
Active, Passive, and Active-Assistive Range of Motion (ROM)
Exercise to Improve Muscle Strength in Post Stroke Clients: A
Systematic Review
Indrawati
1
, I Ketut Sudiana
2
and Muhammad Sajidin
3
1
Faculty of Nursing, Universitas Airlangga, Mulyorejo, Surabaya, Indonesia
2
Faculty of Medicine, Universitas Airlangga, Dharmahusada, Surabaya, Indonesia
3
STIKES Bina Sehat PPNI, Mojokerto, Indonesia
Keywords: Post Stroke, Muscle Strength, Passive ROM, Active ROM, Active-Assistive ROM.
Abstract: Stroke can cause various levels of disorders, such as decreased muscle tone, loss of sensibility in some parts
of the body, decreased ability to move sick limbs and incapacity in certain activities so that exercise therapy
is one way to accelerate the recovery of patients from injuries and diseases in governance using active or
passive movements. This systematic review focuses on giving Range of Motion exercise therapy to muscle
strength, with journal search through Science Direct database, Ebscho, Pro Quest, E-Resources, Sage
Journal and Google Scholar. The year limit used is 10 years (2007-2017). In general, all of the review 14
journals provide results that the Range of Motion exercise provides benefits as an intervention to increase
muscle strength in post-stroke clients because exercise therapy is one way to speed the recovery of patients
from paralysis. The goal of Range of Motion exercise therapy is to maintain muscle flexibility and strength,
maintain joint mobility and prevent deformity, stiffness and muscle contractures. Some of the Range of
Motion exercises describe useful interventions for increased post-stroke client muscle strength. So hopefully
stroke patients and families can be motivated to perform activities of exercise therapy for the improvement
of self-sufficiency post-stroke patients. The success of exercise therapy is strongly influenced by the
patient's own compliance. The recovery therapy should be lived with patience and sincerity as well as
motivation to give the result of reovery from the maximum paralysis of stroke.
1 BACKGROUND
Stroke is a clinical syndrome with symptoms of
local or global brain dysfunction, which can lead to
persistent abnormalities over 24 hours or death
without other causes except for cardiovascular
disorders (WHO, 1982 in Ahmad, 2000). Based on
data from the National Center of Health Statistics
(NCHS) 2010, stroke ranks third cause of death in
the United States after heart disease and cancer
(Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics 2010 Update: A
Report from the American Heart Association),
explains that from 2008, around 795,000 people in
the United States suffer a stroke every year, with
610,000 people getting strokes for the first time and
185,000 people with recurrent stroke (NCHS,
2010).
According to Yayasan Stroke Indonesia
(YASTROKI, 2012) the number of stroke patients
in Indonesia is the largest and ranks first in Asia.
Stroke is also a cause of serious disability settling
number 1 worldwide. The results of Basic Health
Research (Rikesda) data in 2013 found stroke
prevalence in Indonesia of 12.1 per 1000
population. That number rose by 8.3% compared to
Rikesda in 2007. The high rates of death and
disability caused by stroke are related to the
pathophysiological processes occurring within the
cerebral tissue. Reduced blood flow to the cerebral
blood flow (CBF) may affect cerebral
hemodynamics. Changes in cerebral blood flow
lead to disturbances in the central nervous system
and cranial nerves. Such interference may result in
permanent disability of the paralytic device.
Physical changes as often experienced by clients are
paralysis partial motion, loss of swallowing ability,
cognitive impairment, and psychological disorders
(Black & Hawks, 2005). This will impact on the
ability of clients in their daily activities.
Indrawati, ., Sudiana, I. and Sajidin, M.
Active, Passive, and Active-Assistive Range of Motion (ROM) Exercise to Improve Muscle Strength in Post Stroke Clients: A Systematic Review.
DOI: 10.5220/0008324803290337
In Proceedings of the 9th International Nursing Conference (INC 2018), pages 329-337
ISBN: 978-989-758-336-0
Copyright
c
2018 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
329

These conditions will affect the psychology of
the client post stroke. The way to minimize
disability after a stroke is by rehabilitation.
Rehabilitation of stroke patients one of them is with
exercise therapy. Increased exercise intensity is
proportional to improving quality of life. Exercise
therapy is one way to speed the recovery of patients
from injuries and diseases that in governance use
active or passive movements. Passive movement is
motion driven by others and the active motion is the
motion produced by muscle contraction itself. ROM
exercises can be performed on all joints of the body
especially in the head region, upper extremity, and
lower extremities (Doenges, 2002). Thus an early
ROM Practice program on a stroke client that is not
contraindicated is one of the physical mobilization
programs that must be done immediately.
2 METHODS
The method used in this systematic review begins
with topic selection, then the keyword is determined
to search the journal using English on the giving of
Range of Motion exercise therapy to muscle
strength, by searching the journal through Science
Direct database, Ebscho, Pro Quest, E-Resources,
Sage Journal and Google Scholar. The year limit
used is 10 years (2007 -2017) and got 14 journals.
