
Formulation of Moringa oleifera Leaf Extract in Lotion and Gel as
Sunscreen
Nining Sugihartini
1
, M. Alif Fajri
2
, Desty Restia Rahmawati
3
1
Departement of Pharmaceutical Technology, University of Ahmad Dahlan, Jln. Prof. Dr. Soepomo, Janturan, Umbulharjo,
Yogyakarta, Indonesia
2
Pascasarjana of Pharmacy University of Ahmad Dahlan, Jln. Prof. Dr. Soepomo, Janturan, Umbulharjo, Yogyakarta,
Indonesia
3
Faculty of Pharmacy University of Ahmad Dahlan, Jln. Prof. Dr. Soepomo, Janturan, Umbulharjo, Yogyakarta, Indonesia
Keywords: Moringa oleifera, leaf extract, gel, lotion, sunscreen
Abstract: Moringa oleifera leaf extract has an antioxidant activity so it can be used to protect the skin. The aim of this
study is to determine the extract specification and formulation in lotion and gel as sunscreen agent. Moringa
oleifera leaf extract was obtained by maceration method using ethanol 70%. The extracts were identified for
chemical content and specification test of extract. After that, extract was formulated into gel and lotion. The
evaluation of gel and lotion includes physical characteristics (spreadability and adhesivity) and the value of
Sun Protection Factor. The result showed that Moringa oleifera leaf extract contained alcaloids, flavonoids
and poliphenols. The value of moisture content, ash content, acid soluble ash, and β-caroten were 5.75%,
0.19%, 0.16%, and 0.46%, respectively. The IC
50
of antioxidant activity was 516.28. The value of Sun
Protection Factor of the 5% octyl metoxycinnamate solution, gel (contain 5% extract), and lotion (contain
5% extract) were 33.25, 34.75, 24.98, and 25.89, respectively. The lotion and the gels have a strong
sunscreen activity and meet the requirements of physical properties for preparations.
1 INTRODUCTION
Moringa oleifera contains ß-carotene, protein,
vitamin C, calcium and potassium that can be used
as natural antioxidant (Krisnadi, 2013). In addition,
other studies have also shown that moringa leaves
contain phenolic compounds, flavonoids and
carotenoids (Vongsak et al., 2013 and Jayawardana
et al., 2015). Based on the content of active
ingredients, moringa leaves have various properties
such as antioxidants, antimicrobials, natural food
preservatives, and anti-inflammatory (Jayawardhana
et al., 2015; Singh et al., 2009).
Indonesia as a tropical country has a high
intensity of sunlight, so one part of the body that was
affected by the condition is the skin. The skin, as
one of the body's protective organs, can undergo an
excessive dryness (Rawlings et al., 2000).
Therefore, it needs a certain dosage form that can be
used to protect and to maintain the moisture of skin.
Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties of
moringa leaves are expected to protect the skin from
free radicals that are caused by sunlight or other
factors.
A previous study have shown that moringa leaf
extract can be applied in topical form for the
prevention and treatment of oxidative and anti-aging
stress diseases (Atif et al., 2013). A research by
Sugihartini et al. (2016) showed that a 3%
concentration of extract in cream was able to
improve skin smoothness. The increasing
concentration of extract in cream will increase SPF
value. This study will focus on the formulation of
extract in the form of lotion and gel preparation with
an extract concentration of 3%. The evaluations of
dosage form will consist of physical properties of
the preparation and the SPF value.
2 MATERIALS AND METHOD
2.1 Materials
Moringa oleifera leaves was obtained at Yogyakarta,
Indonesia. The ingredients for lotion and gel were
154
Sugihartini, N., Fajri, M. and Rahmawati, D.
Formulation of Moringa oleifera Leaf Extract in Lotion and Gel as Sunscreen.
