
Quality Control of Turmeric Rhizome (Curcuma domestica Val) as
Traditional Medicine from Wonogiri, Central Java
Fatimah Nisma, Ema Dewanti, Rini Prastiwi, Alexander, Wanda Puspita Sari and Wido Artanto
Faculty of Pharmacy and Science, Universitas Muhammadiyah Prof. DR. HAMKA
Islamic Centre Jl. Delima II/IV, Klender Jakarta Timur
Keywords: Curcuma domestica Val, Aflatoxin, Endosulfan, Malathion, HPLC, curcumin, pathogenic bacteria
Abstract: Turmeric is one of the plants that can be used as traditional medicine. To improve the quality of turmeric as
a traditional medicine, turmeric must be free from contamination of pesticide residues, aflatoxin, pathogen
bacteria, and curcumin content contained therein. The aim of this research was to investigate the
contamination of endosulfan and malathion pesticides, aflatoxin B1, Escherichia coli microbial
contamination, Salmonella sp., Staphylococcus aureus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa, as well as to know the
content of curcumin contained in turmeric rhizomes. The sample in this research was taken from Wonogiri
region of Central Java, Indonesia by random sampling. The methods used were HPLC for Aflatoxin B1
analysis and curcumin and Gas Chromatography for residual pesticide analysis of Endosulfan and
Malathion pesticides. Microbial testing included the establishment of Total Plate Count, AKK, MPN
Coliform, and analysis of Escherichia coli microbial contamination, Salmonella sp., Staphylococcus aureus
and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. The results showed that the samples were not contaminated by Aflatoxin B1
and Endosulfan pesticides, but contained a residual malathion with levels of 0.014 mg/kg. Microbial test
results showed that the turmeric samples from the Wonogiri market did not meet the quality requirements
due to contamination of Salmonella sp. and the chopped AKK exceeded the specified limits.
1 INTRODUCTION
Turmeric plant (Curcuma longa L.) is a plant of
biopharmaceutical, a plant that is useful in medicine
and consumed as an effort to overcome health
problems. Treatment using traditional medicine of
turmeric rhizome is one of the alternative therapy
which is done from generation to generation.
Turmeric rhizome contains the active compounds
such as curcumin, essential oils capable of inhibiting
the growth of gram-negative and gram-positive
bacteria. Curcumin in turmeric is an active
compound that gives the yellow colour to turmeric
rhizome, curcumin is produced naturally from
turmeric rhizome together with two other curcumin
analogue compounds that is demethoxycurcumin
and bisdemethoxycurcumin (BPOM, 2011).
Traditionally turmeric is used for the treatment of
itching, tingling, swollen gums, abdominal pain,
ulcers, jaundice, and gastrointestinal.
Turmeric rhizome (Curcuma longa L.) is used
extensively for food, beverage, medicine, cosmetics
and textiles. Standard quality of turmeric to be used
for raw materials of the drug should also be
considered. The quality standard of turmeric should
be highly regarded, the standard quality of turmeric
as a traditional medicine is free of pesticide
contamination, aflatoxin, heavy metals, microbial,
and curcumin levels (BPOM, 2016). Turmeric
contamination of pesticides occurs in turmeric plants
attacked by pests then farmers will spray turmeric
with pesticides. The pesticides which commonly
used are the type of malathion and endosulfan. Both
of these insecticides have a broad spectrum and non-
systemic. The content of pesticides allowed in
turmeric is 0.05 mg/kg for the type of
organophosphate. In addition to using pesticides to
control pests, farmers are also use manure pile for
turmeric growth. Manure pile is derived from animal
waste and can contaminate turmeric, because
bacteria or pathogenic microbes like to live on the
faeces (Paramitasari, 2011). Microbes and
pathogenic bacteria can be coliform, Escherichia
coli, Salmonella sp., Staphylococcus aureus and
Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
The wrong technique of post-harvest turmeric
processing, temperature conditions in the tropics,
Nisma, F., Dewanti, E., Prastiwi, R., Alexander, ., Sari, W. and Artanto, W.
Quality Control of Turmeric Rhizome (Curcuma domestica Val) as Traditional Medicine from Wonogiri, Central Java.
DOI: 10.5220/0008241101590168
In Proceedings of the 1st Muhammadiyah International Conference on Health and Pharmaceutical Development (MICH-PhD 2018), pages 159-168
ISBN: 978-989-758-349-0
Copyright
c
2021 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
159

and high humidity cause the turmeric rhizome to be
easily overgrown by Aspergillus flavus toxigenic
strain, A. parasiticus and A. nonius (Wrather and
Sweet, 2016). The product produced by this
toxigenic strain is aflatoxin. Aflatoxin is myotoxic,
as a secondary metabolic outcomes of these
Aspergillus strains, that can affect immunity, acute
necrosis, cirrhosis and liver carcinoma.
According to WHO, countries in Africa, Asia
and Latin America use herbal medicine as a
complement to the primary treatment they receive.
The traditional medicine failure for certain diseases
such as cancer and the extensive information about
herbal medicine around the world (Sukandar, 2006).
Traditional herbal medicine is a mean of traditional
medicine which is very important for the
distribution of public health. It is seen that these
herb has a huge potential and the prospect to be
developed to be an opportunity for herbalists to
develop their business.
Based on the Regulation of BPOM, traditional
medicine used as an internal medicine should be
aware of pesticide content, aflatoxin, heavy metals
and the presence of microbes such as Salmonella,
Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureus, and
Pseudomonas aeruginosa. These microbes should
not be contained in traditional medicine (BPOM RI,
2014). Escherichia coli bacteria is used as an
indicator of contamination, its presence in processed
products indicates contamination of human or
animal faeces through the water used.
Staphylococcus aureus bacteria is a normal flora
found in the skin and human lining membrane.
While Salmonella sp. is a bacteria that causes
infection. If swallowed into the body, it will cause
symptoms that called Salmonellosis.
