
Series-Parallel Optimization Model for Heat Exchanger Network
Bin Yang
1,2
, Shiqi Liu
1*
and Zhouli Zhao
2
1
School of Mechanical Engineering and Automation, Northeastern University, Shenyang 110819, China
2
Shanghai Baosteel Company, Shanghai 201900,China
Keywords: Series-Parallel Network, Minimum Flow Rate, Mixed-Integer Nonlinear Model, GAMS
Abstract: Based on the parallel heat exchanger network, a series-parallel optimization model of the heat exchanger
network for industrial circulating water system is established. The flow rate and temperature of the heat
exchangers in the network can be calculated automatically. The mathematical formulation exhibit a
mix-integer nonlinear programming (MINLP) structure which can be solved by GAMS. A case study is
done to compare the differences between the series-parallel model and the parallel model. The result shows
that this series-parallel model can reduce fresh water and increase the outlet return temperature obviously.
1 INTRODUCTION
Cooling water system is widely used in factories to
transform waste heat from industrial equipment.
Conventional cooling water systems often use a
parallel heat exchanger network. This will bring a
huge amount of water flow rate and the return
temperature to the cooling tower might be low if the
network is arranged in parallel, which will cause a
poor cooling performance according to the theory of
Kim and Smith (Kim and Smith, 2001). In their
work, the traditional parallel exchanger networks are
changed into series types by applying water pinch
technology so that the bottleneck problems were
solved. However, if the exchangers are changed, the
cooling network might be redesigned, thus the
network will be a lack of flexibility. Therefore,
several authors (Kim et al., 2001; Kim and Smith,
2003; Kuo and Smith, 1998) built mathematical
optimization models to solve the network problem
automatically. Xiao Feng et al. (Xiao et al., 2005)
put forward an intermediate temperature in the water
network design. In this way, the recirculating
cooling water into or out of each cooler would be
from or going to one of the three mains so that the
water flow rate could be reduced and the return
temperature could be increased. Ponce-Ortega et al.
(Ponce-Ortega et al., 2007; Ponce-Ortega et al.,
2010) put forward a mixed-integer nonlinear
programming algorithm for the synthesis of cooling
networks. This work was a development of the
intermediate main which contained several stages
and the capital and utility cost was minimized.
The above papers mainly focused on reducing
the system flow rate and changing the heat
exchanger network structure. This paper proposes a
new series-parallel method to solve the exchanger
network problems. In this method, the water can be
reused so that the total water flow rate will be
reduced.And the outlet temperature can be
increased, which will improve the cooling tower
performance. The mathematical formulation exhibit
a mix-integer nonlinear programming (MINLP)
structure which can be solved by GAMS. A case
study is done to compare flow rate and outlet
temperature between the series-parallel model and
the parallel model.
2 MATHEMATICAL MODEL
In the model formulation, suppose the maximum
amount of heat exchangers is n. HE i and HE j
represents for exchanger i and exchanger j
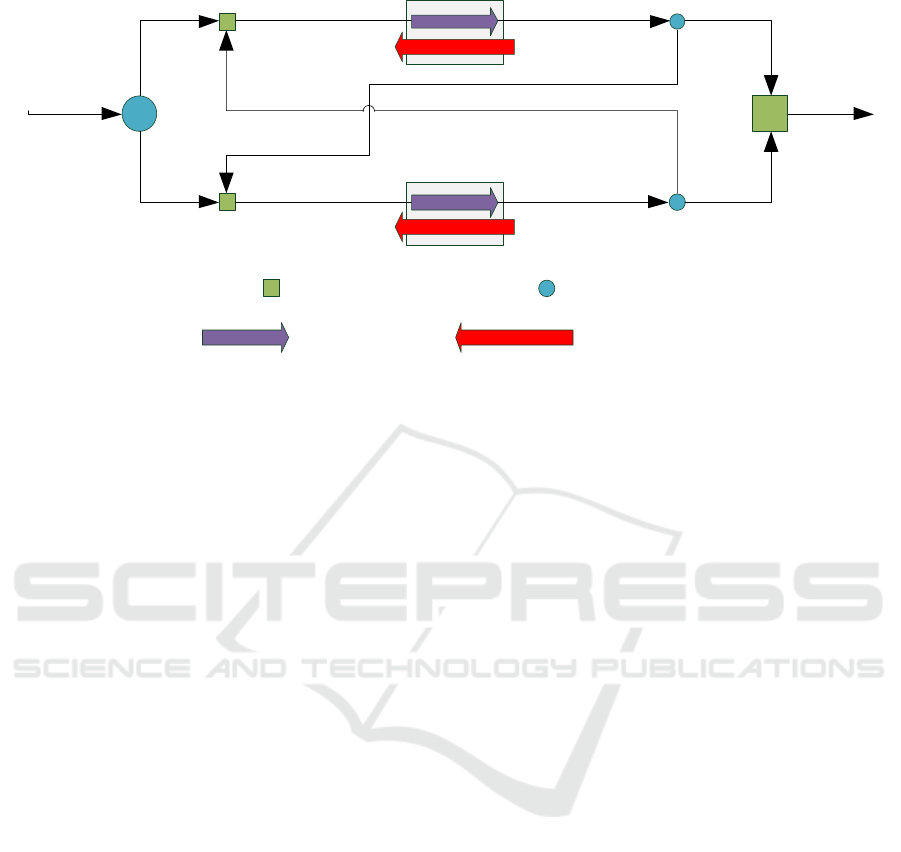
respectively. In Figure 1, the circles represent the
mixing point and the squares represent for splitting
point. At the mixing point of each exchanger, water
mixes by part of fresh water and part of reusing
water from other exchangers. So the inlet mass flow
rate for heat exchanger i can be shown as Eq. (1).
