
Constructed Rapid Infiltration Systems for Urban Runoff
Control: Influences of Medium Contents, Medium Depth and
Hydraulic Load Cycle
Q Feng
1,2,*
, Y Q Sun
1
, X Y Zhao
1
, W Huang
3
, Z X Xue
1,2
and J Y Luo
1,2
1
Key Laboratory of Integrated Regulation and Resource Development on Shallow
Lakes, Ministry of Education, Hohai University, Nanjing 210098, China
2
College of Environment, Hohai University, Nanjing 210098, China
3
Nanjing Urban Planning Bureau, Nanjing 210029, China
Corresponding author and e-mail: Q Feng, xiaofq@hhu.edu.cn
Abstract. The constructed rapid infiltration system (CRIS) has been widely used in urban
stormwater management. However, limited knowledge has been acquired for the selection
and optimization of mediums in CRIS. In this paper, the performance of CRIS was improved
by different contents of natural soil, natural sand and zeolite. Permeability coefficient (K),
uniformity coefficient (K
80
) and pollutants removal efficiencies were used to evaluate the
influences of medium contents on the operation of CRIS in static test. Using the best medium
contents, the effects of medium depth and hydraulic load cycle on CRIS performance were
further investigated. The result shows that the best and cost-effective permeability coefficient
(0.166 cm/min) and high pollutant removal efficiency (> 70%) were obtained when the ratio
of sand : soil : zeolite was 47.5% : 47.5% : 5%. The pollutant removal efficiency in the
surface layer (0 - 30 cm) was significantly higher than that in bottom (50 - 80 cm). Higher
pollutants removal were gotten at hydraulic load cycle of submergencing for 2 hours and
drying for 10 hours. The main factor affecting the removal of COD and ammonia nitrogen
was the change of aerobic environment in CRIS which mainly relied on biofilms to degrade
and adsorb pollutants.
1. Introduction
The amount of pollutants from urban runoff has gradually increased with fast urbanization, which
would cause severe damage to water environment in urban area
[1]. Land infiltration system is a
typical green infrastructure [2]. Because of its low operating cost, good environmental benefits, and
slight ecological impact, it has been used in urban runoff management recently. Nevertheless, the
reduction of soil permeability caused by clogging affects the performance of infiltration system
[3].
Therefore, it is important to find effective ways, such as medium improvement and operation
optimization, to solve these problems in land infiltration system.
Constructed rapid infiltration system (CRIS) is developed based on traditional land infiltration
system [4-6]. Compared with land infiltration systems used in wastewater treatment, multi-medium
with high permeability and strong adsorption capacity such as natural sand, ceramic particles, gangue,
and zeolite were used to replace part of the natural soil in order to improve system performance [7].
Feng, Q., Sun, Y., Zhao, X., Huang, W., Xue, Z. and Luo, J.
Constructed Rapid Infiltration Systems for Urban Runoff Control: Influences of Medium Contents, Medium Depth and Hydraulic Load Cycle.
In Proceedings of the International Workshop on Environmental Management, Science and Engineering (IWEMSE 2018), pages 637-644
ISBN: 978-989-758-344-5
Copyright © 2018 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
637
Current researches have confirmed that the use of particulate filter and adsorbing materials could
increase hydraulic load and enrich pollutants removal [8]. However, limited knowledge has been
acquired of the selection of mediums and optimization of CRIS during urban runoff control.
In view of this, the objective of this paper is to investigate the influences of medium contents,
medium depth and hydraulic load cycle on the pollutants removal by CRIS. Different contents of
natural soil, sand and zeolite were used in CRIS. Permeability coefficient, nonuniformity coefficient,
and pollutant removal efficiencies were used to evaluate the influences of medium contents on the
operation of CRIS. Using the best medium contents, the effects of medium depth and hydraulic load
cycle on CRIS performance were further investigated.
