
The Status of BCG Immunization in Pre-Schoolers in Relation with
Pulmonary Tuberculosis Incidence in North Surabaya
Dini Mei Widayanti, Sapto Dwi Anggoro and Ita Hernawati
STIKES Hang Tuah Surabaya, East Java, Indonesia
Keywords : Immunization, Tuberculosis, Pre-schoolers.
Abstract: Tuberculosis (TB) is an infectious disease caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Immunization is an
attempt to provide immunity to pre-schoolers by introducing vaccines into the body. The purpose of this
study was to analyze the relationship of BCG immunization status and the incidence of TB in pre-schoolers.
The research design used analytical observation with Cross-Sectional approach. Simple random sampling
was taken as data collection technique, with population of 80 pre-schoolers and 67 were appointed as the
respondents. The instruments were interviews and observations. The data were analyzed by Chi-squared test
with significance level of p <0.05. The results of the study indicated that 43 immunized pre-schoolers, 28 of
whom were not infected by lung TB, 9 were infected and 6 were suspects. The other group of 24 non-
immunized pre-schoolers indicated that 14 were not infected, 1 was infected and 9 were suspects. Chi-
square statistical test results showed that BCG immunization status had a relationship with the incidence of
TB in pre-schoolers with p = 0.033 (p <0.05).The research has come to a conclusion that BCG
immunization is very important for pre-schoolers to maintain their immunity. It is expected for parents to be
aware of getting their children immunized.
1 BACKGROUND
Tuberculosis (TB) is an infectious disease caused by
Mycobacterium Tuberculosis. According to Hidayat
(2009), immunization is an effort to provide
immunity to pre-schoolers and children by entering
the vaccine into the body to make antibodies to
prevent certain diseases. Based on the high
incidence of TB incidence in our country and the
unavoidable transmission process, the most effective
prevention is through BCG vaccination (Ikatan
Dokter Anak Indonesia, 2011). Although there has
not been proven the efficacy of BCG immunization
consistently, until now the immunization is still
effective and safe. BCG is one way to control TB
(Rahajoe, 2005 in Welldany Siregar 2008). A child
who has been immunized with BCG and yet he is
infected with TB bacteria, in general it does not
develop into tuberculosis (Mufidah, 2012). But not
all diseases can be prevented by vaccination,
including BCG vaccination to prevent tuberculosis
infection. Reduced protection by BCG is possible
due to many factors such as ineffective and efficient
BCG administration procedures (Islamiati, 2009 in
Miswan efendi 2012). From interviews with a
number of parents it has been found that some pre-
schoolers, who have been immunized in North
Surabaya are infected with TB.
Pulmonary tuberculosis is one of the chronic
infectious diseases that has become global issues
targeted in the MDGs and are also listed in the MSS
of health. In Indonesia, this disease is one of the
national priorities for disease control program
because it has a broad impact on life quality and
economy, and it often leads to death. Nevertheless,
the indicator of MSS of tuberculosis disease is only
'new case finding', whose indicator does not yet fully
describe the treatment of tuberculosis (Laksono,
2012). Eight goals of the MDGs that must be
implemented by each country that declares them; 1)
tackling poverty and hunger, 2) achieving basic
education for all, 3) promoting gender equality and
empowering women, 4) reducing child mortality, 5)
improving maternal health, 6) combating HIV /
AIDS, malaria and other infectious diseases, 7)
ensuring environmental sustainability, and 8)
developing a global partnership for development.
Indonesia as one of the participating countries in
declaring the MDGs' goals has an obligation to
implement efforts to achieve the MDGs targets and
Widayanti, D., Anggoro, S. and Hernawati, I.
The Status of BCG Immunization in Pre-Schoolers in Relation with Pulmonary Tuberculosis Incidence in North Surabaya.
DOI: 10.5220/0008329706150620
In Proceedings of the 9th Inter national Nursing Conference (INC 2018), pages 615-620
ISBN: 978-989-758-336-0
Copyright
c
2018 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
615

to monitor progress towards achievement (Dr.
Afrina Sari).
Tuberculosis (TB) is a serious problem for the
world, because it causes the major deaths compared
to other infectious diseases. It is estimated that about
one-third of the world's population has been infected
by Mycobacterium Tuberculosis. An estimated 95%
of Pulmonary TB cases and 98% of deaths spread
across the world, mostly those in developing
countries (Depkes RI 2007). Globally, there are
8,800,000 new cases of TB in the world in 2010.
