
In Situ Nitrogen Removal by a Newly Isolated Oligotrophic
Aerobic Denitrifier Zoogloea sp. N299, in Relations with
Temperature and Water Pressure in a Reservoir
S L Zhou
1
, Y R Zhang
1
, T L Huang
2, *
, C H Zhang
2
and K K Fang
2
1
School of Environmental Science and Engineering, Hebei University of Science and
Technology, Shijiazhuang, 050018, PR China
2
Key Laboratory of Northwest Water Resource, Environment and Ecology, MOE,
Xi'an University of Architecture and Technology, Xi'an, 710055, PR China
Corresponding author and e-mail: T L Huang, huangtinglin@xauat.edu.cn
Abstract. A series of experiments were conducted to explore the nitrogen removal
characteristics of oligotrophic aerobic denitrifier Zoogloea sp. N299 at different temperature,
water pressure, inoculums conditions. In the in situ temperature gradient experiment of hard
flask (without water pressure influence), the nitrate removal rate of the surface flask system
reaches 99.21 %, the middle reaches 61.1 %, the bottom reaches 57.66 %, and the
corresponding TN removal rate reaches 82.42 %, 38.47 % and 27.10 %, respectively, and
there is no nitrite accumulation in 96 h. While in the soft flask (with water pressure influence),
The TN removal rate of the surface flask reaches 36.40 %, the middle reaches 23.74 %, the
bottom reaches 21.41 %. In the different inoculum experiments, the nitrate removal rate of the
hard flask and soft flask systems reaches 60.81±0.68 % and 52.4±2.31 %, respectively. From
all the results, the water pressure has a disadvantage to the nitrogen removal and the higher
temperature, the better performance of denitrification, and there is no difference in the
different inoculum experiment. It indicated that Zoogloea sp. N299 is able to achieve
effectively denitrification in situ and provide a significant reference to remediate the micro-
polluted reservoir water system.
1. Introduction
With more and more nitrogen discarded into the environment, leading to many serious pollution
problems, especially in source water reservoir. So the removal of the nitrogen has been a necessary
and important topic. However the physical and chemical methods were always used to removal
nitrogen of wastewater, and the traditional biological method was also impractical in natural waters.
Conventional biological denitrification only occur under anaerobic or anoxic conditions with the
reduction of sequence from nitrate to nitrogen gas. The reaction steps are inhibited by oxygen, which
are impractical in natural waters, especially in reservoir.
With the discovery of the first aerobic denitrification bacteria Thiosphaera pantotropha strain by
Robertson and Kuenen (Robertson & Kuenen 1983; Robertson et al. 1985)[1,2], it exhibited the
possibility of the nitrogen removal from the reservoir ecosystem. The aerobic denitrification has
obvious advantages: (1) the nitrification and denitrification can occur in the same treatment system
Zhou, S., Zhang, Y., Huang, T., Zhang, C. and Fang, K.
In Situ Nitrogen Removal by a Newly Isolated Oligotrophic Aerobic Denitrifier Zoogloea Sp. N299, in Relations with Temperature and Water Pressure in a Reservoir.
In Proceedings of the International Workshop on Environmental Management, Science and Engineering (IWEMSE 2018), pages 621-630
ISBN: 978-989-758-344-5
Copyright © 2018 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
621

(Schmidt et al. 2003)[3]; (2) the denitrification can produce the alkalinity to blance the acid of
nitrification. There are recent reports of aerobic denitrification bacteria, such as Thiosphaera
pantotropha (Su et al. 2001)[4], Alcaligenes faecalis, Citrobacter diversus (Huang & Tseng 2001)[5],
Rhodococcus sp. (Chen et al. 2012)[6], Klebsiella pneumonia (Padhi et al. 2013)[7],
Microbacterium sp. (Zhang et al. 2013)[8], Paracoccus versutus (Shi et al. 2013)[9], Acinetobacter
sp.
Previous studies mainly showed the application of aerobic denitrification in wastewater treatment.
