
Acute Generalised Pustular Psoriasis of Von Zumbusch: A
Conflict in the Flare of Psoriatic Arthritis
Sabrina Ab Wahab
1
, Tarita Taib
1
, N. A. Ahmad
1
, M. Kuppusamy
1
, W. S. A. Wan Ahmad Kamal
1
,
L. D. Aminuddin
1
, R. Ridzwan
2
1
Dermatology Unit, Faculty of Medicine, Sungai Buloh Campus, Universiti Teknologi MARA, Sungai Buloh, Selangor,
Malaysia
2
Department of Dermatology, Selayang Hospital, Selayang, Malaysia
Keywords: Generalized pustular psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis, methotrexate, prednisolone, withdrawal.
Abstract: Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune disease with characteristic inflammation of the skin and joints.
Immunosuppressant drugs, especially methotrexate has emerged since the past decade in psoriasis
treatment, mainly for psoriatic arthritis. Withdrawal of immunosuppressant drugs may trigger a more severe
condition; acute generalized pustular psoriasis, which is a rare form of psoriasis. We report a 46 years old
Indian woman, who had chronic plaque psoriasis with psoriatic arthropathy for the past 3 years and was
stable on oral methotrexate 10mg weekly and oral prednisolone 5mg daily. She presented with generalized
pustular eruptions for 1 week associated with fever for 3 weeks and bilateral knee pain. There was
widespread erythema and scaling, painful and studded with pustules appearing on all limbs, trunk and face
with body surface area of more than 90% involved. She had swelling of both knees which was warm and
tender. Further history revealed that she had stopped taking methotrexate for 2 weeks prior. Her condition
was complicated with Klebsiella pneumoniae bacteremia and flare of psoriatic arthropathy. She was started
on oral prednisolone 30mg daily, followed by tapering doses. She was monitored in the ward in view of
high risk of worsening pustular psoriasis while tapering the dose of systemic corticosteroids. Her condition
improved with a short course of oral acitretin 25mg daily. We discussed this case to highlight the dilemma
faced by both dermatologist and rheumatologist when immunosuppressants are withdrawn in psoriatic
patients and the difficulties of managing flares of psoriatic arthropathy in the same settings.
1 INTRODUCTION
Generalized pustular psoriasis (GPP) is a rare and
severe variant of psoriasis characterized by
generalized inflammatory plaques with multiple
sterile pustules (Griffiths & Baker, 2007). The
commonest precipitating factor include abrupt
withdrawal of systemic or ultrapotent topical
corticosteroids and infection (Kamarashev et al.,
2002). Withdrawal of systemic immunosuppressant
therapy is also associated with GPP and risks of
rebound of the disease is of concern. The
complication of GPP is multi-system organ failure
and early recognition and treatment is necessary
(Pomahac et al., 2008).
2 CASE
We report a case of a 46 years old Indian women
who presented with generalized pustular eruptions
for 1 week associated with fever for 3 weeks with
body aches and bilateral knee pain for 1 week. The
rash was described as worsening widespread
erythema and scaling, painful and non-itchy, studded
with pustules appearing on all limbs, trunk and face.
She had swelling of both lower limbs and exfoliated
skin areas over all limbs. She was diagnosed with
plaque psoriasis 4 years prior to this, which
progressed to psoriatic arthritis Her latest dosage
oral methorexate 10mg weekly, however she
stopped the medication herself for 2 months without
advice from doctors. She continued taking oral
prednisolone 5mg daily and was adherent with no
change in dosage. On examination, 90% of body
surface areas were involved. The rash was
Wahab, S., Taib, T., Ahmad, N., Kuppusamy, M., Kamal, W., Aminuddin, L. and Ridzwan, R.
Acute Generalised Pustular Psoriasis of Von Zumbusch: A Conflict in the Flare of Psoriatic Arthritis.
