
The Analysis on Protein Energy Supply Concerning Stunting
Incidents in Young Children Under Five Year Old at Primary Care
Unit of Tanah Kali Kedinding Surabaya
Diyah Arini and Dwi Ernawati
Sekolah Tinggi Ilmu Kesehatan Hang Tuah Surabaya, East Java, Indonesia
Keywords: Energy, Protein, Stunting.
Abstract: The most common problem infectious diseases that can reduce energy and protein intake and could impact
on stunting on toddlers. The highest prevalence of stunting among children under five in Surabaya City in
2016 is found at Tanah Kali Kedinding Primary Care Unit. The purpose of this study is to analyze the intake
of protein energy to stunting events in toddlers. The design is cross-sectional approach with simple random
sampling. The sample size is 71 children. The study population was Toddlers aged 2-5 years who are
stunted. Independent variables are the status of infectious diseases (diarrhea and RTI), economic status,
energy and protein intake . The dependent variable was the incidence of stunting. Microtoise and
questionnaire used to measure the variables with multinomial logit approach. The results showed that there
was a significant relationship between energy intake and incidence of stunting in toddlers with p = 0.001
and there was a significant correlation between protein intake with the incidence of stunting in under five
years, with p-value = 0.006. The primary prevention of stunting events is prenatal and postnatal maternal
and infant interventions in the first 1000th days of life by meeting protein energy requirements.
1 BACKGROUND
Infancy is an important period in the process of
human growth and development. Growth and
development in this age occurs in a rapid period and
will never be repeated, because it is often called the
golden age, but is in this period when they are
susceptible to a disease which affects the nutritional
status of their future. A common problem these days
is that the emergence of infectious diseases can
reduce the intake of toddlers, by consequent it will
have an impact, one of them is
stunting(Soetjiningsih, 2013). Observations and
interviews with health workers in Primary Care Unit
of Tanah Kali Kedinding Surabaya, the incidence of
stunting were higher in the PHC; the main cause is
that the education factor is low (60% majority of
junior), odd jobs such as street vendors and daily
workers whose Minimum Wage income is far from
the other people, only about 500 thousand to 1
million per month. Many mothers also work to
supplement the family income, so it affects the
feeding, nutrition, and parenting / childcare.
Basic Health Research noted that the national
prevalence of stunting was 37.2%, showing an
increase compared to 2010 (35.6%) and 2007
(36.8%), which is composed of 18.0%, is very short
and 19.2 % short, which means there has been an
increase of 1.6%. The prevalence of stunting (height
/ Age) is higher than the prevalence of underweight
or malnutrition (W / A) (19.6%) and the prevalence
of wasting or underweight (weight / height) (5.3%)
among children under five in Indonesia(Kemenkes
RI, 2013). One of the three health centers which
have the highest prevalence of stunting in Surabaya
is Primary Care Unit of Tanah Kali Kedinding
Surabaya equating to 25.37%. In 2013, the
prevalence of stunting in Primary Care Unit of
Tanah Kali Kedinding reached 21.86% and
increased in 2014 to 22.69%, and increased again in
2015 to reach 23.63%. The latest data in 2016,
shows that the prevalence of stunting in the health
center reached 25.37%. Low energy intake on the
incidence of children at risk of stunting 2.52 times
higher compared to the good or normal energy
intake. While the protein intake of <80%. Nutritional
Adequacy Rate (AKG) is at risk of stunting 6.4
596
Arini, D. and Ernawati, D.
The Analysis on Protein Energy Supply Concerning Stunting Incidents in Young Children Under Five Year Old at Primary Care Unit of Tanah Kali Kedinding Surabaya.
DOI: 10.5220/0008329305960600
In Proceedings of the 9th International Nursing Conference (INC 2018), pages 596-600
ISBN: 978-989-758-336-0
Copyright
c
2018 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

times higher than in children with ≥80% protein
consumption. LBW children who experience
indigestion because the gastrointestinal tract is not
functioning properly,(Trihono et al, 2015) , WHO
set of interventions that can be used to combat
stunting is prenatal and postnatal intervention.
