
Comparation of Estradiol and Estriol Serum Levels in Different
Degrees of Melasma Severity in Pregnant Women
Tantari Sugiman, Dyah Ayu Savitri and Arif Widiatmoko
Department of Dermatology and Venereology, Faculty of Medicine, Universitas Brawijaya / dr. Saiful Anwar Regional
General Hospital, Malang, Indonesia
Keywords: Estradiol, Estriol, Melasma, Severity, Pregnancy.
Abstract: Estrogen, estradiol and estriol, is known to be capable of inducing melanogenesis and have been held
responsible for the pigmentation seen in pregnancy. This study was conducted to analyse serum levels of
estradiol and estriol in different degree of melasma severity in pregnant women. A cross-sectional study using
continuous sampling in pregnant women with melasma conducted in June - July 2017 at Dr Saiful Anwar
Regional General Hospital Malang, Indonesia. Inclusion criteria include pregnant women with melasma (15-
49 years). Pregnant women with previous history of non-pregnancy melasma, who are taking hormonal
contraceptives or taking hormonal drugs containing estrogen and taking phototoxic drugs excluded from the
study. History, physical examination, Wood Lamp, and measurement severity melasma using MSS (Melasma
Severity Score) was performed. Blood samples were drawn for serum estradiol and estriol serum examination
using ELISA method. Result from 25 pregnant women with melasma divided into four groups, clear (6
subjects), mild (5 subjects), moderate (9 subjects) and severe (5 subjects). Estradiol serum levels mean were
417.80 (clear), 836.60 (mild), 793.58 (moderate) and 891.00 (severe). Estriol serum levels mean obtained on
clear (94.67), mild (149.88), moderate (199.64) and severe (141.17). Significant different serum levels of
estradiol found in each group of MSS (p=0.015) and serum levels estriol did not significantly differ in each
group of MSS (p=0.454). This study concluded that estradiol serum levels in pregnant women with melasma
were different in melasma severity degrees, but estriol serum levels were not different in melasma severity
degrees.
1 INTRODUCTION
Melasma is also known by the name of chloasma or
mask of pregnancy (Newcomer et al, 1961) as it may
appear during pregnancy and is characterised by
symmetric hyperpigmentation lesions (Grawkrodjer
et al 2002) (Hindrtiatini, 2015). The incidence of
melasma is estimated to be about 0.2-4% of total
patients with skin disease in Indonesia (Praskoeswa,
2002).
Data obtained at dr Saiful Anwar Regional
General Hospital Malang, in 2014 melasma reached
338 (3.4%) patients from total of 9736 patients per
year, as the seventh of ten most common diseases in
the Dermatology and Venereology Outpatient. In
2015, the incidence of melasma decreased to 226
(2.7%) incidence of total 8310 patients per year. The
latest data obtained from Saiful Anwar's Dermatology
and Venereology Outpatients in 2016, the total
number patients of melasma as many as 185 (2.3%)
of total 7945 patients per year.
The predominance of melasma in women supports
the role of female sex hormones in one of the
pathogenesis of melasma, but the mechanism is
unclear (Handel et al, 2014). Estrogen enhancement
that increases α-MSH (Melanocyte-Stimulating
Hormone) expression in keratinocytes is thought to be
an essential key to explain the process of
hyperpigmentation occurring in the skin with
melasma (Im S et al, 2002). Estrogen is a steroid
hormone formed primarily of androstenedione. There
are three types of estrogens namely estrone, estradiol
and estriol.The potential of estradiol is 12 times the
estrone potential and eight times estriol, so estradiol
is considered the primary estrogen (Speroff et al,
2005). A study conducted by Gopichandani et al.
(2015) supports that the pathogenesis of melasma is
primarily affected by estradiol, evidenced by the high
levels of these hormones in melasma in pregnancy
was found to be lower than controls. Other estrogens
such as estriol and estrone are said to affect the
Sugiman, T., Savitri, D. and Widiatmoko, A.
Comparation of Estradiol and Estriol Serum Levels in Different Degrees of Melasma Severity in Pregnant Women.