(Hendry J, WHO, Global Tuberculosis Control
2011). In Indonesia every year there are 1.3 million
children under 15 years old who are infected with
TB germs and annually there are 450,000 child
deaths due to this disease as recorded by Samallo in
FKUI. A preliminary study conducted by researchers
on February 4, 2015, drawn from the data of 5 pre-
schoolers at Perak Timur Surabaya Community
Health Center, resulted in 40% TB, 20% suspect and
40% non-TB.
Tuberculosis (TB) is accepted as a major issue. It
needs a thorough handling as well as the attention of
health care services, government and society as a
whole (Wahyu, 2008). Based on the results of the
theory of several factors related to the occurrence of
lung tuberculosis in children include: immature
immune system, close contact with adults with
tuberculosis nearby (parents, close relatives, and
caregivers), and lack of awareness of parents to
immediately vaccinate BCG in newborns (Wahyu,
2008 in Miswan Efendi 2012). Pre-schoolers who
suffer from pulmonary TB are mostly due to
transmission from adult patients. Transmission of
tuberculosis disease from air contaminated by
Mycobacterium Tuberculosa released by the patients
when cough in the form of droplets (Depkes RI ,
2005). One effort to prevent the occurrence of
pulmonary TB disease is by immunization.
However, reduced protection by BCG is possible
due to many factors such as ineffective and efficient
BCG administration procedures (Islamiati, 2009 in
Miswan Efendi 2012). This study aims at finding the
correlation of the BCG immunization status and
Pulmonary TB incidence in Preschoolers.
2 METHODS
This research used Analytical observation design
with Cross-Sectional approach, by which the
researcher intended to describe the relationship of
BCG Immunization Status with Pulmonary TB
incidence in Toddler in North Surabaya. The
population in this research is all 80 patients of pre-
schoolers at Puskesmas Tambak Gringsing, Perak
Timur of Surabaya. The sample of this research was
a group of 67 respondents who met with the
following criteria: inclusive kriteria is mothers
possessing KMS (Health Status Card) and mothers
with 0-5 year old children. Exclusive kriteria is
mothers who were unwilling to participate in the
research.
The sampling technique undertaken in this
research was simple random sampling. The
independent variable was the status BCG
immunization. In addition, the dependent variable of
this research was the incidence of pulmonary TB in
children under five years old.
The instrument used in this research were
observations and interviews. The Status of BCG
Immunization were looked upon the respondents’
Health Status Card or The so-called KMS. It was
intended to identify the immunization status. Apart
from that medical record document was used to
determine the status of TB incidence in pre-
schoolers with several criteria of: TB-sufferers
(TBSF), TB-suspects (TBSS), and Non-TB-sufferers
(NTBSF). In data collection, the researcher asked
the for informed consents from the respondents prior
to interviews and observations. However, this phase
was initiated with a permit from the Head of East
Perak region Puskesmas.
2.1 Data Analysis
Data analysis technique is done by statistical test
with Chi-Square analysis with significance value
0,05 meaning p <α 0,05 hence hypothesis accepted
which mean there is relation of BCG immunization
status with the incidence of pulmonary tuberculosis
in under five years old children in Tambak
Gringsing, Perak Primary Care Unit of Surabaya. If
p> α 0.05 means the hypothesis is rejected, which
means that there is no relationship between BCG
immunization status and the incidence of pulmonary
tuberculosis in under five years old children in
Tambak Gringsing, Perak Primary Care Unit of
Surabaya.
2.2 Research Ethics
This research has undergone ethical procedure in
terms of: btaining ethical clearance issued by LP3M
Stikes Hang Tuah Surabaya number:
SKET/01.a/III/2015/LP3M/SHT, providing
Informed Consent sheet, assuring confidentiality and
considering anonimity.