Mothers play an important role in supporting efforts
to address nutritional issues, especially in the family
nutritional intake, ranging from food preparation,
selection of groceries, to the food menu. One of the
important programs that should be done by health
workers is Maternal & Child Health Centre. Health
workers should form a cadre of the best goal for the
implementation of education to mothers with young
children effectively and height measurements
reported by appropriate age. The most important
education was exclusively breastfed until 6 months
of age, and from the age of 6 months, in addition to
breastfeeding infants should also be given a
Complementary feeding (MP-ASI) and continued
breastfeeding until the baby is 2 years old or more.
The purpose of this study is to analyze the intake
of protein energy to stunting events in toddlers in the
area of the Tanah Kali Kedinding Surabaya Primary
Care Unit
2 METHODS
This study was design utilizes observational analysis
with cross-sectional approach. The study population
was Toddlers aged 2-5 years who are stunted at
Primary Care Unit of Tanah Kali Kedinding
Surabaya. Probability Sampling with Simple
Random Sampling. The sample size in this study
was 71 respondents. Independent variables in this
study the status of infectious diseases (diarrhea and
RTI), economic status, energy and protein intake.
The dependent variable in this study was the
incidence of stunting. For this study is utilize dan
microtoise instrument used to measure the height of
a toddler with a precision of 0.1 cm and
questionnaires in research Arini Diyah on the
Relationship between breastfeeding patterns with the
frequency of diarrhea and acute respiratory infection
in children 6-12 months of Primary Care Unit at
Balongpangganng Gresik(Arini Diyah, 2011), to
determine the status of infectious disease that affects
children under five as well as a food frequency
questionnaire / FFQ semiquantitative, food intake
Furthermore, the data were processed using
software. The researchers began collecting data after
obtaining informed consent from the parents with
stunting toddler. the researchers measured the height
of the child and provided a questionnaire about the
factors that influence stunting. The questionnaire did
