
Reminiscence Therapy as a Strategy to Prevent Cognitive Decline in
Elderly People
A Systematic Review
Nirmala K.S, Riny Pujiyanti, M. Noor Ifansyah, and I Kadek Dwi Swarjana
Faculty of Nursing, Universitas Airlangga, Mulyorejo, Surabaya, Indonesia
i.kadek.dwi.swarjana-2017@fkp.unair.ac.id
Keywords: Reminiscence therapy, Elderly, Cognitive decline.
Abstract: Dementia is a symptom or a condition which is often happen to some elderly people that decreasing
cognitive ability and also functional and behavior disorder. Reminiscence therapy is one of psychosocial
intervention that is commonly used for the elderly people in dementia that has the main objective as
defending the personal past and perpetuating the identity of the certain person, and also use stimulation,
communication, socialization, and entertainment. The objective of this research is to identify the effectivity
of reminiscence therapy on elderly people with dementia in preventing cognitive decline. The article
searches through the database, for instance, ProQuest, Scopus, Ebsco, Cinahl, and ScienceDirect. The year
limitation range is 9 years (2009-2017). The analysis from the article searches is resulted 15 suitable
articles with the term required. The reminiscence therapy which is used to prevent cognitive decline (the life
quality repairment) is using elderly life story approach with the methods of pictures, multimedia, music,
peer support, and combining. Reminiscence therapy which is using the life story approach with the method
of pictures, multimedia, music, peer support, and combination reliable and effective to increase the life
quality of patients with dementia.
1 BACKGROUND
Dementia is one of the most common diseases in the
elderly and the major cause of
disability worldwide. Elderly with dementia often
exhibit a variety of functional disorders and
behavioral problems (WHO, 2017). The cognitive
function becomes the main focus of various studies
in patients with dementia and is a major feature of
treatment. Meanwhile, non-cognitive
symptoms which occur in the elderly with dementia
is also quite disturbing family members and/or
careers for being a serious thing and can affect the
welfare of patients (Pruszy, 2015). The non-
cognitive symptoms become a dominant problem,
both emotionally and financially (WHO, 2017).
The effectiveness of pharmacological treatment
in dementia patients is quite limited, due to the lack
of curative care. The act of promoting welfare and
quality of life is an important thing can be done to
improve the life of patients with dementia (Algar et
al., in press). Therefore, non-pharmacological
interventions for dementia patients have received
attention in recent years.
One effective non-pharmacological therapy in
the care or treatment of the elderly with dementia
is Reminiscence therapy, which provides emotional
and social benefits. Reminiscence therapy is a
commonly used psychosocial intervention for the
elderly in the treatment of dementia in maintaining
personal pasts and perpetuating the identity of the
person by means of stimulation, communication,
socialization, and entertainment.
Reminiscence can also be considered as a
generator of past memories and events that are
interpreted today (Gonzalez et al., 2015).
The goal of the intervention based on the memento
as discussed in this review is to understand a
person's relationship with his/her past. Thus, the
purpose of this study was to examine the benefits
of reminiscence therapy in elderly with dementia in
preventing cognitive decline.
438
S., N., Pujiyanti, R., Ifansyah, M. and Swarjana, I.
Reminiscence Therapy as a Strategy to Prevent Cognitive Decline in Elderly People.
DOI: 10.5220/0008326404380441
In Proceedings of the 9th International Nursing Conference (INC 2018), pages 438-441
ISBN: 978-989-758-336-0
Copyright
c
2018 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
2 METHODS
This study employed the systematic review design.
Data of this study were taken from database of
ProQuest, Scopus, Ebsco Cinahl, and ScienceDirect
in 2009-2017. The articles were searched with the
keywords of reminiscence therapy, elderly, and
cognitive decline. Every article that included in this
systematic review had ethical clearance approval.
The literature selection was determined by the
following inclusion criteria: (1) the study sample is
the elderly, (2) the articles were published between
2009-2017, (3) the articles were published in
English, (4) the articles focused on the reminiscence
therapy, and (5) the articles focused on nursing. The
exclusion criteria include the sample, not the elderly.
