
Antihyperglycemic Activity of Ethanolic Herb Extract of Ceplukan
(Physalis angulata L.) in Diabetic Hypercholesterolemia in Male
Hamsters
Elly Wardani
*
, Dwitiyanti, Sediarso, Dwina Puspandiyah
Faculty of Pharmacy and Science, Universitas Muhammadiyah Prof. Dr. Hamka, Jakarta, Indonesia
Keywords: Physalis angulata L., Ceplukan herb extract, Antihyperglycemic, blood glucose
Abstract: Diabetes mellitus is a disease characterized by hyperglycemia as well as progressive changes to the
pancreatic beta cell structure. This study was conducted to determine the antihyperglycemic activity of
ceplukan herb extract (Physalis angulata L.) in alloxan-induced male Syrian hamsters and high cholesterol
feed. The study used 24 hamsters divided into six groups. Group I were given a standard diet and regular
drinking water, Group II were given metformin dose 61,66 mg/kg body weight (BW), Group III were
alloxan-induced and high cholesterol feed, Groups IV, V and VI were given extract dose 60, 120 and 240
mg/kg BW respectively. The animals were induced alloxan monohydrate as well as were given high
cholesterol feed during treatment. Blood sampling was performed on the 29th and 44th day using a clinical
spectrophotometer. The results show significant differences between treatment groups (α <0,05), followed
by Tukey test. In conclusion, the preparation of herbal extract test ceplukan at doses of 120 and 240 mg/kg
BW could reduce blood glucose levels by 50.84% and 43.41% which is equivalent to metformin dose of
61.66 mg/kg BW with a percentage of 53.12%.
1 INTRODUCTION
Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a group of metabolic
disorders characterized by hyperglycemia and
abnormalities in carbohydrate, fat, and protein,
resulting from insulin secretion abnormalities,
insulin work or both (Dipiro, 2014). Diabetes
mellitus is divided into two types, namely type I DM
(5%-10% of cases), which is caused by damaged
pancreatic β cells suffered by hereditary or genetic
and type II DM (90% of cases) caused by insulin
resistance due to increased lipolysis, free fatty acid
production or increased glucose production in the
liver (Dipiro, 2015).
DM in Indonesia is a serious threat to health
development, can cause blindnesss, kidney failure,
diabetic feet (gangrene) so it must be amputated,
heart disease and stroke (Depkes, 2013). The World
Health Organization (WHO) Global Status Report
on NCD in 2010 stated that 60% of the cause of
death of all ages in the world is due to non-
communicable diseases and DM is ranked 6th as the
cause of death. Approximately 1.3 million people
die from diabetes and 4% die before the age of 70
years. In 2030, it is estimated that DM will be
ranked 7th as the cause of death worldwide and that
Indonesia will have 21.3 million people with DM
(Depkes, 2013). This condition will make Indonesia
on the 4
th
position after the United States, China and
India as countries that have the largest diabetics with
the largest population in the world (Depkes, 2012).
One of the medicinal plants that can be used as
an antidiabetic agent is ceplukan (Physalis angulata
L.). In West Java, ceplukan has been used as
diabetes drug (Sutjiatmo et al. 2011). Chemical
compounds of this plant include alkaloids,
flavonoids, saponins, fisalin, sterols/terpenes and
citric acid (Depkes, 1995). Traditionally, this plant
has been used to treat boils, and diabetes (Depkes,
1995).
Previous research has shown that the ethanol
extract of ceplukan leaves at 100 mg/kg BW can
reduce blood glucose levels in mice with a
percentage of 56.34% (Kasali, 2016). In isolation
research from ethanol extract of ceplukan fruits at 25
mg/kg BW and 50 mg/kg BW for 15 days can
decrease rat blood glucose level to 38,75% and
27,55% respectively (Raju, 2015). Another study has
Wardani, E., Dwitiyanti, ., Sediarso, . and Puspandiyah, D.
Antihyperglycemic Activity of Ethanolic Herb Extract of Ceplukan (Physalis angulata L.) in Diabetic Hypercholesterolemia in Male Hamsters.
DOI: 10.5220/0008240601330137
In Proceedings of the 1st Muhammadiyah International Conference on Health and Pharmaceutical Development (MICH-PhD 2018), pages 133-137
ISBN: 978-989-758-349-0
Copyright
c
2021 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
133

reported that the fraction of chloroform herb
ceplukan at a dose of 0,5 mg/20g BW, 1 mg/20g
BW and 2 mg/20g BW can reduce blood glucose
levels in mice and the dose 2 mg/20g BW can
reduce blood glucose levels of mice equally to
glibenclamid 0,013 mg/20g BW (Sunaryo et al.
