
Design and Production of FRP Catamaran Boat for Better River
Transportation in Randuboto Village, Sedayu District, Gresik
Regency
Mohammad Sholikhan Arif, Sri Rejeki Wahyu Pribadi, Wing Hendro Prasetyo,
Dedi Budi Purwanto, Gita Marina Ahadyanti, Danu Utama and Rizky Chandra Ariesta
Department of Naval Architecture, Institut Teknologi Sepuluh Nopember, Surabaya, Indonesia
Keywords: FRP Catamaran, Randuboto Village.
Abstract: Gresik is one of the regencies in East Java which has become one of the important port cities of the archipelago
in the past, many of them use the river as a logistics route, At present, the crossing boat in Randuboto Village
have several limitations, namely safety issues, stability issues and wooden boat construction which have some
disadvantages. Catamaran boats have several advantages compared to single-hull boat like better cross-
stability, smaller resistance in the same Breadth. Limited wood supply causes the price of wood to soar and
difficult to obtain. The production of wooden boat is difficult to get raw materials so that the wooden boatyard
are not well developed. Alternative materials that can be used for shipbuilding are fiberglass. Fiberglass
material has several advantages including lightweight, easy to form and cheap. The methods of this research
is conducting a survey to existing wooden boat to get the main dimension of the boat. Secondly, do the design
process like design of linesplan, general arrangement and construction calculation. The result of this research
is catamaran boat that have main dimension L =12 meters, B =3,1 Meters T=0,5 meters H=1,2 meters.
Currently, boatbuilding process is still being carried out.
1 INTRODUCTION
Gresik Regency is a district in East Java Province,
Indonesia. Gresik Regency has an area of 1,191.25
km². The territory of Gresik Regency also includes
Bawean Island, which is 150 km off the coast of the
Java Sea. Gresik Regency borders Surabaya City and
Madura Strait in the east, Lamongan Regency in the
west, Java Sea in the north, Sidoarjo and Mojokerto
Regencies in the south. Gresik is a downstream area
of Bengawan Solo River, and several other rivers
such as Kalimas and Kali Lamong, so the use of
wooden boat transportation to cross from one area to
another (Muhatta and Soesanti, 2018).
The availability of wood in Indonesia as raw
material for boat is increasingly difficult to obtain,
because woods are shrinking every year. With these
conditions, the price of wood will be increasingly
expensive, causing the production costs of building
wooden boat increase. If this continues, the people's
shipyard in Indonesia can no longer meet the needs of
traditional boatbuilding because the capital used is
getting bigger. Therefore, alternative materials for
wood replacement are needed.
Lack of wood material is relatively expensive,
requires regular maintenance. As the age of the boat
increases, the aspect of boat maintenance costs
increases. The age of the vessel increases, it will
affect to cost of exploitation and maintaining the boat.
Thus the maintenance of wooden boat is one of
the problems of traditional fishermen. Maintenance of
wooden boat hull is carried out every 6 months, more
often than fiberglass boats, which is once every 1.5
years. Although the cost is more expensive, fiberglass
boat maintenance results is better and reduce the
frequency of treatment. The reduced frequency of this
treatment can lead to lower initial costs being spent.
The advantages of boat built from FRP are no
leaking in the hull wich continous piece of FRP with
no gap to allow water into hull. FRP does not shrink
or swell so leakage and re-caulking are avoided. FRP
is non-organic and will not rot. As a plastic it cannot
eaten by marine borers. FRP is inert, as a plastic it
will not corrode (Anmarkrud, 2009).
82
Arif, M., Pribadi, S., Prasetyo, W., Purwanto, D., Ahadyanti, G., Utama, D. and Ariesta, R.
Design and Production of FRP Catamaran Boat for Better River Transportation in Randuboto Village, Sedayu District, Gresik Regency.
DOI: 10.5220/0008375000820086
In Proceedings of the 6th International Seminar on Ocean and Coastal Engineering, Environmental and Natural Disaster Management (ISOCEEN 2018), pages 82-86
ISBN: 978-989-758-455-8
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

The advantage of catamaran is that for the same
displacement the catamaran hull has been proven to
produce 20% less resistance compared to monohull
vessels. In addition, the broad deck allows for more
cargo transport (Coackley, 1991).