2. Materials and methods
2.1. Experimental set-up
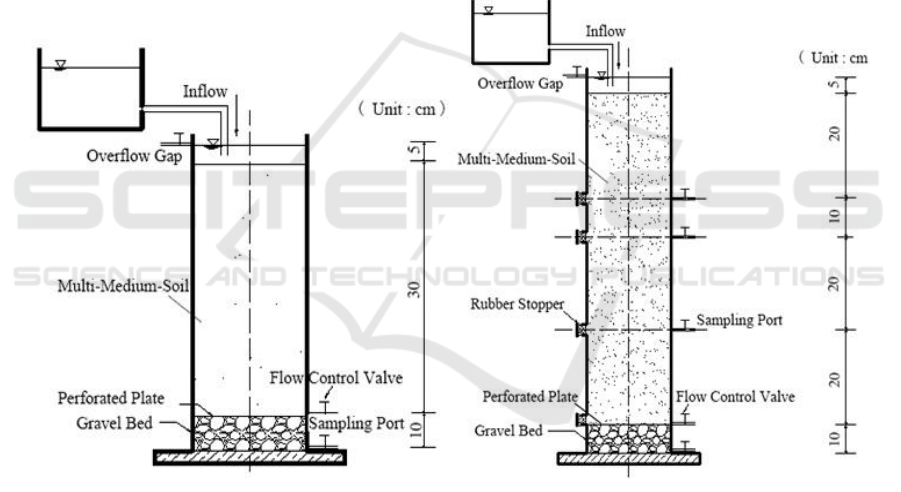
The experiments were conducted in the CRIS columns for static test and dynamic test, respectively
(Figure 1). The diameter of the CRIS columns was 10 cm. The height of the medium layer of CRIS
columns in static test was 30 cm, and the height in dynamic test was 80 cm.
(A) (B)
Figure 1. CRIS columns in static test (A) and dynamic test (B).
2.2. Materials
The columns were filled with different mediums that were uniformly mixed with local natural soil,
coarse sand, and zeolite. Natural soil was from surface silty clay in southern Jiangsu province, and
the maximum permeability coefficient was 0.003 m/d. Coarse sand and zeolite were purchased
locally. The particle size of zeolite was 1.5 - 1.8 mm, which had a specific surface area 200 - 300
m
2
/g.
The urban runoff used in the test was synthesized with potassium hydrogen phthalate
(HOOCC
6
H
4
COOK), glucose (C
6
H
12
O
6
), ammonium sulfate ((NH
4
)
2
SO
4
), potassium dihydrogen
phosphate (KH
2
PO
4
) and potassium nitrate (KNO
3
). The water quality of runoff was determined
according to the monitoring results of rainfall runoff in a certain city in Southern Jiangsu, in which
IWEMSE 2018 - International Workshop on Environmental Management, Science and Engineering
638

COD was 500 ± 10 mg/L, NH
4
+
-N was 5 ± 0.4 mg/L, TN was 20 ± 2 mg/L, and TP was 1 ± 0.02
mg/L.
2.3. Experimental procedure
Influence of medium content on CRIS performance. Four different volume percentages of zeolites
such as 5%, 10%, 15%, and 20% were set in CRIS. Meanwhile, the volume ratios of natural soil and
coarse sand were respectively set to 1 : 4, 1 : 3, 1 : 2, and 1 : 1. Thus, 16 kinds of mediums were
conducted in static test (Table 1). Permeability coefficient, uniformity coefficient (K
80
), and
pollutants removal efficiency were measured to evaluate the influences of medium contents in static
test.
Table 1. Contents of different mediums in CRIS (in volume, %).
No.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
Natural Soil
19.00
18.00
17.00
16.00
23.75
22.50
21.25
20.00
Coarse Sand
76.00
72.00
68.00
64.00
71.25
67.50
63.75
60.00
Zeolite
5.00
10.00
15.00
20.00
5.00
10.00
15.00
20.00
No.
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
Natural Soil
31.67
30.00
28.33
26.67
47.50
45.00
42.50
40.00
Coarse Sand
63.33
60.00
56.67
53.33
47.50
45.00
42.50
40.00
Zeolite
5.00
10.00
15.00
20.00
5.00
10.00
15.00
20.00
Influence of medium depth and hydraulic load cycle on CRIS performance. Five sampling ports were
set in CRIS at the depth of 20, 30, 50, 70, and 80 cm to investigate the impacts of medium depth on
CRIS performance in dynamic test. Four operating conditions, including the ratio of water
submerging time and drying time of 1 : 5 and 1 : 8 while water submerging time was set by 2h and
4h, were respectively determined to examine the water quality at the end of land infiltration system.