DOI: 10.5220/0008241001540158
In Proceedings of the 1st Muhammadiyah International Conference on Health and Pharmaceutical Development (MICH-PhD 2018), pages 154-158
ISBN: 978-989-758-349-0
Copyright
c
2021 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

vaseline album (Brataco, Indonesia), stearic acid
(Brataco, Indonesia), cetyl alcohol (Brataco,
Indonesia), thrietanolamin (Brataco, Indonesia),
dimeticon (Brataco, Indonesia), methyl paraben
(Brataco, Indonesia), propylene glycol (Brataco,
Indonesia), ethanol 0% (pharmaceutical grade),
ethanol 35% (pharmaceutical grade), etanol 70%
(pharmaceutical grade), and aquadest. The
instruments that was used were oven (Binder, ED
115/Esv 00-17289), rotary evaporator (Heidolph,
Germany), analitical balance (Wiggen Hauser),
waterbath (Memert, Germany), pH meter (WTW
82362 Weilheim, Germany), termometer,
sentrifugator (PLC-series), vacuum pump (Rotary
Vane), viskometer Rheosys Merlin VR, freeze dryer
(Virtis, United States), the equipment of adhesivity,
the equioment of spreadability and glassware (Pyrex,
United States).
2.2 Methods
2.2.1 Extraction of Moringa oleifera Leaf
Extract of leaves Moringa oleifera leaves was
obtained by using maceration method. The
maceration method was performed with a ratio of
1:40. The 10 grams of dried sample powder was
extracted by using of 400 mL ethanol 70%
pharmaceutical grade for 72 hours at room
temperature. After that, it was filtered with filter
paper and vacuum pump. The extract was
evaporated by using rotary evaporator and was
continued by using waterbath until dry (Vongsak et
al., 2013).
The extract of moringa leaf was obtained by
maceration method with ethanol 70%. This is based
on research results of Vongsak et al. (2013) which
indicates that the nutritious compounds of phenolic
and flavonoids as antioxidants can be maximized by
using the methods. This study will be identify the
specific and non-specific parameters of moringa leaf
extract.
2.2.2 Specification of Extract
The levels of β-carotene in moringa leaf extract was
determined by using High Performance Liquid
Chromatography. The extracts were also identified
for their chemical content, the extract specification
test included water content, total ash content, acid
soluble ash content.
2.2.3 Formulation of Moringa oleifera
Extract in Lotion and Gel
The composition of lotion and gel that was used in
this study are presented in Table 1 and 2.
The preparations of lotion and gel were
performed by using fusion principle. The water-
soluble and oil-soluble parts was were soluted in
water and then heated at a temperature of 70°C.
Then, the second mixture (water phase) was
gradually added into the first mixture (oil phase) at
70°C and was homogenized. The extract of moringa
was added when it was cold (Munson, 1991).
2.2.4 Evaluation of Physical Characteristic
• Adhesivity test
The gel or lotion was weighed 0.25 g and then was
placed between two glass objects. One kilogram of
load was put on the upper side of glass objects to
give a tension for 5 minutes. After that, the glass
object were put on the tool that had 80 grams of
load. The time was needed for two glass objects
separated after the load of 80 grams release was
noted (Putra and Setyawan, 2014).
• Spreadability test
The gel or lotion was weighed 0.5 g and then was
placed in the middle of a circular glass. The other
glass was placed on the upper side of it for 1 minute.
The diameter of lotion or gel was measured. One
hundred grams of load was placed on the glass for 1
Table 1: The Formulation of Moringa oleifera leaf
extract in lotion.
Composition Weight (g)
Stearic aci
d
4,00
Cetyl alcohol 4,00
Triethanolamine 2,00
Gl
y
cerin 2,00
Meth
y
l
p
a
r
a
b
en 0,20
Propyl
p
araben 0,03
Extract of moringa 3%
Aquadest Add 100
Table 2: The Formulation of Moringa oleifera leaf
extract in gel.
Composition Weight (g)
Carbopol 1
Triethanolamine 0,05
Glycerin 2
Pro
p
y
lene
g
l
y
col 1
Meth
y
l
p
araben 0,03
Extract of morin
g
a 3%, 6%
Aquadest 100
Formulation of Moringa oleifera Leaf Extract in Lotion and Gel as Sunscreen
155
minute and then the diameter of gel or lotion was
measured until getting a constant one (Astuti et al.,
2010).