njiiFjiFiF
n
ijj
,,1,)(),()(
,1
inin
(1)
Yang, B., Liu, S. and Zhao, Z.
Series-Parallel Optimization Model for Heat Exchanger Network.
DOI: 10.5220/0008189703270330
In The Second International Conference on Materials Chemistry and Environmental Protection (MEEP 2018), pages 327-330
ISBN: 978-989-758-360-5
Copyright
c
2019 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
327
And at the splitting point of each exchanger,
water splits into part of outlet water and part of
reused water to other exchangers. The outlet mass
flow rate is the same as the inlet mass flow rate
which can be shown as Eq. (2).
njiiFjiFiF
n
ijj
,,1,)(),()(
,1
outout
(2)
For each exchanger, the mass flow rate from
other exchangers equals the inlet mass flow rate:
njijiFijF ,,1,),(),(
inout
(3)
The total inlet fresh water is:
n
i
iFF
1
inintotal
)(
(4)
The total outlet reused water is:
n
i
iFF
1
outouttotal
)(
(5)
Kim and Smith’s (Xiao et al., 2005) work shows
that because of different inlet temperature, some
exchangers might not need fresh water or reused
water. So on the right side of Eq.
(1),
)(
in
iF
and
),(
in
jiF
may not exist at the same
time.
),(
in
jiB
and
),(
out
jiB
are composed of binary
variables to limit reused water from exchanger i to j.
And
)(
in
iB
,
)(
out
iB
is to limit the inlet and outlet
mass flow rate. For exchanger i, The upper and
lower bounds of the mass flow constraints are shown
as follows:
njiiBUiFiBL
iniini
,,1,)()()(
(6)
)()()(
outout
iBUiFiBL
ii
(7)
),(),(),(
ininin
jiBUjiFjiBL
ii
(8)
),(),(),(
outoutout
jiBUjiFjiBL
ii
(9)
i
L
and
i
U
are the upper and lower bounds of the
water streams respectively. This paper supposes
each stream has the same upper and lower bounds.
The number of reused streams should be limited to a
certain amount.So the constraints are as follows:
n
1i 1
maxin
),(
n
j
NBjiB
(10)
n
1i 1
maxout
),(
n
j
NBjiB
(11)
jijiBjiB 0),(),(
outin
(12)
Suppose the heat that the hot stream i exchangers
is
)(iq
.The inlet temperature of cold stream i is
)(
in
it
,and the outlet temperature is
)(
out
it
.The heat
balance is shown as Eq.(13).
CPiFititiq )())()(()(
inout
(13)
In Eq.(13) CP represents for heat capacity flow
rate for the cold stream i. At the mixing point, the
inlet temperature of cold stream i is the mixing
temperature by fresh water and other exchangers’
used water, so Eq.(14) needs to be satisfied.
n
ijj
iFTjtjiFitiF
,1
ininoutinin
)()(),()()(
(14)
in
T
represents for the inlet temperature of the
total network. At the splitting point, the temperature
equals the outlet temperature of the cold stream. At
the mixing point return to the cooling tower, in
Eq.(15) outlet temperature
out
T
constraint is shown
as follows.
iF
jF
jiF
in
,
jiF
out
,
ijF
in
,
ijF
out
,
otal
F
int
outtotal
F
iF
in
jF
in
iF
out
jF
out
Mixing point
Splitting point
Cold Medium Hot Medium
HE i
HE j
)(
out
iT
)(
in
iT
Figure 1: The structure of series-parallel exchanger network.
MEEP 2018 - The Second International Conference on Materials Chemistry and Environmental Protection
328

n
i
n
i
iFitiFT
1
outout
1
outout
)()()(
(15)
Ponce-Ortega et al. (Ponce-Ortega et al., 2010)
discussed that the d-value between the inlet
temperature of the hot stream and the outlet
temperature of the cold stream should exceed a
certain value. Thus, the inlet and outlet temperature
of the cold stream cannot exceed a certain value.
The temperature value is expressed as
T
. And the
constraints are as follows.
TiTiT )()(
inHOT,out
(16)
)()(
max,inin
iTiT
(17)
In the series-parallel automated design method,
the purpose is to reduce the fresh water.