2012).
2 MATERIALS AND METHODS
2.1 Materials
The ingredients used are ceplukan herb (Physalis
angulata L.). Determination was done at
“Herbarium Bogoriense” Botani section, Pusat
Penelitian Biologi - LIPI Cibinong.
Alloxan monohydrate from Sigma-Aldrich Co.,
USA. Metformin HCL from Sohan Healthcare Pvt
Ltd, Maharashtra. High cholesterol feed, glucose kit
reagent was using commercial kits purchased from
Human Diagnostics Worldwide Germany.
2.2 Animal Subjects
The experiment used twenty-four male Syrian
hamsters (Mesocricetus auratus), aged 3–4 months
and weighed around 80 g. The animals were housed
under standard environmental conditions. The study
protocol was approved by the Health Research
Ethics Committee of Universitas Muhammadiyah
Prof. Dr. Hamka, West Jakarta, Indonesian. The
reference number for approval was 02/18.05/005.
The animal subjects were acclimatized in a cage
for approximately one week to adapt to the new
environment. The animals were divided into 6
groups consisting of 4 hamsters.
2.3 Extraction
One kilogram of ceplukan dried powder (Research
Institute for Spices and Medicinal
Plants/BALITTRO, Bogor, Indonesia) was
macerated with 70% ethanol for 6 hours and was
stirred occasionally to reveal the active ingredients.
The mixture was allowed to stand for 18 hours. The
maceration result was then separated by filtration.
The reproduction process was repeated three times.
The maceration result was concentrated with a
vacuum rotary evaporator until it became a viscous
extract (Department of Health RI, 2008). The
concentrated result was put in a water bath at 40–
50
o
C for one day to obtain an extract with a constant
weight.
2.4 Phytochemical Screening
The phytochemical screening of ceplukan herb
extract included an examination of alkaloids using
Bourchardat reagents, testing flavonoids with
methanol, concentrated HCL and magnesium
powder. Saponin test were perfomed with foam
formation, tannin test with FeCl
3
1% reagent, and
Steroid testing with ethanol, concentrated H
2
SO
4
were done if there is a red or purple color change
indicating the presence of triterpenoids and the green
color indicates steroid presence (Depkes, 1995).
Extract yield was determined by calculating the dry
extract weight obtained from the weight of dry
powder before extraction.
2.5 Category and Animals Subject
Treatment
The experiment was done with a complete
randomized design, using 24 white male, hamsters
divided into six groups consist of 4 rats.
a. Group I: The group was given a standard diet
and regular drinking water.
b. Group II: Positive Control, was given alloxan
monohydrate, high cholesterol feed and
comparative preparations.
c. Group III: Negative Control, was given alloxan
monohydrate, high cholesterol feed and Na-
CMC 0,5%.
d. Group IV: was given alloxan monohydrate, high
cholesterol feed and ethanolic herb extract of
ceplukan dose I.
e. Group V: was given alloxan monohydrate, high
cholesterol feed and ethanolic herb extract of
ceplukan dose II.
f. Group VI: was given alloxan monohydrate, high
cholesterol feed and ethanolic herb extract of
ceplukan dose III.
2.6 Method of Glucose Levels
Measurement
Blood sampling was taken on Day 29 and Day 44;
hamsters were first anaesthetized using ketamine
dose 10 mg/kg BW (Lacy et al. 2009). Blood
collection was performed at the eye orbital sinuses
after the animals were previously preoccupied for 12
hours. The blood was taken as much as one mL, and
was collected in a microtube. The blood was
centrifuged at 4000 rpm for 15 minutes to obtain the
serum (Suharmiati, 2003). Serum was taken ten μL,
was mixed with enzyme reagent (glucose reagent
kit) 1000 μL, then was homogenized using vortex
MICH-PhD 2018 - 1st Muhammadiyah International Conference on Health and Pharmaceutical Development
134

for 1 minute and was incubated for 5 minutes at
37
0
C blood glucose level were tested with a clinical
photometer (Human, 2012).
2.7 Data Analysis
The data using statistical analysis show that the
decrease in percentage data from the initial and late
glucose levels, baseline levels are levels after
alloxan induction and high cholesterol feed while the
final content levels after treatment. The data were
tested for normality and homogeneity and were then
analyzed with one-way ANOVA test with 95%
significance level (α = 0,05). If there is a significant
difference, the data were then analyzed with the
Tukey test (Santosa, 2010).