This search is limited to journals from January 2007
to October 2017. Keywords used are post stroke,
rehabilitation, passive ROM, active ROM, active-
asistive ROM.
Articles were selected for review based on
studies appropriate to the inclusion criteria. The
inclusion criteria in this systematic review are Range
of Motion (ROM) active, passive and active-asistive
for increased muscle strength in post-stroke patients.
Search using the above keywords found 25 journals.
From all journals obtained in accordance with the
theme is 14 journals, then observed and done critical
appraisal.
3 RESULTS
This review system reviewed 14 journals, all
journals discussed the incidence of muscle weakness
(immobilization) which is often called hemiparesis
that occurs in stroke patients. Research conducted by
Fajar Yudha (2014) in the journal The influence of
Range of Motion (ROM) on muscle strength of post-
stroke patients illustrates the effect of intervention
Range of Motion that maintains or maintains muscle
flexibility and strength, maintains joint mobility and
prevents deformities, stiffness and contractures. The
results showed an increase in the average value of
muscle strength first day and day 28 amounted to
0.45. There was an increase in the average value of
the joints on the first day and the 28th day of 6.65.
Proven dg The results of muscle strength statistics
test shows p-test results = 0,001. There is an
influence Range of Motion (ROM) to muscle
strength of patients post-care stroke. This study was
conducted for 4 weeks.
Similar research was also conducted by Kun Ika
Nur Rahayu (2015) with the title describing the
effect of ROM exercises on motor skills that
increase flexibility and wide range of joint motion in
stroke patients because ROM exercises can induce
rangsangn thus increasing the activity of
neuromuscular and muscular chemistry. Stimulation
through the neuromuscular will increase the
stimulation of the stimulating parasympathetic
nerves for the production of asethylcholin resulting
in contraction. This is proved by the results of the
study found that there is influence of Range of
Motion (ROM) training on motoric ability that is
result of data analysis by using Paired Sample T-
Test statistic obtained p-value <0,05 it can be
concluded that H0 is rejected and H1 failed to be
rejected. given Range of Motion 2x exercise a day
for 7 days. The evaluation of this research was done
on the first and the seventh day.
Research with Range of Motion exercise therapy
is the effect of Range of Motion (ROM) exercise on
muscle strength in stroke patients by Claudia
Agustina Sikawin, et al (2014) where the data is
taken through direct observation on the respondents
to look for pre test and post test data. Previously the
patient measured his muscle strength level, after
ituresponden given Range of Motion exercises 5
times a day within 10 minutes and performed as
much as 8 days of exercise. Next will be re-
measured muscle strength levels and proven The
existence of the effect of Range of Motion exercise
on muscle strength in stroke patients. showed
muscle strength score before and after exercises
Range of Motion had an average score increase of
3.87. It is explained that Range of Motion exercise
therapy is one of the advanced therapies in stroke
patients aimed at improving cerebral blood flow,
minimizing defects caused to improve motor sensory
function.
Similar research is also conducted by Irene H.L.,
et al (2016), where researchers explain that there is a
significant association of weight support exercises
INC 2018 - The 9th International Nursing Conference: Nurses at The Forefront Transforming Care, Science and Research
330

arms and is beneficial for subacute stroke patients
with moderate to severe arm disorders, particularly
to improve vertical control such as shoulder flexion,
and no side effects on the muscles. Training is done
for 45 minutes every day, 5 days a week for 5
weeks. Exercise therapy is done in rehabilitation,
arms will neutralize the weight of one arm's arm and
use both arms where a healthy arm is assisted to
support. Furthermore, the movement follows the
direction and the gabar by pressing the button of the
existing screen then it will deliver a signal to the
brain to do movement/ ROM move the hands and
arms. In this study explained that through this
exercise therapy the patient has his own initiative to
move the sick arm. The Interobserver Reliability and
Sources of Variation explain that the Range of
Motion exercise therapy is done passively (PROM)
so that the ROM assessment with standard protocol
hydrogoniometer and performed by 2 trained
physical therapists resulting in a high interobserver
reliability index for all arm movements. Error
variance makes a major contribution to the variety of
measurement results. Exercise therapy is done 2
times a day for 1 week showing significant
improvement.
Results of research conducted by Prok,
Winona.et al (2016) where the study included in a
Range of Motion active-asisitive study where the
study used 18 stroke patients given treatment in the
form of motion exercises active, ie holding a rubber
ball for one (1) month, then muscle strength
measured using handgrip Dynamometer. The results
showed that there was significant effect of active
motion exercises gripping rubber balls on hand
muscle strength of stroke (p=0.000) because the
training of gripping exercises was a mood of the
sensory stimuli and the pressure on the end organ
receptor encapsulated in the upper ekstermitas.