• The measurement of pH
The pH values of lotion and gel were determined by
using pH meter after 500 mg of gel or lotion was
soluted in 5 ml of distilled water (Naibaho et al.,
2013).
• The measurement of Viscosity
The viscosity of lotion or gel was measured by
using Viscosimeter Rheosys Merlin VR.
2.2.5 The Measurement of Sun Protection
Factor Value
The values of Sun Protection Factor (SPF) of the gel
and the lotion were determined based on a set
method by Bambal et al. (2011). A total of 1 gram of
sample was added to Erlenmeyer and then was
added with ethanol up to 100 ml. The solution was
sonicated for 5 minutes and then the mixture was
filtered. A total of 10 ml of first filtrate was
discarded. Furthermore, filtrate was taken as much
as 5 ml and then was added ethanol up to 50 ml.
Five ml of the solution was taken and was added
with ethanol to 25 ml. The spectral absorbance was
read by using spectrophotometer at 290-320 nm with
a wavelength interval of 5 nm. The SPF value was
calculated based on the equation (1):
SPF
spectrophotometric
(1)
2.2.6 Data Analysis
The data were analysed by ANOVA test to find the
level of differences between the formulas.
3 RESULT AND DISCUSSION
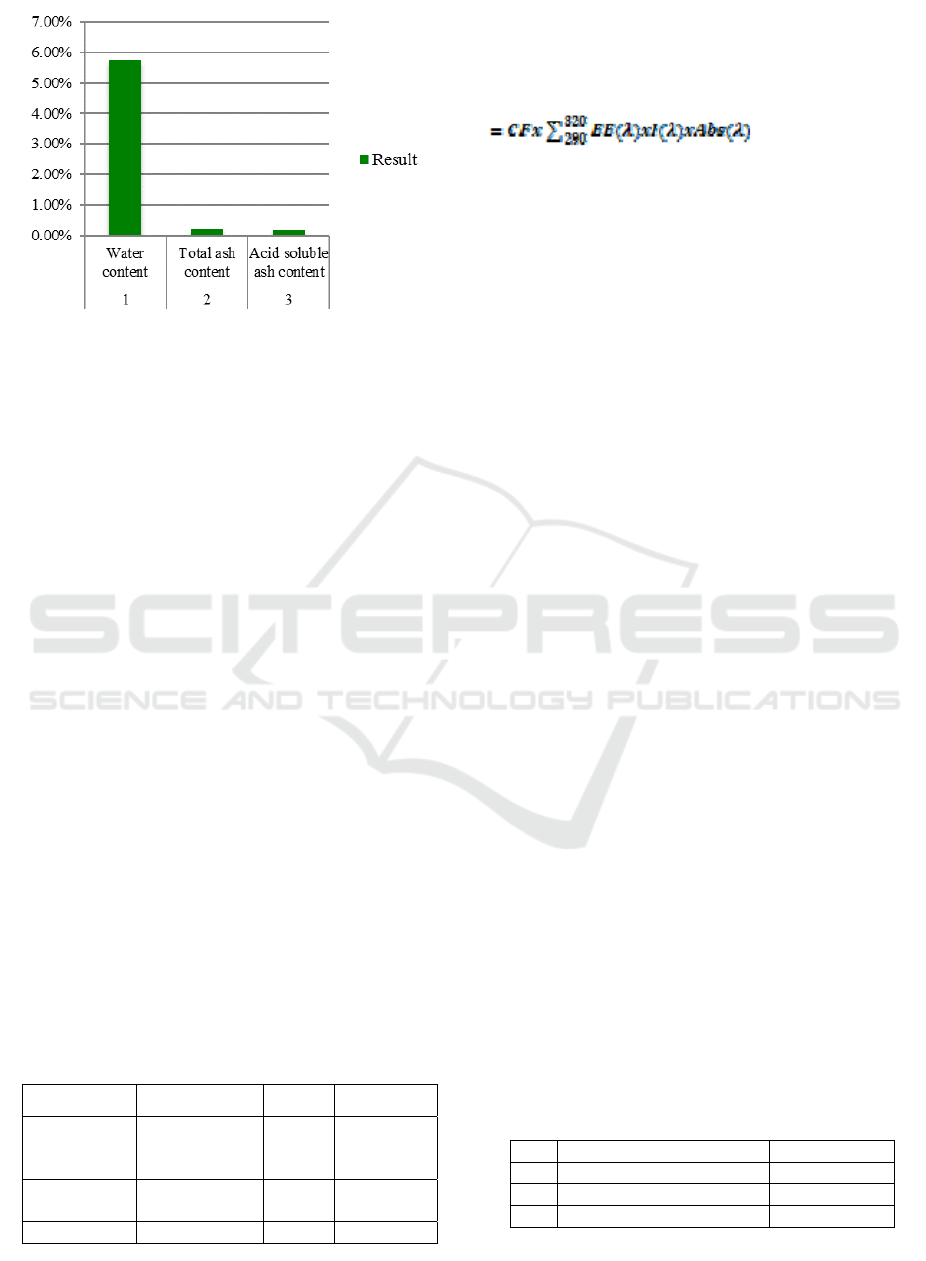
The extract obtained in this study was evaluated for
water content, total ash and acid soluble ash content
as presented in Figure 1. The total ash content and
acid soluble ash content of moringa leaf extract
fullfilled the requirement (≤0.20%) based on Herbal
