
Reconstruction with Rotation Flap of Infraorbital Dextra Basal Cell
Carcinoma
Fitriah, Yulia Farida Yahya, Hartika Ketty Marpaung, Theresia L. Toruan.
Department of Dermatology and Venereology Faculty of Medicine Sriwijaya University/Dr. Moh. Hoesin General Hospital
Palembang, Indonesia
Keywords: Basal cell carcinoma, dermoscopy, histopathology, rotational flap
Abstract: Basal cell carcinoma (BCC) is the most common cancer with an incidence rate approximately 70-80% among
all skin malignancies. BCC in the head and neck usually presents as slow growing, well-defined, papule or
nodul. It is locally destructive lesion and could cause serious disfigurement. However, the case of metastasise
rarely occured. Nevertheless, various treatments are available, in which the surgical excision is found to be
the most effective one. Unfortunately, in facial area, any tumor excision may be aesthetically detrimental,
therefore difficult to restore. In such case, the use of local flap such as rotational flap, is the standard option
for reconstuction. This paper is to report a case of infraorbital dextra basal cell carcinoma with rotational flap
as the reconstruction method. Reconstruction with rotational flap technique on infraorbital region give a good
outcome and easy to learn with a minimal time and give an aesthetically good result.
1 INTRODUCTION
Basal cell carcinoma (BCC) is derived from the non-
keratinizing cells originating from the basal layer of
the epidermis. BCC generally characterized by slow
growth, minimal soft tissue invasiveness and a high
cure rate. However, in certain occasion it could derive
an agressive form causing deep tissue invasion with
regional or distant metastasis and potentially
recurrence. It commonly located in the facial region,
whilsy seldom occured in the area of limbs and trunk.
Correspondingly, the management of BCC is guided
by the anatomic location and the histological features.
As for the treatment, it consists of the surgical and the
non-surgical procedure. The surgical therapy includes
standard excision, Mohs micrographic surgery, and
cryosurgery (Carucci, 2012), (Madan, 2016).
Surgical excision of tumors from the face may create
a defect that is difficult to restore. Sometimes
excision of all tumors requires closure of wounds
caused by an excision known as a flap. Flaps are
commonly classified according to their primary
movement as advancement, rotation transposition, or
interpolation. The use of regional flaps like rotational
flap are very useful and versatile local flaps (Seehan,
2012), (Cook, 2005).
2 CASE
A 43-year-old woman presented with
hyperpigmented nodule on infraorbital dextra since
two years ago. The nodule gradually became enlarged
and itchy. Approximately 1 year ago,
hyperpigmentation nodule got bigger, and easily
bleed even with a gently touch. From the edge of the
nodule, few ulcers also arised. During physical
examination, the generalized status was within
normal range. The findings in Dermatologicus status
from infraorbital dextra region: hyperpigmentation
nodule, size 1.8 x 0.9cm, solitary, irregular, ulcerated
plaque and rolled out edges. The multiple blue gray
globules and ulceration were found in the two images
obtained by the Dermoscopy examination. While as
for laboratory examination yielded normal.
Histopathological examination was found nodulo
infiltrative based on growth pattern including
aggressive BCC. The incision in the margin area was
not free from tumor. The patient treated with in toto
excision followed by rotational flap reconstruction.
Patients were given systemic drugs, cephadroxil dose
of 500mg every 12 hours for 7 days and mefenamic
acid dose of 500mg every 8 hours after surgery.
Fitriah, ., Yahya, Y., Marpaung, H. and Toruan, T.
Reconstruction with Rotation Flap of Infraorbital Dextra Basal Cell Carcinoma.
