
The Comparison Effect between Albumin Infusion and Normal
Protein Diet on the Acceleration of Wound Healing: A Randomized
Control Trial
Arie Utariani
1
, Eddy Rahardjo
1
, David Sontani Perdanakusuma
2
, Nancy Margarita Rehatta
1
, Hamzah,
Kohar Hari Santoso
1
, Bambang Pujo Semedi
1
1
Department of Anesthesiology and Reanimation, Faculty of Medicine, Universitas Airlangga, Indonesia
2
Department of Plastic Reconstructive and Aesthethic Surgery, Faculty of Medicine, Universitas Airlangga, Indonesia
Keywords: Hypoalbuminemia, albumin infusion, nutrition, wound healing.
Abstract: The aim of this study was to compare the role between albumin infusion or normal protein diet in the
process of wound healing during the state of hypoalbuminemia. The samples were fifteen Sprague Dawley
Rats that met inclusion criteria which were fed with casein for standardization and fed with casein 2% for
14 days to induce the state of hypoalbuminemia. Then the samples were divided into three groups: group
(A) preoperative albumin infusion, group (B) pre and postoperative 20% diet casein, and group (C) fed with
2% casein as control. The four incisions (2 cm each) were made on the back of the rat, kept in sterile
dressing, and evaluated on day 1, 3, 5, and 7. Measurement of the wound area using VisiTrak and statistical
analysis used ANOVA methods. The acceleration of wound healing in the hypoalbuminemia group starting
on the third day and maximal acceleration was achieved by feeding the protein on the fifth day sooner than
albumin infusion group.
1 INTRODUCTION
Wound is discontinue of the tissue or skin that may
be caused by trauma, surgical procedures,
neuropathic, vascular disorders, suppression and
malignancy (Baranoski, et al., 2003; Dipietro, Luisa,
Aime, Burns, 2003). The process of wound healing
on the damaged tissue begins increased cellular
activity and metabolic intensity. The wound healing
process occurs in 3 phases: (1) the inflammatory
phase, (2) the proliferative phase and (3) the
remodeling phase (Hess and Cathy, 2002; Dipietro,
Luisa, Aime, Burns, 2003; Enoch and Price, 2004).
In all phases of wound healing requires adequate
blood flow, tissue perfusion and oxygenation
(Jonsson, et al., 1991; Leaper, 2007). In patients
with malnutrition with less nutritional adequacy
would have a high risk of infection, wound healing
time, and length of stay in the hospital. One of the
proteins that are important in the wound healing
process is albumin (Haydock and Hill, 1986; Agung
and Hendro, 2005).
The study of pre operative albumin levels associated
with long-term complications of wound healing with
normal albumin levels was significantly associated
(p <0.05) with post operative wound healing, 23% -
52.46% in elective and 29% found in 44% of
patients with orthopedic surgery (Haydock and Hill,
1986; Agung and Hendro, 2005).
Protein is needed in every stage of wound
healing of the inflammatory phase, the proliferative
phase and the formation of granulation until the
remodeling phase. One of the roles of proteins is the
formation of collagen tissue to determine the
strength of the wound. Low protein intake even in a
short time can affect the speed of wound healing
significantly (Agung and Hendro, 2005).
So in this study we wanted to prove the role of
albumin either be given normal protein diet and
given preoperative albumin infusion to the
circumstances hypoalbuminemic prior to the
occurrence of an injury, so that it can be used as a
reference for the management of the use of albumin
in the state hypoalbuminemia who will do the
surgery planned or emergency, so as to help reduce
mortality and morbidity.
312
Utariani, A., Rahardjo, E., Perdanakusuma, D., Rehatta, N., Hamzah, ., Santoso, K. and Semedi, B.
The Comparison Effect between Albumin Infusion and Normal Protein Diet on the Acceleration of Wound Healing: A Randomized Control Trial.