Based on the preface above, it is necessary to
conduct a research about the quality of turmeric
rhizome originating from Wonogiri, Central Java,
because the region became the centre of traditional
herbal medicine industry including turmeric (Sakti,
2009). The method used to determine the pesticides
types, malathion and endosulfan, is by gas
chromatography for analysis of Aflatoxin B1 and
curcumin using HCV microbial testing conducted
include the determination of Total Plate Count,
AKK MPN Coliform as well as analysts.
2 METHODOLOGY
The instruments used in this research were: HPLC,
GC (Variant 450GC), column C18. The materials
used were: Turmeric, Peptone Dilution Fluid (PDF),
Plate Count Agar (PCA), Potato Dextrose Agar
(PDA), Lactose Broth (LB), Brilliant Green Lactose
Bile Agar 2% (BGLB 2%), Eosin Methylene Blue
Agar (EMBA), Mac-Conkey broth (MCB), Nutrient
Agar (NA), Tryptone Broth (TB), methyl red-Voges
proskauer (MR-VP), Simmon’s Citrate Agar,
Trypticase Soy Broth (TSB), Baird Parker Agar
(BPA), Brain-Heart Infusion Broth (BHIB),
Tetrathionate Brilliant Green Broth (TBGB),
Selenite Cystine Broth (SCB), Salmonella-Shigella
Agar (SSA), Triple Sugar Iron Agar (TSIA),
Cetrimide Agar. The turmeric (Curcuma longa L.)
rhizomes used were from Wonogiri, Central Java
and in the form of powder and dry sliced
2.1 Simplicia Characteristic Tests
The macroscopic examination was performed by
observing the morphology of turmeric rhizomes by
considering the colour, shape, size, and texture.
Microscopic examination of the rhizomes was by
putting the simplicia powder on the object glass that
is dripped with distilled water and covered with a
cover glass, and then being observed under a
microscope.
2.2 Pesticide Test
A total of 10 grams of turmeric rhizome powder was
added with 75 ml of acetone mixture: 1: 1 v/v
dichloromethane and left for one night for static
extraction process. The powder is filtered with
Whatman no. 40 filter paper, then concentrated with
a vacuum rotary evaporator until only 1 mL
remaining. The sample was then purified by passing
it to a chromatographic column containing
anhydrous sodium sulfate. Samples were then ready
to be injected into gas chromatography (Deptan,
2006).
2.3 Aflatoxin Test
As total of 10 grams of turmeric rhizome powder
was added with methanol and aqua bikes mixture
(80:20), and left for one night for static extraction
process. The powder was then filtrated with
Whatman no. 40 filter paper, then concentrated by
vacuum rotary evaporator, then rinsed with methanol
gradually, and collected in test tube up to 10 mL.
Samples are then ready to be injected into high
performance liquid chromatography (Deptan, 2006).
MICH-PhD 2018 - 1st Muhammadiyah International Conference on Health and Pharmaceutical Development
160

2.4 Identification and Determination of
Curcumin Levels
2.4.1 Determination of Curcumin Levels
with HPLC
A total of 100.0 mg of turmeric extract samples was
added into a 100.0 ml measuring flask of 15.0 ml of
0.01 N H
2
SO
4
, then in the ultrasonic and added 96%
ethanol until the limit mark. The solution was
filtered with 0.2 μm membrane into the VCC vial
and injected as much of 50 μl for 12 minutes.
Identification of active substance were done by
comparing between sample retention time and
standard curcumin retention time.
2.4.2 Qualitative Identification of Curcumin
with Thin Layer Chromatography
Method
Qualitative analysis of the curcumin was performed
using thin layer chromatography method using
stationary phase silica gel silicone 60 F254 and the
mobile phase used was chloroform: methanol (95: 5)
v / v., then observed on 366 nm UV rays
.
2.5 Microbial Contamination on
Turmeric Sample Test
2.5.1 Homogenization and Sample Dilution
A total of 10 grams of turmeric samples were
dissolved in 90 ml of Peptone Dilution Fluid (PDF)
media, resulting from 10
-1
dilution. The resultant
dilution was piped as much as 1 ml and inserted into
the first tube and dilution of the PDF, resulting 10
-2
10
-3
, 10
-4
, 10
-5
, and 10
-6
(Radji, 2011).
2.5.2 Total Plate Count Determination
Each result of turmeric sample was piped as much
as 1 ml, then inserted into a Petri dish containing
15-20 ml of Plate Count Agar (PCA) medium. After
the media froze, the Petri dish is incubated at 37°C
for 24-48 hours with the position reversed. (Radji,
2011).
2.6 Total Number of Mold and Yeast
Examination
The petri dish which contained 15-20 Potato
Dextrose Agar (PDA) medium was prepared in
advance. As much as 0.5 ml diluted sample of
turmeric was put into the surface of the PDA
medium, then it was incubated at 20-25°C for five
days in a reversed position. The colonies growing on
the media were
observed and counted on the fifth
day (Radji, 2011).
2.7 Coliform Examination
Coliform examination was performed using Most
Probable Number method, 5 tubes system. This
method includes:
2.7.1 Presumptive Test
The samples were taken into tubes containing
Lactose Broth Media (LB). Next, the samples were
inserted into second 5 tubes containing 5 ml of LB
medium of single concentration. The area of
inverted Durham tube. 0.1 ml of the sample was
inserted into a row containing 5 ml of single
nutritional LB medium and inverted Durham tube
(Radji 2011).
Then the tubes were incubated at 37 °C for 24 -
48 hours. The gas-filled tube proceeded with the
assertion test. This estimate test was to detect the
presence or absence of bacteria capable of
fermenting lactose that indicates the presence of
colibacteria (Radji, 2011).
2.7.2 Confirmative Test
A total of 1 culture from the number of tubes which
were forming the gas in the LB media estimator test
was transferred into a tube containing 10 ml of
Brilliant Green Lactose Bile Broth 2% (BGLB 2%),
with an inverted Durham tube in it and 2 tubes of the
same for sample and control (Radji, 2011).