Treatment of excitatory will cause a rapid response
to sarf to perform action on the stimulus. This
mechanism is called feedback.
The results are supported by research conducted
by Ni Made Dwi et al (2016) obtained a significant
difference between the value of handheld muscle
strength before and after being given a ROM
exercise with rubber ball for 10 minutes. It can be
said that ROM exercise with rubber ball can increase
handheld muscle strength of non hemorrhagic stroke
patients who experience weakness if done by the
therapist in accordance with the operational standard
of ROM exercise procedure with rubber ball as well
as the cooperation between the patient and the
therapist in the treatment therapy process.
Andika Sulistiawan (2014) mentions in the
results of this study found that all stroke patients
who do therapy grasping the ball slowly get a
recovery of stroke disease they suffered in which the
distribution of respondents about grasping the ball
before being given numerous interventions among
stroke patients who find difficulty in moving their
hands. Miftahul Cilia et al (2016) mention the effect
of ROM exercise on the degree of stroke joint
motion of stroke patients. Another study of ROM
exercises on top extermity is Effectifity Range of
Motion (ROM) on powers stroke patients limb
muscles by Havid et al (2012) where prior to ROM
therapy, the degree of patient's muscle strength is
classified as degree 1 (only tone change) degree 3
(able to move joints, can defy gravity, not strong
against prisoners). After ROM therapy, the degree of
patient's muscle strength is classified as 2 degrees
(able to move the joints, can not go against gravity)
to 4 degrees (capable of moving the joints, can defy
gravity, strong against mild resistance). There is a
difference (increase) degree of muscle strength of
patients before and after therapy ROM with p value
= 0.003 <0.05. ROM therapy is effective in
increasing the muscle strength of the stroke of the
stroke patients because ROM therapy effectively can
improve the degree of muscle strength ekstermitas
non hemorrhagic stroke patients because the goal of
ROM exercise it self is to maintain or maintain
muscle strength, joints and stimulate blood
circulation and prevent deformity. However,
unstable patient conditions such as vital signs that
often change during illness also become one of the
obstacles.
Similar research is also conducted by Murtaqib
(2013) showed that there was a difference in the
average range of elbow joint motion before the
active ROM, ie 125.27 degrees of flexion and
extension of 28.27 degrees, after exercise of flexion
movement of 136.37 and extension of 8.47 degrees.
or in other words there is a significant influence
between active ROM exercises against elbow joint
motion in stroke patients. Active ROM exercises are
performed 3 times a day because ROM exercises can
stimulate blood circulation, maintain muscle
elasticity and reduce pain and joint stiffness. This is
reinforced by Wahyudin's research., et al. (2008)
The effect of PNF on the strength of prehension
function in hemorrhagic and non-hemorrhagic stroke
patients in which this study studied differences in
the effect of PNF method on the strength of
prehension in hemorrhagic stroke and non-
haemorrhagic stroke . Treatment of PNF method
therapy therapy to hemorrhagic stroke patients is
Active, Passive, and Active-Assistive Range of Motion (ROM) Exercise to Improve Muscle Strength in Post Stroke Clients: A Systematic
Review
331

beneficial to the enhancement of strength of
prehension function.
Research from IB Putu Putrawan., et al (2011)
said that the measuring tool to measure handheld
muscle strength is handgrip Dinamometer which
will be used to determine the strength of the hand
grip which will require a combination of action from
a number of muscles of the hands and forearms and
this action is very important for daily activities. The
strength of hand grip is a common method used to
estimate the strength of upper ekstremity muscle.
From the results of this study explained that in
elderly women have hand grip strength is lower than
in men. The strength of hand grips is positively
associated with weight and waist circumference,
there is an increasingly thinness of the elderly will
lower the grip of his hand, and this will lead to the
consequent decline in functional quality for basic
daily living activity. Most importantly, the results of
this study indicate that the elderly population who
are in a state of poor nutritional status will
experience greater difficulties in independently
beraktives in society. The strength of hand grips is
positively related to nutritional status. Although
once controlled for other variables in the regression
analysis, poor nutritional status remains a significant
factor determining the strength of hand grips in both
men and women.
Another study was also conducted by Gehan A.
Younis and Safaa E. Sayed Ahmed (2015)
explaining that the results of this study indicate that
50% of patients with ventilation experience pain
which is severe before starting a passive motion
exercise program. But after 60 minutes of
intervention about two-thirds (60%) of critical
patients have no pain. Slight changes in the mean
score of physiologic parameters after 5 and 20
minutes after intervention compared with the mean
score before the intervention was observed. After 60
minutes of intervention, this average score returns to
their baseline. Also, the intensity of behavioral pain
decreased after 60 minutes compared before the
intervention. Based on the findings of this study, it is
advisable to conduct early passive motion exercises
for ventilated patients in the context of the
mobilization protocol. A Journal also mentioned that
the effect of duration of stretching of the hamstring
muscle group for increasing range of motion in
people aged 65 years or older by J Brent Feland ,. Et
al (2001) where the stretching protocol for elderly
people (65 years) has not been studied to determine
the effectiveness of increasing Range of Motion
(ROM). The purpose of this study was to determine
which of the 3 stretching durations would yield and
retain the greatest advantage in ROM knee extension
with the femur held at 90 degrees of hip flexion in a
group of elderly individuals.