3 RESULTS
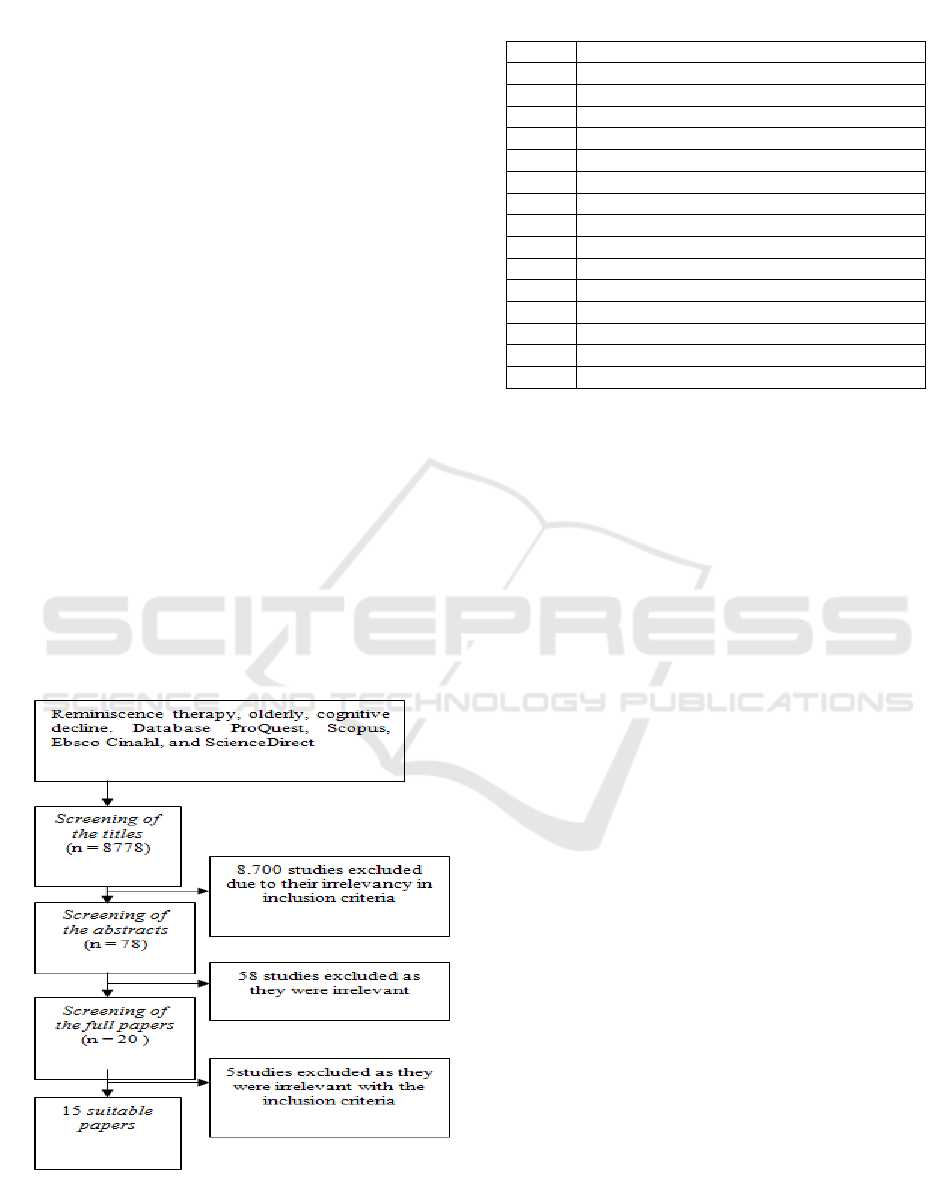
From the article and journal searching, 8.778 papers
were found from databases, including 1215 articles
in ProQuest, 823 articles in Scopus, 1651 articles at
Ebsco Ciahl, and 3257 articles in ScienceDirect. The
detailed identification and selection processes of the
papers can be seen in Figure 1. The results of the
paper selection were according to the inclusion
criteria and then were given sequence number to
facilitate the review process (Table 1).
Figure 1: The Paper Selection Processes.
The results of the study conducted by Azcurra
(2012) were with the population of 135 respondents
selected from patients who have undergone long
treatment and then divided into three
groups: intervention, active control, and passive
control. The intervention provided by stimulus of
respondent’s memory by showing photography,
recordings and newspaper clipping, that
reminiscience therapy by using life story reliable
approach and effectively improve the quality of life
in patients with dementia performed as many as 24
sessions in one week. It is directly proportional to
the research done by Bailey (2017) in a number
of 26 elderly in the intervention group and 25 elderly
in the control group.
The interventions provided are environmental
supports, individualized behavioral activity
programs, and the usual nursing home activities that
showed a positive impact in improving the quality of
life of the elderly. Based on the research done by
Yasuda (2013) there was two sessions of
intervention. First session the patient was asked
to see the preferred TV program while on the second
session the patient was asked to sit in front of
the computer to have a conversation
via videophone of their old pictures.
The result showed that between reminiscence
therapy and videophone had a positive effect on
increasing the concentration of the elderly.