All tubes were incubated at 37 °C for 24 - 48
hours, until the gas was formed in tubes. A tube
with gas was tested with Eosin Methylene Blue Agar
medium. Using an inoculation needle, the gas-
formed tube was inoculated on the EMBA plate by
scraping it and then incubated at 37 °C for 24 hours
(Radji, 2011).
2.7.3 Complete Test
The gas-containing tube in the assertion test was
taken using Ose, then it was scraped onto EMBA
media. The tubes were incubated at 37 °C for 24 - 48
hours (Radji, 2011).
2.7.4 Gram Staining
A small amount of microbial growth was taken
using the Ose tip, then spread onto droplet of water
Quality Control of Turmeric Rhizome (Curcuma domestica Val) as Traditional Medicine from Wonogiri, Central Java
161

over the object glass and dried by fixating on a small
flame. The main paint solution (Crystalline violet)
then washed with running water and dried. Then the
preparation was stained with Lugol solution (I
2
+ KI
solution) and allowed for 45-60 seconds. The color
disappears by dipping the preparations into 96%
alcohol while being shaken for 30 seconds or until
no more dyestuff flows from the preparation. Then
the safranine was dropped into the preparation and
be left for 1 minute, and rinse with running water
and then dry. The object was then examined under
the microscope (Radji, 2011).
2.8 Microbial Pathogen Contamination
Analysis
2.8.1 Sample Homogenization and Dilution
• Contamination Analysis of Escherichia coli
The total of 10
-1
dilution was taken and inoculated
into three tubes containing the Mac Conkey broth
medium (MCB) and there was a Durham tube in it.
While contamination analysis of Staphylococcus
aureus, homogenized and diluted with a PDF
solution until 10
-1
dilution. Then the sample was
taken and added into a test tube containing 18 ml
Trypticase Soy Broth (TSB).
• Contamination Analysis of Salmonella thypi
This analysis used Lactose Broth (LB) solution, by
transferring 25 ml samples aseptically into a bottle
containing 225 mL of LB media sample.
• Contamination Analysis of Pseudomonas
aeruginosa
This analysis used enrichment medium of 100 ml of
Tetrathionate Brilliant Green Broth (TBGB) medium
and 100 ml of Selenite Cystine Broth (SCB)
medium, each then incubated at 37 °C for 24 hours
(Radji, 2011).
2.8.2 Growing into Selective Use
The tube which was positive of E. coli, the gas on
the Durham, was taken into a selective solid medium
Eosin Methylene Blue Agar (EMBA). The next step
was confirmatory testing, IMVIC test, by
inoculating bacterial culture on NA media into
indole, methyl red, Voges Proskauer, and citrate
(IMVIC).
Staphylococcus aureus was inoculated into
Brain-Heart Infusion Broth (BHIB) media. As much
as 1 ml of each culture in BHIB was piped and
transferred into a sterile test tube. Furthermore, 0.3
ml plasma was added in each tube. Plasma clotting
showed positive Staphylococcus aureus coagulase.
Salmonella sp. bacteria, was identified by
inoculating 1 tangle culture in a Petri dish containing
Salmonella-Shigella Agar (SSA) medium. The
alleged Salmonella sp. colony was characterized by
a colorless colony to pink, clear to opaque (Radji,
2011). The next phase was confirmation test. In this
test, 2-5 specific colonies of SSA selective medium
were selected and inoculated on NA media. Then the
colonies on NA medium were inoculated with
puncture and scratching methods on the Triple Sugar
Iron (TSIA) medium. If on the slant, Salmonella
ferment lactose or sucrose then the color of the
media turns yellow and if Salmonella does not
ferment lactose or sucrose then the color of the
media remains red or unchanged.
While Pseudomonas aeruginosa used the TSB
cultures and inoculated on the surface of Cetrimide
Agar (Cet.A) medium. Observed the growth of
greenish colony (Radji, 2011). Further test on
suspected colonies of Pseudomonas aeruginosa, a
catalase test of the NA culture was tilted by taking
the colony using an aseptic Ose needle. Placed on a
glass object that was previously cleaned with 70%
flattened alcohol, then added a drop of 3% hydrogen
peroxide solution. Positive results are characterized
by gas formation (Radji, 2011).
3 RESULT AND DISCUSSION
3.1 Materials
The materials used were rhizomes and turmeric
powder (Curcuma domestica Val.) which were
obtained from Wonogiri market region of Central
Java, because Wonogiri is a central area of
traditional medicine (herbal medicine), and in that
area there are many small or medium industries that
produce traditional medicine (herbal medicine)
where one of the raw materials is turmeric.
3.2 Sample Identification
3.2.1 The Macroscopic Test
The Macroscopic examination aimed to observe the
colour, shape, size and texture of turmeric rhizomes.
As seen in table 1.
According to Pharmacopoeia Herbal Indonesia
(2008), fresh turmeric colourized by yellow-orange,
reddish orange-yellow to brownish orange-yellow
and has a round shape up to rounded, sometimes
branching, a width of 0.5 cm to 3 cm, length 2 cm to
6 cm. Based on the results of macroscopic tests, it
MICH-PhD 2018 - 1st Muhammadiyah International Conference on Health and Pharmaceutical Development
162

showed that the inside was yellow in colour, while
the exterior was brownish and elliptical with a width
of ± 2.5 cm, and length ± 4.5 cm.
3.2.2 Microscopic Test
This microscopic test was performed to see the
anatomy of turmeric tissue, by putting the simplicia
powder on the object glass that has been dripped
with distilled water and covered with a cover glass,
then viewed under a microscope. Microscopic test
results from turmeric powder showed that it has
epidermal tissue, stomata cells, bearing files and hair
cover. It has one-layer epidermis, polygonal-shaped
flat, cell wall pouring. Covering hair, conical,
straight, or slightly crooked; length of 20 μm to 890
μm, thick wall. Perindrem consisted of 6 to 9 layers
of cells in the shape of a long facet, the wall
penetrates. Single grain starch is oval end having
bulge or round to almost triangle with one side
rounded (Farmakope Herbal Indonesia, 2008). The
anatomy of tissue in turmeric has a characteristic
that is the presence of parenkim, cell clumps and
hair cover. The observable tissue anatomy included
wood vessels, parenchyma and starch grains. It can
be seen in the Figure 1
.