DOI: 10.5220/0008151600950099
In Proceedings of the 23rd Regional Conference of Dermatology (RCD 2018), pages 95-99
ISBN: 978-989-758-494-7
Copyright
c
2021 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
95

cytoplasm and estrogen core receptors that are known
expressed in melanocytes (Gopichandani et al, 2015).
In pregnancy especially in the third trimester, high
levels of estriol and estradiol are associated with high
levels of α-MSH which can increase tyrosinase and
dopachrome tautomerase production so that
melanogenesis increased and vulnerable to melasma
(Ortonne et al, 2009).
Melasma Area Severity Index (MASI) is used to
measure the clinical severity quantity of melasma
(Kimbrough et al, 1994). In addition to the MASI
scheme, a global degree of severity is also required to
estimate treatment success in melasma clinical trials.
Melasma Severity Score (MSS), used as a worldwide
degree, is commonly used in clinical trials research
and is expected to be clinically meaningful in
describing the severity of disease that is easy to use in
clinicians and patients (Rodrigues et al, 2016).
Miranti et al. (2016) reported that serum estradiol
levels were slightly higher in pregnant women with
melasma than pregnant women without melasma, but
this increase in numbers was not significant. That is,
serum estradiol levels are associated with the age of
pregnant women and gestational age, but not related
to MASI score or melasma types. Meanwhile, no
literature has examined serum estriol, which
produced only during pregnancy against the severity
of melasma. The study objective is to compare serum
estradiol and estriol levels in degrees of melasma
severity in pregnant women.
2 METHOD
This study used cross-sectional observational analysis
in Pregnancy Outpatient Clinic, Dermatology and
Venereology Outpatients Clinic in dr Saiful Anwar
Regional General Hospital Malang and Physiology
Laboratory Faculty of Medicine Universitas
Brawijaya Malang, East Java, Indonesia. After
Hospital Ethics Committee approvement, this study
carried out from June to July 2017. Calculation
sample was using single population proportion at a
precision of 5%, 95% confidence interval and
prevalence of melasma in pregnancy 43,5%
(r=0,435).
9
This study population was 25 pregnant
women with melasma visited Outpatient Clinic.
Samples in this research are all population that fulfil
the criteria of inclusion and exclusion. Inclusion
criteria including pregnant women with melasma
aged 15-49 years, pregnant women with melasma that
appear during pregnancy either primigravida or
multigravida and willing to be the subject of research
and signed informed consent. Exclusion criteria for
pregnant women with prior history of melasma that
appear not during pregnancy, pregnant women using
hormonal contraceptives and hormone replacement
therapy (estrogen, progesterone or both), pregnant
women taking phototoxic drug (antibiotics, NSAIDs,
diuretics, retinoids, epidermal growth factor
inhibitors, anti-fungal, tranexamic acid,
antihistamines and neuroleptics), and Gemelli
pregnancy.
The diagnosis of melasma and determination of
severity made by anamnesis, physical examination
with a typical clinical picture then calculated
Melasma Severity Score by converting MASI score
into MSS. Melasma Severity Score divided into clear
(0-6.9), mild (> 6.9), moderate (>12,4) and severe
(>20,2).
11
Measurements made by three consecutive
examiners on the same day. Collect 5cc of blood
samples in a tube of SST (Serum Separator Tubes)
then centrifuge for 10 minutes at 2000-3000 rpm
within 20 minutes. After all samples collected, serum
estradiol and estriol levels evaluated by ELISA
method. After filling the data on the data collection
sheets, then the data is processed using the Statistical
Package for Social Sciences (SPSS) version 18. Test
the normality of population data comparability using
Kolmogorov-Smirnov test. The difference analysis
serum estradiol and estriol level in each group of MSS
using One-Way ANOVA.
3 RESULT
In this study, the samples obtained as many as 25
pregnant women with melasma with the age range 15-
49 years. The mean age of the study subjects was
32.50 with a standard deviation of 7.77. The age of
majority of subjects with melasma is 31-40 years.