Further studies by Hsu (2017) was associated with
the predictors of the non-pharmacological
intervention effect on cognitive function and
behavioral and psychological symptoms of older
people with dementia in reminiscence therapy. The
interventions were recalling past events or
experiences, sharing personal life stories by using
tangible prompts. The intervention results showed
Table 1: The selected papers list.
No.
Author(s)
1.
(Azcurra, 2012)
2.
(Woods et al., 2009)
3.
(Bailey et al., 2017)
4.
(Yasuda et al., 2013)
5.
(Hsu et al., 2017)
6.
(Randall and Neill, 2011)
7.
(Gudex et al., 2010)
8.
(Pringle and Somerville, 2013)
9.
(Gonzalez et al., 2015)
10.
(Elfrink et al., 2017)
11.
(Charlesworth et al., 2016)
12.
(Allen et al., 2014)
13.
(Mahendran et al., 2017)
14.
(Wang, Yen and OuYang, 2009)
15.
(Ito et al., 2007)
Reminiscence Therapy as a Strategy to Prevent Cognitive Decline in Elderly People
439

that the reminiscence therapy is able to
repair and maintain the cognitive abilities of elderly
who do as much as 6 months.
4 DISCUSSION
Elderly people with dementia will experience
decreased memory and functional disorders and
behaviors that affect their behavior in daily life so
that it can create personal, family, and
environmental difficulties where the elderly
live. Therefore, a way that can improve the
condition especially non pharmacological way is
needed. There have been many researchers looking
for ways to overcome the problems that exist. Then,
some methods or ways to overcome the things or
problems were found and one of them is
called reminiscence therapy.
Reminiscence therapy is a commonly used
psychosocial intervention for the elderly in the
treatment of dementia. It is a way of preserving the
personal past and perpetuating the identity of the
person and using stimulation,communication,
socialization, and entertainment. This therapy
consists of several ways or intervention with the
same goal that is to maintain and improve the
elderly's memory in order to carry out daily
activities independently. This therapy can maintain
and improve the expected memory quality of life
elderly to be better than before getting the therapy.
Fifteen journal using reminiscience intervention
with the tools such as pictures, multimedia, music,
peer support, and a combination of the four tools
showed a significant effect on improving the quality
of life of elderly with dementia.
In reminiscence intervention with the help of
picture using life story approach was for instance
about the reminiscence of the childhood, schooldays,
working life, marriage, holiday, and journey.
The respondents were given a memory
stimulus by showing photography, recordings, and
newspaper clippings about their life since childhood
until now. In addition, families or counselors are
also involved in the intervention to increase social
support for elderly with dementia. This
implementation was given into several sessions,
namely 12-24 sessions, where each session was held
for 2 hours.
The results of the implementation showed that
these interventions are effective in improving the
quality of life and good relationships with the
environment in the elderly with dementia.
The reminiscence interventions with multimedia
tools, including Online Life Story Book (OLSB ), it
is used to restore memories so as to enhance feelings
of pleasure and trust. This study has the following
four secondary objectives namely: 1) studying the
effectiveness of interventions on the burden and
quality of life primary informal caregivers; 2)
providing an initial health evaluation; 3) studying
(time for ) nursing home admissions as long-term
effects, and 4) providing process evaluation.
The Online Life Story Book is an e-health
application that allows placing personal memories
on a dynamic timeline. OLSB materials consist of
personal information, such as photos at school,
holiday activities, weddings, or activities with
family and children. Interventions were conducted in
5 sessions for 8-10 weeks. The implementation
results showed that these interventions were
effective in improving the cognitive function and in
reducing depressed feeling in people with dementia.
In reminescence intervention with music aids, it
consists of Art Therapy (AR) and Music
Reminiscence Activity (MRA), which aim to
strengthen the system of attention and improve
cognition. The intervention is given for 9 months
divided into two sessions, the first session was given
every week for 3 months, while the second session
was given bi-weekly for 6 months. The
implementation results showed that the intervention
is effective in maintaining and improving cognitive
abilities of elderly with dementia.
Different researchers on two articles discussed
the reminiscence therapy with peer
support method. Peer support can help the memory
of the elderly because in peer support elderly can tell
the experience and success of the past. In addition,
between peer support and the elderly can exchange
information.
Further, researchers on five articles used the
method of combining pictures, music, object, and
communicating the specific topic followed by
singing. This combined method is effective in
preventing cognitive decline in the elderly. This
method was performed sequentially in the therapy
session starting from the greetings, the orientation of
reality, telling about certain topics (childhood
memories, these events one's life, and events in the
past ), followed by singing and closing.
5 CONCLUSIONS
The reminiscence therapy by using life story
approach is reliable and effective to improve the
quality of life in dementia patients.