The pictures above shows that the microscopic
test using a microscope with 10x18 magnification,
produced the anatomy of turmeric tissue namely
xylem, covering hair, and starch grain periderm.
This result was in accordance with the requirements
of Pharmacopoeia Herbal Indonesia Issue 1 (2008).
3.2.3 Chemical Identification Test
The identification of the turmeric sample was carried
out using chemical reactions. Turmeric that had been
dubbed and added with Materia Medika Indonesia
volumes VI 1977. The resulting chemical
identification test of turmeric rhizomes can be seen
in Table 2.
The table above shows that the sample used is
true turmeric powder because the results obtained
are in accordance with the chemical identification
test according to Materia Medika Indonesia (1977).
3.2.4 Loss on Drying Test
Loss on drying aimed to provide a maximum (range)
of the number of compounds lost in the drying
process (MOH RI, 1995). Loss in drying test results
is seen on Table 3.
The result above showed that the sample meets
the requirements because according to
Pharmacopoeia Herbal Indonesia Edition I (2008),
the limit of loss on drying is less than 12%.
Table 1: Macroscopic test result of turmeric.
Macrosco
p
ic Turmeric
Colour yellow on the inside, brown
on the outside
Sha
p
e oval sli
g
hlt
y
roun
d
Table 2: Results of chemical turmeric powder
identification test.
Turmeric
p
owde
r
Reagent Result
2 m
g
5 dro
p
of sulfuric acid P Blood re
d
2 m
g
5 dro
p
of chloric acid P Brown
2 mg 5 drop of natrium dioxide
solution 5% b/v
Red-
orange
2 mg 5 drop of ammonia (25%)
P
Red-
orange
2 mg 5 drop of iron (III)
chloride solution P 5% b/v
Brown
2 mg 5 drop of lead (II) acetate
solution P 5% b/v
Pink
Table 3: Loss on drying test result.
Handling Result
Loss on Drying 5,37%
Figure 1: The microscopic test result of turmeric: a)
xylem with thickening of stairs and parenchyma with
secretion cells, b) Starch grain periderm, c) Covering
hair with irregular lumps colourized by yellow to
brown.
(a)
(b)
(c)
Quality Control of Turmeric Rhizome (Curcuma domestica Val) as Traditional Medicine from Wonogiri, Central Java
163
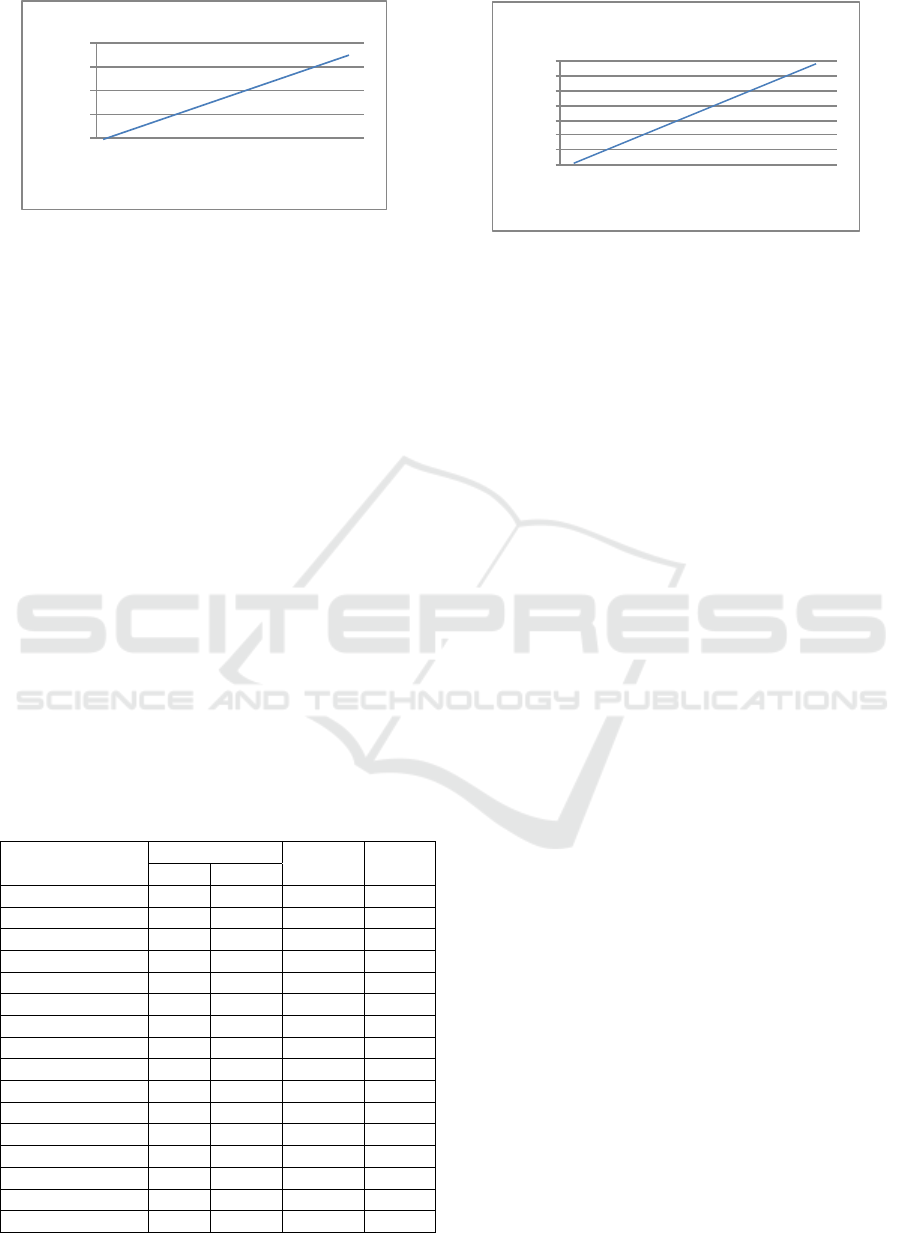
3.3 Pesticide Test
3.3.1 Standard Normative Endosulfan
Curve
Preparation of standard solution of Endosulfan by
making five concentrations in acetone solution.