INC 2018 - The 9th International Nursing Conference: Nurses at The Forefront Transforming Care, Science and Research
616
3 RESULTS
3.1 Research Results
3.1.1 Respondents’ Characteristics
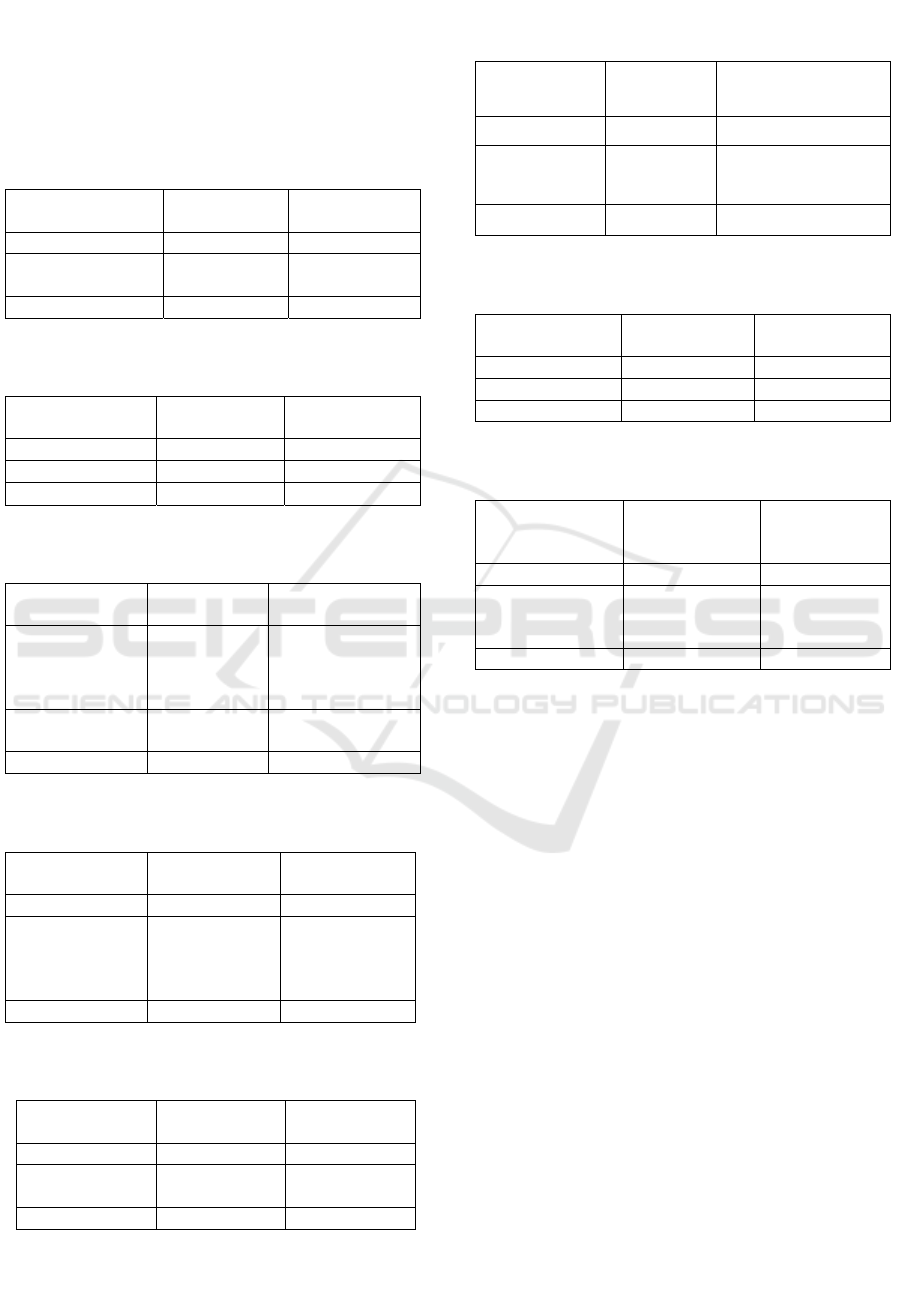
Based on table 1, it was found that most of the
respondents aged> 30 years. Based on table 2, it was
found that most of the respondents are female. Based
on table 3, it was found that the respondents'
education was secondary school. Based on table 4, it
was found that the majority of respondents' parents’
occupation was house-wife. Based on table 5, it was
found that the respondents’ family income was
<2.700.000. Based on table 6, it is found that the
majority of the respondents was 2-4 years 53.7% (36
respondents). Based on table 7 The majority of the
respondents’ sex was female. Based on table 8, it
was found that the respondent's time of getting
vaccination was mostly at the age of 1-5 months old.
3.1.2 Variables
Specific data presented table data about the
relationship of BCG immunization status with the
incidence of pulmonary tuberculosis in under five
years old children in Tambak Gringsing, Perak
Primary Care Unit of Surabaya. From these results
can be known whether or not there is a strong
relationship between the two variables with
Table 1: Respondents’ characteristics based on age.