DOI: 10.5220/0008156403120315
In Proceedings of the 23rd Regional Conference of Dermatology (RCD 2018), pages 312-315
ISBN: 978-989-758-494-7
Copyright
c
2021 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
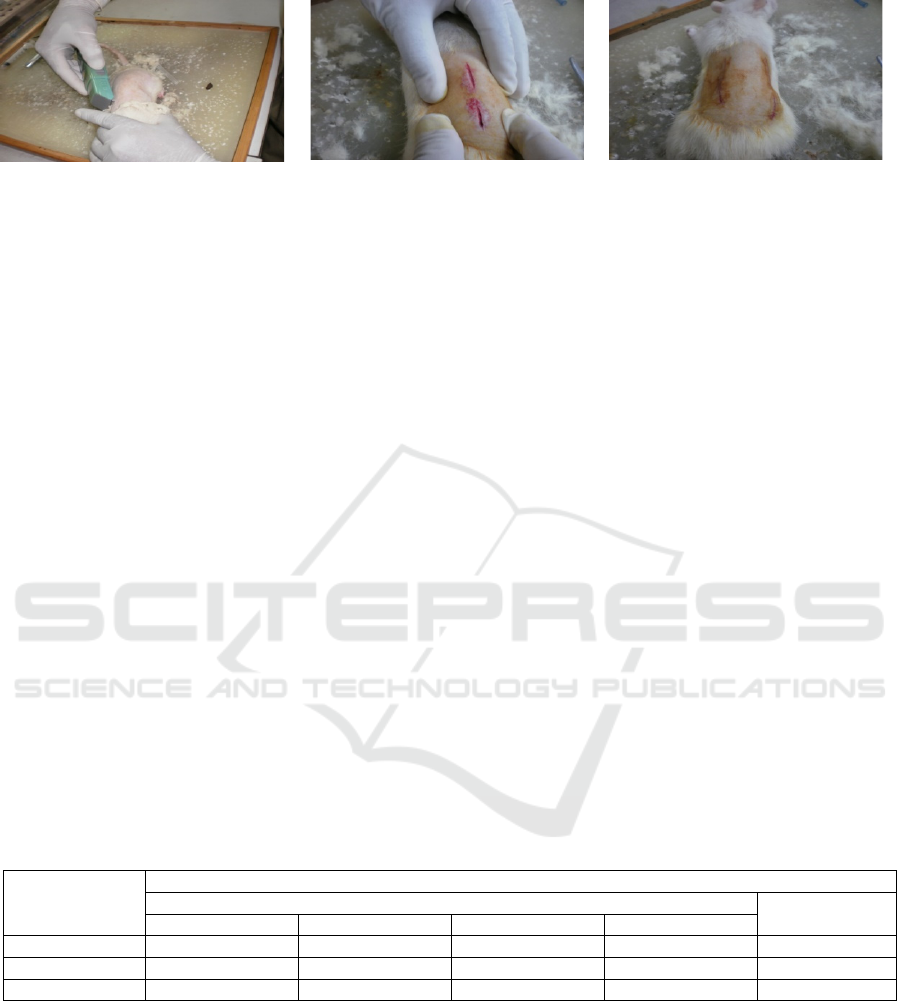
Figure 1: Sprague Dawley Rats : (A) kept in steril dressing; (B) incisions 2 cm each; and (C) healed wound.
2 MATERIAL AND METHODS
This research was an experimental research. The
design used in this research is randomize post test
only control group design. The samples were fifteen
Sprague Dawley Rats that met inclusion criteria
which were fed with casein for standardization and
fed with casein 2% for 14 days to induce the state of
hypoalbuminemia. Then the samples were divided
into three groups: group (A) preoperative albumin
infusion, group (B) pre and postoperative 20% diet
casein, and group (C) fed with 2% casein as control.
The four incisions (2 cm each) were made on the
back of the rat, kept in sterile dressing, and
evaluated on day 1, 3, 5, and 7 (Figure 1). Heal skin
tissue when fused with the tensile strength 2.62 N /
mm², was not found signs of inflammation, observed
7 days after injury (Forrest and Corter, 1995 ;
Gottrup, Melling, and Hollander, 2005).
Measurement of wound area used visitrak tool and
statistical analysis used ANOVA methods.
3 RESULTS
At the beginning of albumin analysis with
homogeneity between groups using the Tukey HSD
(p = 0129) obtained a homogeneous variance. And
the Kolmogorove-Smirnov normality test of Z
obtained the normal distribution (p = 0.490). To
know the difference between the initial albumin
group used one-way analysis of variance (one-way
ANOVA) obtained the value of F = 2.200 and p =
0.016. Initial albumin difference between groups did
not show any significant difference, and this group
has a homogeneous distribution.
Measurement of wound area using visitrak tool
and with statistical analysis seen in table 1, on day 3
of wound on preoperative albumin infusion (A) were
almost the same as normal protein diet (B), but on
day 5 in normal protein diet (B) an acceleration of
wound closure were faster than preoperative
albumin infusion (A) and on the seventh day of
normal protein diet (B) showed faster wound healing
compared to preoperative albumin infusion (A).
Table 1: Comparison of mean and standard deviation of wound days to 1,3,5,7 after surgery between groups: group (A)
preoperative albumin infusion, group (B) pre and postoperative 20% diet casein, and group (C) fed with 2% casein
(hypoalbumin) as control.