Standard normative uptake measurements were
performed using gas chromatography with an
electron detector (ECD), an oven temperature of
150ºC. The raw solution was injected into the ECD
for 20 minutes to get the peak. The result of the
linear line equation of the curve is y = 64935x +
19368 with the correlation coefficient (r) = 0.991.
The value of (r) = 0.991 on the endosulfan
calibration curve (figure 2) showed that the line
formed between the endosulfan concentration with
the area are in accordance with line linearity
requirements, because the linearity test is done by
making the calibration curve, which can produce the
equation of the regression line with the correlation
coefficient (r) ≥ 0.9990.
Table 4: Results of pesticide test of endosulfan and
malathion types.
Tested subtance
Content
(pp
m
)
Average
(ppm)
SD
1 2
Organochorine 0 0 0 0
Lindan
(
ɤ-BHC
)
0 0 0 0
Aldrin 0 0 0 0
He
p
taklo
r
0 0 0 0
Dieldrin 0 0 0 0
DDT 0 0 0 0
Endrin 0 0 0 0
Endosulfan* 0 0 0 0
Or
g
ano
p
hos
p
hate
Diazinon 0 0 0 0
Fenitrotion 0 0 0 0
Metidation 0 0 0 0
Malathion * 0,028 0,0015 0,014 0,0187
Klorfiri
p
os 0 0 0 0
Parathion 0,041 0,090 0,065 0,035
Profenopos 0 0 0 0
* Tested Substance
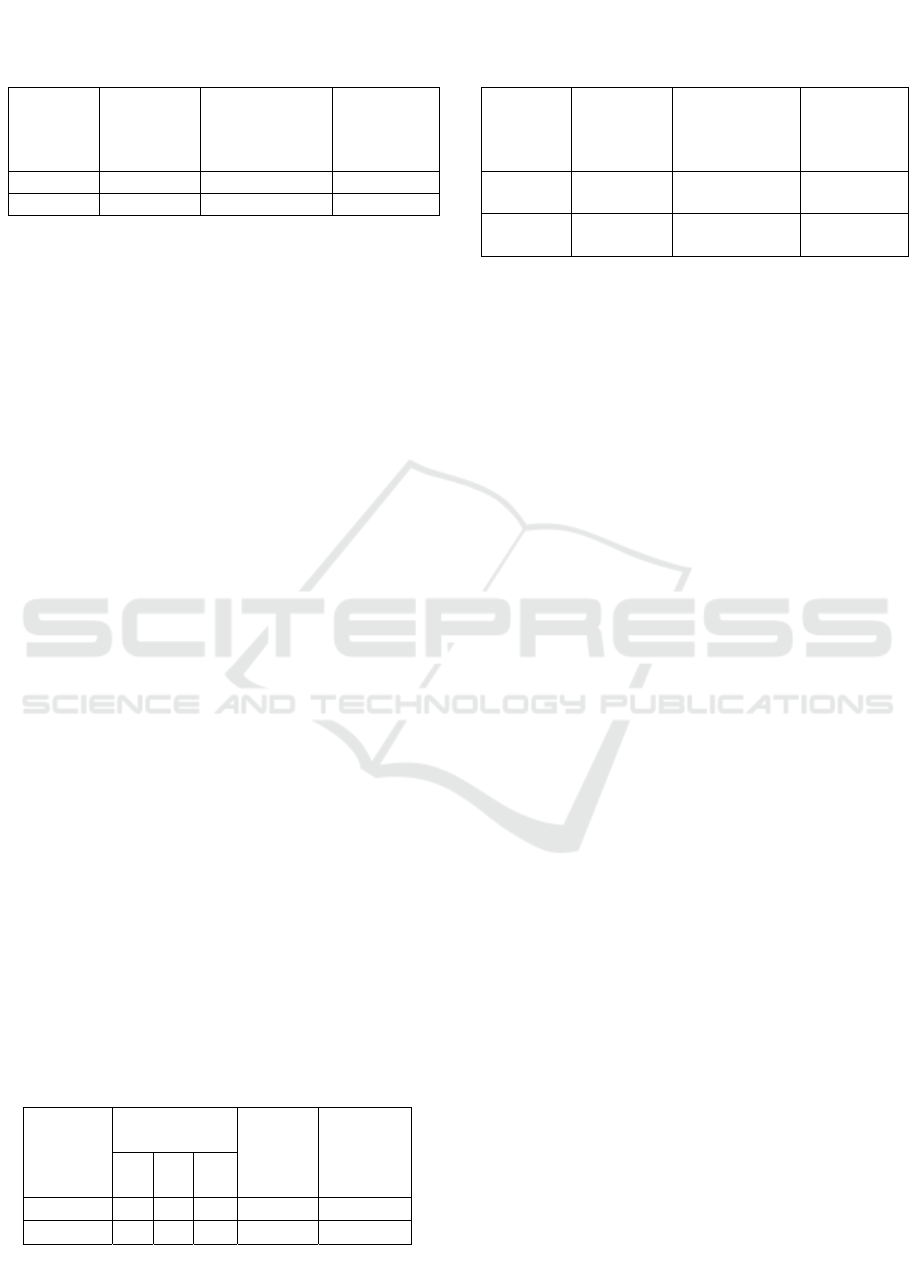
3.3.2 Standard Normative Malathion Curve
Standard normative uptake measurements were
performed using gas chromatography with an
electron detecting detector (ECD), an oven
temperature of 150 ºC. The standard solution was
injected into the apparatus for 20 min to get the peak
in appendix 4. The result of the linear line equation
of the curve is y = 12666x + 4449 with the
correlation coefficient (r) = 0.992 (figure 3).