Characteristics
(
mother’s a
g
e
)
Frequency Percentage
(
%
)
<25
y
ea
r
5 7.5
25-30 year
>30
y
ea
r
30
32
44.8
47.8
Total 67 100
Table 2: Respondents’ characteristics based on the
parents’ sex.
Characteristic
(sex)
Frequency Percentage (%)
Female 45 67.2
Male 22 32.8
Total 67 100
Table 3: Respondents’ characteristics based on the
parents’ educational background.
Characteristic
(
p
endidikan
)
Frequency Percentage (%)
Uneducated
Primary
Junior Hi
g
h
0
14
25
0
20.9
37.3
Senior High
College
25
3
37.3
4.5
Total 67 100
Table 4: Respondents’ characteristics based on the
parents’ occupation.
Characteristic
(
occu
p
ation
)
Frequency Percentage (%)
Civil Servant 2 3
Private
Own Business
House-wife
Unemployed
11
14
37
3
16.4
20.9
55.2
4.5
Total 67 100
Table 5: Respondents’ characteristics based on
parents’ income.
Characteristic
(
income
)
Frequency Percentage
(
%
)
<2.700.000 53 79.1
2.700.000
>2.700.000
12
2
17.9
3
Total 67 100
Table 6: Respondents’ characteristics based on
children’s age.
Characteristics
(Current age)
Frequency Percentage (%)
1-2 year 13 19.4
2-4 year
5 year
36
18
53.7
26.9
total 67 100
Table 7: Respondents’ characteristics based on the
children sex.
Characteristic
(Children’s Sex)
Frequency Percentage (%)
Female 35 52.2
Male 32 47.8
Total 67 100
Table 8: Respondents’ characteristics based on under
five-year-old children’s time of BCG immunization.
Characteristic
(Age when
Immunized
)
Frequency Percentage
(%)
Not immunize
d
24 35.8
1-5 months
6-10 months
11-15 months
39
3
1
58.2
4.5
1.5
Total 67 100
The Status of BCG Immunization in Pre-Schoolers in Relation with Pulmonary Tuberculosis Incidence in North Surabaya
617
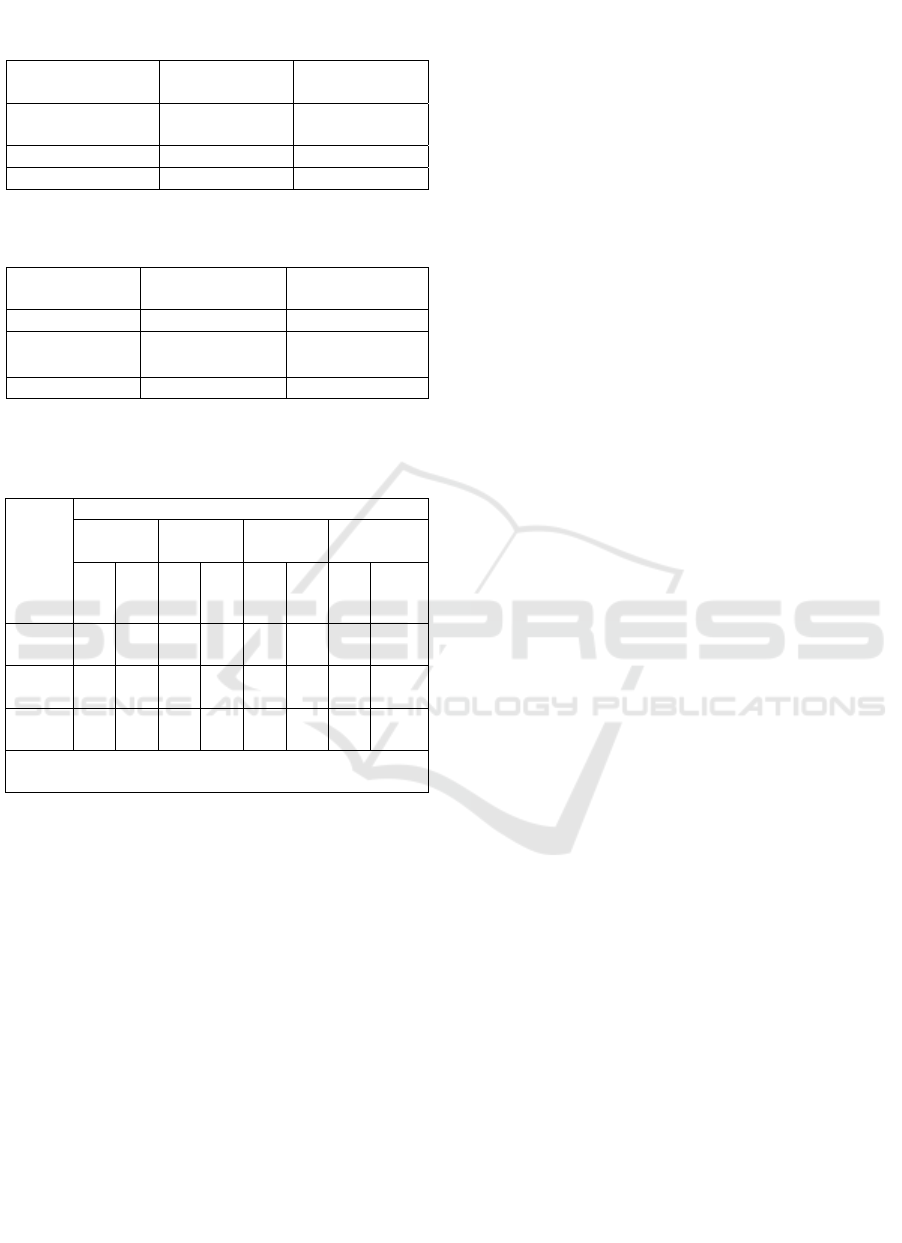
statistical analysis Chi-Square test. Table 9 showed
that respondents based on immunization status who
did not immunize BCG were 35.8% (24
respondents), and BCG immunization was 64.2%
(43 respondents). Table 10 shows that 62.7% (42
respondents) did not have TB, which suspected TB
as much as 22.4% (15 respondents), and 14.9% for
TB (10 respondents). Table 11 showed the
relationship of immunization status and the
incidence of tuberculosis in children. Based on Chi-
Square test results obtained value = 0.033 <α = 0.05,
which means there is a statistically significant
relationship between immunization status and the