DOI: 10.5220/0008160104770480
In Proceedings of the 23rd Regional Conference of Dermatology (RCD 2018), pages 477-480
ISBN: 978-989-758-494-7
Copyright
c
2021 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
477
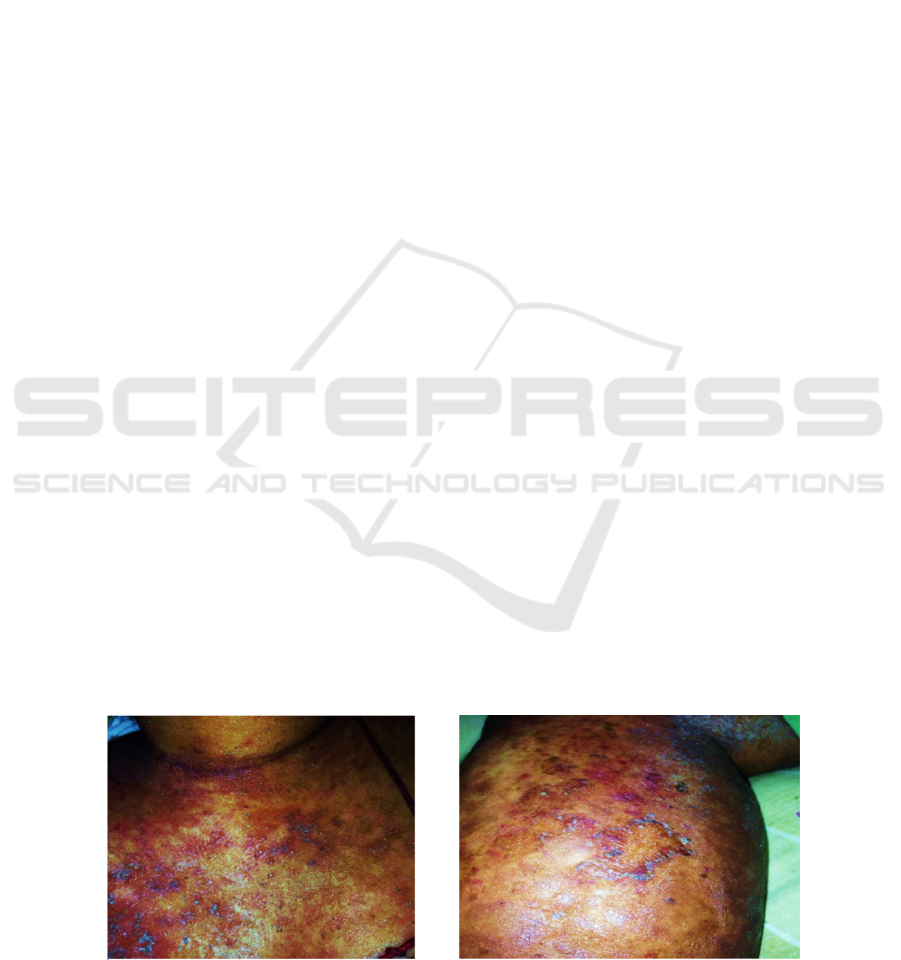
characterized as multiple pustules about 1–2 mm in
size and located on the anterior chest (figure 1), both
arms, abdomen and both lower limbs (figure 2).
There were few pustular lesions over the chin and
perioral. The pustules were studded on erythematous
plaques with scales and desquamation. Multiple
erythematous plaque with scales were seen. Her face
and scalp had faint erythematous plaque with thick
scales. There was onycholysis of both finger nails
and toes. Bilateral knee was swollen and tender upon
palpation, warm to touch and erythematous changes
over the overlying skin area.
Blood investigations showed white cell count of
21.32 x 10
9
/L, with neutrophil predominance 82% ,
haemoglobin of 10.9 /dl and platelet 442 x 10
9
/L .
Inflammatory markers were raised, erythrocyte
sedimentary rate was 107mm/hr and C-reactive
protein was 28.7 mg/L . She had liver impairment ,
with raised alanine aminotransferase (ALT) 96 IU/L
and alkaline phosphate (ALP) was 211 IU/L . Her
renal profile was normal and corrected calcium was
2.28 mmol/l. Anti streptolysin O titer was negative.
Pus cultures from the pustules showed no growth.
She was diagnoses with acute generalized pustular
psoriasis. The identified triggering factor was the
withdrawal of the immunosuppressant drug,
methotrexate. She required skin nursing with
potassium permanganate dressing and emollients.
Topical corticosteroids applied included
hydrocortisone 1% ointment and bethamethasone
valearate 1:4 cream twice daily. Blood cultures taken
grew Klebsiella Pneumoniae sensitive to ampicillin
and she was on intravenous piperacillin tazobactam
4.5 g TDS for 1 week.