In this paper, the process of design and production
of FRP catamaran boat for river crossings in Gresik.
Boat design has the advantage of being safer and
more comfortable, better stability and can carry more
loads.
2 METHOD
Generally, catamaran boat design and construction
process uses spiral design method, with engineering
design to get more optimal design.
A survey of existing vessels is carried out to
determine the current condition of the ship. The
survey method is to measure the dimensions of the
ship so that the length, width and loaded of the ship
are obtained. Another objective of surveying the
condition of the boat is to know the aspect of safety,
stability of the boat
Figure 1: Condition of Existing Wooden boat.
We can see in Figure 1, existing crossing river
boat made of wood, have one hull of the boat (less
stability) and no railings to protect passengers from
the danger of being plunged into the river. and there
are no lifejacket as important safety equipment for
passengers. From the survey results, then we design
safe crossing vessels, have good stability and
consider passenger safety aspects (Watson, 1998). the
results of the data obtained from the survey of the
condition of the existing vessels are as follows:
Table 1: Data obtained from Existing boat.
Dimension
Length : 12 meters
Breadth : 3 meters
Height : 0,9 meters
Draft : 0,49 meters
Speed : 10 knots
No. Amount of Motorcycle : 7
No. Amount of Passenger : 10 persons
Engine capacity : P
2.1 Lines Plan
Lines plan is the initial design of the crossing river
boat which consists of 3 main design namely body
plan (front rear view), sheer plan (side view) and Half
Breadth Plan (Ferry, 2013).
The lines plan design is based on the results of the
survey on existing crossing vessels and incorporates
other design parameters such as aspects of feasibility,
safety and design parameters of catamaran vessels
(Liu, 1998). The following figure is the linesplan
design that has been made using CAD software.
Figure 2: Lines plan of Catamaran Boat.
2.2 3D Conceptual Design
After the catamaran lines plan has been made, the
next step is to create a 3D / conceptual design of the
boat. The 3D design results from the catamaran ship
crossing the Bengawan Solo river are as follows:
Design and Production of FRP Catamaran Boat for Better River Transportation in Randuboto Village, Sedayu District, Gresik Regency
83
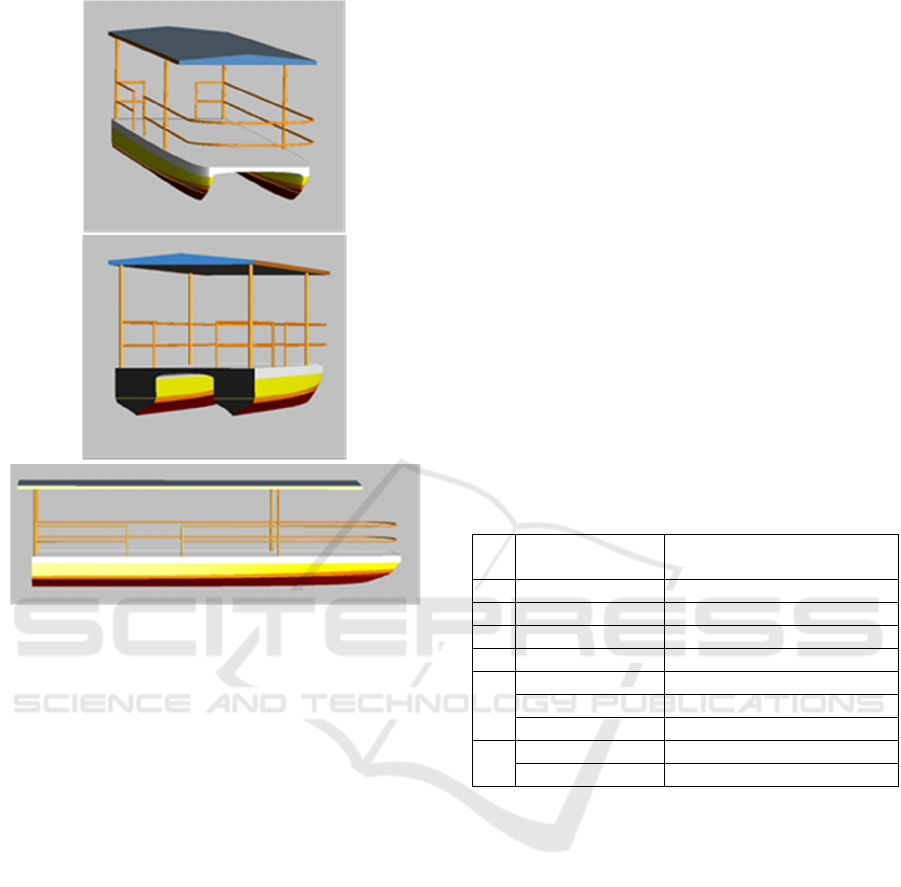
Figure 3: 3D Conceptual Design.