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Based on the results of the determination, indicating
that the plant is Physalis angulata L. included in
Solanaceae. Data extraction of ceplukan herb such
as weigh ceplukan fresh and dry, weigh of ceplukan
extrac and extract yield are given in Table 1.
Parts of ceplukan that used is the herbaceous
part. A report by The Department of Health (1995)
stated that chemical compounds found in ceplukan
include alkaloids, flavonoids, saponins, fisalin,
sterols/terpene and citric acid. Alkaloids, flavonoids,
saponins, and steroids could be obtained by
phytochemical screening. (Table 2). The results of
extract quality characteristics showed specific smell,
thick form and had a drying loss of 9.59% can be
seen in table 3.
Metformin was used as a comparative drug in
this study because it is a first-line antidiabetic drug
against DM2 patients with a history of obesity. In
this study, the test animals not only being treatment
to become hyperglycemia, but also induced to be
hypercholesterolemia. Then, induction of alloxan
will damage cells β Langerhans pancreatic cells to
inhibit the production of insulin. Therefore
metformin has a mechanism of increasing peripheral
tissue sensitivity of insulin (Suharmiati, 2003) and it
was chosen as a comparative drug preparation in this
study because the mechanism was aligned with the
alloxan to correct the damage caused by alloxan.
Feeding for the hypercholesterolemic hamsters
was performed for 44 days to maintain the stability
of cholesterol. On Day 22, alloxan was induced
intraperitoneally with a dose of 180 mg/kg BW.
Before blood sample collection, the hamsters were
fasted for 12 hours to avoid the effect of increased
glucose level after meal. Measurement of baseline
blood glucose level of the test animals were
performed on Day 29 to determine whether the
induced alloxan had successfully increased the blood
glucose level. After the level of glucose and
cholesterol were stated to increase pathologically
(the level of complication was achieved), then the
extract was orally administered by using feeding
tube. The extract was given every morning for 14
days. On Day 44, the final blood glucose level was
checked to see whether there is a decrease or not.
The data of the percentage of decrease of blood
glucose level was examined by normal distribution
test {(α = 0,202) > 0,05} and homogeneity test {(α =
0,104) > 0,05} which show that the data is normally
distributed and homogeneous. One-way ANOVA
test was run to test whether the mean of % decrease
in the blood glucose level is the same or
significantly different. The result {(α = 0,000) <
0,05} shows that there are significant differences
between all groups. Then the one-way ANOVA
results were further examined with the Tukey test to
Table 2: Results of Phytochemical Extract Screening
No. Chemical
com
p
oun
d
Extract
1. Alkaloi
d
+
2. Saponin +
3. Tanin -
4. Flavonoi
d
+
5. Steroi
d
+
6. Triter
p