She was maintained on oral prednisolone 30mg
od and dosage was tapered slowly. She was
monitored in the ward in view of high risk of
worsening pustular psoriasis during the period of
withdrawing the systemic corticosteroids. Oral
acitretin 25mg od was started, however it was given
only for a short duration for as patient could not
tolerate the medication. Side effects of actitretin was
observed as she had dry lips, mouth and eyes and
skin peeling. The pustular lesions cleared with the
short course acitretin
.
3 DISCUSSION
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune disease with
characteristic inflammation of the skin and joints. At
present, guidelines have recommended that
methotrexate is preferred in psoriatic arthritis with
skin involvement (Gossec et al., 2015).
Dermatologists usually avoids systemic
corticosteroids when treating psoriasis because of
the potential risk of pustular psoriasis when systemic
corticosteroids are discontinued. In contrast,
rheumatologists often use systemic corticosteroids,
in smaller dosages of 5-10 mg/d for the treatment of
psoriatic arthritis and combined with methotrexate.
Generalized pustular psoriasis (GPP) was
described in in 1968 by Baker and Ryan and
categorized into four clinical variants: acute GPP of
von Zumbusch; subacute annular pustular psoriasis
(APP); exanthematic; and localized GPP (Baker &
Ryan, 1968). Systemic features are commonly
involved, and patients appear ill, febrile, malaise
with leukocytosis. Derangement in liver enzymes
and elevation of acute phase reactants are associated
with this disease. Complications reported are sepsis
and renal, hepatic, respiratory, and cardiac failure.
Case reports have described in severe psoriasis
with pronounced arthritis presenting with pustular
exacerbation after withdrawal of an
immunosuppressant drug (Kamarashev et al., 2002;
Benner et al., 2009). In this present case, withdrawal
of systemic immunosuppressants therapy triggered
the pustular psoriasis. After restarted on systemic
Figure 1: Multiple pustules seen on
erythematous plaques on anterior chest.
Figure 2: Multiple pustules on the scaly
erythematous plaque seen on right leg.
RCD 2018 - The 23rd Regional Conference of Dermatology 2018
478

corticosteroids, the patient was closely monitored for
any rebound of her condition. A case review by
Choon et al. described the commonest triggering
factor was withdrawal of systemic therapy and was
associated with higher risks of recurrent flares of
GPP apart from other factors such as pregnancy and
upper respiratory tract infection (Choon et al., 2014).
Despite early identification of the factors
mentioned, GPP may still lead to unstable disease
and frequently occurring pustular flares. Majority of
corticosteroid induced GPP had mild psoriasis
requiring systemic steroid indicated for both
psoriatic lesions or arthritis (Choon et al., 2014).
Corticosteroid has been well known as a trigger or
aggravating factor for GPP ,and well reported in
various case series , with strong association
withdrawal of steroids (Brennet et al., 2009; Borges-
Costa et al., 2011) . Patients are more commonly on
these drugs when there is association with psoriatic
arthritis.
Management GPP variant of psoriasis is still
based on evidence from case reports and no
universal guidelines are available at present. In this
case, patient was given acitretin, however she
developed side effects such as dry lips, mouth and
eyes and skin peeling which are very common and
not tolerable to some patients and was therefore
withheld. Concerns on risk recurrence of pustular
eruption and the need to maintain steroids for her
arthritis arise in our case. The initial preference of
methotrexate usage is due to its known therapeutic
efficacy in improving both chronic plaque psoriasis
and arthropathy.
Biologics alone or in combination with acitretin
should be considered as have been describes in
recent case reports in managing GPP. Evidence of
rapid resolution of GPP with biologics especially
with infliximab and also Etanercept was observed
(Chandran & Chong, 2005). Combination therapy
has also reported efficacy, acitretin combined with a
biologic agent, adalimumab resulted in clearance of
pustular lesions over 10 months (Gallo et al., 2013).
However further studies are needed to address the
efficacy of the biologics especially which agent
would be more beneficial in both pustular psoriasis
and psoriatic arthropathies.
