
The Effect of Parenting Efficacy on the Social-Emotional
Development of Children in B-Class Kindergarten
Evania Yafie
Faculty of Education, State University of Malang, Malang, Indonesia
Keywords: Parenting Efficacy, Social-Emotional, Early Childhood.
Abstract: Family is the first informal institution in which children grow and develop, internalizing values, norms and
beliefs as well as a place in which disciplines are applied to form principles of the mental and self in the
future, and for children to get the required attention and love from the parents and the family which can raise
their potentials and development. One of the ways to measure the parents' parenting skills is by parenting self-
efficacy, that is, a self-evaluation towards their ability in playing the parenting roles to give positive effects
to the behaviours and developments of the children. This study aims to examine the effect of parenting
efficacy on children's social-emotional development. The research method used in this study is descriptive
quantitative with explanatory method. The sample was taken by random sampling technique with 100 students
from 4 B-class kindergartens in Malang Regency. The data are analysed using simple regression analysis with
a result showing that parenting efficacy has positive and significant effects on children's social-emotional
development. The higher the parent's efficacy level, their children's social-emotional development gets higher
too. Parenting efficacy needs more attention in order to maximally improve children's development.
1 INTRODUCTION
Parenting skill has an important role as it is one of the
most influencing factors in a child's growth and
development. Kazdin (1987), found that parenting
skill program is usually based on social-learning
principles with a notion that reinforced actions will
occur more often. One of the main cognitive elements
in parenting competence is parenting-self-efficacy
which defines as a self-referent estimation towards
one's ability/competence in playing the parenting role
to give positive effects on their children's
development and behaviour (Coleman and Karraker,
2003). Parenting efficacy or the belief of the parents
in doing their job has a big role in forming the way
they treat their children, including shaping their
children's development in the future because the
parents are the main player in dealing with family
lives and the people in it (Berndt, 1997b, 1997a).
Researches proven that mothers with lower levels
of self-efficacy tend to be more aggressive in
interacting with their children (Jeynes, 2003).
Coleman and Karraker (2003), further show that
parenting self-efficacy refers more to the ability of the
mother in playing her role as the caregiver compared
to the father. Besides, it is also believed that higher
levels of parenting self-efficacy is strongly associated
with the parents' capacity in providing adaptive,
stimulating and nurturing environment for the
children. However, this parenting self-efficacy level
will decrease as the children get older (Coleman and
Karraker, 2003). Then, if the parents face some
difficulties in the (parenting) process, negative effects
will happen to them (Coleman and Karraker, 2003).
Some of these negative effects were found in research
about parenting self-efficacy and depression on the
parents, like defensive and controlling parenting
techniques, high levels of stress, passive and negative
stress-controlling acts in parenting, as well as feelings
of helplessness and frustration (Coleman and
Karraker, 2003).
Parenting efficacy seems like a critical factor that
influences the child's development in the family
system. Parents' perception about their competence in
parenting plays an important role in building a strong,
affectionate parent-child relation. It is their love and
affection that are believed to form the basic cognitive
structures in the child's psychological development
and interpersonal function (Trunzo, 2006).
Various cases have been found in this area,
ranging from small cases to the big ones. For
example, a mother complains about her whiny child,
78
Yafie, E.
The Effect of Parenting Efficacy on the Social-Emotional Development of Children in B-Class Kindergarten.
DOI: 10.5220/0008408000780083
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Learning Innovation (ICLI 2018), pages 78-83
ISBN: 978-989-758-391-9
Copyright
c
2019 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

disagreeing or disobedient, difficult to ask for naps,
difficult in bathing or eating, stingy so a fight often
happens, a child who likes to bang its head on the
floor when what it doesn't get what it wants, up to the
points about "beyond-normal" juveniles delinquency.
There are many of these mothers hitting their kids as
a form of punishment when they seem tough to be
controlled. There are even some who still continue
physically hurting their kids even after they
apologized.
Parenting efficacy will also have an influence to
all aspects of the children's development. These
aspects are associated with the development of their
physic-motor, cognition, language, norms and values,
spiritual beliefs, art and social-emotion. These
aspects do not develop independently, but rather as an
integrated system, a harmony. If one of them faces an
obstruction and is "late," it will affect the other as well
(Dabrowska and Pisula, 2010). One that is most
probable to be obstructed is the child's social-
emotional development. Goleman (1995) notes that
emotional development appears earlier than social or
cognitive ones. As a baby, this skill is a tool to
communicate with their environment. During early
childhood, the child's emotion reaches maturity.