For examples, Pai et al. (Pai et al. 1999)[10] added the aerobic denitrification bacteria
(Psychrobacter immobilis T6, Ochrobactrum anthropi T23, and Alcaligenes denitrificans T25.) to
activated sludge to treat a synthetic wastewater; Bouchez et al. (Bouchez et al. 2009)[11] showed that
the aerobic denitrifier (Microvirgula aerodenitrificans) were embedded within an alginate, and
alginate fragments adhered to existing flocs and were progressively colonized by the indigenous flora;
Gupta et al. (Gupta & Gupta 2001)[12] showed that the alkalinity could be increased through the
aerobic denitrifier in nitrification stage (Thiosphaera pantotropha); Ma et al. (Wang et al. 2007)[13]
showed that biological treatment of nitrate wastewater with aerobic denitrifiers in a bioceramic
reactor was successful. However, there are rarely reports of aerobic denitrification bacteria isolated
from the reservoir for bioremediation of source water ecosystem. Our research team has been
researching the aerobic denitrifiers for a while. The goal of the study was to determine the
effectiveness of denitrification with a low C/N ratio and a high dissolved oxygen concentration, and
the performance of nitrogen removal in different temperature, water pressure and inoculums in situ.
2. Material and methods
2.1. Microorganism
The strain was isolated from the sediment samples of Zhoucun reservoir (N34°57′, E117°40′21″) in
Shandong Province, China and identified as Zoogloea sp. N299 (GenBank No. KP717093). This
isolated strain could express periplasmic nitrate reductase which is essential for the aerobic
denitrification.
2.2. The relationship between OD value and colony of the N299
In order to reflect the number of colony through the OD value (optical density) of aerobic
denitrification bacteria in the medium, it is necessary to study the relationship between OD and
colony number. The aerobic denitrifying bacteria N299 was precultured 24 h in 50 mL/150mL
Erlenmeyer flask at 30 °C, 120 rpm, in screening medium (SM) of pH 7.2 (in g/L: CH
3
COONa 0.1;
NaNO
3
0.02; K
2
HPO
4
•3H
2
O 0.02; CaCl
2
0.01; MgCl
2
•6H
2
O 0.01). The N299 was inoculated at 2 %
(v/v) into 150 mL/250 mL Erlenmeyer flask 24 h, the cell pellet was prepared by centrifuging a 10
mL sample of broth culture at 5000 rpm for 10 min and then decanted the supernatant after washing
twice with distilled water. Then through adding the distilled water, we got a series of OD. The
diluents were streaked on a solid screening medium (SM) of pH 7.2 (in g/L: CH
3
COONa 0.1; NaNO
3
0.02; K
2
HPO
4
•3H
2
O 0.02; CaCl
2
0.01; MgCl
2
•6H
2
O 0.01; agar 20.00) and incubated at 30 °C for 5
days. Prominent single colonies were harvested and the number of colonies of every OD suspension
was calculated.
2.3. The temperature distribution of the reservoir
Based on the measurement the temperature of 0.5, 2.5, 5, 5.5, 6, 6.5, 7, 7.5, 8, 9, 10, 12.5, 15 m in 0,
24, 36, 48, 60, 72 h and 96 h, we got the temperature distribution.
2.4. The temperature gradient experiment of N299 in situ
Based on the temperature distribution of the reservoir, we designed three temperature gradient
experiment, 30 ± 2 °C in the surface water layer (0.5 m), 18.5 ± 0.5 °C in the middle water layer (7.5
IWEMSE 2018 - International Workshop on Environmental Management, Science and Engineering
622
m), and 11.5 ± 0.5 °C in the bottom water layer (15 m). And we used the hard flask and soft flask to
study the influence of the water pressure in the reservoir. The aerobic denitrifying bacteria N299 was
precultured 24 h in 50 mL liquid medium (without agar) in 100 mL Erlenmeyer flask at 30 °C, 120
rpm, in order to be activated. Then the N299 was inoculated at 1 ‰ (v/v) (5 mL/5L) into 5L hard
flask and soft flask respectively. The nitrate, nitrite, ammonia, TN, TDN, TOC and cell optical
density (OD) were measured to reflect the denitrification performance of N299.
2.5. The different inoculums experiment of N299 in situ
In order to study the practical inoculums of N299 to remediate the micro-polluted source water, we
designed the different inoculums of N299 experiments which were located in the middle of the
reservoir (7.5 m), meanwhile we used the hard flask and soft flask systems to explore the influence of
the water pressure to denitrification process in the reservoir. After precultured, the N299 was
inoculated in 5 L flask system. The inoculums gradient: 1 mL/5L, 2mL/5L, 5mL/5L, 10mL/5L.
2.6. Analytical methods
The optical density of the culture broth was measured at 600nm (OD
600
) using a spectrophotometer.