The test operating conditions for the study of hydraulic load cycle effects are shown in Table 2. The
depth of submerging in the upper part of the layer was ensured to be 5 cm, so that the test columns
could be maintained at constant head with the temperature from 19 °C to 24 °C in water.
Table 2. Test conditions setting for different hydraulic load cycle.
No.
1
2
3
4
Submerging Time (h)
2
4
2
4
Drying Time (h)
10
20
16
32
2.4. Analytical methods
The permeability coefficient (K) and the nonuniformity coefficient (K
80
) were determined by the
Standard Methods. The procedures for determining COD, TN, NH
4
+
-N and TP were detailed in the
Standard Methods[9]. The pH and DO values were determined with pH meter (HACH-sension2) and
portable dissolved oxygen meter (HACH-HQ30d), respectively[10]. The temperature was measured
with a thermometer. All assays were performed in triplicate, an analysis of variance (ANOVA) was
used to test the significance of the results and p < 0.05 was considered to be statistically significant.
3. Results and discussion
3.1. Selection and optimization of multi-medium proportion of CRIS
Figure 2 showed the static removal effect of CRIS on various pollutants in rainfall runoff under
different medium contents. The removal of COD and TP varied greatly in different reactors. However,
the presence of zeolite in CRIS effectively improved the adsorption of nitrogen. The removal
efficiency of NH
4
+
-N from all multi-medium-soil can reach over 60%, and the removal efficiencies of
Constructed Rapid Infiltration Systems for Urban Runoff Control: Influences of Medium Contents, Medium Depth and Hydraulic Load
Cycle
639
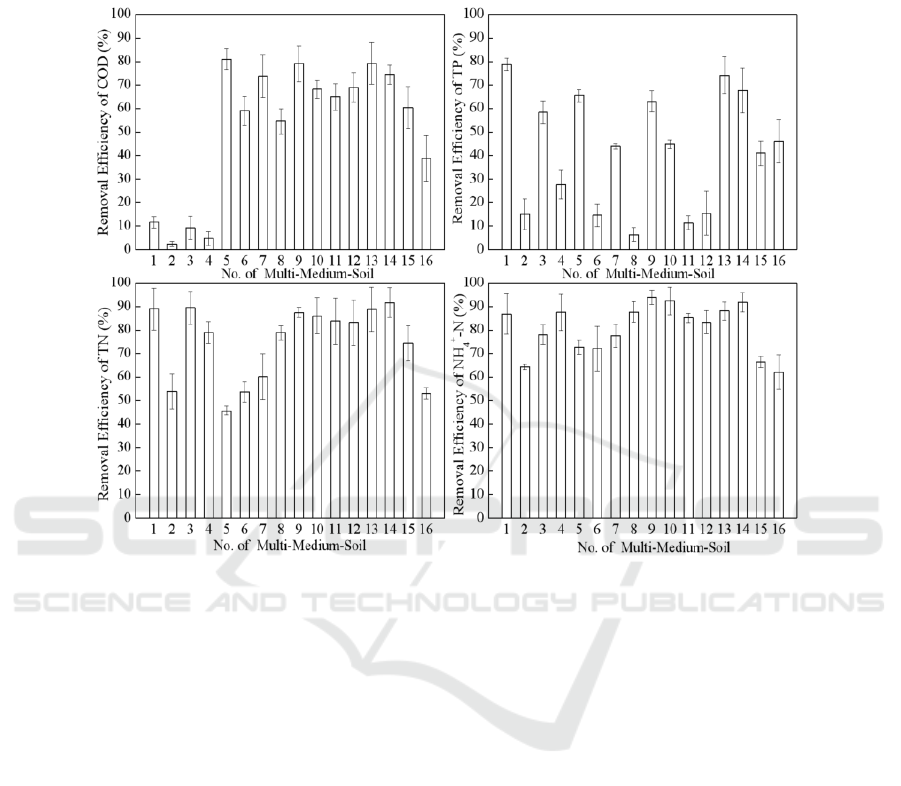
TN were also above 45%, which was significantly higher than that of COD and TP. By
comprehensive evaluation of the removal efficiency of all typical pollutants, the reactors with No. 9,
13, and 14 soil medium were preferred in CRISs (The pollutant removal efficiencies were > 80% for
NH
4
+
-N and TN, and > 60% for COD and TP).