incidence of pulmonary TB in infants.
4 DISCUSSION
4.1 BCG Immunization Status of
Children Under 5 Years Old at
Tambak Gringsing, Perak Timur of
Surabaya
The results of the research in Table 5.9 showed that
respondents were 24 respondents (35.8%) who were
not immunized and 43 respondents (64.2%) were
immunized.
According to Maryanti, et al (2011) BCG
immunization is a preventive effort for the type of
tuberculosis infection (TB) in children. An
immunization used to prevent the occurrence of
severe TB disease due to the incidence of primary or
minor TB disease can occur despite BCG
immunization, prevention of BCG immunization for
severe tuberculosis such as tuberculosis in the lining
of the brain, tuberculosis Milier (in all lung fields) or
TB BCG bone immunization is a vaccine containing
TB germs that have been attenuated.
The frequency of BCG immunization is 0-11
months, but it is generally given to 2 or 3 months of
age (Hidayat, 2009).
4.2 The Incidence of Pulmonary TB
The result of the research in table 5.10 shows that
the respondents of lung tuberculosis cases in infants
as many as 42 respondents (62.7%) did not suffer
tuberculosis with respondents who vaccinated at 1-5
months of age as many as 25 (64.1%) respondents,
6-10 months 2 (66.7% ) of respondents, and 11-15
month olds as many as 1 (100%) respondents, while
unvaccinated were 14 (58.3%) respondents.
Because BCG immunization is an immunization
given to infants aged 0-2 months who aims to
prevent tuberculosis. Due to an imperfect immune
system, close contact with adults with tuberculosis
around them (parents, close relatives, and carers)
(Wahyu, 2008).
According to Herry (2011), there are three
pulmonary TB risk factors, namely density, density
of residence affecting the cause of disease
transmission. The more densely settled, the more
rapid the disease transmitted through the air, the
temperature in the room closely related to the
density of shelter and ventilation. Pulmonary TB
germs will become inactive by sunlight that can kill
the vital function of the organism. Density of
residence set by Depkes (2008).
Table 9: Respondents’ characteristics based on
immunization status.
Immunization
Status
Frequency Percentage (%)
Non BCG
immunized
24 35.8
BCG Immunized 43 64.2
Total 67 100
Table 10: The incidence of pulmonary tb in children
under 5 year old.