Nitrate, nitrite, ammonia, and TN were determined by the procedures detailed in the standard
methods (Chinese 2002)[14]. Briefly, Nitrite was determined by N-(1-naphthalene) diaminoethane
photometry method; Ammonium was determined by the method of Nessler’s reagent
spectrophotometry; TN, TDN and nitrate were measured by hydrochloric acid photometry method;
TOC analysed by TOC analyser (ET1020A); Aerobic denitrifying bacteria colonies were measured
by plate count; T and DO were measured by HQ30d (HACH Company, USA); The samples of
nitrate, nitrite, ammonia and TDN were filtrated using a 0.45μm cellulose acetate filter for removing
bacteria.
3. Results
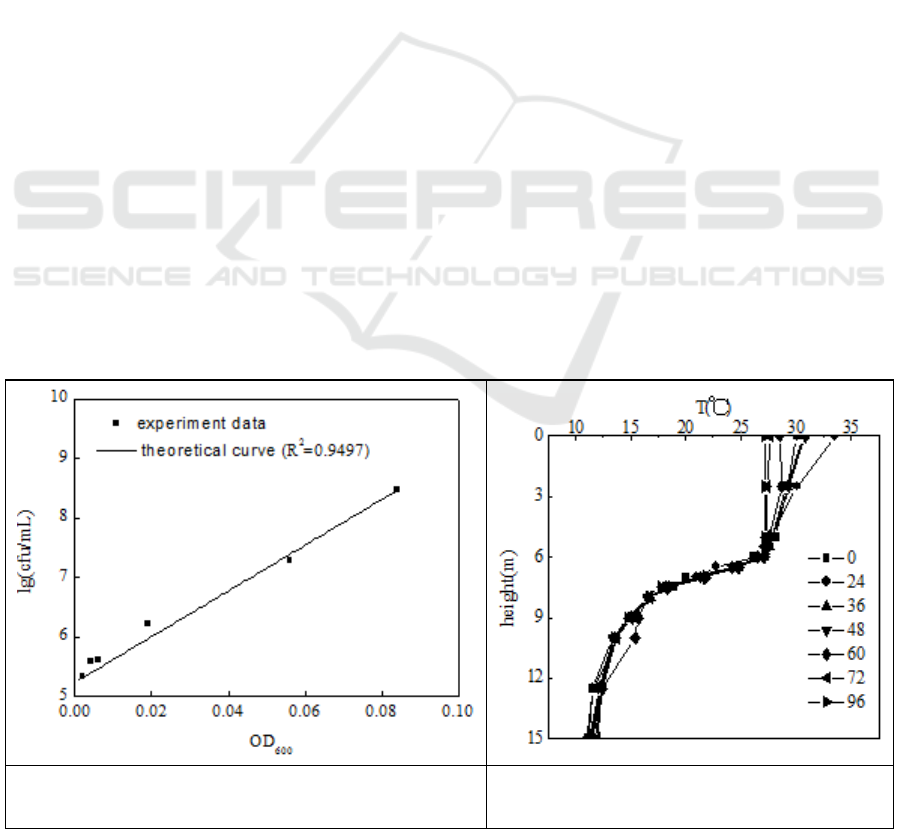
3.1. The relationship between OD and colony of the N299
The relationship (figure 1) was showed in the following: y (lg(colony)) = 5.23 + 38.51x (OD
600
). The
correlation coefficient R
2
=0.9497. Then, we can get the colonies of the medium through measuring
the OD
600
.
Figure 1. The relationship between OD600 and
colonies’ number of N299.
Figure 2. The temperature distribution in
the reservoir.
In Situ Nitrogen Removal by a Newly Isolated Oligotrophic Aerobic Denitrifier Zoogloea Sp. N299, in Relations with Temperature and
Water Pressure in a Reservoir
623

3.2. The temperature distribution of the reservoir
In the figure 2, in 96 h the temperature distribution maintains a stable state. Based on the temperature
distribution of the reservoir, we designed three temperature gradient: the surface water layer, the
middle water layer, the bottom water layer. The schematic diagram of the flask experiments in situ
was shown in figure 3. In detail, Figure3-a, the temperature gradient experiment of hard flask in situ;
3b, the temperature gradient experiment of soft flask in situ; 3c, the different inoculums of N299 in
hard flask in situ; 3d, the different inoculums of N299 in soft flask in situ
Figure 3. The schematic diagram of the flask experimental systems in situ.