We can see in the figure 3 above, the catamaran
boat conceptual design that has been made has several
advantages: it has railing to protect passengers from
danger of falling into the river, there is a roof that
protects passengers from the sun's heat and rainy
weather. Catamaran boats provide better stability than
one hull boat. with the same width, catamaran boat
have a smaller resistance compared to one hull boat.
2.3 FRP Construction Calculation
In building a ship, the applicable regulations in the
area of the ship will be used. The purpose of using
rules is to ensure that the construction of the ship that
has been built meets the standards and seaworthy.
In Indonesia, rules that are commonly used are
rules issued by the Bureau Indonesian Classification
(BKI). Rules of the Indonesian Classification Bureau
regarding fiberglass construction vessels include
(Biro Klasifikasi Indonesia, 2015, 2016):
• Rules for FRP and Wooden Fishing Vessel up to
24 m, 2015 edition
• Rules for Fiberglass Reinforced Plastic Ships,
2016 edition
• Rules for Non-Metallic Materials, 2014 edition
In the BKI rules mentioned above, the required
construction measures are specified, the strength
standards of fiberglass materials and material testing
standards
Under the rules of BKI Fiberglass Reinforced
Plastic 2016, results from FRP testing
which is composed of chopped strand mats and
woven roving must not be less than what has been
determined as follows (Biro Klasifikasi Indonesia,
2015, 2016):
1. Tensile Strength: 98 N / mm2
2. Modulus of Tensile Elasticity: 6.86 x 103 N /
mm2
3. Bending Strength: 150 N / mm2
4. Modulus of Bending Elasticity : 6.86 x 103 N /
mm2
The results of construction calculations carried out,
obtained fiberglass laminate arrangement of
catamaran boat. The laminate structure of FRP
catamaran boat construction is as follows:
Table 2: Lamination Schedule of FRP Catamaran Boat.
No.
Construction of
ship
FRP Laminate Arrangement
1 Bottom Plating G+2M300+4M450+4WR800
2 Side Shell G+2M300+2M450+3WR800
3 Deck Plating 4M450+Ply 9 mn
4 Frames
Transver frames 3M450+2WR800
Side longitudinal 3M450+3WR800
Center girder 3M450+2WR800
5
Deck Transverse 3M450+2WR800
Deck Longitudinal 3M450+2WR800
3 FRP CATAMARAN BOAT
BUILDING
After designing lines plan, general arrangement and
calculation of boat construction, the next step is FRP
catamaran boat building; . the steps in boat building
of FRP catamaran boat are mold making, gel coating,
hand lay up, Unplugging from molding, framing and
stiffening section, and Finishing.
3.1 Mold Making
FRP boat molds are composed of wooden frames, 6
mm plywood and melamine plywood. Wooden
frames are used to strengthen the mold, the body of
the ship on the mold is formed using triplex and
melamine plywood. Triplex joints on the mold are
ISOCEEN 2018 - 6th International Seminar on Ocean and Coastal Engineering, Environmental and Natural Disaster Management
84

caulked to flatten the surface of the mold in order to
smooth the hull.