Figure 2. Effects of CRIS on the static removal of various pollutants in rainfall runoff under different
medium contents.
Figure 3 shows the nonuniformity coefficient K
80
and the permeability coefficient K of the matrix
under different medium contents. K
80
of the matrix from the mediums with different ratios ranged
from 7.32 to 8.36, and K ranged 0.011 to 0.166 cm/min. Further analysis indicated that the negative
correlation between the permeability coefficient and the nonuniformity coefficient was evident.
It was also found that the particle grading condition was the main factor affecting the permeability
coefficient of the mixed matrix. By changing the composition of three different materials and grades
of infiltration medium, the permeability coefficient can be changed with the same proportions of
medium materials. The permeability coefficient of the infiltration medium was increased, and thus
the hydraulic load of the CRIS can be improved.
IWEMSE 2018 - International Workshop on Environmental Management, Science and Engineering
640

Figure 3. Nonuniformity coefficient K
80
and the permeability coefficient K of the matrix under
different medium contents.
The permeability coefficient of the No. 13 soil medium was 0.1660 cm/min, which was much
higher than 0.0126 cm/min of No. 9 and 0.0594 cm/min of No. 14. Meanwhile, its removal efficiency
of COD, NH
4
+
-N, TN, and TP reached respectively 79.20%, 88.09%, 88.76%, and 74.11%, which
was also the highest in all the three reactors. The best and cost-effective permeability coefficient
(0.166 cm/min) and high pollutant removal efficiency (> 70%) were obtained when the ratio of sand :
soil : zeolite was 47.5% : 47.5% : 5%.
3.2. Influence of different medium depth on pollutants degradation
The thickness of the soil layer was an important parameter in the design of CRIS. To achieve better
treatment effects, the thickness of the soil layer should not be too thin. Meanwhile, it should not be
too thick due to the terrain conditions and the difficulty of construction. Figure 4 shows the treatment
effects of medium depth (20, 30, 50, 70 and 80 cm) on various contaminants.
As can be seen from Figure 4, the removal efficiency of contaminants incremented with the
increase of medium depth in CRIS. The removal efficiency of NH
4
+
-N, TN, and COD showed that
the pollutants removal efficiency in the upper of CRIS (30 - 50 cm) was significantly higher than that
in the lower part except TP. In general, increasing medium depth in certain range can enhance the
treatment effects of CRIS and ultimately improve the quality of the effluent water. However, a
plateau would be observed with the excessive increase of medium depth which was quite
uneconomic.
The removal of organic contaminants by CRIS was mainly caused by mechanical interception,
adsorption and biodegradation. The organic contaminants in the influent were all soluble, so they
were mainly removed by the adsorption and biodegradation of the biofilm on the surface of the
multi-medium material.
The mechanism for the nitrogen removal included volatilization, adsorption, nitrification, and
denitrification in CRIS. The volatilization is very weak with pH ranged from 6.5 to 7.5 in this test.
The zeolites configured in CRIS had a strong NH
4
+
-N selective adsorption capacity and played
important roles in the initial nitrogen removal. Meanwhile, the dynamic test results showed that the
degradation of nitrogen by CRIS kept at a high level, which indicating the major role of nitrification
and denitrification processes for nitrogen reduction. The short of oxygen supply was supposed to be
the main reason that limited the NH
4
+
-N removal in CRIS. The surface reoxygenation in CRIS was
advantageous to the increase of nitrifying bacteria abundances and activities, which was in
accordance with the efficient nitrogen removal in surface layer (30 cm). It further confirmed the fact
Constructed Rapid Infiltration Systems for Urban Runoff Control: Influences of Medium Contents, Medium Depth and Hydraulic Load
Cycle
641

from another aspect that microbial nitrification played an important role in the nitrogen removal from
CRIS.