enoi
d
-
N
ote: “+” (positive), “-“ (ne
g
ative)
Table 1: Data extraction results
No. Type Result
1. Ce
p
lukan Fresh 15 k
g
2. Ce
p
lukan Dr
y
1,5 k
g
3. Ce
p
lukan Powde
r
1,1 k
g
4. Macerate of Powde
r
1 kg
5. Extract 158,86 g
6. Extract Yiel
d
15,886 %
Table 3: Extract characteristics
No. Type of Test Extract
1. Organoleptic
Smell S
p
ecific
Colo
r
Brown Green
Form Thick, bitte
r
2. Flavors 9,59%
Antihyperglycemic Activity of Ethanolic Herb Extract of Ceplukan (Physalis angulata L.) in Diabetic Hypercholesterolemia in Male
Hamsters
135
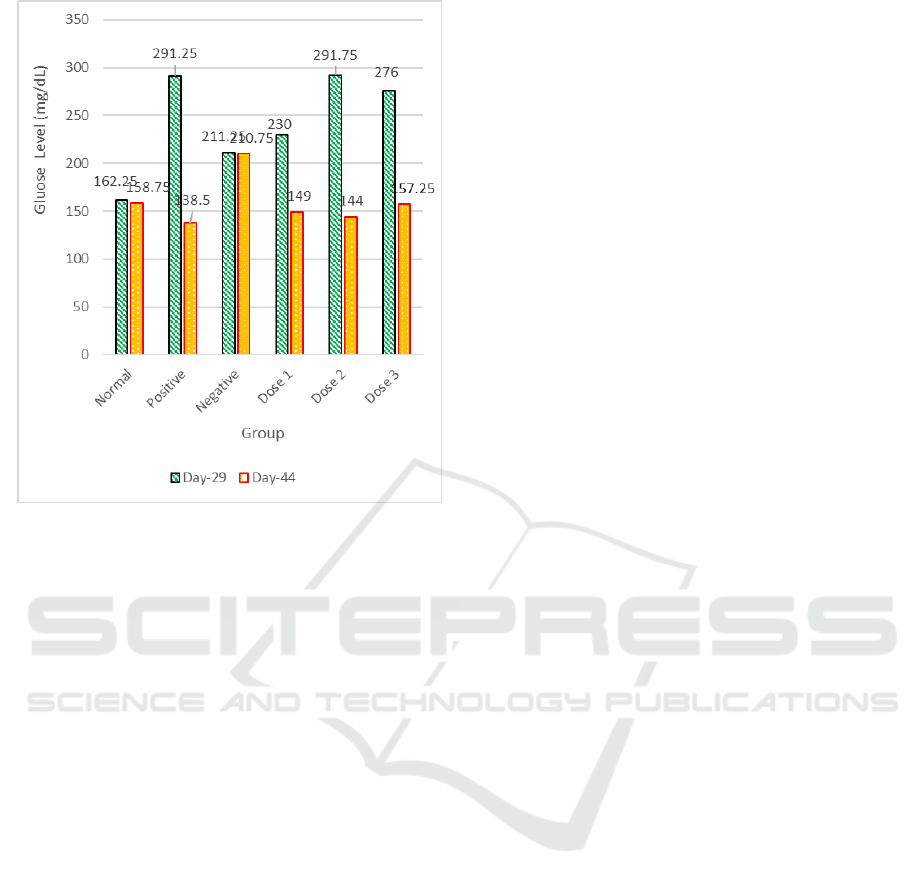
know which group has, or has no significant
difference between normal control, negative control,
positive control, Dose 1, Dose 2 and Dose 3.
The-ability to decrease blood glucose is related
to the biological activity of compounds in ceplukan
plants. The compounds contained are flavonoids,
alkaloids, steroids, and saponins. The chemical
content of steroids can stimulate the release of
insulin from the pancreas to lower blood glucose
levels (Sediarso et al. 2008). Insulin will then work
to increase the transport of glucose from the blood
into cells by increasing the permeability of the cell
membrane to glucose. Once inside the cell, glucose
will then be used to generate energy. The liver and
muscles will convert glucose into glycogen and will
then be stored there. This conversion causes the
blood glucose level in the body decreases slowly
(Gustina, 2012).
Figure 1 shows the plasma glucose levels of the
experimental animals. The highest decrease in blood
glucose was shown by Dose 2 (120 mg/kg BW)
which was 50,84% compared to Dose 3 (240 mg/kg
BW) which was 43,41% and Dose 1 (60 mg/kg BW)
which was 34,74%. All pharmacologic responses
must have the maximum effect (Emax), regardless
of the high concentration that occurs, a point is
reached when adding the concentration does not
increase the response (Katzung et al. 2014). This
occurs in Dose 2 that was smaller than Dose 3, but
Dose 2 gave a greater decrease effect compared to
Dose 3, the maximum effect occurred in Dose 2;
although Dose 3 twice higher. Therefore, this study
shows that Dose 2 (120 mg/kg BW) has a better
activity in lowering blood glu
cose by 50,84%.
4 CONCLUSION
It can be concluded that ceplukan extract can lower
blood glucose levels in male hamsters with
hypercholesterolemia and hyperglycemia. Dose 2
(120 mg/kg BW) has a better activity in lowering
blood glucose by 50,84% and equivalent to
metformin dose 61,66 mg/kg BW which was
53,12%.
FUTURE RECOMMENDATION
The next stage of the research may focus on the
content of plant compounds and fractionation phase
as a decrease in blood glucose levels.
REFERENCE
Departemen Kesehatan RI. 1995. Farmakope Indonesia.
Edisi IV. Departemen Kesehatan Republik
Indonesia, Jakarta. Hal 7, 410
Departemen Kesehatan RI. 1995. Materia Medika
Indonesia. Jilid VI. Departemen Kesehatan RI.
Jakarta. Hal. 195,199
Departemen Kesehatan RI. 2008. Farmakope Herbal.