)min(
intotal
FOB
(18)
The program is shown above. The objective
function is Eq.(18) to reduce cooling system flow
rate, which can increase the outlet temperature
simultaneously. Eq.(1) to Eq.(5) are equality
constraints and Eq.(6) to Eq.(12) are inequality
constraints and logical constraints to limit heat
exchange cold medium flow rate. Eq.(13) to Eq.(17)
are temperature constraints.
),(
in
jiB
and
),(
out
jiB
are binary variables while others are continuous
variables. There are nonlinear constraints in
Eq.(13)-(15). So the mathematical problem is a
mix-integer nonlinear programming (MINLP).
GAMS is an efficient mathematical tool for solving
optimization problems. This article uses one of the
solvers named DICOPT to solve this MINLP
problem.
3 CASE STUDY
The case study is used to validate the mathematical
problems and compare the traditional parallel heat
exchange network and series-parallel model of this
work. Suppose there are 4 hot streams in the cooling
water system, the hot stream operation data are
shown in the following Table.
Table 1: Hot stream data.
Exchanger
1
2
3
4
Inlet Temperature/℃
50
55
75
75
Outlet Temperature/℃
30
45
45
60
CP(kW/℃)
15
80
20
40
Suppose each heat exchanger contains only one
hot stream and one cold stream. According to the hot
stream data in Table 1, suppose the temperature
difference
T
in Eq.(16) is 10℃. Then the cold
medium data can be calculated in Table 2. The
maximum inlet and outlet temperature and CP are
shown as follows.
Table 2: Cold medium data.
Heat Exchanger
1
2
3
4
Maximum Inlet
Temperature/℃
20
35
35
50
Maximum Outlet
Temperature/℃
40
45
65
65
Maximum CP(kW/℃)
15
80
20
40
According to the model above, the exchanger
network can be designed in a series-parallel method.
The cold stream data is used to solve the model to
optimize the minimum flow rate of the total system.
The problem is solved by GAMS. And the results
are shown as the following Figures and Table.
Figure 2 and Figure 3 shows the differences
between the parallel model and the series-parallel
model. In the parallel model, the CP is 155 kW/℃.
Suppose the cooling water specific heat capacity is
4.18 kJ/(kg℃). So the total mass flow rate is
37.1kg/s. While in the series-model the mass flow
rate is 12.4 kg/s. The outlet return temperature of the
parallel is 34.8℃ while that of the series-parallel
model is 64.2℃. According to the theory of Kim and
Smith (Kim and Smith, 2001), the higher the return
temperature of the cooling tower is, the better the
cooling tower performance will become.
HE1
HE2
HE3
HE4
80
15
20
40
155
20°C
34.8°C
Figure 2: Parallel optimization model.
HE1
HE2
HE4
HE3
15
29
8
52
15
32
12
20
20°C
64.2°C
40°C
45°C
65°C
63.8°C
Figure 3: Series-parallel optimization model.
Series-Parallel Optimization Model for Heat Exchanger Network
329

From the below Table 3, we can conclude that
the series-parallel model can save large amount of
fresh water and increase the outlet return
temperature. From the perspective of economic and
energy efficiency, series-parallel model can save
costs and improve tower performance.
Table 3: Comparison of different models
model
Mass Flow
Rate(kg/s)
Outlet
Temperature/℃
parallel
37.1
34.8
series-parallel
12.4
64.2
4 CONCLUSIONS
This work builds a mixed-integer nonlinear
programming (MINLP) algorithm and solves the
model by GAMS. A case study explains that in the
automated series-parallel model, the water flow rate
can be reduced by almost 24.7kg/s and the
temperature might be increased by 29.4℃. The
improved optimization model can reduce operating
costs and improve cooling tower performance which
is important for improving the efficiency of the
entire circulating water system.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
This work was financially supported by Science and
technology committee of Shanghai (13dz1201700)
fund.
REFERENCES
Kim, J. K., Savulescu, L., Smith, R., 2001. Design of
cooling systems for effluent temperature reduction[J].
Chemical Engineering Science, 56(5): 1811-1830.
Kim, J. K., Smith, R., 2001. Cooling water system
design[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 56(12):
3641-3658.
Kim, J. K., Smith, R., 2003. Automated retrofit design of
cooling-water systems[J]. Aiche Journal, 49(7):
1712-1730.
Kuo, W. C. J., Smith, R., 1998. Design of Water-Using
Systems Involving Regeneration[J]. Process Safety &
Environmental Protection, 76(2): 94-114.
Ponce-Ortega, J. M., Serna-González, M.,
Jiménez-Gutiérrez, A., 2007. MINLP synthesis of
optimal cooling networks[J]. Chemical Engineering
Science, 62(21): 5728-5735.
Ponce-Ortega, J. M., Serna-González, M.,
Jiménez-Gutiérrez, A., 2010. Optimization model for
re-circulating cooling water systems[J]. Computers &
Chemical Engineering, 34(2): 177-195.
Xiao, F., Shen, R., Wang, B., 2005. Recirculating
Cooling-Water Network with an Intermediate
Cooling-Water Main[J]. Energy & Fuels, 19(4):
1723-1728.
MEEP 2018 - The Second International Conference on Materials Chemistry and Environmental Protection
330