Figure 4. Removal efficiency of various contaminants with different medium depth.
The removal efficiency of TP was declined with the increase of medium depth. It may be
attributed to the release of phosphorus under anaerobic conditions by related microorganisms. The
surface layer (30 cm) in CRIS was in aerobic conditions. Microorganisms could absorb phosphorus
from water efficiently, and thus the removal efficiency of TP gradually increased. However, in deep
layer (50 - 80 cm), the phosphorus release increased significantly by the microorganism due to the
scarcity of DO, resulting in a decrease of TP removal efficiency.
3.3. Effects of different hydraulic load cycles on the pollutants degradation
It can be seen from Figure 5 that the removal efficiencies of COD and NH
4
+
-N were in the order of
column 1> column 2> column 4> column 3. It can be mainly explained via the influence of different
submerging-drying time cycles on the internal aerobic environment and microbial community in
CRIS. The submerging-drying time ratio of column 1 and column 2 was 1 : 5, while the
submerging-drying time radio of column 3 and column 4 was 1 : 8. Since the DO of CRIS mainly
depended on its saturation in influent . The reoxygenation of the surface medium was more complete
and thus was beneficial to the formation of the aerobic environment for columns 1 and 2 with higher
submerging-drying frequency while the ability of COD degradation and NH
4
+
-N nitrification were
stronger. In addition, the cycle of submerging-drying contributed to the stability of the internal
aerobic environment of the CRIS, which was also the key to the removal of COD and NH
4
+
-N.
Compared with other hydraulic load cycles, the submerging time of 2 hours and the drying time of 10
hours created a more stable microscopic aerobic environment. However, the submerging time of 2
hours and the drying time of 16 hours may cause drastic changes in aerobic environment of
microorganisms inside the CRIS, resulting in the worst removal efficiency of COD and NH
4
+
-N.
IWEMSE 2018 - International Workshop on Environmental Management, Science and Engineering
642
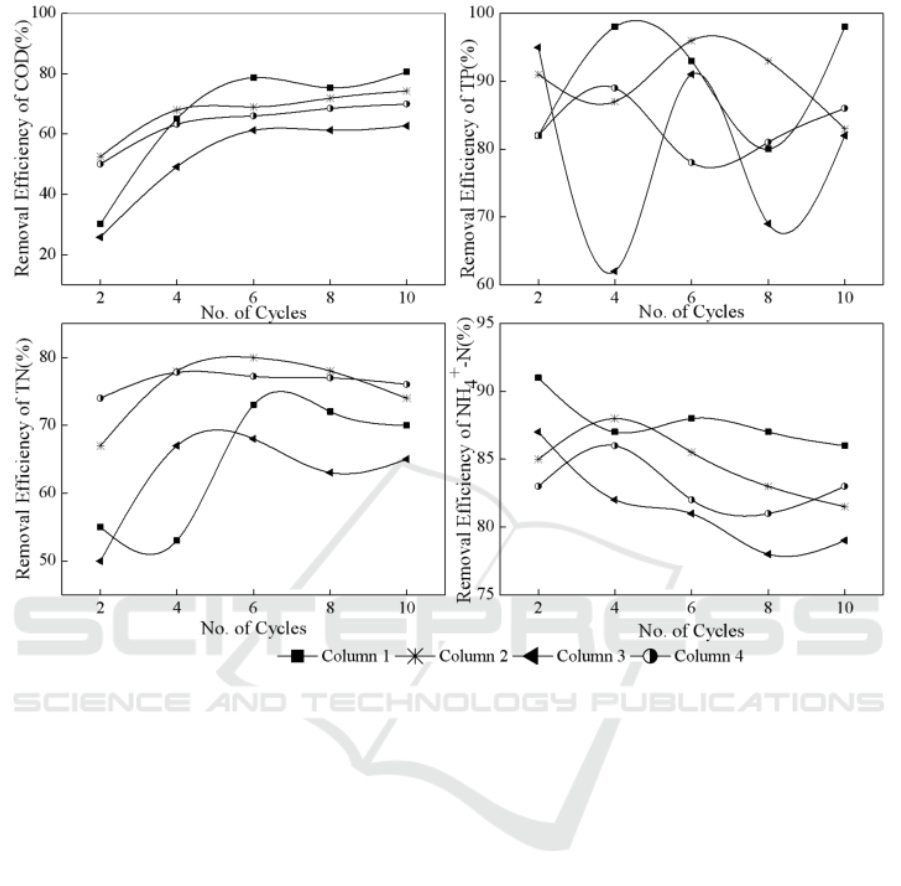
Figure 5. Removal efficiency of pollutants under different hydraulic load cycles.