The Range of Motion is measured once a week
for 10 weeks to determine treatment and residual
effects. The 60 second stretch yields a higher level
of ROM gain (clash 60 seconds52.4° per week,
stretching 30 seconds 51.3° per week, stretching 15
seconds 50.6° per week), which lasts longer than
Profits in other groups (group 4 still had ROM 5.4°
more 4 weeks after treatment than in pretest
compared to 0.7° and 0.8° for groups 2 and 3,
respectively). Extremity can experience weakness or
paralysis in different degrees depending on the
disrupted part. Stroke patients with long-term
immobilization conditions will facilitate the
formation of DVT, muscle atrophy, contractures and
joint pain and decubitus. Range of Motion (ROM)
exercise is one form of rehabilitation exercise that is
considered very effective to prevent disability in
patients with stroke, whether it is active ROM,
passive ROM or active-asistive ROM.
4 DISCUSSION
In general, all of the reviewed journals provide
results that range of motion (ROM) exercise therapy
both active, passive and active-assistive provide
significant benefits to increased muscle strength and
range of upper extremity motion and or articles
explaining if ROM exercise therapy is accompanied
PNF is a ROM exercise therapy that is structured
and sequential with the therapy therapist by the
therapist so that the results obtained more leverage.
Stroke disorder function of the nervous system
that occurs suddenly and caused by blood circulation
disorders in the brain either the clogging of blood
vessels of the brain or rupture of blood vessels in the
brain where the brain that should get the supply of
oxygen and nutrients to be disturbed. Stroke can
cause various degrees of disturbance, such as
decreased muscle tone, loss of sensibility in some
parts of the body, decreased ability to move sick
limbs and incapacity in certain activities. Stroke
patients who experience weakness on one side of the
limb due to a reduction in muscle tone, so unable to
move his body (immobilization). The way to
minimize disability after a stroke is by rehabilitation.
Rehabilitation of stroke patients one of them is with
exercise therapy (Mubarak, 2008).
This is in accordance with the Decree of the
Minister of Health (KepMenKes) No.1363 /
MENKES / SK / XII / 2001, Article 1 that exercise
INC 2018 - The 9th International Nursing Conference: Nurses at The Forefront Transforming Care, Science and Research
332

therapy by physiotherapy is a form of health service
aimed at individuals and or groups to develop,
maintain and restore motion and function the body
throughout the life cycle by using manual handling,
improvement of motion, equipment (physical,
electrotherapy and mechanical) function and
communication training (Menkes, 2001).
Therefore, ROM and early treatment is
necessary. According to some studies, the success of
motion exercise therapy (ROM) is strongly
influenced by the patient's own compliance. As for
ROM and treatment should be endured with patience
and sincerity, self-motivation of family and close
friends is also needed to give healing result from
maximal paralysis of stroke, try to adapt to the
situation as well as undergo therapy exercises
performed by physiotherapy regularly. Previous
research has shown that adherence to exercise
therapy increases muscle strength and range of
paralyzed motion in post-stroke patients. ROM
exercises on motor skills include increased
flexibility and wide range of joint motion in stroke
patients because ROM exercises can induce
rangsangn thus increasing activity from
neuromuscular and muscular chemistry.
Range of Motion exercise therapy is one of the
advanced therapies in stroke patients aimed at
increasing brain blood flow, minimizing defects
caused to improve motor sensory function. Influence
of intervention range of motion is to maintain or
maintain flexibility and muscle strength, maintain
joint mobility and prevent deformity, stiffness and
contractures. Exercise therapy is one way to speed
the recovery of patients from injuries and diseases
that in pentalaksanannya use active or passive
movements. Passive movement is motion driven by
others and the active motion is the motion produced
by muscle contraction itself. The movements in
ROM exercise therapy include flexion, extension,
hyper extension, circumcision, abduction, adduction
and opposition.
5 CONCLUSIONS
Range of Motion (ROM) Exercise Therapy is an
effective way of treating muscle weakness or
prolonged paralysis, therefore nursing or
rehabilitation services should schedule and provide a
special place for stroke patients with hemiparesis
especially in the rehabilitation process of ROM
activity or exercise. As for the family to always
supervise, motivate and encourage patients to
perform continuity of ROM exercises, regularity of
activities and medical visits. Because the way to
minimize disability after a stroke is by rehabilitation.