3.3.3 Pesticide Content on Sample
The sample of turmeric was measured using gas
chromatography. In this gas chromatography, the
system was arranged with 1mL/minute flow
velocity, using gas phase N
2
with 80 psi flow
pressure, stationary phase VFRV 1701 Pesticide
capillary with diameter 0.25 μm, 30 m long, ECD
detector (Electron Capture Detector) and at a
temperature of 300 ° C. The measurement results is
seen on Table 4.
The results of pesticide residue analysis on
turmeric rhizome showed that the sample was not
detected containing pesticide residue organochlorine
especially for endosulfan type, because the use of
pesticides for the group of organochlorines has been
banned by the Minister of Agriculture with Law No.
434.1/kpts/TP.270/7/2001 due to its persistent in the
environment (Isnawati, 2005). The result of the test
was the contamination of organophosphate pesticide
residue of malathion type with concentration of
0.014 ppm. Judging from the resultant content of the
sample, it still fulfilled the requirement because
based on the quality requirement of turmeric
simplistic of the Food and Drug Control Agency
concerning the Maximum Limit of Pesticide Residue
by 0,05ppm (BPOM, 2006). The test results also
detected other types of pesticides group, other
organophosphates Parathion with levels of 0.065
ppm. This is because the organophosphates in the
0
10
20
30
40
0 0.2 0.4 0.6
Total area counts
Endosulfan Concentration (ppm)
Figure 2: Results of endosulfan calibration.
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
0 0.2 0.4 0.6
Total area counts
Malathion Concentration (ppm)
Figure 3: Results of malathion calibration curve.
MICH-PhD 2018 - 1st Muhammadiyah International Conference on Health and Pharmaceutical Development
164

turmeric rhizome can be induced by the use of
pesticides directly and indirectly (due to
contamination of surrounding pesticides). Pesticides
move from agricultural land to rivers and lakes
carried by rain or evaporation left behind or
dissolved in the flow of the surface, located on the
soil layer and dissolved along with the groundwater
flow. (Djojosumarto, 2008).
3.4 Aflatoxin Contamination Analysis
The result of analysis of aflatoxin contamination on
turmeric rhizome by HPLC method. The prepared
sample was then measured using HPLC with a
wavelength of 365 nm.
Analysis of turmeric rhizome aimed to
identify the absence of aflatoxin B1 in the sample.
Aflatoxin B1 analysis on samples showed negative
or undetectable results, this may be due to the
aflatoxin content of the turmeric sample was small,
so the test did not show results, because handing in
pre and post-harvest was good, so that the turmeric
was not contaminated by aflatoxin.
3.5 Curcumin Analysis
3.5.1 Qualitative and Quantitative
Curcuminoid Analysis
The qualitative test of curcumin compound was done
by Thin Layer Chromatography (TLC) method using
chloroform: methanol (95: 5) v/v and the stationary
phase used was silica gel 60 F254 (Pharmacopoeia
Herbal, 2008). The result of curcuminoid
identification by Thin Layer Chromatography can be
seen in Figure 4.
The curcumin identification performed was
observed with UV cabinet on 366 nm UV rays, the
detection did not use spray reagent because
curcuminoid was visible under UV light at 366 nm
wavelength. The curcuminoid identification result
shows that there are 3 rickshaws in which curcumin
compound (X) is a constituent of turmeric, while
desmethoxycurcumin (Y) and
bidesmethoxycurcumin (Z) are the identifying
compounds of curcuminoid. The result of
identification of the spots obtained looks like
standard spotted results with Rf value of 0.68 and
the Rf value of the four samples is also equal to the
standard. The spots are curcumin compounds
because they have the same color and Rf values in
each sample and the comparators used.
3.5.2 Curcumin Content Test with HPLC
After testing curcumin with TLC, High Performance
Liquid Chromatography was performed. 96%
ethanol was used as a solvent in the determination of
curcumin content by using HPLC. Curcumin testing
method with gradient technique using 0.1%
Trifluoroacetic acid (TFA) motion phase and
Acetonitrile at 425 nm wavelength for 12 minutes
with a flow rate of 1.0 ml/min. Tests using a
gradient system aimed to separate samples
containing components with a very diverse polarity
that can provide good results. Determination of the
level of curcumin with this gradient system obtained
3 chromatograms at the standard and the first
chromatogram sample is curcumin ranging from
retention time 8.6 minutes, followed by
chromatogram desmethoxycurcumin at retention
time 9,2 minutes and bidesmethoxycurcumin at
retention time 9.7 minutes
.
Result of curcumin with HPLC test found that
the turmeric plants a good place to grow turmeric
growth. Land in the Wonogiri area has alluvial soil
type where this type of soil is good for turmeric
growth (Raharjo and Rostiana, 2005). Alluvial soil is
a soil formed from fine deposits. This type of soil is
widely used in agriculture due to its nature which
has a high nutrient content. Turmeric plants can
grow well in rainfall ranging from 2000 to 4000
ml/year and has rainfall ranging from 2,790 mm.
Figure 4: Result of curcumin content identification with
TLC at wavelength 366 nm. (X): Curcumin; (Y):
Demetoxicurcumin; (Z): Bisdemetoxicurcumin; (STD):
Standard of Curcumin.
Quality Control of Turmeric Rhizome (Curcuma domestica Val) as Traditional Medicine from Wonogiri, Central Java
165
3.6 Bacteria Test
3.6.1 Total Plate Count Test Result
The powder and rizhomes turmeric samples were
grown on Seed Plate Count Agar (PCA) hatching
medium calculated bacterial growth. Bacteria that
can be calculated ranges from 30-300 colonies, so
the results obtained as in Table 5.
The total number or amount of aerobic bacteria
from the turmeric sample powder and chopped is
between 1.17 X 10
4
to 3.45 X 10
6
bacteria per ml of
sample. According to the provisions stipulated by
the Head of the Food and Drug Supervisory Agency
No. 12 of 2014, on the requirements of traditional
medicine that the total number of chopped plates and
powder ≤ 106 then the turmeric sample from the
eligible Wonogiri Market is set.