Children start to become aware of the things their
emotion can cause. They begin to develop the
understanding of other's feelings, such as how others
would feel when they get hurt so they start learning to
control their emotion.
Through this research I want to evaluate how far
the effect of parenting efficacy on children's social-
emotional development goes. This particular
developmental stage is very important because social-
emotional behaviours will certainly have relations to
their lives in the future. The stronger the
pressure/stress emotion gives, the harder it is for them
to balance their body to do certain actions. If the
action matches their emotion, they will gladly do it
and will mentally increase their concentration while
their psyche gives positive support(s) in improving
motivation and interest in pursuing and learning this
particular thing they like. Gardner (1983) also states
that a positive state a child encounters, where he/she
likes what they do, has the persistence, and feels
involved in what they are learning, will further
develop a more optimal competition. By building
emotional bond, that is creating fun learning and
eliminating threats in the atmosphere, the students'
active role in studying will improve (Mashar, 2011).
The child's social-emotional development can be
seen from their interaction skill with others in social
contexts using specific methods that are socially
acceptable or norms which at the same time useful to
them as well as others (Coolahan et al., 2000). Their
social-emotional development should constantly
receive stimuli so that they have a feeling of empathy,
by which they express their caring of others,
generosity and teamwork. Toddlers start to have the
capability to adapt, moving from being egocentric to
being cooperative or socio-centric. Social-emotional
development of 5/6-year-olds is also observable from
their interaction and blending abilities to form groups
of friends in doing children's social activities. They
begin to work as a team, create and follow rules inside
their group(s), understand others and build friendship
(Williams and Monsma, 2006). Based on
observations in kindergartens across Malang
Regency, I found that socialization on the matter and
children's tendencies to share and cooperate are still
minimal. They are still egoistic and always want to
win in playing their games. There are even a few that
dominate certain games or toys. This is by no doubt a
form of social-emotional problems occurring in
children. We need a correct method so that their
social-emotional competence develops optimally.
This is where stimuli need to be given through fun
and relaxed teaching techniques. One method is role-
playing. As for the purpose of this study is to examine
the effects or influences of parenting efficacy on the
social-emotional development of children in B-class
kindergarten.
Based on the matter explained above, the
hypothesis of this study is as follows:
H0: There are no effects parenting efficacy
gives to the social-emotional development of
children in B-class kindergarten in Malang
regency.
H1: There is an effect/there are some effects
parenting efficacy gives to the social-emotional
development of children in B-class
kindergarten in Malang Regency..
2 METHOD
The research method used in this study is descriptive
quantitative with explanatory method (explanatory
research). Singarimbun and Effendi (2009), defines
explanatory research as a research in which the
researcher explains the cause-and-effect relation
among variables through the testing of the hypothesis.
This study uses quantitative approach because
numbers are used throughout the analysis. The data
are collected using questionnaires which are then
analysed to find the effect(s) the variables give using
regression analysis.
The Effect of Parenting Efficacy on the Social-Emotional Development of Children in B-Class Kindergarten
79

There are two variables in this study: independent
and dependent variables. The independent variable in
this study is parenting efficacy, while the dependent
one is social-emotional development.
According to the theoretical concept defined
above, the variables, indicators and items presented in
this study is as explained in the Table 1.
Table 1: Dimension and indicator social-emotional variable.
Dimension
Indicator
a. Able to interact with friends of the
same age and adults
1. Willing to play with friends of the same age without discriminating (skin
color, breed, hair, religion, etc.)
2. Willing to appreciate others
3. Asking friends to play/study together
4. Playing together (e.g. halma, snakes & ladders, etc.)
5. Communicating to older people when doing something (e.g. baking
cookies, cooking, etc.)