Rehabilitation of stroke patients one of them is with
exercise therapy. Increased exercise intensity is
proportional to improving quality of life.
All the studies that have been in the study of
ROM exercises on post stroke clients can be one
alternative rehabilitation intervention in post stroke
clients. Where the ultimate goal of client care with
stroke itself is to restore physical and psychological
abilities. In order for the client is able to adapt to the
new conditions, able to adjust and improve quality
of life in post-stroke clients. Stroke patients who
have hemiparesis are treated immediately to be
curative measures such as treatment and
hospitalization, rehabilitative action by
physiotherapy in the form of Range Of Motion
exercise therapy whether active, passive or active-
asistive.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
Thanks to the Institute for Research and Community
Service, University of Jenderal Soedirman that has
provided research grants under contract number
4869 / UN23.14 / PN / 2017.
REFERENCES
Andika Sulistiawan., (2014 ). Pengaruh terapi aktif
menggenggam bola terhadap kekuatan otot
pasien stroke di RSSN Bukittinggi, Jurnal
Kesehatan STIKES Prima Nusantara Bukittinggi,
Vol.5. No.1. Januari, 2013.
Chaidir., Reni., (2014). Pengaruh Range of Motion
pada Ekstremitas Atas dengan Bola Karet
Terhadap Kekuatan Otot Pasien Stroke
Hemoragi di Ruang Rawat Stroke RSSN
Bukittinggi Tahun 2012.‘Afiyah Vol.1, No. 1.
Claudia Agustina Sikawin, et al., ( 2014). Pengaruh
latihan Range Of Motion (ROM) terhadap
kekuatan otot pada pasien stroke di irna f
neurologi BLU RSUP Prof. dr. r. d. Kandou
Manado, Ejournal Keperawatan (e-Kp) Volume
1. Nomor 1. Agustus 2013.
Fajar Yudha, et al., (2014). Pengaruh range of
motion (ROM) terhadap kekuatan otot pasien
pasca perawatan stroke, Jurnal Keperawatan,
Volume X, no.2, Oktober 2014.ISSN 1907-0357.
Gehan A. Younis and Safaa E. Sayed Ahmed,
(2015). Effectiveness of Passive Range of
Active, Passive, and Active-Assistive Range of Motion (ROM) Exercise to Improve Muscle Strength in Post Stroke Clients: A Systematic
Review
333

Motion Exercises on Hemodynamic parameters
and Behavioral pain Intensity among Adult
Mechanically Ventilated Patients. IOSR Journal
of Nursing and Health Science (IOSR-JNHS) e-
ISSN: 2320–1959.p- ISSN: 2320–1940 Volume
4, Issue 6 Ver. I (Nov. - Dec. 2015), PP 47-59
www.iosrjournals.org
Havid, et all., (2012). Effectifity Range of motion
(ROM) on powers stroke patients limb muscles,
Akper PKU Muhammadiyah Surakarta, yang
diakses tanggal 3 Agustus 2017.
IB Putu Putrawan, et al., ( 2011). Faktor – faktor
yang menentukan kekuatan genggaman tangan
pada pasien lanjut usia di Panti Wredha Tangtu
dan Poliklinik Geriatri RSUP Sanglah –
Denpasar. Jurnal Penyakit dalam,Vol.12
no.2.Mei 2011.
IreneH.L ,et all., (2016). Effects of Arm Weight
Support Training to Promote Recovery of Upper
Limb Function for Subacute Patients after Stroke
with Different Levels of Arm Impairments,
Hindawi Pubishing corporation BioMed
Reseacrh International, Vol.2016, article ID
9346374, 9 pags
J Brent Feland, et all., (2001). The Effect of
Duration of Stretching of the Hamstring Muscle
Group for Increasing Range of Motion in People
Aged 65 Years or Older. Physical Therapy .
Volume 81 . Number 5 . May 2001
Kun IKa Nur Rahayu., (2015). The Influence of
Range of Motion Exercise to Motor Capability of
Post-Stroke Patient at the Gambiran
Hospital,Jurnal keperawatan, P-ISSN 2086-3071
E-ISSN 2443-0900. Hal:102-107.
Mubarak, IW. & Chayatin, N. (2008). Kebutuhan
dasar Manusia. Jakarta : EGC
Murtaqib., (2013). Pengaruh Latihan Range of
Motion (ROM) aktif terhadap Perubahan
Rentang Gerak Sendi pada Penderita Stroke di
Kec. Tanggul Kab. Jember.. Jurnal IKESMA
Volume 9 Nomor 2 September 2013 Hal : 107 –
115.