3.6.2 Total Number of Mold and Yeast
Result
In this test, samples of turmeric powder and chopped
were grown on Potato Dextrose Agar media (PDA)
and calculated the growth of mold and yeast.
Colonies that can be calculated ranging from 30-300
colonies, resulting in Table 6.
The fungi were a group of eukaryotic
microorganisms that vary widely, so the ability to
take advantage of nutrients from the environment
and metabolic abilities of fungi also vary widely.
The total amount of mould and yeast from the
turmeric sample obtained was 8.85 X 10
3
to 4.6 X
10
4
mould and yeast per ml sample. The total
amount of mould and yeast in the turmeric powder
had fulfilled the requirements set by the Head of the
Food and Drug Administration Law No. 12 of 2014
of traditional medicine that is 10
4
, but the chopped
sample did not meet it, maybe the case in tttthe
process of storing the simplicia that have not met the
criteria.
3.6.3 Most Probable Number (MPN) of
Coliform Examination Result
Coliform examination results of turmeric (powder
and chopped) showed a positive result of the
presence of Coliform bacteria, thus the examination
was followed by IMVIC test. The complete
Coliform test consists of 3 stages: test of predictor,
test of confirmation and complete test. In the LB
(Lactose Broth) probe test, a positive result is seen
by bubbles forming on the Durham tube. The
formation of gas in Durham tubes as a result of
lactose fermentation does not necessarily indicate
the number of Coliform bacteria, because lactose can
also be fermented by other microbes such as lactic
acid bacteria. Therefore, the positive probable test
should be continued with the assertion test, the
BGLB (Brilliant Green Lactose Bile Broth) test
containing bile salt is a component that can inhibit
bacterial growth besides Coliform, and give
Coliform bacteria chance to grow well.
The result of the research of turmeric samples
in the form of powder and chopped on medium
(BGLB) showed negative result, with MPN value
9/100 small on chopped and <2/100 ml on powder
(table 7). Furthermore, the tube showed a positive in
the assertion test, followed by a test by inoculating a
dispute of the assay test results into a Petri dish
containing the Eosin Methylene Blue Agar (EMBA)
medium and incubated at 37 °C for 24-48 hour
.
Table 5: The result of tests of total plate count on
powder and chopped.
Turmeric Number of
colonies
(Colony/g)
Maximum
Limit of
Microbial
Contamination
Information
Powder 1,17 X 10
4
≤ 10
6
colony/g Qualifie
d
Choppe
d
7 X 10
4
≤ 10
6
colony/g Qualifie
d
Table 6: Result of determination of total number of
mold and yeast turmeric powder and chopped.
Turmeric
Sample
Number of
Colonies
(Colony/g)
Maximum
Limit of
Microbial
Contamination
Information
Powder 0,885 X
10
4
≤ 10
4
colony/g Qualified
Chopped 1,13 X 10
4
≤ 10
4
colony/g Not
qualifie
d
Table 7: Results of the Coliform MPN examination
turmeric powder and chopped.
Turmeric
Sample
Lactose Broth
Number
of
Postive
Tubes
MPN/100
ml
10
ml
1
ml
0,1
ml
Chopped 2 3 0 2-3-0 9
Powder 0 0 0 0-0-0 <2
MICH-PhD 2018 - 1st Muhammadiyah International Conference on Health and Pharmaceutical Development
166
3.6.4 Pathogen Microbial Contamination
Analysis Result
The presence of pathogenic bacteria in food should
be avoided so that product users are protected from
adverse effects caused by consumed products. One
cause of disease transmission and the cause of
poisoning is contamination of microbes in a food.
Microbes in terms of bacteria, such as Escherichia
coli, Staphylococcus aureus, Salmonella, and
Pseudomonas aeruginosa can contaminate food
consumed by humans. The examination results (
table
8) of pathogenic microbial contamination was
obtained as follows:
Escherichia coli
The formation of gas in Durham tubes as a result of
lactose fermentation does not necessarily indicate
the number of Coliform bacteria, because lactose can
also be fermented by other microbes such as lactic
acid bacteria. The results of the E. coli test showed a
negative on the chopped sample and the positive on
the powder sample in MCB medium. The positive of
the powder samples were scratched onto the EMBA
media. The results of the casting on the EMBA
media showed negative or no gloss, so the negative
E. coli test results on both the turmeric sample were
concluded.
Staphylococcus aureus
Staphylococcus aureus is a normal flora found in
human skin. It is a type of pathogenic bacteria that
can cause infection and abnormalities in the skin
(Radji, 2011). Ecologically, Staphylococcus aureus
is closely related to humans especially in the skin,
nose and throat. Thus, food and drink are mostly
polluted through management by humans. Overall,
these organisms are not strongly competitive with
others and consequently these bacteria have no
important role in uncooked food ingredients.
However, in cooked or salted food, where
existing organisms have been damaged by warming
or growth inhibited by salt concentrations,
Staphylococcus aureus cells may continue to
progress to a dangerous level. Poisoning due to
Staphylococcus aureus contaminated food is mostly
related to food products that have been cooked
especially those managed by humans. The symptoms
of Staphylococcus aureus contaminated food are
intoxicated. The growth of these organisms in food
produces toxic enterotoxins, which when ingested
may result in abrupt on slaught, stomach cramps and
severe vomiting. Diarrhea may also occur (Buckle et
al., 2007).
The examination result of pathogenic microbial
Staphylococcus aureus planted into BPA media
(Baird Parker Agar) showed negative result. This
medium contained lithium chloride and tellurite to
grow the microbes in the sample, as well as pyruvate
and glycine that support the growth of
Staphylococcus aureus bacteria. If the samples
contain Staphylococcus aureus bacteria, colony will
grow glossy black colour, as the results of the
analysis did not show a shiny black result, turmerics
from Wonogiri Market were negative from
Staphylococcus aureus microbial pathogens.
Salmonella sp.