INC 2018 - The 9th International Nursing Conference: Nurses at The Forefront Transforming Care, Science and Research
440

ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
Thank you to God, for blessing this opportunity to
make all this possible and Dr. Ah Yusuf, S.Kp.,
M.Kes for the advice.
REFERENCES
Allen, R. S. et al. (2014) ‘Can senior volunteers deliver
reminiscence and creative activity interventions?
results of the legacy intervention family enactment
randomized controlled trial’, Journal of Pain and
Symptom Management. Elsevier Inc, 48(4), pp. 590–
601. doi: 10.1016/j.jpainsymman.2013.11.012.
Azcurra, D. J. L. S. (2012) ‘Intervenção com um programa
de reminiscência para melhorar qualidade de vida de
residentes com Alzheimer com cuidados prolongados.
ensaio controlado randomizado’, Revista Brasileira de
Psiquiatria, 34(4), pp. 422–433. doi:
10.1016/j.rbp.2012.05.008.
Bailey, E. M. et al. (2017) ‘A Randomized Controlled
Trial of a Therapeutic Intervention for Nursing Home
Residents With Dementia and Depressive Symptoms’,
Journal of Applied Gerontology, 36(7), pp. 895–908.
doi: 10.1177/0733464815627956.
Charlesworth, G. et al. (2016) ‘Peer support and
reminiscence therapy for people with dementia and
their family carers: a factorial pragmatic randomised
trial’, Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery &
Psychiatry, 87(11), pp. 1218–1228. doi: 10.1136/jnnp-
2016-313736.
Elfrink, T. R. et al. (2017) ‘The effectiveness of creating
an online life story book on persons with early
dementia and their informal caregivers: a protocol of a
randomized controlled trial’, BMC Geriatrics. BMC
Geriatrics, 17(1), p. 95. doi: 10.1186/s12877-017-
0471-y.
Gonzalez, J. et al. (2015) ‘Reminiscence and dementia: A
therapeutic intervention’, International
Psychogeriatrics, 27(10), pp. 1731–1737. doi:
10.1017/S1041610215000344.
Gudex, C. et al. (2010) ‘Consequences from use of
reminiscence - a randomised intervention study in ten
Danish nursing homes’, BMC Geriatrics, 10(1), p. 33.
doi: 10.1186/1471-2318-10-33.
Hsu, T.-J. et al. (2017) ‘Predictors of non-pharmacological
intervention effect on cognitive function and
behavioral and psychological symptoms of older
people with dementia’, Geriatrics & Gerontology
International, 17, pp. 28–35. doi: 10.1111/ggi.13037.
Ito, T. et al. (2007) ‘A randomized controlled trial of the
group reminiscence approach in patients with vascular
dementia’, Dementia and Geriatric Cognitive
Disorders, 24(1), pp. 48–54. doi: 10.1159/000103631.
Mahendran, R. et al. (2017) ‘Art therapy and music
reminiscence activity in the prevention of cognitive
decline: study protocol for a randomized controlled
trial’, Trials. Trials, 18(1), p. 324. doi:
10.1186/s13063-017-2080-7.
Pringle, A. and Somerville, S. (2013) ‘Computer-assisted
reminiscence therapy: developing practice’, Mental
Health Practice, 17(4), pp. 34–37. doi:
10.7748/mhp2013.12.17.4.34.e830.
Pruszy, J. J. (2015) ‘Non-cognitive symptoms of dementia
Niekognitywne objawy demencji’, (7), pp. 477–481.
Randall, C. P. and Neill, A. J. O. (2011)
‘Reminiscence of People With Dementia Mediated by
Multimedia Artifacts’, I Can, (November). doi:
10.1093/glycob/cww118.
Wang, J. J., Yen, M. and OuYang, W. C. (2009) ‘Group
reminiscence intervention in Taiwanese elders with
dementia’, Archives of Gerontology and Geriatrics,
49(2), pp. 227–232. doi:
10.1016/j.archger.2008.08.007.
WHO (2017) Dementia. Available at:
http://www.who.int/news-room/fact-
sheets/detail/dementia.
Woods, R. T. et al. (2009) ‘Reminiscence groups for
people with dementia and their family carers:
pragmatic eight-centre randomised trial of joint
reminiscence and maintenance versus usual treatment:
a protocol’, Trials, 10(1), p. 64. doi: 10.1186/1745-
6215-10-64.
Yasuda, K. et al. (2013) ‘Daily Assistance for Individuals
With Dementia via Videophone’, American Journal of
Alzheimer’s Disease & Other Dementiasr, 28(5), pp.
508–516. doi: 10.1177/1533317513494440.
Reminiscence Therapy as a Strategy to Prevent Cognitive Decline in Elderly People
441