DOI: 10.5220/0008161105190522
In Proceedings of the 23rd Regional Conference of Dermatology (RCD 2018), pages 519-522
ISBN: 978-989-758-494-7
Copyright
c
2021 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
519
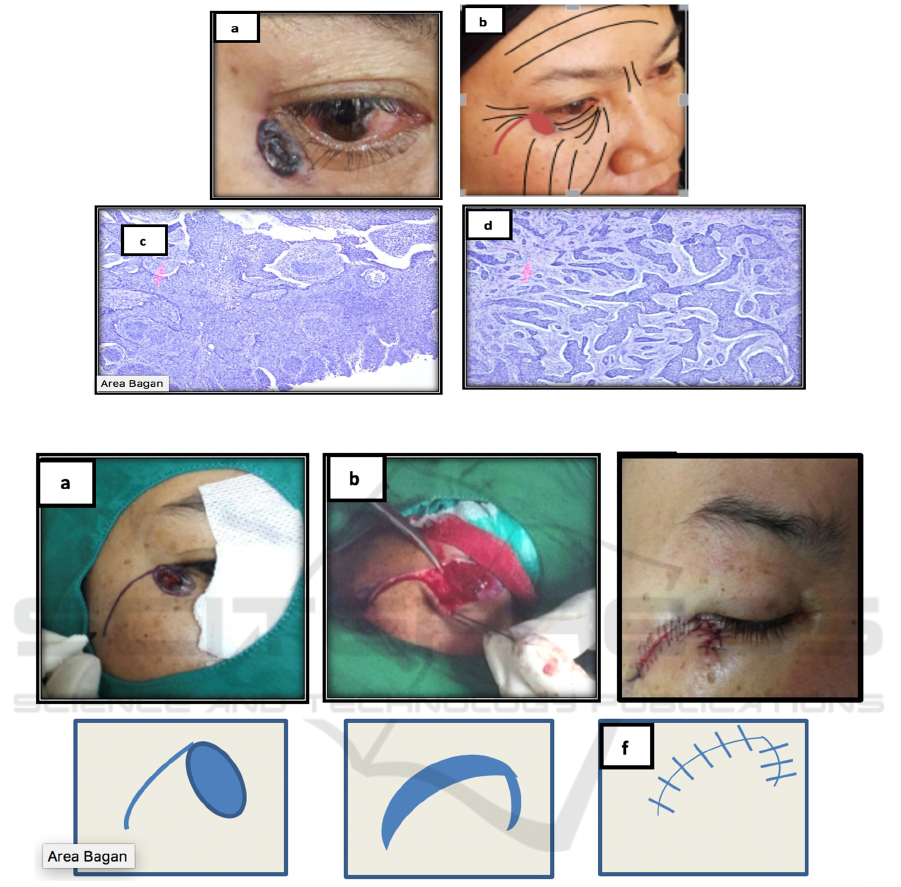
Figure 1: a,b) Location of the tumor c,d) histopathological examination.
Figure 2: a) Sketch of rotation flap pattern. b) In toto excision c) Post wound suture excision with rotation flap. d,e,f) Rotation
flap with simple curved design from the primary defect. The rotating end portion is located shorter than the primary defect
that flap will cover the furthest edge of wound if the flap edge is expanded with secondary defects.
3 DISCUSSION
Basal cell carcinoma includes non-melanoma skin
cancer which is a malignant skin tumor originating
from stem cells in the basal layer of the epidermis and
a small part originates from the outer layer of unit
pilosebasea root sheath.
6
According to Moore GM
(2012) retrospective study, the incidence of BCC is
more frequent among Caucasian race. The trend of
skin cancer in Asia shows that BCC increase most
often at the age of more than 60 years of old (Moore,
2012).
Diagnosis of this case based on clinical features,
dermoscopy and histopathology examination. In the
clinical features corresponded to the nodular type
BCC. Nodular type cell BCC is the most commonly
found variant with clinical features of dome shaped,
translucent, and pearly edges spread to the periphery.
Nodular type basal cell carcinoma is common in the
head and neck. Histopathologic examination shows
RCD 2018 - The 23rd Regional Conference of Dermatology 2018
520

nodulo infiltrative based on growth pattern including
aggressive BCC.
BCC on the facial region may yield higher degree
of subclinical spread compare to tumor’s arising
elsewhere. Generally, the cosmetic outcome for the
standard surgical excision is quite satisfying.
Howbeit the lesion removal procedure in which a
significant excision on the margins area needed,
could caused an alarming tissue losses. Special
attention therefore needed to avoid further damages,
for fuctional and cosmetic importance, to certain
locations in the facial region such as the periocular,
perioral and perinasal areas (Jadotte, 2010). In the
current presented case, the location of the tumor was
in the infraorbital dextra, which is considerably a
difficult area. Therefore, the flap selection after
surgery should be adjusted to avoid the lid retraction
as the aftermath.
Additionally, there are several schematic
classifications for flap surgery. The Flap is
categorized based on the blood vessels supply
(random or axial), primary motion (advancement,
rotation, transpotation), configuration (rhomboid or
bilobed) and location (local or distant) (Cook, 2005).
Rotational flap include rotation movement flap.
Rotational flap is flap tissue that transferred over an
area of unaffected skin to reach defect (Chen, 2009).
The procedure of surgery include preoperative,
operative and pascaoperative. The preoperative
planning include examine the patient in the upright
position in both static and dynamic situation. Flap
design with consideration of aesthetic boundaries,
relaxed tension line and decision margin excision. in
this case wound closure using rotational flap. Flap
design was done as preoperative procedure.