3.3. The temperature gradient experiment of hard flask in situ
As shown in figure 4a, the nitrate of surface system decreased from 3.77 mg/L to 0.03 mg/L, the
middle system from 3.77 mg/L to 1.47 mg/L, the bottom system from 3.77 mg/L to 1.60 mg/L, in 96
h. It is obvious that the performance of the nitrogen removal of the surface system is the best. In
figure 4b and figure 4c, the nitrate removal rates of surface system reached 99.21 %, the middle
reached 61.1 %, the bottom reached 57.66 %, and no nitrite accumulation in 96 h. The removal rate
of nitrate correlated strongly with the growth rate of isolate N299. Because carbon is essential for cell
growth and nitrate reduction processes, the optimal quantity of carbon is a key parameter in the
denitrification process. With the death of N299, the ammonia started to release into the water. In
figure 4d, the ammonia in surface and middle system had a light increase, but 48 h, the ammonia
began to decrease which correlated strongly with the growth rate of isolate N299. As shown in figure
4e and figure 4f, the 82.42 % of TN in surface system, 38.47 % in middle system, and 27.10 % in
bottom system changed into gas and achieved removal.
In the figure 4e, the C/N from 4.67 reached 6.78 in surface system, 0.93 in middle system, 0.68 in
bottom system, because of the lack of the carbon source, the denitrification can’t continue further. In
0 ~ 24 h, the strain was in logarithmic phase and had the highest performance of denitrification.
Moreover, the temperature maintained stable and the DO was in 4 ~ 8 mg/L.
3.4. The temperature gradient experiment of soft flask in situ
As shown in figure 4g, figure 4h and figure 4i, the nitrate removal rate of surface system reached
48.98 %, the middle reached 53.45 %, the bottom reached 56.08 %, and no nitrite accumulation in 96
h. The removal rate of nitrate correlated strongly with the growth rate of isolate N299. With the death
7.5m
anchor
1
2
3
4
anchor
Floating body
water
1
2
7.5m
anchor
7.5m
anchor
a
b
c
d
15m
15m
0.5m 0.5m
3
4
IWEMSE 2018 - International Workshop on Environmental Management, Science and Engineering
624

of N299, the ammonia started to release to the water, which correlated strongly with the growth rate
of isolate N299. As shown in figure 4k and figure 4l, the 36.40 % of TN in surface system, 23.74 %
in middle system, and 21.41 % in bottom system changed into gas and achieved removal. Compared
with the hard flask experiment, the water depth (hydrostatic pressure) was disadvantage to
denitrification process. In the figure 4k, the C/N from 4.67 reached 1.15 in surface system, 0.75 in
middle system, 0.82 in bottom system, because of the low C/N, the denitrification can’t continue
further. Moreover, the temperature maintained stable and the DO was in 4 ~ 8 mg/L.
Figure 4. The temperature gradient experiment in hard flask and soft flask systems, respectively.
0 12 24 36 48 60 72 84 96
0.0
0.8
1.6
2.4
3.2
4.0
0 12 24 36 48 60 72 84 96
0
20
40
60
80
100
0 12 24 36 48 60 72 84 96
0.00
0.04
0.08
0.12
0.16
0.20
0 12 24 36 48 60 72 84 96
0.0
0.3
0.6
0.9
1.2
1.5
0 12 24 36 48 60 72 84 96
0.0
0.8
1.6
2.4
3.2
4.0
0 12 24 36 48 60 72 84 96
0
15
30
45
60
75
90
a
NO
3
-N(mg/L)
0.5 7.5 15
b
NO
3
-N(%)
c
NO
2
-N(mg/L)
d
NH
+
4
-N(mg/L)
e
TN(mg/L)
f
TN(%)
0 12 24 36 48 60 72 84 96
0.0
0.8
1.6
2.4
3.2
4.0
0 12 24 36 48 60 72 84 96
0
20
40
60
80
100
0 12 24 36 48 60 72 84 96
0.00
0.05
0.10
0.15
0.20
0 12 24 36 48 60 72 84 96
0.0
0.3
0.6
0.9
1.2
1.5
0 12 24 36 48 60 72 84 96
2.0
2.4
2.8
3.2
3.6
4.0
0 12 24 36 48 60 72 84 96
0
15
30
45
60
75
90
g
NO
3
-N(mg/L)
h
NO
3
-N(%)
i
NO
2
-N(mg/L)
j
NH
+
4
-N(mg/L)
k
TN(mg/L)
T(h)
l
TN(%)
T(h)
In Situ Nitrogen Removal by a Newly Isolated Oligotrophic Aerobic Denitrifier Zoogloea Sp. N299, in Relations with Temperature and
Water Pressure in a Reservoir
625

3.5. The different inoculums of N299 in hard flask
The different inoculums experiment chose the temperature of in the middle of the reservoir (7.5 m) to
simulate the temperature of the whole reservoir. We designed four inoculums gradient: 1mL/5L
system, 2mL/5L system, 5mL/5L system, 10mL/5L system.