Miftahul Cilia, et all., (2016). The Effect of ROM
Exercise on Range Of Motion of Patients with
stroke in inpatients room at Regional Public
Hospital (RSUD) of dr.Soedirman Mangun
Soemarso in Wonogiri. Di akses tanggal 3
Agustus
Ni Made Dwi, et al., (2016). The Effects Of ROM
Exercise With a Rubber Ball To Muscular Stregh
Handheld Non-Hemoragrhgic Stroke Patients,
Jurnal keperawatan Bulelelng.
Prok, Winona.et al., (2016). Pengaruh Latihan
Gerak Aktif Menggenggam Bola Pada Pasien
Stroke Diukur dengan Handgrip Dynamometer,
Jurnal e-Clinic (eCl), Volume 4, Nomor 1,
Januari-April 2016.
Wahyudin, et al., ( 2008). Pengaruh pemberian PNF
terhadap kekuatan fungsi prehension pada
pasien stroke hemoragik dan non hemoragik.
Jurnal Fisioterapi Indonesia Vol.8. no.1, April
2008.
Yudha, fajar., (2014). Pengaruh Range of Motion
(ROM) Terhadap Kekuatan Otot Pasien Pasca
Perawatan Stroke. Jurnal Keperawatan Vol. X,
No. 2, 203 – 208.
INC 2018 - The 9th International Nursing Conference: Nurses at The Forefront Transforming Care, Science and Research
334
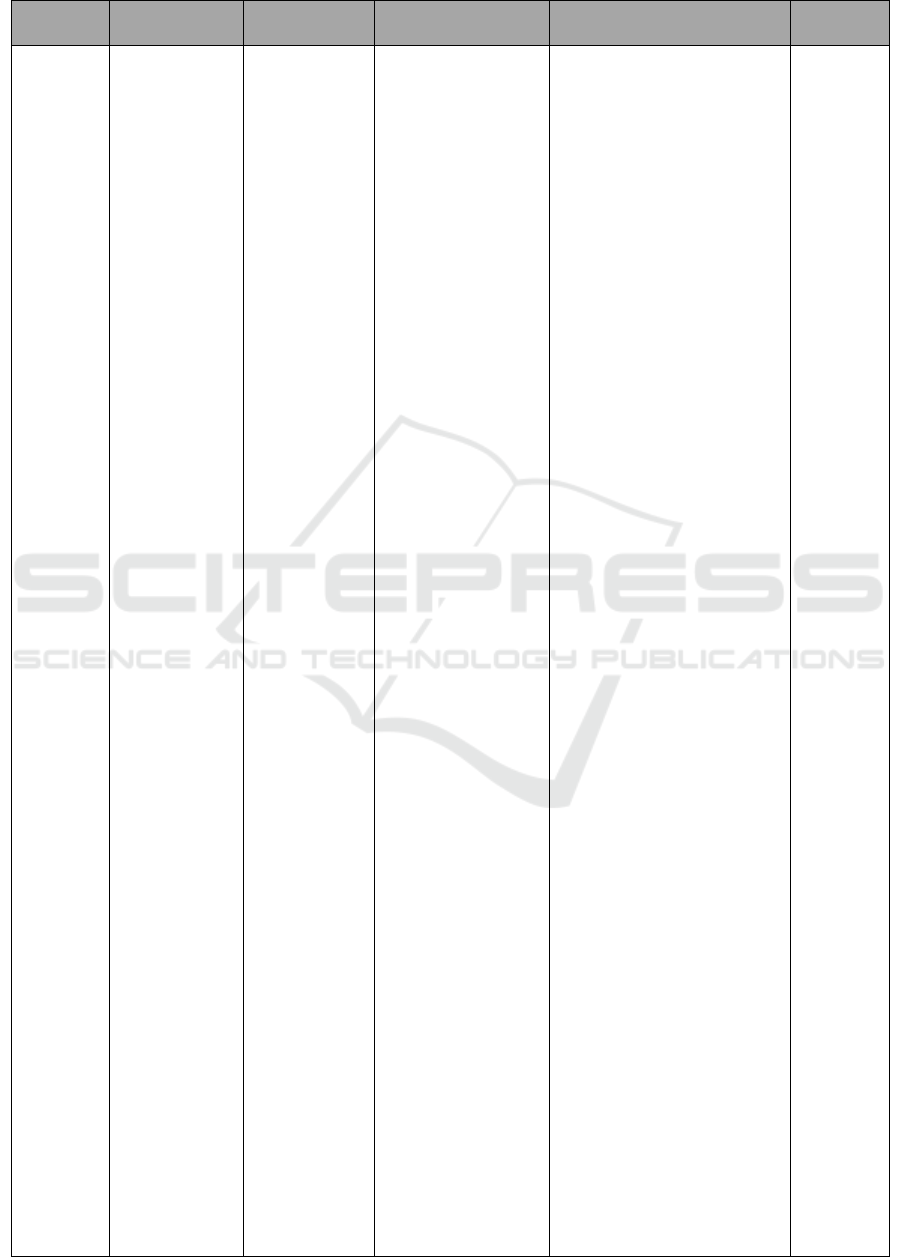
Tabel 1: Summary of studies include.