The Incidence
of TB
Frequency Percentage (%)
Not Infecte
d
42 62.7
TB Suspects
TB Infected
15
10
22.4
14.9
Total 67 100
Table 11: The correlation of BCG immunization status
and the incidence of pulmonary tb in children under 5
year old at Tambak Gringsing, Perak.
BCG
Imm
uniza
tion
Statu
s
Incidence in under 5 Year old Children
Non TB
Suspect
s
TB Total
f % f % f % n %
No
14
58
,3
9
37
,5
1
4,
2
24 100
Yes
28
65
,1
6
14
,0
9
20
,9
43 100
Total
42
62
,7
15
22
,4
10
14
,9
67 100
Result of Chi-Square didapatkan
nilai ρ = 0.033 < α = 0.05
INC 2018 - The 9th International Nursing Conference: Nurses at The Forefront Transforming Care, Science and Research
618

Contact history, close and prolonged contact
with adult TB sufferers who live at home, also
facilitate the occurrence of TB transmission. House
contact with TB patients is one of the risk factors for
TB.
4.3 The Correlation of BCG
Immunization Status and The
Incidence of Pulmonary TB
The relationship between immunization status
relationship with the incidence of pulmonary
tuberculosis in infants as shown in Table 5.11
according to Chi-Square test results obtained ρ =
0.033 <α = 0.05, it means statistically there is a
relationship of BCG immunization status with the
incidence of pulmonary tuberculosis in toddlers at
Tambak Gringsing, Perak Timur Primary Care Unit
of Surabaya..
Based on the research data, 67 (100%) were not
immunized with BCG of 24 people (62.7%) and
those who did not have TB 14 people (58.3%) were
more dominant than those who did not immunize
with the suspect as many as 9 people (37.5%),
immunization with TB as much as 1 (4.2%). BCG
immunization is an immunization given to infants
aged 0-2 months who aims to prevent tuberculosis
(TB). According to Maryanti, et al (2011) BCG
vaccine given to infants aged 0-12 months by
intracutan injection with a dose of 0.05 ml. BCG
vaccine otherwise successful when tubercular
conversion occurs at the injection site.
Based on the result of the immunization research,
there were 43 people (64.2%) who had not TB 28
people (65.1%), the TB 9 people (20.9%), and the
suspect 6 people (14.0%). According to Rahajoe,
2005 in Welldany siregar 2008 Although it has not
proven the efficacy of BCG immunization
consistently, so now the immunization is still
effective and safe given. BCG is one of the efforts of
TB prevention efforts. The occurrence of pulmonary
tuberculosis in children can be caused by several
things other than due to contact with adult patients
and BCG immunization.
Other factors include children occupying densely
populated homes, children's homes in humid
conditions, house ventilation and children's
inadequate temperature, insufficient house lighting,
exposure to cigarette smoke, economic status,
nutritional status and toddlers who are not
exclusively breastfed.
5 CONCLUSIONS
Based on the results of the research that has been
done in Ponds Gringsing Area Puskesmas Perak
Timur Surabaya, it can be concluded as follows: 1)
BCG immunization was mostly given to pre-
schoolers; 2) Most pre-schoolers do not suffer from
Pulmonary TB; 3) There is a relationship between
the status of BCG immunization with the incidence
of pulmonary tuberculosis. This study could be
accepted as a source of information for future
research, healthcare services, as well as parents.
However, this study could be lack of accuracy in
determining Limitations of the study were in terms
some technical problems in collecting data that
might affect the accuracy of data report.
REFERENCES
Aru W, Bambang S. Dkk. (2006). Buku Ajar Ilmu
Penyakit Dalam. Jakarta:Pusat Penerbit Departemen.
Artikelkesehatananak.com/imunisasi-bcg-gagal.html.
Tanggal 10/03/2015. jam 16.30.
Behrman, Richard E, Kligman, robert M.. Dkk. (2012).
Ilmu Kesehatan Anak Nelson. Jakarta : EGC.
Depkes RI. (2007). Pedoman Nasional Penanggulangan
Tuberkulosis. Jakarta: Depkes RI
_________. (2007). Pedoman Nasional Penanggulangan
Tuberkulosis. Jakarta.
Depkes, RI. (2002). Pedoman Nasional Penanggulangan
Tuberkulosis. Jakarta.
dr. Genis Ginanjur W. (2008). Panduan Parktis Mencegah
Dan Menangkal TBC Pada Anak. Jakarta: Dian
Rakyat.