not name each of the toddlers but was given a code
to keep confidentiality. The analysis of data was
multinomial logit approach.
3 RESULTS
3.1. General Data
Table 1: Distribution of respondents by age of the
children, the father's height, mother's height, and
length of infants born at Primary Care Unit of Tanah
Kali Kedinding Surabaya
Characteristics of
Res
p
ondents
Frequency
(
f
)
Percentage
(
%
)
A
g
e Toddle
r
2-3 years 31 43.7
3-4 years 25 35.2
4-5 years 15 21.1
Hei
g
ht Da
d
≤ 150 c
m
57.0
151-160 c
m
25 35.2
161-170 c
m
31 43.7
> 170 c
m
10 14.1
Hei
g
ht Mrs.
≤ 150 c
m
26 36.6
151-160 c
m
37 52.1
161-170 c
m
8 11.3
> 170 c
m
00
The number of
infants in the
famil
y
<2 37 52.1
≥ 2 34 47.9
The number of
children
dependent parent
1
p
erson 17 23.9
2
p
ersons 40 56.3
≥ 3 14 19.7
Born Body
Length
≤ 45 c
m
68.5
46-50 c
m
49 69.0
51-55 c
m
16 22.5
> 55 c
m
00
The Analysis on Protein Energy Supply Concerning Stunting Incidents in Young Children Under Five Year Old at Primary Care Unit of
Tanah Kali Kedinding Surabaya
597
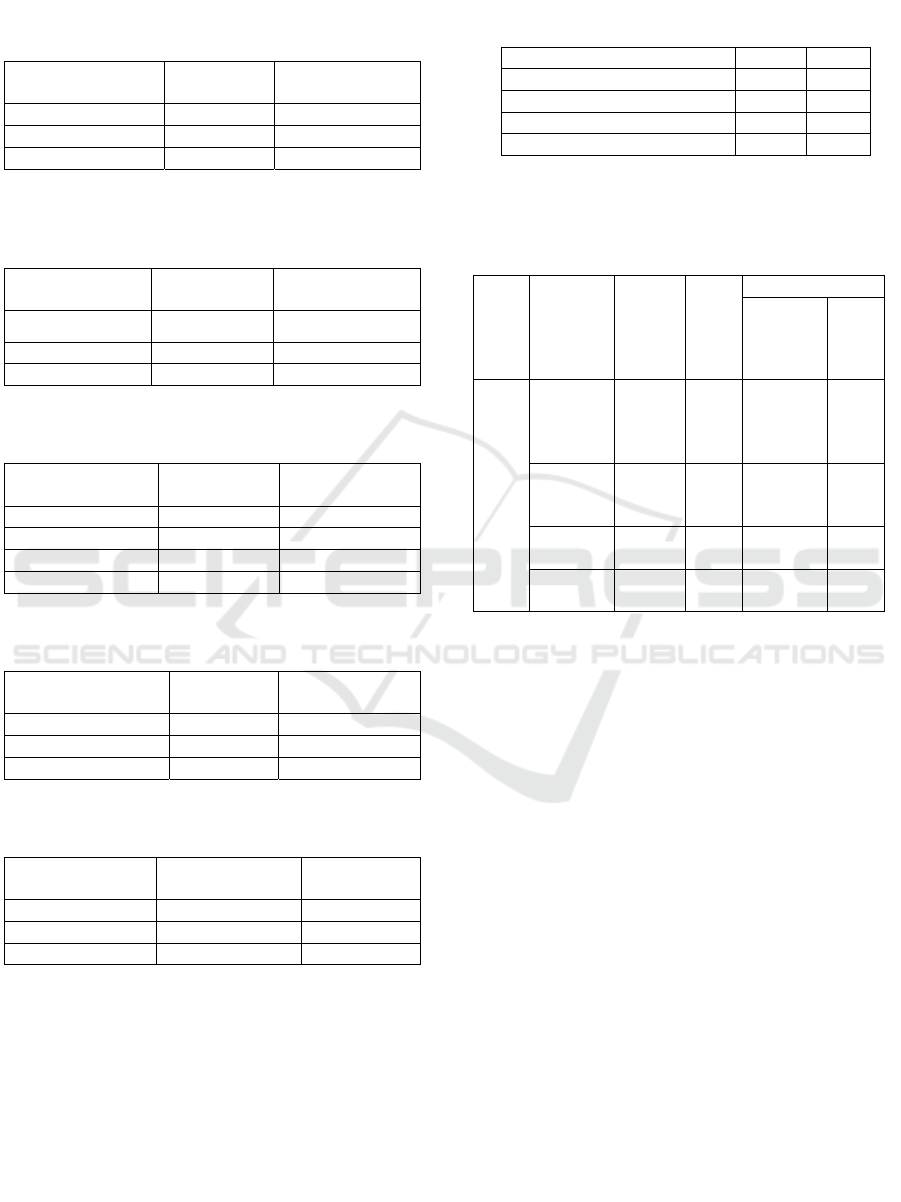
3.2 Custom Data
Table 7: Distribution of respondents by measurement
results based on the factors that influence the incidence of
stunting in primary care unit of Tanah Kali Kedinding
Surabaya
Variables Score Sign
Status of infectious diseases 7.324 0.007
Family Economic Status 6,918 0.009
Ener
gy
intake 10.701 0,001
Protein intake 7.614 0,006
Table 8: Distribution of respondents by measurement
results based on the factors that most influence the
incidence of stunting in primary care unit of Tanah Kali
Kedinding Surabaya
Dep
ende
nt
Vari
able
Indepen
dent
Variable
p
value
Exp
(B)
95% C
I
Lower Upp
er
Stun
-ting
Status of
infectio
us
diseases
0.998 3x
108
0,001
Family
Econom
ic Status
0.998 6x
107
0,001
Energy
intake
0.998 3x
108
0,001
Protein
intake
.120 65x
102
.613 68.
95
The results of the multinomial logit analysis
conducted last modelling results can be inferred
from the 4 factors that affected to the incidence of
stunting in Primary Care Unit of Tanah Kali
Kedinding Surabaya. protein obtained showed the p-
value = 0.12 with OR 65x102 means of protein
intake in infants have risk factors for 65x102 times
higher than any other factor.