Author /
Year
Sample size Study Design Intervention Outcome
Articles
Quality
Fajar
Yudha,
2014
Kun IKa
Nur
Rahayu,
2015
Claudia
Agustina
Sikawin,
et al. 2014
Irene H.L
.,et al.
2016
Lex D de
jong .,et
all. 2012
Prok,
Winona.et
al. 2016
Ni Made
Dwi et al :
2016)
consecutive
sampling
20 respondents
16
Respondents.
Purposive
Samling
Purposive
Sampling
15
Respondents
Prospective
single-group
cohort study.
48 classified
into 3 groups
48
Respondents
18
Respondents
with Purposive
sampling
13 respondents
Non Probabilty
sampling with
Purposiv
sampling
10
Respondents
Total Sampling
Quasy
Experiment
(pre and post
test design)
Cross
Sectional (Pre
Ekeperimental
Pre-post Test
One Group
Design)
Quasi
Eksperimen
with
Nonequivalent
Control Group
Design
method
RCT
Cross
Sectional (Pre
Ekeperimental
Pre-post Test
One Group
Design)
Quasi
Experiment
(pre and post
one group
design)
pre-
eksperimental
One Group
PreTest-
PostTest and
Paired T-test
Exercise range of
motion to measure
muscle strength of
patients
Exercise range of
motion to measure
muscle strength of
patients
Exercise range of
motion to measure
muscle strength of
patients
ROM exercise
therapy on
ArmeoSpring is
done for 45 minutes
every day, 5 days
once a week,
ROM exercise
therapy with
measurement on
range of motion of
joints with
Hydrogoniometer
Active motion
exercises, ie holding
a rubber ball for one
(1) month, then
muscle strength
measured using
handgrip
Dynamometer.
ROM exercises with
rubber balls for 5 to
10 minutes in non
hemorrhagic stroke
patients
The results showed an
increase in the average value
of muscle strength first day
and day 28 amounted to 6.65.
Which means There is
influence Range Of Motion
(ROM) to muscle strength of
patients post-care stroke.
Patients were given range of
motion 2x daily exercise for 7
days. The evaluation of this
research was done on the first
and the seventh day.
Previously the patient
measured his muscle strength
level, after which respondents
were given range of motion
exercise 5 times a day within
10 minutes and performed as
much as 8 days of exercise.
Muscle strength score before
and after exercises range of
motion had an average score
increase of 3.87.
There is a significant
association Weight-weight
support exercises are
beneficial for subacute stroke
patients with moderate to
severe arms disorders,
especially to improve vertical
control such as shoulder
flexion, and no adverse
muscle effects
The ROM assessment by
standard protocol,
hydrogoniometer, and 2
trained physical therapists
resulted in a high
interobserver reliability index
for all arm movements.
The results showed that there
was significant effect of
active motion exercises
gripping rubber ball against
hand muscle strength of
stroke (p = 0,000)
Strong
Moderate
Strong
Strong
Moderate
Moderate
Strong
Strong
Moderate
Active, Passive, and Active-Assistive Range of Motion (ROM) Exercise to Improve Muscle Strength in Post Stroke Clients: A Systematic
Review
335

Andika
Sulistiawa
n, 2014
Miftahul
Cilia et
all,2016
Havid et
all, 2011
Murtaqib.
2013
Wahyudin
., et al.
2008
IB Putu
Putrawan.,
et al. 2011
Gehan A.
Younis
and Safaa
E. Sayed
Ahmed,
2015
50 respondents
with 25 control
groups and 25
intervention
groups Total
Sampling
Non
Probability
with accidental
Sampling
method
56
Respondents
30
Respondents
Total Sampling
16
Respondents
Purposive
sampling
91
Respondents
Consist of 38
males, 53
females
Random
Sampling
40
Respondents
pre experiment
(pre-post test
design)
Pre
experiment
Purposive
sampling
(pre-post test
design)
pre
eksperimental
one design
pretest-postest
non random
Experiment
(two group
pretest post
test)
Quasi
eksperimental
with pre test
and post test
design
approach
Quasi
eksperimental
Exercise therapy
holds a rubber ball to
assess muscle
strength
ROM exercise
therapy to measure
range of motion of
the joints
ROM exercise
therapy to measure
muscle mass
disorder
Exercise ROM
Therapy Exercise
Flexion Extension
ROM exercise
therapy with PNF
method to measure
Prehension Function
in Hemorrhagic
Stroke and
Stroke Non
Hemoragic
ROM exercise
therapy for the
elderly to mnegukur
handheld with
Handgrip
Dynamometer
Passive ROM
exercise therapy
From result of research got
average value of handheld
muscle strength of non
hemorrhagic stroke patient
before given ROM training
with rubber ball that is 8,46.