Age of pregnancy obtained in the third trimester of 21
people (84%) followed by the second trimester as
much as three people (12%) and one person (4%) first
trimester of the 25 subjects, the duration of exposure
to sunlight less than 6 hours as many as seven people
(28%) and as many as 18 people (72%) experienced a
duration of exposure to sunlight more than 6 hours a
day. Followed by sun exposure time at 09.00 to 15.00
as many as 18 people (72%) and sunlight exposure
time is less than 09.00 as many as seven people
(28%).
RCD 2018 - The 23rd Regional Conference of Dermatology 2018
96
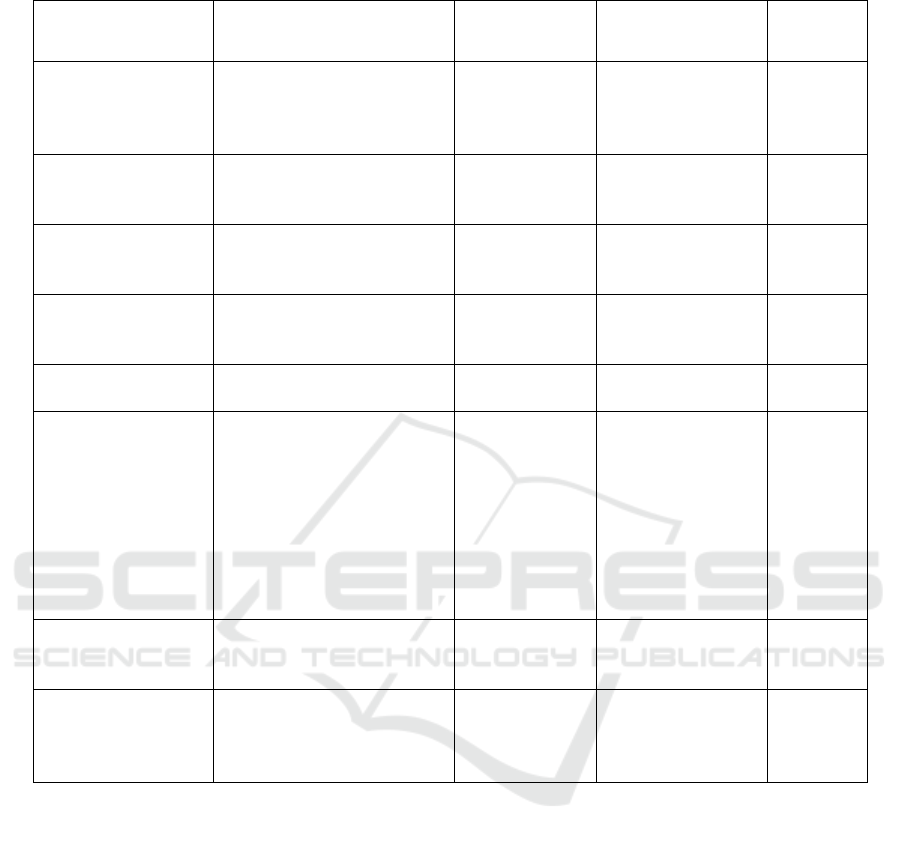
Table 1: Baseline Characteristics.
Group
Amount
(n=25)
Percentage
(n=100%)
p
Age
15-20
21-30
31-40
41-49
2
6
13
4
8%
24%
52%
16%
0.489
Gestational age
(Trimester)
I
II
III
1
3
21
4%
12%
84%
0.206
Sunlight exposure
duration
(Hours)
< 6
> 6
7
18
28%
72%
0.861
Sunlight exposure
timing
< 09.00
09.00 – 15.00
7
18
28%
72%
0.861
Genetic
Yes
No
13
12
52%
28%
0.925
Co-existing
Diasease
None
Preecclampsia
Hyperemesis gravidarum
VSD
Asthma
Big baby
Condylomata acuminata
Anemia
Hepatitis B
14
4
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
56%
16%
4%
4%
4%
4%
4%
4%
4%
0.399
Melasma type
Epidermal
Dermal
Mixed
17
3
5
68%
12%
20%
0.701
MSS
Clean
Mild
Moderate
Severe
6
5
9
5
24%
20%
36%
20%
0.632
*p<0.05: significant different using Chi Square
Family history with melasma in 25 subjects found
13 people (52%) with positive family history with
melasma, and 12 people (48%) did not get family
history with melasma. In 25 subjects, there were other
coexisting diseases of 4 persons (16%) followed by
hyperemesis gravidarum, congenital heart disease
Ventricular Heart Disease, asthma, large infants,
condylomata acuminate, anemia and hepatitis B. Of
the 25 subjects, the type of melasma epidermal
epidermal (17%), dermal type 3 people (12%) and
mixed type 5 people (20%). The degree of melasma
severity obtained from 25 study subjects was 6 (24%)
clear, 5 (20%) mild, 9 (36%) moderate, and 5 (20%)
severe. Table 1 shows that age, the age of pregnancy,
duration and time of sun-exposure, genetic, co-
existing diseases, type of melasma and MSS
(Melasma Severity Score) showed no significant
difference (p> 0.05).