4 DISCUSSION
There is a significant association between infectious
disease status in this regarding the incidence of
diarrhea and acute respiratory infection in infants.
This can be seen from the value of p = 0.007 (p
<0.05). The results showed that 36 toddlers and 14
toddlers severe stunting have ever experienced
infectious diseases (diarrhea or RTI) in the past year.
Infectious diseases is one of the direct causes of
infant nutritional status in addition to the
consumption of food.
Children who do not consume the nutrients
needed by the body will result in a low immunity, so
Table 2: Distribution of respondent toddler based on
primary care unit of Tanah Kali Kedinding Surabaya
Height Frequency
(f)
Percentage (%)
Stunting 57 19.7
Severe stuntin
g
14 80.3
amount 71 100
Table 3: Distribution of respondents by status of
infectious diseases at primary care unit of Tanah Kali
Kedinding Surabaya
Infectious
Disease Status
Frequency (f) Percentage (%)
There is 50 70.4
No 21 29.6
amount 71 100
Table 4: Distribution of respondents by economic status
in primary care unit of Tanah Kali Kedinding Surabaya
Family Economic
Status
Frequency (f) Percentage (%)
Low 50 70.4
secondary 20 28.2
Hi
g
h 1 1.4
a
mount
7
1
1
00
Table 5: Distribution of respondents by energy intake in
primary care unit of Tanah Kali Kedinding Surabaya
Energy intake Frequency
(f)
Percentage (%)
Low 44 62.0
Enou
g
h 27 38.0
amount 71 100
Table 6: Distribution of respondents by protein intake
on primary care unit of Tanah Kali Kedinding Surabaya
Protein intake Frequency (f) Percentage
(%)
Low 43 60.6
Enou
g
h 28 39.4
amount 71 100
INC 2018 - The 9th International Nursing Conference: Nurses at The Forefront Transforming Care, Science and Research
598

susceptible to disease infection, otherwise infections
such as diarrhea and RTI will result in the intake of
nutrients cannot be absorbed properly.(Ernawati
Dwi, 2014). The Research on stunting in the UK
shows the results of ongoing analysis of diarrhea to
stunting. Based on 24-month old children who
continuously experienced diarrhea for more than 14
days have a greater chance of experiencing stunting,
than children aged 24 months who had diarrhea for
less than 14 days(Checkley et al., 2008)
Toddlers who often suffer acute diarrhea will be
at greater risk of growing into stunting. During
diarrhea, bacteria get into the small intestine and
undergo multiplication. The bacteria release toxins
that will affect small intestinal mucosal cells
(stimulates enzyme adenilsiklase). These enzymes
transform Adenosine Tri Phosphate (ATP) to cyclic
Adenosine Mono Phosphate (cAMP) and cAMP
increased the expected increase in Cl ion secretion
into the intestinal lumen. Isotonic solution secretion
by intestinal mucosa (hypersecretion) as a result of
the formation of toxins will make the function more
absorption of intestinal mucosa impaired (decreased
number sakaridase enzyme, lipase, and
protease)(Almatsier Sunita, 2011). This results in
malabsorption of nutrients, dehydration and loss of
nutrients. If the condition is not treated immediately
and be balanced with adequate food intake, then
there will be severe dehydration, malnutrition and
failure to thrive. Diarrhea impact on linear growth in
children. If the child often had diarrhea within the
first 24 months of life, the child tends to be shorter
on 1.5 times(Checkley et al., 2008). Based on
previous research, on the 20 largest countries in the
world there is an 80% of children who had suffered
stunting, child malnutrition is accompanied by cases
of diarrhea by 51%, in the case of malaria by 57%,
cases of pneumonia by 52%, and measles cases by
45% ending in death(Hussein and Adam, 2015)
There is a significant correlation between the
economic status of families with incidence of
stunting in children under five in Primary Care Unit
of Tanah Kali Kedinding Surabaya, this can be seen
from the value of p = 0.009 (p <0.05). Showed that
36 toddlers and 14 toddlers severe stunting stunting
have parents with low economic status. Research in
Indonesia and Bangladesh show that children from
low-income families have higher risk of stunting
compared to children from families of higher
socioeconomic. This indicates that the family
economic circumstances affect the incidence of
stunting among children under five(Semba, 2016),
Social and economic factors include per capita
income, parental education, mother knowledge about
nutrition has also indirectly associated with the
incidence of stunting (Dian Hidayati, T. M. Thaib,
2010).