And the average value of
handheld muscle strength
after being given ROM
exercise with rubber ball for 5
to 10 minutes has increased ie
11.23. Based on result of
paired t-test shows that result
p value = 0.0001
The results of this study
found that all stroke patients
who do therapy grasping the
ball slowly get a recovery
against stroke that they
suffered in the distribution of
respondents about holding the
ball before the intervention
was given many among stroke
patients who find difficulty in
moving his hands.
The result of this research is
that the pre test of motion
range of respondents most of
the category dg not at all have
the ability to do joint motion
of 87.5%, and perform the
range of motion of joints with
partial category (12,5%).
showed that most
respondentst dg category did
joint motion of equal to
81,3% and dg tdk totally have
ability to do range of motion
of joints is equal to (18,8%)
After ROM therapy, the
degree of patient's muscle
strength is classified as 2
degrees (able to move the
joints, can not defy gravity) to
4 degrees (capable of moving
the joints, against gravity
The results showed that there
was a difference in the
average range of elbow joint
motion before the active
ROM, ie 125.27 degrees of
flexion and extension of
28.27 degrees, after exercise
Strong
Strong
Moderate
Strong
Moderate
INC 2018 - The 9th International Nursing Conference: Nurses at The Forefront Transforming Care, Science and Research
336
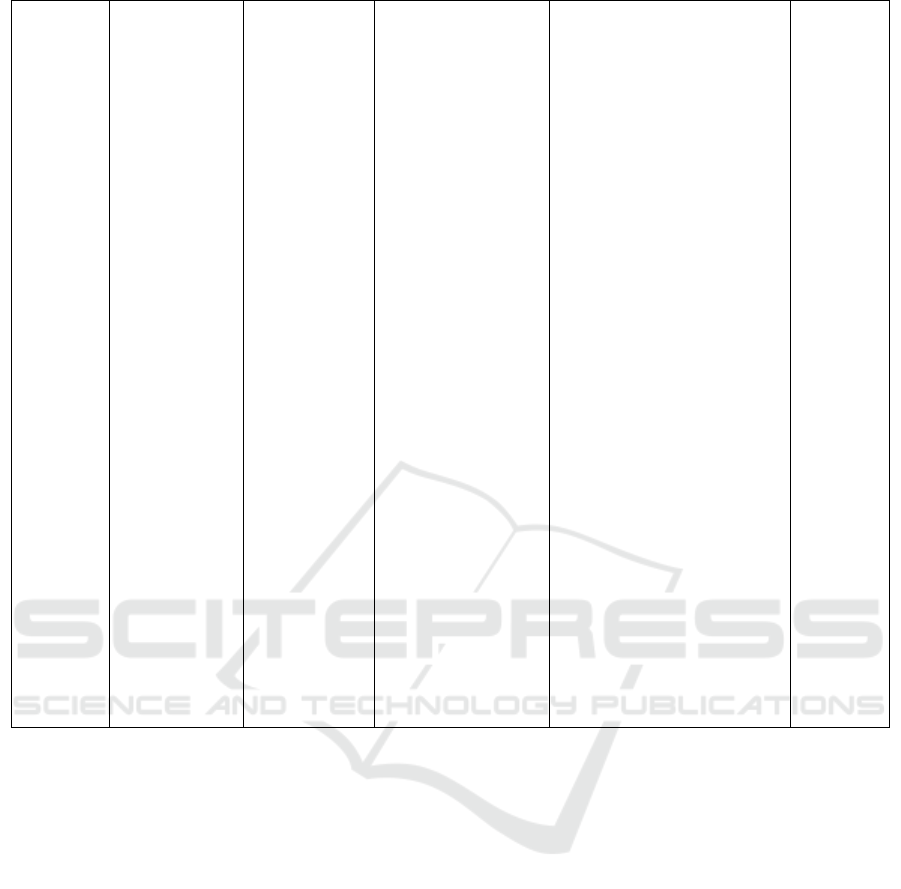
quasi
experimental
design.
of flexion movement of
136.37 and extension of 8.47
degrees. Or in other words
there is a significant influence
between active ROM
exercises against elbow joint
range in stroke patients
There was no significant
difference in the effect of
PNF treatment on
hemorrhagic stroke and non-
hemorrhagic healing stroke
phase to increase the strength
of prehension function.
From the results of this study
can be concluded that in
women elderly women have a
lower hand grip hand than
men
These results indicate that
50% of ventilated patients
experience severe pain before
starting a passive motion
exercise program. But after
60 minutes of intervention
about two-thirds (60%) of
critical patients have no pain.
Active, Passive, and Active-Assistive Range of Motion (ROM) Exercise to Improve Muscle Strength in Post Stroke Clients: A Systematic
Review
337