Figure 4: Mold making Process and mold result.
To produce this catamaran boat, only one mold is
needed due to symmetrical catamaran hull. Ready
mold need to clean and mash before lay-up, but not
enough to just be cleaned and mashed. Repair any
holes with appropriate filler. To repair a hole in
corner of plywood, apply a fiberglass patch measured
and cut to fit the hole and apply resin. For the best
results, sand the surface of the mold.
3.2 Gel Coating
The mold surface is waxed as much as 5-7 times for
new molds. The last process in making the mold is the
provision of PVA (Polyvinyl Acrylate) membrane,
this is so that the boat does not stick to the mold. The
process of FRP boat lamination begins with the
provision of Gelcoat layer (the outer layer as a
protective hull) on the mold, this layer is given 2
times so that the resulting FRP catamaran boat is
thicker in color.
Figure 5: Gel Coating Process.
3.3 Hand Lay Up
The next step after gelcoating is hand laying up,
installation of the first layer with MAT 300 fiber
material, so that the coating can attach well to the
complicated parts of the ship (corners, etc.). The
second layer is fiber MAT 450 material (thicker than
MAT 300), then we give WR 800 layer, the next layer
uses MAT 450 and so on to the last layer according
to the lamination schedule.
Figure 6: FRP Lamination Process.
The first coat is called seal coat, Using a roller to
apply on the suface of boat and firm pressure and
directional strokes to spread the resin as evenly as
possible. Cut fiberglass cloth to the shape needed and
attach the fiberglass cloth to the hull using tape, tacks
or staples. The second coat is called the bond coat.
Before this coat applied working from one end of the
hull to the other, apply the bond coat over the
fiberglass. Remove the material attach to fiberglass
cloth to the boat before the bond coat sets up
completely and repeat. The finish coat should be
smooth and even, but should also be thick enough to
allow sand the hull evenly without damaging the
cloth. Give the final coat enough time to dry,
preferably overnight.
Releasing is the FRP Hull release process, which
has been finished laminated and in a curing condition,
from the ship's mold.
3.4 Framing and Stiffening Sections
Frames serves as a reinforcement for the boat. Boat
frame is made of a mixture between CSM and WR
which is molded to "U" form profile. Fiberglass boat
frame consists of several types of construction,
including: Web Frame, Girder, Stiffener, Side Girder,
Center Girder and Side Stringer.
Design and Production of FRP Catamaran Boat for Better River Transportation in Randuboto Village, Sedayu District, Gresik Regency
85