6. Communicating with friends when having problems (e.g. getting sick, sad,
etc.)
b. Able to show their confidence
1. Dare to ask and/or answer questions
2. Dare to give opinions (in simple ways)
3. Making simple decisions
4. Pretending they have jobs
5. Working independently
6. Dare to tell stories
c. Able to show attitudes of independence
1. Button or zip their clothes by themselves
2. Tie or untie their shoe laces
3. Dare to go to school and back home alone (for those whose house is close
to the school)
4. Bath and do toilet stuff on their own (toilet training)
5. Do their assignments themselves
6. Play games they like
7. Taking care of themselves without the help of others (e.g. putting on
clothes, brushing their teeth, eating, etc.)
d. Able to express proper emotion
1. Willing to be parted from the mother
2. Accepting criticism and advice
3. Help solving problems
4. Expressing their feelings (e.g. anger, sadness, happiness, surprised, etc.)
e. Being used to show discipline and
obedience
1. Throwing trashes in the provided cans
2. Putting back toys on their places
3. Obeying rules
4. Being at school on time
f. Being responsible
1. Doing assignments from the teachers
2. Taking care of their own or others' belonging
3. Finishing their task
4. Responsible for orders given to them
5. Taking care of their stuff
6. Being cooperative in finishing group task(s)
g. Being used to protecting the
environment
1. Protecting the environment, for example, not scratching the walls, throwing
trashes in the provided cans, etc.
2. Saving water and electricity (using them less)
3. Doing the dishes
ICLI 2018 - 2nd International Conference on Learning Innovation
80
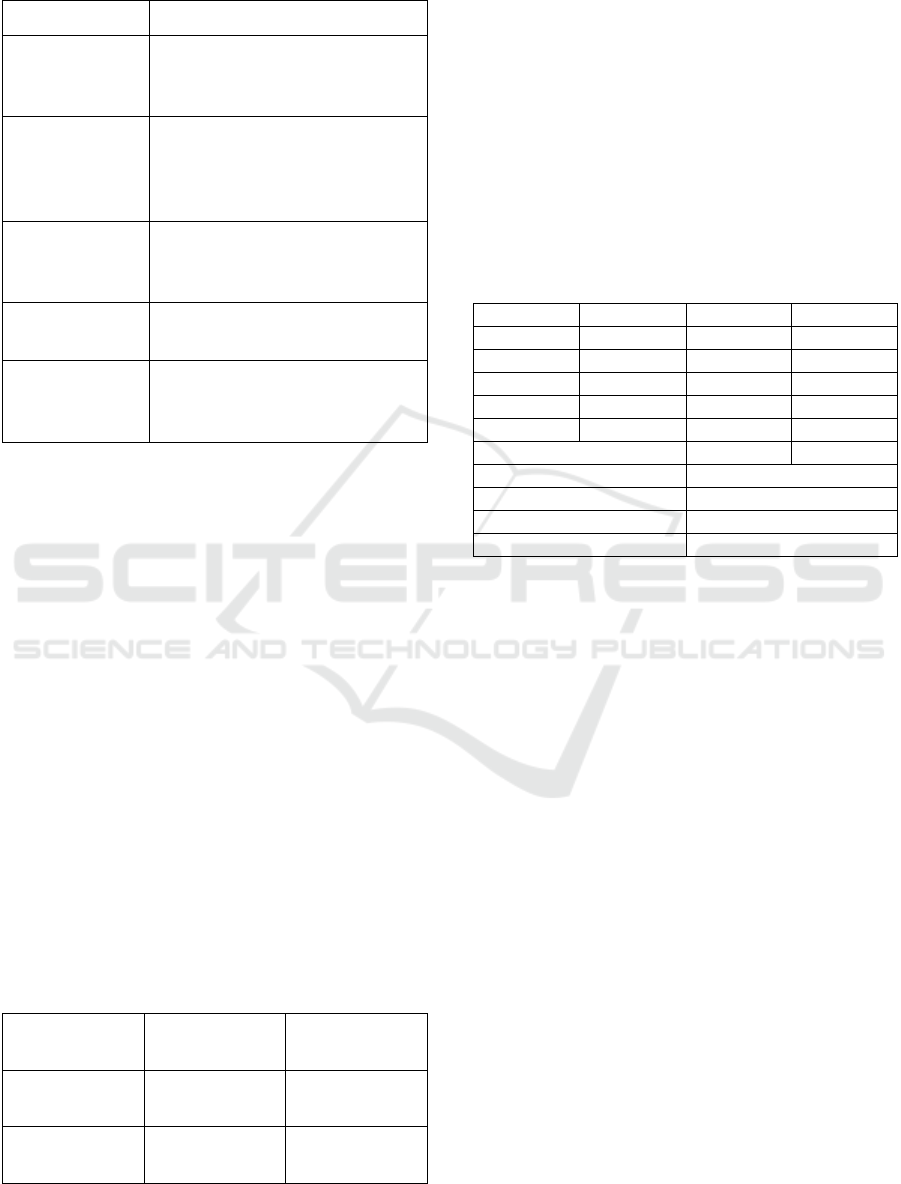
Table 2: Dimension and indicator social-emotional
variable.