Salmonella test is used to establish the presence of
pathogenic microbial Salmonella sp. These
microbial pathogens are Gram-negative microbes
that are stick-shaped and cause typhoid, paralysis
and foodborne diseases. Salmonella sp. consists of
2500 serotypes which are all pathogenic in both
humans and animals. TSIA is rich in lactose,
sucrose, dextrose, ferrous sulfate. The medium is
used to sort out microorganisms that have the ability
to degrade sulfur and ferment carbohydrates. With
the fermentation of phenol red, if microorganisms
can not ferment the three types of sugar (sucrose,
lactose, glucose) present in the media then the media
will turn yellow. If microorganisms can only
ferment dextrose. The occurrence of dextrose
fermentation by Salmonella will decrease the pH to
acid condition. This condition causes phenol red (red
medium) changes to yellow. That is what happened
on examination of bacterial pathogen powder and
turmeric samples from Wonogiri Market.
Table 8: Result of pathogen microbes.
Turmeric Sample
Bacteria Identification Test
Escherichia coli Staphylococcus
aureus
Salmonella Pseudomonas
aeruginosa
Chopped
Negative Negative Positive Negative
Powder
Negative Negative Positive Negative
Quality Control of Turmeric Rhizome (Curcuma domestica Val) as Traditional Medicine from Wonogiri, Central Java
167

Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Medium Cet. A (Cetrimide Agar) is commonly used
for the isolation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Cet. A
is a quarternary ammonium compound that can
inhibit the growth of other bacteria, but does not
occur in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. The
examination result of chrysanthemum and turmeric
powder from Wonogiri are negatively contain
Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
4 CONCLUSION AND
SUGGESTION
4.1 Conclusion
Based on the research on turmeric rhizome from
Wonogiri area, it can be concluded that the samples
did not contain endosulfan type organochlorinated
pesticide residues, but it contained pesticidal residue
from organophosphate type that is malathion, with
0,014 ppm concentration level. The curcumin level
met the requirements of Pharmacopoeia Herbs of ≤
6.6% and the curcumin content was 7,8482%.
Contamination of Salmonella sp. bacteria was found,
and thus it did not meet the requirements of the
Regulation of the Head of the Food and Drug
Supervisory Agency No. 12 of 2014 about
traditional medicine
.
4.2 Suggestion
We recommend to test other quality standards such
as the heavy metal test on turmeric samples from
Wonogiri.
REFERENCES
ATSDR. 2003. Toxicological profile for malathion.
Department of Public Health and Human Services,
Public Health Service.[online].
http://www.atsdr.cdc.gov [08 December 2012].
Chattopadhyay I., Biswas K., Bandyopadhyay U. And
Banerjee R.K. 2004. Turmeric and curcumin:
Biological actions and medicinal applications. Current
Science. 87: 44-53
Dapertemen Kesehatan RI. 2008. Farmakope Herbal
Indonesia. Edisi I. Dapertemen Kesehatan Republik
Indonesia. Jakarta
Dapertemen Kesehatan RI. 1977. Materia Medika
Indonesia. Jilid VI. Dapertemen Kesehatan Republik
Indonesia. Jakarta. Pp. 326, 333-337.
Djojosumarto, P., 2008. Pestisida dan Aplikasinya, PT.
Agromedia Pustaka, Jakarta. Pp. 1, 6, 7
Dwidjoseputro. 1989. Dasar-dasar Mikrobiologi. Jakarta:
Jambatan
Hendayana S. 2006. Kimia Pemisahan (Metode
Kromatografi dan Elektroforeeesis Modern).
Isnawati A., Doraham Mutiatikum. 2005. Penetapan Kadar
Residu Organoklorin dan Toksiran Residu Kesehatan
Masyarakat terhadap Residu pestisida Organoklorin
pada 10 Komiditi pangan. Artikel. Media Litbang
Kesehatan Volume XV no 2, Jakarta.
Putra EDL. Kromatografi Cair Kinerja Tinggi Dalam
Bidang Farmasi.
http://repository.usu.ac.id/bitstream/123456789/3616/
1/farmasi effendy2.pdf. [3 February 2015]
Radji M. 2011. Buku Ajar Mikrobiologi: Panduan
Mahasiswa Farmasi dan Kedokteran. Buku
Kedokteran EGC, Jakarta. Pp. 4, 21, 107, 113, 201.
Rahayu, E. S., Sri Raharjo dan Rahmianna A. A. 2003.
Cemaran aflatoksin pada produksi jagung di daerah
Jawa Timur. Agritech 23:174-183.
Rahayu SW., Hartati D.,Mulyono A.. Analisa Residu
Pestisida Organoklorin pada rimpang Kunyit
(Curcuma domestica) secara M spektrofotometri Ultra
Violet Visibel.
Riana M., 2007. Toksikologi pestisida dan penanganan
akibat keracunan pestisida. Jurnal Media Litbang
Kesehatan Volume XVII Nomor 3.Hlm 10-11.
Rohman A., 2009. Kromatografi untuk Analisa Obat.
Graha Ilmu.Yogyakarta. Pp. 1, 111
Rukmana, R. 1999. Kunyit. Kanisius Cetakan Pertama.
Yogyakarta
Runia, Y.A., 2008. Faktor-faktor yang berhubungan
dengan keracunan pestisida Organofosfat, Karbamat
dan kejadian anemia pada petani hortikultura di Desa
Tejosari Kecamatan Ngablak Kabupaten Magelang.
Skripsi Sarjana. Fakultas Kesehatan Masyarakat.
Universitas Diponegoro, Semarang.
http://eprints.undip.ac.id/17532/1/YODENCA_ASSTI
_RUNIA.pdf. [25 April 2015]
Said, A. 2007. Khasiat & Manfaat Kunyit
. PT. Sinar
Wadja Lestari. Jakarta
Zulaikhah ST. 2005. Analisis Faktor-Faktor Yang
Berhubungan Dengan Pencemaran Mikroba Pada
Jamu Gendong di Kota Semarang. Tesis. Magister
Kesehatan Lingkungan Program Pasca Sarjana
Universitas Diponegoro. Semarang.
MICH-PhD 2018 - 1st Muhammadiyah International Conference on Health and Pharmaceutical Development
168