4 CONCLUSION
Withdrawal of immunosuppressant drugs may
trigger generalized pustular psoriasis and infection
may worsened the pustular psoriasis flare. Acitretin
has been shown to improve the pustular psoriasis in
our case. The associated psoriatic arthropathy in
patients with generalized pustular psoriasis need to
be managed with caution when tapering the
corticosteroid due to the risk of rebound of pustular
psoriasis.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
We would like to thank our Head of Department, Dr
Mohd Arif bin Mohd Zim for his support in
reporting this case.
REFERENCES
Baker, H., Ryan, T.J. 1968. Generalized pustular psoriasis.
British Journal of Dermatology. 80(12):771-93.
Borges-Costa, J., Silva, R., Gonçalves, L., Filipe, P.,
Soares de Almeida, L., Marques Gomes, M., 2011.
Clinical and Laboratory Features in Acute Generalized
Pustular Psoriasis. American Journal of Clinical
Dermatology 12, 271–276. doi:10.2165/11586900-
000000000-00000
Brenner, M., Molin, S., Ruebsam, K., Weisenseel, P.,
Ruzicka, T., Prinz, J.C., 2009. Generalized pustular
psoriasis induced by systemic glucocorticosteroids:
Four cases and recommendations for treatment. British
Journal of Dermatology. doi:10.1111/j.1365-
2133.2009.09348.x
Chandran, N.S., Chong, W.S., 2010. A dramatic response
to a single dose of infliximab as rescue therapy in
acute generalized pustular psoriasis of von Zumbusch
associated with a neutrophilic cholangitis.
Australasian Journal of Dermatology 51, 29–31.
doi:10.1111/j.1440-0960.2009.00588.x
Choon, S.E., Lai, N.M., Mohammad, N.A., Nanu, N.M.,
Tey, K.E., Chew, S.F., 2014. Clinical profile,
morbidity, and outcome of adult-onset generalized
pustular psoriasis: ANALYSIS of 102 cases seen in a
tertiary hospital in Johor, Malaysia. International
Journal of Dermatology 53, 676–684.
doi:10.1111/ijd.12070
Gallo, E., Llamas-Velasco, M., Daudén, E., García-Diez,
A., 2013. Refractory generalized pustular psoriasis
responsive to a combination of adalimumab and
acitretin. International Journal of Dermatology 52,
1610–1611. doi:10.1111/j.1365-4632.2012.05472.x
Gossec, L., Smolen, J.S., Ramiro, S., De Wit, M., Cutolo,
M., Dougados, M., Emery, P., Landewé, R., Oliver, S.,
Aletaha, D., Betteridge, N., Braun, J., Burmester, G.,
Cañete, J.D., Damjanov, N., FitzGerald, O., Haglund,
E., Helliwell, P., Kvien, T.K., Lories, R., Luger, T.,
Maccarone, M., Marzo-Ortega, H., McGonagle, D.,
McInnes, I.B., Olivieri, I., Pavelka, K., Schett, G.,
Sieper, J., Van Den Bosch, F., Veale, D.J.,
Wollenhaupt, J., Zink, A., Van Der Heijde, D., 2016.
European League Against Rheumatism (EULAR)
Acute Generalised Pustular Psoriasis of Von Zumbusch: A Conflict in the Flare of Psoriatic Arthritis
479

recommendations for the management of psoriatic
arthritis with pharmacological therapies: 2015 update.
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 75, 499–510.
doi:10.1136/annrheumdis-2015-208337
Griffiths, C.E.M.C., Barker, J.J.N.W.N., 2007.
Pathogenesis and clinical features of psoriasis. The
Lancet 370, 263–71. doi:10.1016/S0140-
6736(07)61128-3
Kamarashev, J., Lor, P., Forster, A., Heinzerling, L., Burg,
G., Nestle, F.O., 2002. Generalised pustular psoriasis
induced by cyclosporin a withdrawal responding to the
tumour necrosis factor alpha inhibitor etanercept.
Dermatology (Basel, Switzerland) 205, 213–216.
doi:10.1159/000063919
Pomahac, B., Lim, J., Liu, A., 2008. A case report of
generalized pustulosis with systemic manifestations
requiring burn intensive care unit admission. Journal
of Burn Care and Research 29, 1004–1008.
doi:10.1097/BCR.0b013e31818ba0d3
RCD 2018 - The 23rd Regional Conference of Dermatology 2018
480