Dimension
Indicator
a. Discipline
1. Parents are able to guide
their children to obey the
rules
b. Achievement
2. Teaching the children doing
their academic or non-
academic (self-improvement)
tasks
c. Recreation
3. Able to allocate the time and
provide fun activities for the
children
d. Nurturance
4. Being affectionate and loving
parents
e. Health
5. Able to perform the proper
treatments when the children
get ill/sick
The population in this study is all of the students
in 4 B-class kindergartens in Malang Regency. 100
students are taken as the sample, picked using random
sampling technique. Random sampling is a sampling
technique that randomly picks individuals in the
population as the sample in the research.
The measurement scale used is Likert Scale
format. The kinds of questions or statements
presented in the questionnaire are closed-ended with
5 options/answers for each. The data are then
analysed using simple regression analysis.
3 RESULT AND DISCUSSION
Validity testing on the research instrument is done by
comparing corrected item-total correlation values
using product-moment correlation. As for reliability,
the test is done using Cronbach Alpha. The results of
the tests shown at Table 3.
Table 3: Test results of the instrument's validity and
reliability
Variable
Correlation
Values
Cronbach Alpha
Social-emotional
development
0.609-0.888
0.830
Parenting
efficacy
0.525-0.818
0.872
From the validity test we can see that all
instruments in both parenting efficacy and social-
emotional variables have r-count value > than r-table
0.1964 obtained from (n-2) 98 sample that we can
come to a conclusion that all instruments in parenting
efficacy and children's social-emotional development
variables are valid. Meanwhile, reliability test from
table 3 also shows that the Cronbach Alpha values are
all above 0.60 which means that the research
variables are reliable and is suitable for further
research.
Next, the descriptive analysis result of parenting
efficacy is shown at Table 4.
Table 4: Descriptive analysis of parents' parenting efficacy.
Range
Category
N
%
4.21-5.00
Very High
6
6%
3.41-4.20
High
86
86%
2.61-3.40
Medium
8
8%
1.81-2.60
Low
0
0%
1.00-1.80
Very Low
0
0%
Total
100
100%
Average
3,93
Max
4,40
Min
3,30
Standard Deviation
0,26
In the Table 4, the parents' parenting efficacy is
divided into 5 categories: very high, high, medium,
low, and very low. There are 6 respondents (6%)
within the range of 4.21-5.00 (very high), 86
respondents (86%) within the range of 3.41-4.20
(high), 8 respondents (8%) within the range of 2.61-
3.40 (medium), and no respondent (0%) is in low
(1.81-2.60 range) or very low (1.00-1.80 range)
categories. From this we can observe that parents'
parenting efficacy sits within the range of 2.61-3.40
(high). Next, according to the table the class-
experiment pre-test about the parents' parenting
efficacy resulted in the average value of 3,93;
maximum value of 4,40; minimum value of 3,30; and
standard deviation of 0,26.