Figure 5. The different inoculums experiment in the hard flask and Soft flask system, respectively.
0 12 24 36 48 60 72 84 96
0.0
0.8
1.6
2.4
3.2
4.0
0 12 24 36 48 60 72 84 96
0
20
40
60
80
100
0 12 24 36 48 60 72 84 96
0.00
0.05
0.10
0.15
0.20
0 12 24 36 48 60 72 84 96
0.0
0.4
0.8
1.2
1.6
2.0
0 12 24 36 48 60 72 84 96
2.0
2.4
2.8
3.2
3.6
4.0
0 12 24 36 48 60 72 84 96
0
10
20
30
40
50
1 2 5 10
a
NO
3
-N(mg/L)
b
NO
3
-N(%)
c
NO
2
-N(mg/L)
d
NH
+
4
-N(mg/L)
e
TN(mg/L)
f
TN(%)
0 12 24 36 48 60 72 84 96
0.0
0.8
1.6
2.4
3.2
4.0
0 12 24 36 48 60 72 84 96
0
20
40
60
80
100
0 12 24 36 48 60 72 84 96
0.00
0.05
0.10
0.15
0.20
0 12 24 36 48 60 72 84 96
0.0
0.3
0.6
0.9
1.2
1.5
0 12 24 36 48 60 72 84 96
2.0
2.4
2.8
3.2
3.6
4.0
0 12 24 36 48 60 72 84 96
0
10
20
30
40
50
g
NO
3
-N(mg/L)
h
NO
3
-N(%)
i
NO
2
-N(mg/L)
j
NH
+
4
-N(mg/L)
k
TN(mg/L)
T(h)
l
TN(%)
T(h)
IWEMSE 2018 - International Workshop on Environmental Management, Science and Engineering
626

As shown in figure 5, the nitrate removal rate of the 1 my/5L system reached 61.60%, the 2 mL/5L
reached 60.02 %, the 5 mL/5L reached 61.08 %, and the 10 mL/5L reached 60.55 %, in 96 h. And
there was no nitrite accumulation in whole experiment (figure 5c).
The removal rate of nitrate correlated strongly with the growth rate of isolate N299. With the
death of N299, the ammonia started to release to the water, the ammonia began to increase which
correlated strongly with the growth rate of isolate N299. As shown in figure 5, the 29.94 % of TN in
1 mL/5L system, 27.10 % in 2 mL/5L, 38.47% in 5 mL/5L, and 27.10 % in 10 mL/5L were changed
into gas and achieved nitrogen removal. In the figure 5e, the C/N from 4.67 reached 0.54 in 5 mL/5L
system, in 36 h. Because of the lack of the carbon source, the denitrification can’t continue further. In
0 ~ 24 h, the strain was in logarithmic phase and had the highest performances of denitrification.
Moreover, the temperature maintained stable and the DO was in 4 ~ 8 mg/L.
3.6 The different inoculums of N299 in soft flask
As shown in figure 5g and figure 5h, the nitrate removal rate of the 1 mL/5L system reached 55.03%,
the 2 mL/5L reached 49.77 %, the 5 mL/5L reached 53.45 %, and the 10 mL/5L reached 51.35 %, in
96 h. And there was no nitrite accumulation in whole experiment(figure 5i). The removal rate of
nitrate correlated strongly with the growth rate of isolate N299. With the dead of N299, the ammonia
started to release to the water, in figure 6j, the ammonia began to increase which correlated strongly
with the growth rate of isolate N299. As shown in figure 5k and figure 5l, the 16.24 % of TN in 1
mL/5L system, 29.94 % in 2 mL/5L, 23.74 % in 5 mL/5L, and 24.77 % in 10 mL/5L were changed
into gas and achieved removal. The 2 mL/5L system owned the best denitrification ability. The water
pressure had a bad effect on denitrification.