Pharmacopoeia (year). The extracts were also
evaluated for their chemical content including
alkaloids, flavonoids and polyphenols as presented
in Table 3.
The extract was also analysed for the level of β
carotene as active substance in the extract. The
extract potency was evaluated based on antioxidant
activity by calculating IC
50
and SPF values. The
result of the assay of β-carotene, IC50 and SPF
values was presented in table 4.
The test results show that IC
50
was 516.28. This
means that the antioxidant activity of moringa leaf
extract was weak. However, the extract has a high
SPF value of 33.25 which means it has a strong
sunscreen activity. The step after the extract
specification was formulation of extracts for the
preparation of lotions and gels. The preparations
were then evaluated for physical properties as
presented in Figure 2 and table 5. The test results
show that all the preparations also met the
requirements of pH, viscosity, adhesivity and
spreadability.
The test results show that the pH values of the
lotion (4.75) and the gel (5.66) met the requirements
of pH of the skin preparation that are between 4.5 to
Table 3: Result of identification of chemical content on
moringa extract.
Test Reagen Result Evidence
Alkaloid HCL 2N,
Dragendorf
and maye
r
+ There was
sediment
Flavanoid Ethanol 70%,
amonia
+ Yellow
Pol
yp
henol FeCL
3
+ Green dar
k
Table 4: The number of β carotene, IC
50
and SPF value
of
extract moringa.