There are several principles in the Flap, namely,
1) primary defect; is the post tumor removal wound
which intended to be closed while also acted as the
recipient from the subsequent skin-flap. 2) Secondary
defect; is the Flaps’ procreated wound. It derived
from the incision and removal of the surrounding skin
layer and the subcutaneous tissue, to overlay the
primary defect (thus called the donor) 3) the primary
flap motion is the displacement movement that will
be placed above to cover the primary defect. 4)
Secondary movement is the displacement movement
that is placed into around tissue of primary defect
using flap (Cook, 2005).
The surgical field should include the contralateral
aspect of the surgical wound (i.e. the entire face
should be prepped in the usual sterile fashion). This
will allow the intraoperative assesment of flap
movement on tissue symetry and free margins. BCC
with diameter less than 2 cm, approximately 85%
successful removal of all tumors with margin excision
3 mm while 95% with margin excision 4-5 mm
(Madan, 2016), (Abullarade, 2013).
Undermining
should be perfomed to release vertical and pivotal
tissue restraint and elasticity and the plane of flap
elevation and undermining should match the wound
depth closely.
In this case wide local excision with 3mm margin
was carried out to prevent recurrences. Rotational
flap was done to maintain function and physical
aesthetic post operative. The rotating end portion is
located shorter than the primary defect that flap will
cover the furthest edge of wound if the flap edge is
expanded with secondary defects. After the incision,
the undermining was done with blunt scissors that
made the flap easily rotated towards the wound.
Triangular sutures are done on the end flap and the
donor tissue. Finally, the lateral initiation line is
sutured in interupted while the cranial side lines are
sutured with the continuous suture.
Post operative care after flap reconstruction is
similar for other wound. A pressure dressing, include
ointment shoud be applied over the flap. The initial
dressing should be removed after 24-48 h, the area
cleaned and a dressing of ointment and tape reapplied
(Chen, 2009). In this case
dressing include ointment
applied over the flap.
4 CONCLUSION
We reported BCC cases with nodular infiltrates type
in 43 years old woman. The BCC is treated with the
toto surgical excision with the rotational flaps. The
rotational flap technique can close the primary defect
seemlessly while at the same time causing less lesion’
tension. In the histopathologic examination, the
nodulo infiltrative BCC is found, with the none-free
margin therefore required more observation.
REFERENCES
De Abullarade, J., 2013. Aesthetic considerations in
forehead reconstruction in skin carcinoma. J Cancer
Ther, 4, 20-3.
Carucci, J.A., Leffel, D.J., Pettersen, J.S., 2012. Basal cell
carcinoma. In: Wolf K, Goldsmith LA, Katz SI,
Gilchrest BA, Paller AS, Leffel DJ. Fitzpatrick’s
Dermatology in general medicine. 8
th
ed. New York:
McGraw-Hill, . p.1294-1303.
Chen, T.M., Nguyen, T.H., Wanitphakdeedecha,, 2009.
Flaps In. Vidimos AT, Ammirati CT, Lopez CP.
Dermatology Surgery. 1
st
ed.Elsevier. p163-188.
Reconstruction with Rotation Flap of Infraorbital Dextra Basal Cell Carcinoma
521

Cook JL, Goldman GD, Holmess TE., 2005. Random
pattern cutaneous flap. In: Robinson JK, Hanke CW,
Sengelmann RD, Siegel DM. Surgery of the skin. 1
ed
.
Philadelphia; Elsivier Mosby.2005.p.311-44.
Correia de Sá, T.R., Silva, R., & Lopes, J.M., 2015. Basal
cell carcinoma of the skin (part 1): epidemiology,
pathology, and genetic syndromes. Future Oncology.
11(22), 3011-3021.
Jadotte, Y.T., Sarkissian, N.A., Kadire, H., Lambert, W.C,
2010. . CASE REPORT superficial spreading basal cell
carcinoma of the face: A surgical challenge. E plasty
10:e46.
Madan, V,. Lear, J.T., 2016. Basal cell carcinoma. In:
Griffiths C, Barker J, Bleiker T, Chlmmers R, Creamer
D. Rook's Textbook of Dermatology. 9
th
ed. Oxford:
Wiley Blackwellp.141.1-17.
Moore, G.M., & Bennett, R.G., 2012. Basal cell carcinoma
in Asians: a retrospective analysis of ten patients.
Journal. of the skin, 1-5.
Raasch, B., 2009. Management of superficial basal cell
carcinoma: Focus on imiquimod. Clin Cosmet Investig
Dermatol, 2, pp. ,65-75.
Seehan, J.M., Kingsley, M., Rohrer, T.E, 2012.. Excisional
surgery and repair, flap, and grafts. In: Wolf K,
Goldsmith LA, Katz SI, Gilchrest BA, Paller AS, Leffel
DJ. Fitzpatrick’s Dermatology in general medicine. 8
th
.
New York: McGraw-Hill, p. 2921-49.
RCD 2018 - The 23rd Regional Conference of Dermatology 2018
522