There is a significant relationship between
energy intake with stunting under-fives in Primary
Care Unit of Tanah Kali Kedinding Surabaya, this
can be seen from the value of p = 0.001 (p <0.05).
Showed that 30 toddlers and 14 toddlers severe
stunting has a low energy intake. The body is
experiencing a shortage of energy will experience
negative energy balance will be reduced so that the
weight of body weight should be. This will inhibit
growth in children and cause weight loss and tissue
damage in adults(Siagian Albiner, 2010), The intake
of nutrients that children need a complete continue
during the growth process continues because the
growth process is influenced by the food given to
children. The food given should be appropriate both
type and quantity to their nutritional content. The
child's body still needs all the main nutrients are
carbohydrates, fat, protein, fiber, vitamins and
minerals, if the lack of the growth of children,
including his height will be disrupted(Almatsier
Sunita, 2011), Adequate nutrition is necessary to
ensure optimal growth and development of infants
and children. Daily nutritional needs are used to run
and maintain the normal function of the body can be
done by selecting and food intake was good (quality
and quantity)(Sutomo Anggraini, 2010).
Food is a source of energy to support all human
activities. Their burning carbohydrates, protein, and
fat in the human body produces energy. Therefore,
in order that adequate human energy needed food
into the body adequately. Nutrient intake is not
adequate, especially of total energy, protein, fat and
micronutrients, are associated with physical growth
deficit in pre-school children(Almatsier Sunita,
2011), However, consumption, diet enough not
guarantee normal physical growth, because the
incidence of other diseases, such as acute or chronic
infection, can affect a complex process to the
occurrence or maintenance of growth deficits in
children. RISKESDAS data analysis in 2013 showed
no significant relationship between energy
consumption with the incidence of stunting in
children aged 12-59 months in Sumatra (Almatsier
Sunita, 2011).
There is a significant correlation between protein
intake with the incidence of stunting in children
under five in Primary Care Unit of Tanah Kali
Kedinding Surabaya, that can be seen from the value
of p = 0.006 (p <0.05). Showed that 30 toddlers and
13 toddlers with severe stunting has a low protein
intake. Malawi has a child stunting in serum
The Analysis on Protein Energy Supply Concerning Stunting Incidents in Young Children Under Five Year Old at Primary Care Unit of
Tanah Kali Kedinding Surabaya
599

concentrations of total 9 amino acids that are
required only 10-20 percent lower than a child who
is not stunting. Moreover, stunting children have low
serum concentrations of significant conditions
required amino acids (arginine, glycine, glutamine),
amino acids that are not needed (asparagine,
glutamate, serine), and 6 different sphingolipid than
children who are not stunting (Semba, 2016).
Other studies have shown that there is a
relationship type and amount of consumption can
affect the nutritional status that the end result
appears stunting in infants as in Budiarti research
that the type and amount of food is related to the
incidence of malnutrition in children under five in
Maternal & Child Health Centre of Kenanga 3 Bulak
Banteng Surabaya(Budiarti Astrida, Hastuti Puji,
2017) RISKESDAS shows the results of data
analysis in different provinces, there is a significant
correlation between protein intake with the
incidence of stunting in children under five
(Kemenkes RI, 2013).