No Test Result
1. The number of β karoten 0,024 mg/ml
2. The value of IC
50
516,28
3. The value of SPF 33.25±0.98
Figure 1: Result of water content, total ash content
and acid soluble ash content in the extract of
MICH-PhD 2018 - 1st Muhammadiyah International Conference on Health and Pharmaceutical Development
156
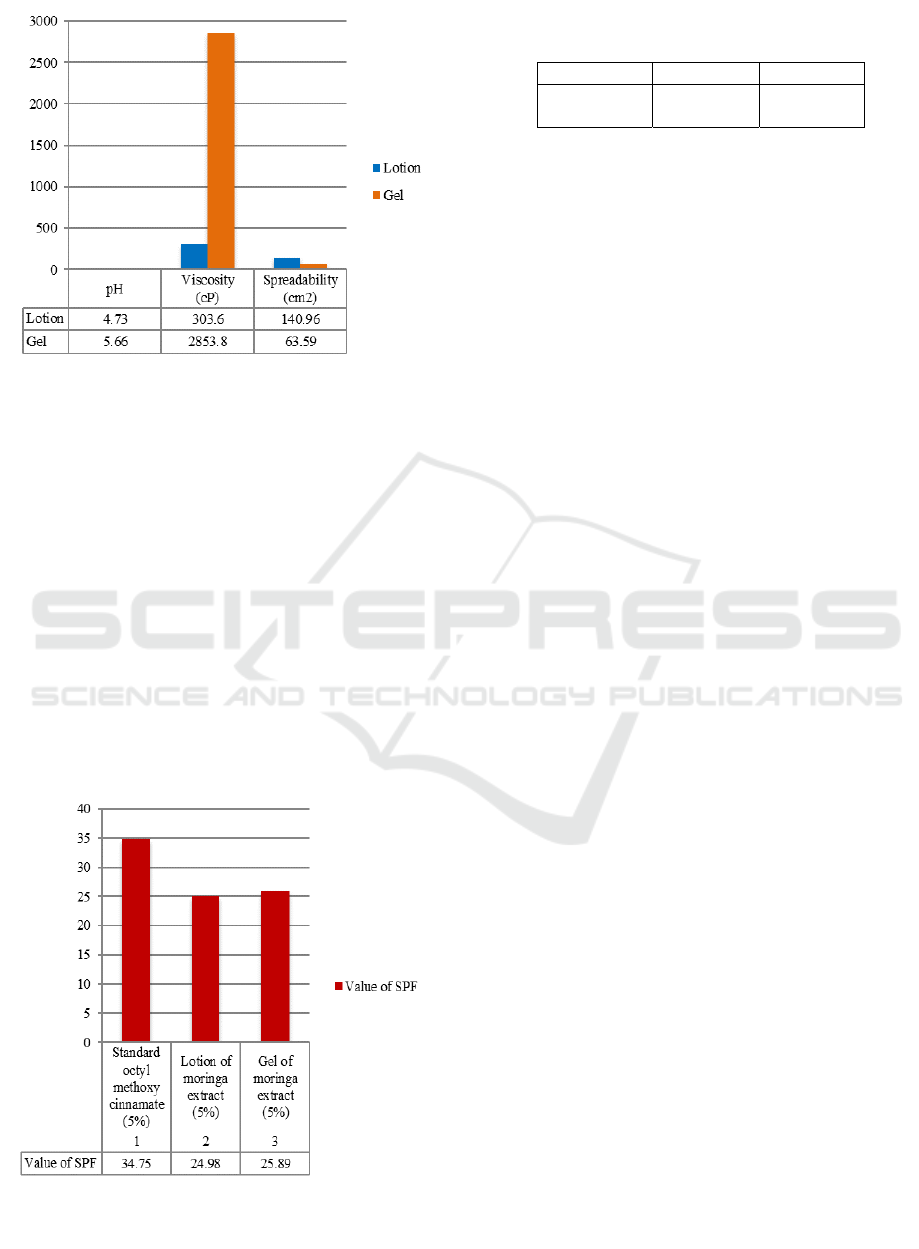
6.5 (Swastika et al., 2013). Otherwise, it will cause
irritation. The viscosity of the lotion (303.6 cP) was
lower than gel (2,853.8 cP) which resulted in a
thinner consistency. It also increased the lotion’s
spreadability and decreased its adhesivity (Vicky et
al., 2016; Latifah et al., 2016). The lotion and the
gel met the requirements of adhesivity, that is at
least 4 seconds, spreadability, that is between 5-7
cm
2
(Ulaen et al., 2012; Garg et al., 2002).
The potencies of lotion and gel of moringa leaf
extract as a sunscreen agent were evaluated based on
SPF values as presented in Figure 3. The results
show that, at concentration of 5%, both gel and
lotion have a strong activity as sunscreen although
the values were lower than the standard octyl
methoxycinnamate. The existing sunscreen activity
may be due to the presence of active ingredients
such as alkaloids, flavonoids and polyphenols that
are able to absorb the sunlight.