The TDN removal rate reached 42.31 % in 1 mL/5L, 42.05 % in 2 mL/5L, 35.55 % in 5 mL/5L,
and 32.43 % in 10 mL/5L, in 96 h. In the figure 5k, the C/N from 4.67 reached 0.93 in 1 mL/5L
system, 0.74 in 2 mL/5L system, 0.99 in 5 mL/5L, 0.92 in 10 mL/5L, in 36 h. Because of the lack of
the carbon source, the denitrification can’t continue further.
4. Discussion
Based on the temperature distribution of the reservoir, we designed three temperature gradient
experiments. Denitrification process is sensitive to temperature, and denitrification rate doubles with
every 4 °C increase (Zaitsev et al. 2008)[15]. As shown in Figure 4, temperature had a pronounced
effect on nitrogen removal by isolate N299. The nitrate removal percentage of hard flask experiment
increased from 57.66 % at 11.5 ± 0.5 °C to 99.21 % at 30±2 °C in 96 h. The TN removal percentage
of hard flask experiment increased from 27.10 % at 11.5 ± 0.5 °C to 38.47 % at 18.5 ± 0.5 °C to
82.42 % at 30 ± 2 °C in 96 h. Meanwhile, the nitrogen removal of hard flask was consistent with the
soft flask experiment. The TN removal percentage of soft flask experiment increased from 21.41 %
at 11.5 ± 0.5 °C to 23.74 % at 18.5 ± 0.5 °C to 36.40 % at 30 ± 2 °C in 96 h. A remarkable decrease
in nitrate and TN removal were found when the temperature increased from 11.5 ± 0.5 °C to 30 ±
2 °C. The optimal temperature for nitrogen removal was 30 ± 2 °C for N299, and the nitrogen
removal rate was higher than that of other bacteria capable of aerobic denitrification (Wei et al. 2010;
Wei et al. 2012)[16,17]. Moreover, the excellent adaptability to low temperature presented by strain
N299 is beneficial for nitrogen removal from water in cold regions.
In the temperature gradient experiment, in 7.5 m, the TN removal rate of the hard flask reached
38.47 %, however the soft flask system reached 23.74 %; in 15 m, the TN removal rate of the hard
flask reached 27.10 %, however the soft flask system reached 21.41 %. Table 1 showed a clear
relationship between environment variables and uncovered nitrogen in hard and soft flask experiment
systems, obviously. The bivariate analysis has indicated that uncovered nitrogen (gaseous N removal)
significantly correlated with the height (R=-0.9468) and (R=-0.9291), and temperature (R=0.9813)
and (R=0.9702) in hard and soft flask systems, respectively. Obviously, the hard flask system had a
In Situ Nitrogen Removal by a Newly Isolated Oligotrophic Aerobic Denitrifier Zoogloea Sp. N299, in Relations with Temperature and
Water Pressure in a Reservoir
627

better nitrogen removal performance than the soft flask system, which indicated that the water
pressure had a disadvantage to denitrification process. As we all known, the Carbon source, DO
concentration, C/N, and Temperature were the critical factors of denitrification, while the strains,
reactors and other unknown conditions also had some effect on the nitrogen removal (Tanner et al.
1999)[18]. The previous studies (Bartlett 2002; Picard & Daniel 2013)[19,20] showed that the high
static water pressure could influence on microbial growth and metabolic processes, which were
consistent with our results. There were some combined factors (DO, pH, and static water pressure) in
this in situ flask experiment, therefore, we only conducted a qualitative analysis between static water
pressure and denitrification. In order to explore the mechanism obviously, we would study further in
the future. In the different inoculums experiment, the nitrogen removal rate of the hard flask system
was better than the soft flask system. All in all, the nitrogen removal rate of the hard flask was higher
than the soft flask in the same water layer. The water pressure had a bad influence in the nitrogen
removal.
Table 1. Correlation analysis of environment variables and uncovered nitrogen in hard and soft flask
experiment systems.
System
Parameters
Depth
Temperature
DO
OD
TN R.E.
a
Hard flask
experiment
system
Depth
1
Temperature
-0.9910
1
DO
0.6820
-0.7737
1
OD
-0.4096
0.5280
-0.9465
1
TN R.E.