The nitrogen in the test water was mainly in the form of NO
3
-
and NH
4
+
. The concentration of
NH
4
+
was 5 mg/L. The removal mechanism of TN by CRIS could mainly be attributed to the
combined effects of nitrification and denitrification considering the characteristics of influent. It can
be seen from Figure 5 that the removal efficiency of TN was better in column 4 and 2. The long
submerging time in column 4 and 2 may prevent the transport of oxygen in the topsoil layer and
make the denitrification fully performed, which resulted in the higher removal efficiency of TN. The
above results showed that the smaller the submerging-drying ratio was, the more favorable
performance of TN removal could be achieved.
It can also be seen from Figure 5 that under different hydraulic load cycles, the removal
efficiencies of TP in CRIS were all over 60%. However, the removal efficiencies were varied
significantly during the whole operating time which required further study in details.
4. Conclusions
CRIS was an effective strategy for the pollutants control of urban runoff. The best and cost-effective
permeability coefficient (0.166 cm/min) and high pollutant removal efficiency (> 70%) were
obtained when the ratio of sand : soil : zeolite was 47.5% : 47.5% : 5%.The pollutants removal in the
surface layer (0 - 30 cm) of CRIS was significantly higher than that in the deeper layer (50 - 80 cm).
Higher pollutants removal were obtained at the hydraulic load cycle of 2 hours submergencing and
10 hours drying. Under such conditions, the removal rates of COD, NH
4
+
N, TN, and TP reached
80%, 85%, 65%, and 90%, respectively. The adsorption and degradation of pollutants on
multi-medium surface biofilm were the main mechanisms for the efficient pollutants removal in
Constructed Rapid Infiltration Systems for Urban Runoff Control: Influences of Medium Contents, Medium Depth and Hydraulic Load
Cycle
643

CRIS and the variation of aerobic environment was important to the removal of COD and nitrogen.
Acknowledgements
, tment NO:
2014ZX07305-
her Education Institutions
References
[1] Kedar S, Pike W T, Standley I M, Calcutt S B, Bowles N, Blaes B, Irom F, Mojarradi M, Vance
S D and Bills B G 2016 Lpi Contributions
[2] Lee J H, Bang K W, Jr L H K, Choe J S and Yu M J 2002 Sci. Total Environ. p 163-175
[3] Ic E 2000 Water Res. p
3675-3681
[4] Zhang X, Guo L, Huang H, Jiang Y, Li M and Leng Y 2016 Water Res. p 280-291
[5] Chen J M 2011 Advanced Materials Research. p 1735-1739
[6] Lian Y, Xu M, Zhong Y, Yang Y, Chen F and Guo J 2014 PLoS One. p 114723
[7] Jiang X, Ma M, Li J, Lu A and Zhong Z 2011 J. Earth Sci.-China. p 669-676
[8] Cao J, Yu Y, Xie K, Luo J, Feng Q, Fang F, Li C and Xue Z 2017 RSC Adv. p 55088-55097
[9] Clesceri L, Greenberg A S and Eaton D L 2005 American Journal of Public Health & the
Nations Health. p 387
[10] Kang A, Wang L and Zhang B 2017 Journal of Residuals Science & Technology. p 115-120
IWEMSE 2018 - International Workshop on Environmental Management, Science and Engineering
644