In Table 2, serum estradiol level in clear group
was 417.80 ± 265.02, the mild group was 836.60 ±
390.89, the moderate group was 793.58 ± 189.87, and
the severe group was 891.00 ± 194.89. Estriol serum
levels obtained on average at the clear group of 94.67
± 93.12, the mild group of 149.88 ± 109.87, the
moderate group of 199.64 ± 46.52, and the severe
group of 141.17 ± 98.69. Based on analysis difference
from table 2, there was a significant different serum
level of estradiol in each group of MSS (p=0.015) and
serum levels estriol did not significantly differ in each
group degrees of MSS (p=0.454).
Comparation of Estradiol and Estriol Serum Levels in Different Degrees of Melasma Severity in Pregnant Women
97

Table 2:. Average of Serum Estradiol and Estriol Level in
Groups of MSS.
MSS
Estradiol
Estriol
Mean
p-value
Mean
p-
value
Clear
417.80
*0.015
94.67
0.454
Mild
836.60
149.88
Moderat
e
793.58
199.64
Severe
891.00
141.17
*p<0.05 : signficant different
4 DISCUSSION
Melasma severity score obtained from the average of
25 subjects of the most moderate study (9 subjects),
followed by clear (6 subjects), mild (5 subjects) and
included severe (5 subjects). There were a significant
different serum estradiol levels but not significantly
different serum estriol levels in each MSS group. In
melasma pathogenesis, increased estrogen will bind
to the estrogen receptor on melanocytes thus
stimulating the production of melanin. The increased
estrogen will increase the stimulation of melanin
production so that it is suspected to affect the severity
of melasma. Estrogen levels in pregnant women
dominated by forms of estradiol and estriol
(Dameveska, 2014).
Estrogen receptor (ER) is a steroid hormone
receptor in the cell nucleus. ER has two subtypes
namely ERα and ER-β. Estradiol has a high affinity
that activates both these receptors potentially.
Activation of ER triggers the modulation of
transcription and expression of genes in the
melanocyte. The biologic effects of estradiol, is
considered the most active form of estrogen and has a
high potential for melanogenesis, are mediated by
estrogen-alpha receptors (ER-α), and estrogen-beta
receptors (ER-β) expressed by human skin cells. The
physiological function of estriol is still not fully
understood. Estriol is short-acting estrogen, meaning
it has the lowest affinity for estrogen receptors alpha
and beta compared with estradiol and estrone
(Thornton, 2002).
Although estriol is an estrogen with the lowest
affinity to estrogen receptors compared with
estradiol, several theories mention the mechanism of
action of estriol and estradiol. According to other
literature by Cohen in 1985, said that estriol could
compete with estradiol in binding to estrogen
receptors in the uterus. This relationship evidenced by
the physiological differences in the amount of
estradiol and estriol. Also, physiologically estriol
production is controlled by estradiol production, but
when pregnant estriol production no longer controlled
by estradiol evidenced by high estriol counts until the
end of pregnancy (Cohen, 1985).
In this study, estradiol was significantly different
in each group MSS while estriol was not significant
difference may be due to the affinity of estriol bonds
with estrogen receptors in melanocytes weaker than
the affinity of estradiol bonds with estrogen receptors.