4 CONCLUSION
Moringa leaf extract contains alkaloids, flavonoids
and polyphenols and meets the requirements of
moisture content, ash content and acid soluble ash
content. The extract has a weak antioxidant activity
but a strong activity as a sunscreen. Similarly, when
it has been formulated in the preparation forms, of
lotion and the gel have a strong sunscreen activity
and meet the requirements of physical properties of
preparations.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
This study was supported by PUPS LPP grant in
2017.
REFERENCES
Astuti, I.Y., Hartanti, D.,Aminiati A., Majalah Obat
Tradisional, 15, 94-99 (2010).
Atif, A., Akhtar, N., Mumtaz, A.M., Khan.M.S.,
Iqbal,F.M and Zaidi.S., 2013, In Vivo Skin Irritation
Potential of a Cream Containing Moringa oleifera
Leaf Extract, American Journal of Pharmacy and
Pharmacology, 7(6) : 289-293.
Garg A, Aggarwal ID, Garg S, Sigla AK, 2002 An Update,
Pharmaceutical Technology 84.
Jayawardana B.C, Liyanage R, Lalantha N, Iddamalgoda
S,Weththasinghe P, 2015, Antioxidant and
antimicrobial activity of drumstick (Moringa oleifera)
leaves in herbal chicken sausages, Food Science and
Technology, 64: 1204-1208.
Krisnadi, A.D., 2013, e-book Kelor Super Nutrisi. Blora:
Kelorina.com.
Latifah F, Sugihartini N, Yuwono T 2016 Trad. Med.
Journal 21(1): 1.
Naibaho, D.H., Yamkan, V.Y., Weni, Wiyono, Pengaruh
Basis Salep Terhadap Formulasi Sediaan Salep
Ekstrak Daun Kemangi (Ocimum sanctum L.) pada
Table 5: The result of evaluation of physical
characteristic of gel and lotion.
Test Lotion Gel
Adhesivity
(
minute
)
>10 >10
Figure 2: The result of evaluation of physical
characteristic of gel and lotion.
Figure 3: The values of SPF of standard, lotion, and gel.
Formulation of Moringa oleifera Leaf Extract in Lotion and Gel as Sunscreen
157

Kulit Punggung Kelinci yang Dibuat Infeksi
Staphylococcus aureus. Jurnal Ilmiah Farmasi, 2(2)
(2013).
Putra, A.D., Setyawan, E.I., Media Farmasi, 11(2), 137
(2014).
Singh B.N., Singh B.R., Singh R.L., Prakash D., R.
Dhakarey, Upadhyay G., Singh H.B., 2009, Oxidative
DNA damage protective activity, antioxidant and anti-
quorum sensing potentials of Moringa oleifera, Food
and Chemical Technology, 47: 1109-1116.
Swastika, A., Mufrod, Purwanto., Trad Med Journal,
18(3),132-140 (2013)
Ulaen, Selfie PJ, Banne, Yos S, Ririn A. Pembuatan Salep
Anti Jerawat dari Ekstrak Rimpang Temulawak
(Curcuma xanthorrhiza Roxb.). JIF. 2012;3 (2): 45-9.
Vicky AK, Sugihartini N, Yuwono T 2016 Proc. Int. Conf.
of CONFAST 2016 Conference series: International
Conference on Industrial Biology (Yogyakarta) 1746
(1) (AIP Conference) p 10.1063
Vongsak, B., Sithisarn, P., Mangmool, S.,
Thongpraditchote, S., Wongkrajang, Y., Gritsanapan,
W. 2013.Maximizing total phenolics, total flavonoids
contents and antioxidant activity of Moringa oleifera
leaf extract by the appropriate extraction method.
Industrial Crops and Products, 44: 566-571.
MICH-PhD 2018 - 1st Muhammadiyah International Conference on Health and Pharmaceutical Development
158