Group
Wound’s Width
Mean ± SD
n
1 3 5 7
A 5,40 ± 1,81 3,40 ± 1,14 2,40 ± 0,89 2,60 ± 1,52 5
B 5,40 ± 0,89 3,40 ± 1,14 1,80 ± 0,84 1,80 ± 0,84 5
C 6,00 ± 1,58 6,20 ± 1,92 5,80 ± 1,48 5.60 ± 0,90 5
In the state of hypoalbuminemia (C) widened the
wound area still same until the seventh day, but we
got a slowing of wound closure in preoperative
albumin infusion (A) and normal protein diet (B)
(Figure 2).
The Comparison Effect between Albumin Infusion and Normal Protein Diet on the Acceleration of Wound Healing: A Randomized Control
Trial
313
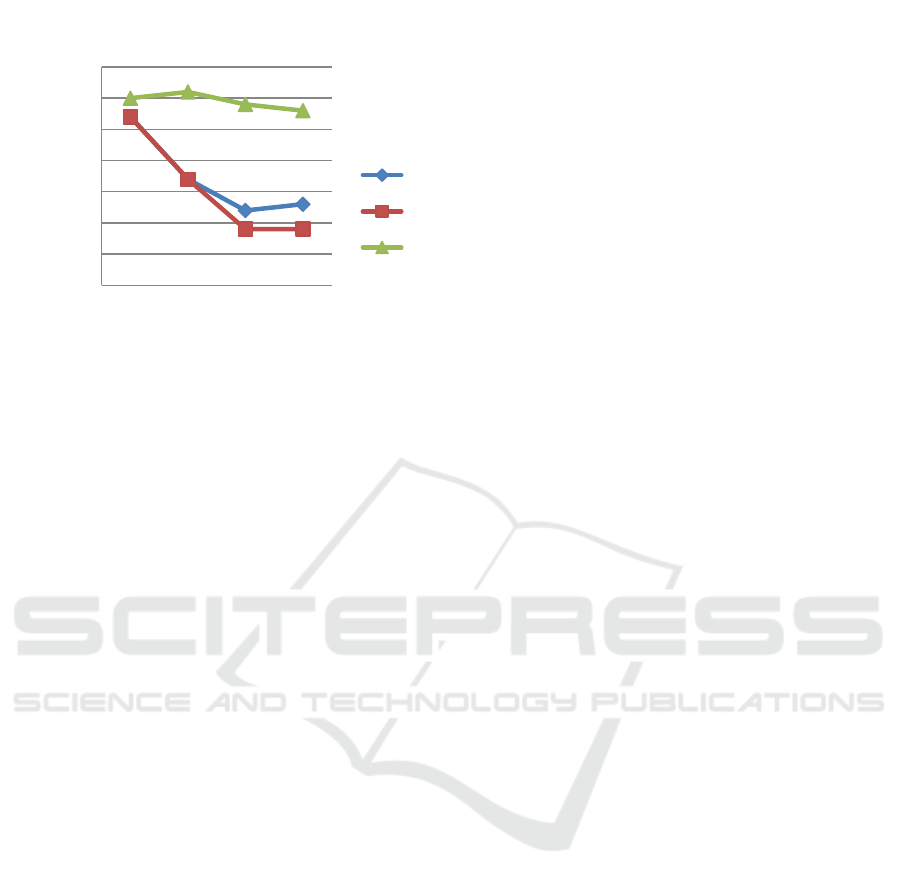
Figure 2: Wound’s Width.
4 DISCUSSION
This study described the role of albumin on wound
healing in hypoalbuminemia state. Improving the
hypoalbuminemia state by using an preoperative
albumin infusion or normal protein diet was a
solution to this problem, since albumin was one of
the important proteins in the wound healing process
(Haydock and Hill, 1986; Agung and Hendro, 2005).
To obtain an optimal wound healing was needed
nutritional adequacy. In people with malnutrition
will had a high risk of infection, prolong wound
healing, prolong hospitality, and increased risk of
death (Pedersen, 1992). This situation can be due to
decreased synthesis of proteins needed for growth
and repair of cells, which may affect metabolic
function and decrease the body's immune response,
duration of the inflammatory phase, a decrease of
fibroblasts, the synthesis of proteoglycans, collagen,
neoangiogenesis and improved form of injury
(Stadelmann, Digenis, and Tobin, 1998; Hunt, Hopf,
and Hussain, 2000). Patients with serum
albumin levels above 3 gm/dl were much more
likely to have uncomplicated wound healing (Casey
et al., 1983).
Measurement of wound area using visitrak tool
and with statistical analysis seen in table 1, on day 3
of wound on preoperative albumin infusion (A) were
almost the same as normal protein diet (B), but on
day 5 in normal protein diet (B) an acceleration of
wound closure were faster than preoperative
albumin infusion (A) and on the seventh day of
normal protein diet (B) showed faster wound healing
compared to preoperative albumin infusion (A). This
is according to research Repertinger (2004) occurred
after the fifth full reepitelialisasi EGFR wild-animal
in mice, whereas the increase in epithelial
proliferation has begun on day three (Repertinger et
al., 2004).