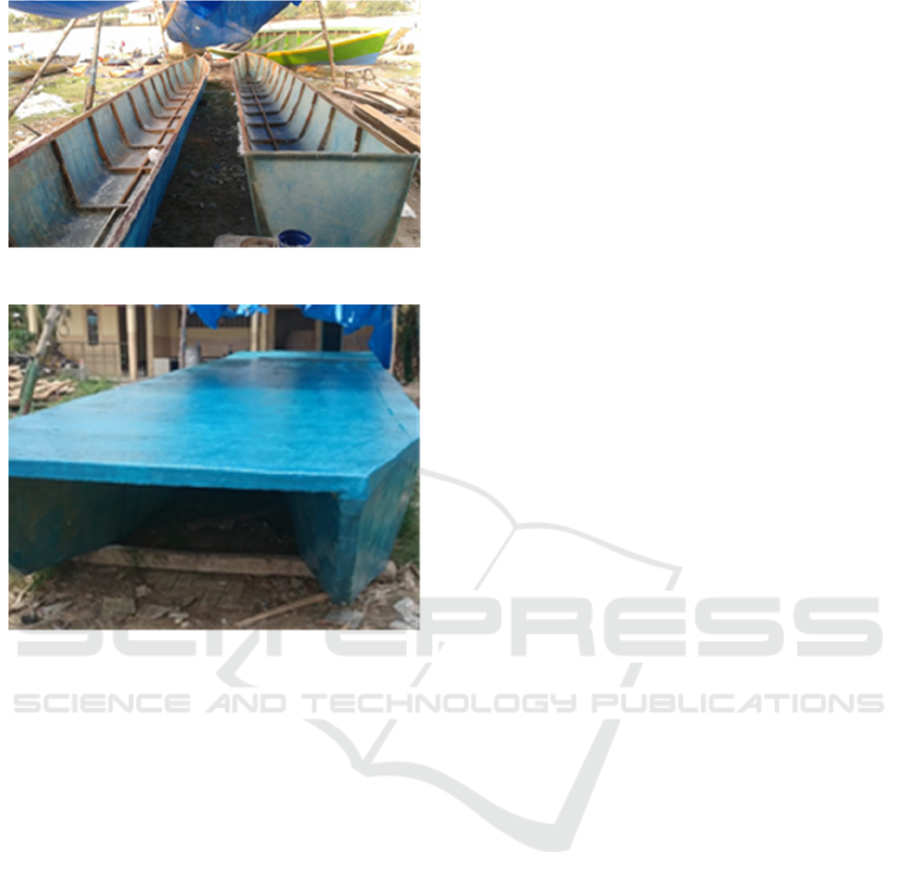

Figure 7: Frame installation result.
Figure 8: Catamaran Boat has been finished.
4 SUMMARY
This article analyzed design and production of
catamaran boat using Fiberglass Reinforced Plastic
as the material with crossing route in Bengawan solo
river in Gresik. Technical analysis conducted with
preliminary design. Using parent base design
methods, the main dimensions of FRP Catamaran
Boat as follows: L (length) = 12 [m] B (Width) = 3.1
[m] H (High) = 1.2 [m] T (Loaded) = 0.5 [m]. From
the results of technical analysis obtained design of
lines plan, general arrangement and boat construction
of Catamaran boat made of fiberglass reinforced
Plastic. catamaran boat conceptual design that has
been made has several advantages: it has railing to
protect passengers from danger of falling into the
river, it has a roof that protects passengers from the
sun's heat and rainy weather. Catamaran boats
provide better stability than one hull boat. with the
same width, catamaran boat have a smaller resistance
compared to existing boat.
The Boatbuilding process of FRP Catamaran Boat
has been carried out, consist of mold making process,
polishing, Gel coating, hand laying up, releasing and
Finishing
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
This research project was financially supported by
Institut Teknologi Sepuluh Nopember under the
grant: Pengabdian Masyarakat Berbasis Penelitian
2018. This boat using FRP Product from PT. Justus
Kimiaraya.
REFERENCES
Anmarkrud, Thomas, 2009. Fishing boat construction: 4.
Building an undecked fibreglass reinforced plastic boat.
FAO Fisheries and Aquaculture Technical Paper 507.
Biro Klasifikasi Indonesia. 2015. Guidance for FRP and
Wooden Fishing Vessel Up To 24m. Jakarta: BKI.
Biro Klasifikasi Indonesia. 2016. Rules for Fiberglass
Reinforced Plastic. Jakarta: BKI.
Coackley, 1991. Ned. Fishing Boat Construction, 2:
Building a Fiberglass Fishing Boat. No. 321. Food &
Agriculture Org.
Ferry, M. 2013. Comparative Study Of Hybrid Catamaran
Versus Diesel Monohull Boat As Ferry For Short
Distance Routes. The Indonesian Journal of Naval
Architecture 1.1.
Liu, Qian, et al. 1998. Effects of Principal Dimensions,
Moulded Lines and Parameters of Channel on Speed
and Powering of Catamaran Planins Boat. Shipbuilding
of China 3: 001.
Muhatta, Z., and N. Soesanti, 2018. The toponymy of the
ancient port city of Gresik in the northern coastal area
of Java, Cultural Dynamics in a Globalized World.
Watson D, 1998. Practical Ship Design, Butterworth
Heinemann, Oxford.
ISOCEEN 2018 - 6th International Seminar on Ocean and Coastal Engineering, Environmental and Natural Disaster Management
86
