one-time coagulation
(9g/L).
a. Comparison of turbidity removal.
b. Comparison of COD removal.
Figure 4. Comparison of coagulation effect between two-time coagulation and one-time
coagulation.
4. Conclusions
The coagulation effect of PAC and PFS compounding is obviously better than that of traditional
single coagulation. And the turbidity from 74 NTU to 21.2 NTU, the COD removal rate rose from
29.7% to 33%.
The coagulation effect of two-time coagulation is better than that of one-time coagulation,
because the two-time coagulation processes fully exerted the effect of contact flocculation that is the
larger mature flocs adsorb the tiny floc in the water on the surface and remove it from the water.
When the dosage of coagulant is the same, the removal rate of turbidity and COD is obviously
improved. And the turbidity decreased from 95 NTU to 6.85 NTU and the removal rate of COD
increased from 35% to 54.3%.
At the same time, the two-time coagulation also has the advantages that the coagulant dosage is
greatly reduced, the amount of coagulation supernatant is greatly increased, the turbidity of the
supernatant can be very low, the flocs are large and the sedimentation is fast. It is foreseeable that the
two-time coagulation secondary coagulation method could be further applied in the field of high
turbidity water treatment.
Acknowledgement
This work was supported by Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province (ZR2017MEE020).
References
[1] Zhang H, Sun L P, Ying A N, Gao S Q and Wang A Q 2010 Research Advances in
Characteristics of MSW Landfill Leachate Sichuan Environment 29 (2) pp 113-118
[2] Xiao C B, Pang B L, Ren Y S, Wen X, Gao Y G and X Z Gao 2012 Landfill leachate treatment
Enhanced Coagulation for Landfill Leachate Pretreatment
435

project in refuse incineration power plant China Water & Wastewater 28(10) pp 77-79
[3] Gao J, Oloibiri V, Chys M, Audenaert W, Decostere B, Y He and et al 2015 The present status
of landfill leachate treatment and its development trend from a technological point of view
Reviews in Environmental Science & Bio/Technology 14(1) pp 93-122
[4] Yan F, Li J, Xiao G and Pan W 2010 Treatment of landfill leachate by coupling system of
titanium dioxide and ultrasonic Chinese Journal Of Environmental Engineering 4(2) pp
383-386
[5] Sabour M R, Lak M G and Rabbani O 2011 Evaluation of the main parameters affecting the
fenton oxidation process in municipal landfill leachate treatment Waste Manag Res 29(4)
pp 397-405
[6] Fu J T, Wang L, Li X W, Yang S X, Zhang L Q and Ma L 2017 A pilot study on the reduction
of leachate from waste incinerati on power plant by stro membrane Membrane Science &
Technology 37(2) pp 120-123
[7] Bashir M J K, Xian T M, Shehzad A, Sethupahi S, Aun N C and Amr S A 2016 Sequential
treatment for landfill leachate by applying coagulation-adsorption process Geosystem
Engineering 20(1) pp 9-20
[8] Shang P, Liu T L and Kong X J 2011 Pretreatment of landfill leachate using PAC, PFS
coagulation and chemical precipitation China Water & Wastewater 27(1) pp 65-67
IWEMSE 2018 - International Workshop on Environmental Management, Science and Engineering
436