Edisi 1. Depkes RI. Jakarta
Depkes RI. 2012. Kemitraan Pemerintah Dan Swasta
Dalam Pengendalian Diabetes Melitus Di Indonesia.
http://www.depkes.go.id/article/view/2053/kemitraan-
pemerintah-dan-swasta-dalam-pengendalian-diabetes-
melitus-di-indonesia-.html. Diakses 8 Februari 201
Depkes RI. 2013. Diabetes Melitus Penyebab Kematian
Nomor 6 Di Dunia: Kemenkes Tawarkan Solusi
Cerdik Melalui Posbind.
http://www.depkes.go.id/article/view/2383/diabetes-
melitus-penyebab-kematian-nomor-6-di-dunia-
kemenkes-tawarkan-solusi-cerdik-melalui-
posbindu.html. Diakses 8Februari 2017
Dipiro JT, Talbert RL, Yee GC, Matzke GR, Wells BG,
Posey LM. 2014. Pharmacotherapy: A
Phatophysiologic Approach. Ninth edition. USA: The
McGraw-Hill Companies. Page. 2546
Dipiro JT, Talbert RL, Yee GC, Matzke GR, Wells BG,
Posey LM. 2015. Pharmacotherapy Hanbook. Ninth
Figure 1: The average percentage decrease in blood
glucose levels in the administration of ceplukan herb
extract
MICH-PhD 2018 - 1st Muhammadiyah International Conference on Health and Pharmaceutical Development
136

edition. USA: The McGraw-Hill Companies. Page.
161
Gustina NMR. 2012. Aktivitas Ekstrak, Fraksi Pelarut dan
Senyawa Flavonoid Daun Sukun (Artocarpus altilis)
Terhadap Enzim α-Glukosidasi sebagai Antidiabetes.
Dalam: Skripsi. Bogor. Institut Pertanian Bogor
Human. 2012. Glucose Liquicolor. Human Gesellschaft
for Biochemica and Diagnostica mbH. Germany
Kasali FM, Fokunang CN, Ngoupayo Joseph, Ngameni
Bathelemy, Fokunang ET, Njinkio Borgia, Kechia
Frederick, Kadima JN, Marthe Tsague, Victor Oyono,
Mbacham Wilfred, Ngadjui BT. 2016. Evaluation of
the Antidiabetic Properties of Hydro-Alcoholic Extract
and Its Fractions from Physalis peruviana L. Leaves
on Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Wistar Rats.
Journal of Diseases and Medicinal Plants Vol.2 No.6.
Cameroon
Katzung BG, Masters SB, Trevor AJ. 2014. Farmakologi
Dasar dan Klinik Ed 12. Penerbit Buku Kedokteran
EGC, Jakarta. Hal 54
Lacy CF, Abreg JA, Amstrong LL, Goldman MP, Lance
LL. 2009. E-book Drug Information Handbook. Edisi
17. Lexi-Comp for the American Pharmacists
Association
Raju Proka, Mamidala Estari. 2015. Anti-Diabetic
Activity Of Compound Isolated From Physalis
angulata Fruit Extracts In Alloxan Induced Diabetic
Rats. The American Journal Of Science And Medical
Research. Vol 1 No.1. India
Santosa S. 2010. Statistik Parametrik. Elex Media
Komputindo. Jakarta
Sediarso, Sunaryo H, Amalia N. 2008. Efek Antidiabetes
dan Identifikasi Senyawa Dominan dalam Fraksi
Kloroform Herba Ceplukan (Physalis angulata L.).
Jurnal Farmasi Indonesia.Vol. 4. Jakarta
Suharmiati. 2003. Pengujian Bioaktivitas Anti Diabetes
Mellitus Tumbuhan Obat. Majalah Cermin Dunia
Kedokteran No. 140. Surabaya. Hal. 8-13
Sunaryo H, Kusmardi, Trianingsih W. 2012. Uji Aktivitas
Antidiabetes Senyawa Aktif Dari Fraksi Kloroform
Herba Ceplukan (Physalis angulata L.) Terhadap
Penurunan Kadar Glukosa Darah dan Perbaikan Sel
Langerhans Pankreas Pada Mencit yang Diinduksi
Aloksan. Jurnal Farmasains. Vol 1 No. 5. Jakarta.
Hal. 251
Sutjiatmo AB, Sukandar EY, Ratnawati Yulia,
Kusmaningati Suswini, Wulandari Asri, Narvikasari
Suci. 2011. Efek Antidiabetes Herba Ceplukan
(Physalis angulata Linn.) Pada Mencit Diabetes
Dengan Induksi Aloksan: dalam Jurnal Farmasi
Indonesia Vol.5 no.4 Juli. Hal. 166-171
Antihyperglycemic Activity of Ethanolic Herb Extract of Ceplukan (Physalis angulata L.) in Diabetic Hypercholesterolemia in Male
Hamsters
137