-0.9468
0.9813
-0.8811
0.6815
1
Soft flask
experiment
system
Depth
Temperature
-0.9910
1
DO
0.7595
-0.8397
1
OD
0.7107
-0.6103
0.0822
1
TN R.E.
-0.9291
0.9702
-0.9463
-0.4001
1
a
TN R.E., mean TN removal rate; uncovered nitrogen means gaseous nitrogen.
It is known that insufficient carbon supply impairs both microbial growth and electron donor for
denitrification (Lin et al. 2010; Zheng et al. 2012)[21,22]. Xu et al. (Zhu et al. 2012)[23] showed that
an aerobic denitrifier (Pseudomonas mendocina 3-7) could exhibit the aerobic denitrification
characteristic under the low substrate level (TOC, 48 mg/L and nitrate 4 mg/L), the removal
efficiencies of nitrate and TN were 31.7 % and 45.0 %, at 30 °C with a shaking speed of 150 rpm,
respectively. Zhao et al. (Zhao et al. 2010)[24] pointed out that an aerobic denitrifier ( Acinetobacter
calcoaceticus HNR ) ,isolated from a Membrane Bioreactor (MBR), could removal 40.2% of
ammonia at 30 °C with a shaking speed of 120 rpm. Yang et al. (Yang et al. 2011)[25] found out an
aerobic denitrifier (Bacillus subtilis A1) from ammonium-rich wastewater in situ, which could
removal TN stabilized at approximately 81.3% at 28 °C with a C/N of 6. However, in this study, the
removal efficiencies of nitrate and TN were 99.21 % and 82.42 %, at 30 ± 2 °C ,and inoculums had
a slight effect on nitrogen removal, which is consistent with our previous studies. Hence, fewer
requirements for C/N ratio and inoculum by strain N299 would be favourable for the treatment of
oligotrophic source water.
IWEMSE 2018 - International Workshop on Environmental Management, Science and Engineering
628

5. Conclusions
The OD of the strain N299 and the colony of the strain N299 had a good linear relationship. In the
temperature gradient experiment, the nitrogen removal rate increased significantly, and the strain
N299 showed a nice denitrification from 11.5 ± 0.5 °C to 30 ± 2 °C. Based on the hard flask
experiment and soft flask experiment, this study concluded the water pressure was not advantage to
the nitrogen removal. However, their removal rates did not significantly increase if the inoculum
ranges from 1 mL/5L to 10 mL/5L. Considering the practical requirements of biological inoculation,
the low inoculum period had practical significance
Acknowledgment
This study was funded by the National Science and Technology Pillar Program (No.
2012BAC04B02). Specially thanks to the anonymous reviewers for their valuable remarks on the
manuscript.
References
[1] Robertson L A and Kuenen J G 1983 Thiosphaera pantotropha gen.nov.sp.nov.a
Facultatively Anaerobic Facultatively Autotrophic Sulphur Bacterium Journal of
General Microbiology 129 2847-55
[2] Robertson L A, Kuenen J G and Kleijntjens R 1985 Aerobic denitrification and
heterotrophic nitrification by Thiosphaera pantotropha Antonie van Leeuwenhoek
51, 445
[3] Schmidt I, Sliekers O, Schmid M, Bock E, Fuerst J, Kuenen J. G, Jetten M S M and
Strous M 2003 New concepts of microbial treatment processes for the nitrogen
removal in wastewater. FEMS Microbiology Reviews 27(4) 481-92
[4] Su J J, Liu B Y and Liu C Y 2001 Comparison of aerobic denitrification under high
oxygen atmosphere by Thiosphaera pantotropha ATCC 35512 and Pseudomonas
stutzeri SU2 newly isolated from the activated sludge of a piggery wastewater
treatment system Journal of Applied Microbiology 90(3) 457-62
[5] Huang H K and Tseng S K 2001 Nitrate reduction by Citrobacter diversus under
aerobic environment Applied microbiology and biotechnology 55(1),90-4
[6] Chen P Z, Li J, Li Q X, Wang Y C, Li S P, Ren T Z and Wang L G 2012 Simultaneous
heterotrophic nitrification and aerobic denitrification by bacterium Rhodococcus sp.