Efendi, miswan. (2012). Dalam Skripsi : Hubungan
Kontak Dengan Penderita Dewasa Dan Imunisasi Bcg
Dengan Kejadian Tuberkulosis Paru Balita Di Poli
Anak Rsud Dr. M. Yunus Bengkulu Tahun 2012.
Bengkulu.http/stikesdehasen.ac.id/downlot.php?File=
Skripsi%20Tuk%20 kaset.pdf.Tanggal 02/03/2015.
Jam 16.00
Hidayat, A. Aziz Alimul. (2009). Pengantar Ilmu
Keperawatan Anak 1. Jakarta: Salemba Medika.
Hidayat, A. Aziz Alimul. (2012). Pengantar Ilmu Anak 2.
Jakarta: Salemba medika.
IDAI. (2011). Pedoman Imunisasi Di Indonesia Edisi
Keempat. Jakarta: Badan Penerbit Ikatan Dokter Anak
Indonesia.
IDAI. (2011). Panduan Imunisasi Anak (Mencegah Lebih
Baik Dari Pada Mengobati). Jakarta: Badan Penerbit
Ikatan Dokter Anak Indonesia.
Laksono, Agung Dwi dkk. (2012). Kajian Standar
Pelayanan Minimal Penyakit Tuberkulosis Terkait
Indikator Millennium Development
Goals.http://ejournal.litbang.depkes.go.id/index.php/h
The Status of BCG Immunization in Pre-Schoolers in Relation with Pulmonary Tuberculosis Incidence in North Surabaya
619

sr/article/view/3000, diunduh pada tanggal 26 Maret
2015 pada jam 07.00 WIB.
Mandal, B. K.. Dkk. (2008). Penyakit Infeksi. Ed ke-6.
Jakarta: Erlangga.
Maryanti, Dwi, Dkk. (2011). Buku Ajar Neonatus, Bayi
Dan Balita. Jakarta: TIM.
Maryunani, Anik. (2010). Ilmu Kesehatan Anak Dalam
Kebidanan. Jakarta: TIM.
Mufidah, Fatchul. (2012). Cermati Penyakit-Penyakit
yang Rentan Di Derita Anak Usia Sekolah. Jogjakarta:
Flashbooks.
Ngastiyah. (2005). Perawatan Anak Sakit. Jakarta. EGC.
Putra, Sitiatava Rizema. (2012). Asuhan Neonatus Bayi
Dan Balita Untuk Keperawatan Dan Kebidanan.
Jogjakarta: D-Medika.
Rudolph, Abraham M. Dkk. (2006). Buku Ajar Pediatri
Rudolph. Ed.20. vol.1. Jakarta: EGC.
Setiadi. (2013). Konsep Dan Praktik Penulisan Kiset
keperawatan. Ed 2. Yogyakarta: Graha Ilmu.
Septiari, Bety Bea. (2012). Mencetak Balita Cerdas Dan
Pola Asuh Orang Tua. Yogyakarta: Nuha Medika.
Soegeng soegijanto. (2007). Kumpulan Makalah Penyakit
Tropis Ian infeksi Di Indonesia. Surabaya: Airlangga
University Press.
Sunyoto Danang, Setiawan Ari. (2013). Buku Ajar
Statistik Kesehatan Paramatrik, Non Paramatik,
Validitas, Dan Reliabilitas. Yogyakarta: Nuha
Medika.
Triton. (2006). Mengasuh Dan Perkembangan Balita.
Yogyakarta: Oryza.
Usu intutional Respository : Open acces Respitory-
perbedaan hasil uji montoux pada anak umur 3 bulan-
16 bulan yang kontak serumah dengan penderita
tuberkulosis BTA (+) yang telah diimunisasi dan
belum imunisasi BCG. Tanggal 11/03/2015. 14.00.
Wahyuni, Sri. (2011). Asuhan Neonatus, Bayi Dan Balita.
Jakarta: EGC.
Widoyono. (2011). Penyakit Tropis (Epidemiologi,
Penularan, Pencegahan Dan Pemberantasannya). Ed
ke-2. Jakarta: Erlangga.
Yamin, Sofyan dan Heri Kurniawan. (2011). SPSS
Complete Teknik Analisis Statistik Terlengkap dengan
Software SPSS. Jakarta : Salemba Infotek
INC 2018 - The 9th International Nursing Conference: Nurses at The Forefront Transforming Care, Science and Research
620