The theory of estradiol and estriol work mechanisms
according to Cohen can also support the results of
research that estradiol has an important role in the
severity of melasma. There is yet another study that
measures serum estriol levels in pregnant women
with melasma so that no data support the results of
this study.
Several weaknesses in this study may be due to
measurement MSS method is done through the
conversion of MASI score measured subjectively
depending on the examiner although it minimised by
involving three examiners. More research is needed
to determine the correlation between serum level
estradiol in each group MSS. Also, melasma is a local
hyperpigmentation disorder of the facial skin so that
research variables may not be able to describe as
taken from serum blood circulation. A
histopathologic study of melasma skin lesions should
be performed.
5 CONCLUSION
In pregnant women with melasma, the serum
estradiol level was significantly different in degrees
of melasma severity, while estriol did not differ.
REFERENCES
Cohen SL (1985) A function for estriol during human
pregnancy-a hypothesis. Clin Biochem 18: 85-7
Damevska, K. 2014. New Aspects of Melasma. Serbian
Journal of Dermatology and Venereology. 6(1): 5-18.
Gopichandani, K., Arora, P., Garga, U., Bhardwaj, M.,
Sharma, N., Krishan R., et al., 2015. Hormon Profile of
Melasma in Indian Females. Pigment
International (2):85 -90
Grawkrodjer DJ., 2002. Pigmentation. In: Dermatology an
Illustrated Colour Text. 3rd ed. British: Crurchill
Livingstone; p.70-1
RCD 2018 - The 23rd Regional Conference of Dermatology 2018
98

Handel AC, Miot LDB, Miot HA., 2014. Melasma: a
clinical and epidemiological review. Annals Brasillian
Dermatology ; 89(5):771-82
Hindritiani, R., 2015. Melasma. In Toruan, S. (eds): Skin
Pigmentation. Study Group of Cosmetic Dermatology
Indonesia, 114-25
Im S, Kim J, On WY, Kang WH., 2002. Increased
expression of alpha melanocyte stimulating
hormone in the lesional skin of melasma. British
Journal Dermatology 146: 165-7.
Kimbrough-Green CK, Griffiths CE, Finkel LJ, Hamilton
TA, Bulengo-Ransby SM, Ellis CN, et al., 1994.
Topical retinoic acid (tretinoin) for melasma in black
patients. A vehicle controlled clinical trial. Archieve of
Dermatology; 130:727-33.
Miranti, A. Anwar, A. Djawad, K. Pattelongi, I. Wahab, S.
Abdullah, N., 2016. Analysis Level of Serum Estradiol
Hormone of Pregnant Women with Melasma. American
Journal of Clinical and Experimental Medicine. Vol,4,
No 2. p 26-9
Newcomer, V. D., M. C. Lindbert, and T. H. Stenbert.,
1961. A melanosis of the face (“chloasma”). Archives
of Dermatology. 83:284–97.
Prakoeswa S., 2002. Colorimetric measurements and light
sensitivity from ultraviolet light of the three variants of
the skin color of Indonesia: light brown, moderate, and
dark brown. Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas
Airlangga.
Ortonne, JP. Arellano, I. Berneburg, M. Cestari, T. Chan,
H. Grimes, P. et al., 2009. A global survey of the role
of ultraviolet radiation and hormonal influences in the
development of melasma. Joural of European Academy
Dermatology Venerology, 23: 1254–62
Rodrigues M, Ayala-Corts AS, Rodrguez-Armbula A,
Hynan LS, Pandya AG. 2016. Interpretability of the
Modified Melasma Area and Severity Index
(mMASI). JAMA Dermatology. 152(9):1051-2
Speroff, L., Glass,R.H., Kase, N.G., 2005. Menopause and
Perimenopausal Transition. In : Clinical Gynecologic
Endocrinology and Infertility. Lippincott Williamsand
Wilkins. 7th. Ed. Philadelphia. p. 643-07
Thornton MJ. 2002. The biological actions of estrogens on
skin. Experimental Dermatology; 11:487-502.
Comparation of Estradiol and Estriol Serum Levels in Different Degrees of Melasma Severity in Pregnant Women
99