CPZ24. Bioresour Technol 116,266-70
[7] Padhi S K, Tripathy S, Sen R, Mahapatra A S, Mohanty S and Maiti N K 2013
Characterisation of heterotrophic nitrifying and aerobic denitrifying Klebsiella
pneumoniae CF-S9 strain for bioremediation of wastewater. International
Biodeterioration & Biodegradation 78, 67-73
[8] Zhang D, Li W, Huang X, Qin W and Liu M 2013 Removal of ammonium in surface
water at low temperature by a newly isolated Microbacterium sp. strain SFA13
Bioresource technology 137 147-52
[9] Shi Z, Zhang Y, Zhou J T, Chen M X and Wang X J 2013 Biological removal of
nitrate and ammonium under aerobic atmosphere by Paracoccus versutus LYM.
Bioresource technology 148 144-8
[10] Pai S L, Chong N M and Chen C H 1999 Potential applications of aerobic denitrifying
bacteria as bioagents in wastewater treatment. Bioresource technology 68(2) 179-85
[11] Bouchez T, Patureau D, Delgenès J P and Moletta R 2009 Successful bacterial
In Situ Nitrogen Removal by a Newly Isolated Oligotrophic Aerobic Denitrifier Zoogloea Sp. N299, in Relations with Temperature and
Water Pressure in a Reservoir
629

incorporation into activated sludge flocs using alginate Bioresource technology
100(2) 1031-2
[12] Gupta A B and Gupta S K 2001 Simultaneous carbon and nitrogen removal from high
strength domestic wastewater in an aerobic RBC biofilm Water Research 35(7)
1714-22
[13] Wang H Y, Ma F, Su J F, Zuo W, Zhang J and Zhang X X 2007 Aerobic
denitrification of nitrate wastewater and changes of microbial community structure
in a bio-ceramic reactor Journal of Environmental Sciences 28(12), 2856-60
[14] Chinese N 2002 Water and wastewater monitoring methods In, Chinese Environmental
Science Publishing House p. 806
[15] Zaitsev G, Mettänen T and Langwaldt J 2008 Removal of ammonium and nitrate from
cold inorganic mine water by fixed-bed biofilm reactors. Minerals Engineering 21(1) 10-5
[16] Wei W, Huang T L and Li N 2012 Denitrification characteristics of in-situ biological
inoculation under conditions of low temperature and poor nutrient Water
Technology (in Chinese) 6, 8-12
[17] Wei W, Huang T L, Su J F, Wang C Y, Huang Z and Li N 2010 Isolation and
identification of an oligotrophic and aerobic denitrification and its denitrification
characteristics. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 19 2166-71
[18] Tanner C C, D'Eugenio J, McBride G B, Sukias J P and Thompson K 1999 Effect of
water level fluctuation on nitrogen removal from constructed wetland mesocosms
Ecological Engineering 12(1) 67-92
[19] Bartlett D H 2002 Pressure effects on in vivo microbial processes. Biochimica et
Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Protein Structure and Molecular Enzymology 1595(1) 367-
81
[20] Picard A. and Daniel I. (2013). Pressure as an environmental parameter for microbial
life—A review Biophysical chemistry 183, 30-41
[21] Lin Y, Kong H, Wu D, Li C, Wang R. and Tanaka S 2010 Physiological and molecular
biological characteristics of heterotrophic ammonia oxidation by Bacillus sp. LY.
World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology 26(9) 1605-12
[22] Zheng H Y, Liu Y, Gao X Y, Ai G M, Miao L L and Liu Z P 2012 Characterization of
a marine origin aerobic nitrifying–denitrifying bacterium Journal of Bioscience and
Bioengineering 114(1) 33-7
[23] Zhu L, Ding W, Feng L J, Dai X and Xu X Y 2012 Characteristics of an aerobic
denitrifier that utilizes ammonium and nitrate simultaneously under the oligotrophic
niche. Environmental Science and Pollution Research 19(8), 3185-91
[24] Zhao B, He Y. L, Hughes J and Zhang X F 2010 Heterotrophic nitrogen removal by a
newly isolated Acinetobacter calcoaceticus HNR Bioresource technology 101(14)
5194-200
[25] Yang X P, Wang S M, Zhang D W and Zhou L X 2011 Isolation and nitrogen removal
characteristics of an aerobic heterotrophic nitrifying–denitrifying bacterium,
Bacillus subtilis A1 Bioresource technology 102(2) 854-62
IWEMSE 2018 - International Workshop on Environmental Management, Science and Engineering
630