In the state of hypoalbuminemia (C) widened the
wound area still same until the seventh day, but we
got a slowing of wound closure in preoperative
albumin infusion (A) and normal protein diet (B)
(Figure 2).
In this study the contribution to normal protein
diet did not differ significantly with preoperative
albumin infusion to help repair damaged tissue. So
we argued for giving nutritional and or albumin
infusion on hypoalbuminemia state may affected
directly or indirectly the target tissue, particularly
affect cytokine production and inflammation and
affect the expression of proteins and growth factors
required in the wound healing process.
5 CONCLUSION
The acceleration of wound healing in the
hypoalbuminemia group starting on the third day
and maximal acceleration was achieved by feeding
the protein on the fifth day sooner than albumin
infusion group.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
I would like to give thanks to Prof. Dr. H. R. Eddy
Rahardjo, dr., SpAn., KIC. as promoter and Prof.
Dr. David S. Perdanakusuma, dr., SpBP(K). as co-
promoter for their support in overcoming numerous
obstacles I have been facing through my research. I
would like to thank my friends for accepting nothing
less than excellence from me. Last but not the least,
I would like to thank my family: my husband and to
my sons for supporting me spiritually throughout
writing this thesis and my life in general.
REFERENCES
Agung, M., Hendro, W., 2005. Pengaruh kadar albumin
serum terhadap lamanya penyembuhan luka operasi.
Dexa Media, I(18).
Baranoski, S., Elizabeth, A.A., et al., 2003. Book Wound
Care Essentials Practice Principles. Lippincott
Williams and Wilkins.
Casey, J., Flinn, W.R., Yao, J.S., Fahey, V., Pawlowski, J.,
Bergan, J.J., 1983. Correlation of immune and
5,4
3,4
2,4
2,6
5,4
3,4
1,8 1,8
6,0
6,2
5,8
5,6
0,0
1,0
2,0
3,0
4,0
5,0
6,0
7,0
1st 3rd 5th 7th
cm
day
Wound’sWidth
A
B
C
RCD 2018 - The 23rd Regional Conference of Dermatology 2018
314

nutritional status with wound complications in patients
undergoing vascular operations. Surgery, 93(6):822-7.
Dipietro, Luisa A., Aime I., Burns, 2003. Wound healing:
methods and protocols (methods in molecular
medicine ser). Philadelphia: Totowa.
Enoch, S., Price, P., 2004. Cellular, molecular and
biochemical differences in the pathophysiology of
healing between acute wounds, chronic wounds and
wounds in the aged.
Forrest, A.P., Corter, D.C., 1995. Principle and Practice
of Surgery 3rd ed. Edinburgh: Churchill Livingstone.
Gottrup, F., Melling, A., Hollander, D.A., 2005. An
overview of surgical site infections: Aetiology,
incidence and risk factors.
Haydock, D.A., Hill, G.L., 1986. Impaired wound healing
in surgical patients with varying degrees of
malnutrition. JPEN Journal Of Parenteral And
Enteral Nutrition, 10(6):550-4.
Hess, Cathy, T., 2002. Clinical Guide To Wound Care; 4th
Ed. Philadelphia: PA. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins.
Hunt, T.K., Hopf, H., Hussain, Z., 2000. Physiology of
wound healing. Advances In Skin & Wound Care, 13(2
Suppl):6-11.
Jonsson, K., Jensen, J.A., Goodson, W.H., Scheuenstuhl,
H., West, J., Hopf, H.W. et al., 1991. Tissue
oxygenation, anemia, and perfusion in relation to
wound healing in surgical patients. Annals of Surgery,
214(5):605-13.
Leaper, D., 2007. Perfusion, oxygenation and warming.
International Wound Journal, 4 Suppl 3:4-8.
Pedersen, 1992. Nutrition as a prognastic indicator in
amputations. A prospective of 47 cases. Acta Qitrop
Seand, 63(6):657-8.
Repertinger, S.K., Campagnaro, E., Fuhrman, J., El-
Abaseri, T., Yuspa, S.H., Hansen, L.A., 2004. EGFR
enhances early healing after cutaneous incisional
wounding. The Journal Of Investigative Dermatology,
123(5):982-9.
Stadelmann, W.K., Digenis, A.G., Tobin, G.R., 1998.
Impediments to wound healing. American Journal Of
Surgery, 176(2A Suppl):39s-47s.
The Comparison Effect between Albumin Infusion and Normal Protein Diet on the Acceleration of Wound Healing: A Randomized Control
Trial
315