Basic health research data consistently shows
that the average intake of calories and protein in
toddlers are still under Nutritional Adequacy Rate
(AKG). As a result of these circumstances, children
under five women and children under five
Indonesian men have an average height of each 6.7
cm and 7.3 cm shorter than the WHO reference
standard, 2005. Protein is needed for physical
growth, especially in height, because proteins are the
main component of bones. Protein is essential for the
normal functioning of almost all cells and metabolic
processes, thus a deficit in this nutrient has many
clinical effect(Kemenkes RI, 2013). Interventions to
address stunting in Indonesia has strived good
government through the Ministry of Health and
related agencies. Interventions related to energy and
protein intake is agriculture ministry efforts to
fortify foodstuffs (Salt, Flour and cooking oil) and
the efforts of the health ministry of education and
nutrition through Maternal & Child Health Centre
so that the incidence of stunting in Indonesia soon
declined and did not happen again (Tim Nasional
Percepatan Penanggulangan Kemiskinan, 2017).
5 CONCLUSIONS
The analysis showed that the factor protein intake
has a protein intake in infants with risk factors for
65x102 times higher than the factor of infectious
disease status, economic status, and energy intake.
The primary prevention of stunting events is prenatal
and postnatal maternal and infant interventions in
the first 1000th days of life by meeting protein
energy requirements.
REFERENCES
Almatsier Sunita (2011) Prinsip Dasar Ilmu Gizi. Jakarta:
PT Gramedia Pustaka.
Arini Diyah (2011) ‘Hubungan Antara Pola Pemberian
ASI Dengan Frekuensi Kejadian Diare Dan ISPA Pada
Anak 6-12 Bulan Di Wilayah Puskesmas
Balongpanggang Gresik’.
Budiarti Astrida, Hastuti Puji, A. V. (2017) ‘Correlation
Between Dietary Intake With Protein Energy
Malnutrition of Child 1-5 Years Old In Posyandu’, in
Proceeding of Surabaya International Health
Conference. Surabaya, pp. 455–460.
Checkley, W. et al. (2008) ‘Multi-country analysis of the
effects of diarrhoea on childhood stunting’,
International Journal of Epidemiology, 37(4), pp.
816–830. doi: 10.1093/ije/dyn099.
Dian Hidayati, T. M. Thaib, D. S. (2010) ‘Faktor-Faktor
Yang Berhubungan Dengan Stunting Pada Balita Usia
12-59 Bulan Di Kecamatan Darul Kamal Kabupaten
Aceh Besar’.
Ernawati Dwi (2014) ‘Pijat Bayi Mempengaruhi Kadar
Kortisol Dan Kuantitas Tidur Bayi Yang Mengalami
Hospitalisasi Dengan Pendekatan Teori Comfort
Kolcaba’, Jurnal Ilmiah Kesehatan, 7, pp. 138–150.
Hussein, A. M. and Adam, D. (2015) ‘Risk Factors of
Protein Energy Malnutrition Deficiency among
Children Under Five Years at Alruhal Camp-Kass
Locality South Darfur State 2012 Sudan’, Journal of
Bacteriology & Parasitology, 6(6), pp. 8–11. doi:
10.4172/2155-9597.1000252.
Kemenkes RI (2013) Riset Kesehatan Dasar. Jakarta:
Badan penelitian dan pengembangan Kesehatan.
Semba, R. D. (2016) ‘The rise and fall of protein
malnutrition in global health’, Annals of Nutrition and
Metabolism, 69(2), pp. 79–88. doi:
10.1159/000449175.
Siagian Albiner (2010) Epidemiologi Gizi. Jakarta: EGC.
Soetjiningsih (2013) Tumbuh Kembang Anak. Jakarta:
EGC.
Sutomo Anggraini (2010) Makanan Sehat Pendamping
ASI. Jakarta: Demedia.
Tim Nasional Percepatan Penanggulangan Kemiskinan
(2017) 100 Kabupaten/Kota Prioritas Untuk
Intervensi Anak Kerdir (Stunting), Ringkasan. Jakarta:
Sekretariat Wakil Presiden Republik Indonesia.
Trihono et al (2015) Pendek (stunting) di Indonesia,
Masalah dan solusinya. Edited by Sudomo. Jakarta:
Lembaga penerbit Balitbangkes.
INC 2018 - The 9th International Nursing Conference: Nurses at The Forefront Transforming Care, Science and Research
600