In the table 5 the children's social-emotional
development is divided into 5 categories: very high,
high, medium, low, and very low. There are 24
respondents (24%) within the range of 4.21-5.00
(very high), 76 respondents (76%) within the range of
3.41-4.20 (high), and no respondent (0%) is in the
medium (2.61-3.40 range), low (1.81-2.60 range) or
very low (1.00-1.80 range) categories. Next, we can
see from the table that the class-control post-test
about the social-emotional development resulted in
the average value of 3,99; maximum value of 4,41;
The Effect of Parenting Efficacy on the Social-Emotional Development of Children in B-Class Kindergarten
81
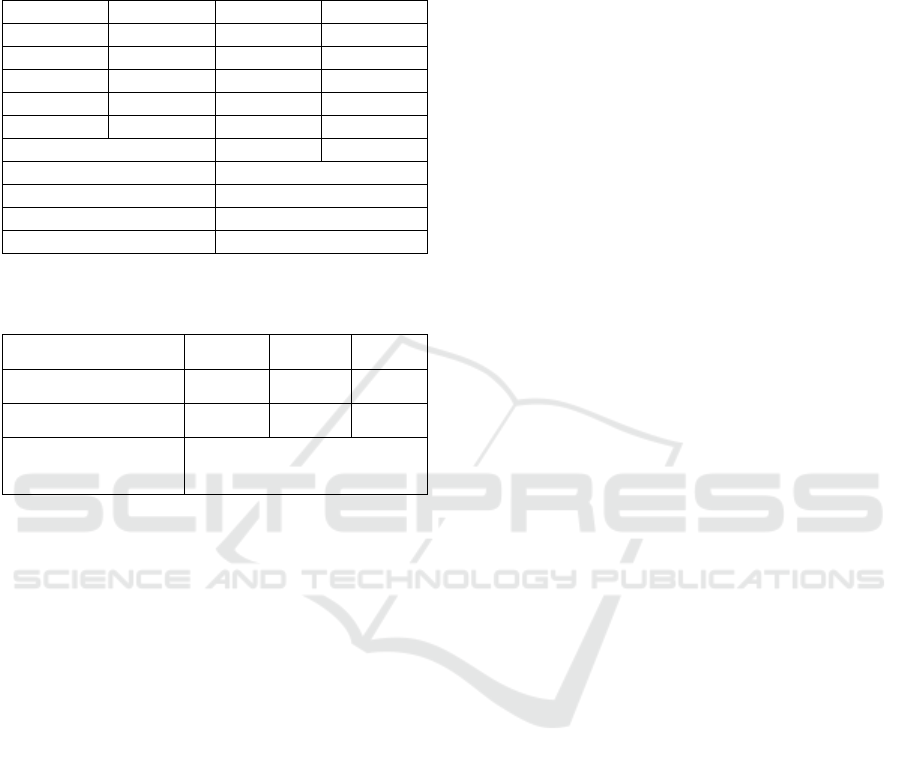
minimum value of 3,31; and standard deviation of
0,23.
Table 5: Descriptive analysis of children's social-emotional
development.
Range
Category
N
%
4.21-5.00
Very High
24
24%
3.41-4.20
High
76
76%
2.61-3.40
Medium
0
0%
1.81-2.60
Low
0
0%
1.00-1.80
Very Low
0
0%
Total
100
100%
Average
3,93
Max
4,40
Min
3,30
Standard Deviation
0,26
Table 6: Regression analysis.
Model
Beta
T
Sig.
Constant
0.133
Social-emotional
0.564
3.344
0.00
Coefficient of
determination
48.5%
As for the regression analysis, the result is positive
and significant as can be seen in the Table 6. From the
result of the regression analysis Table 6, it is clear that
there is positive and significant effect parenting
efficacy gives to children's social-emotional
development as can be seen from the significance
value 0.00<0.05 and the coefficient of determination
at 48.5%.
The analysis proves from table 6 that parenting
efficacy has an effect on the social-emotional
development of children in B-class kindergartens in
Malang Regency which are TK PGRI 5 Kromengan,
PAUD Mawar Putih Pakisaji, TK Dharmawanita
Pucang-songo, and TK Muslimat 1 Pulung-dowo,
Tumpang. This means that better parenting efficacy
will result in the better social-emotional development
experienced by children as seen from their
interactions with either friends of the same age or
adults, their willingness to show their confidence and
independence, their ability to express proper emotion,
as well as their disciplined, responsible and
environment-friendly actions.
There have been many experts who state that
children in kindergartens have unique personalities.
Some experts in education and psychology see this
period as the one that needs the best treatment or
guidance. It is looking in table 1 about dimension and
indicator variable Social and Emotional for Children.
Hurlock (2003) believes that the age of 3-6 years is a
sensitive period, that is, a period in which particular
functions need to be stimulated, guided so that they
can develop well. Kartono (2000) further explains
that kindergarten children have these unique traits: (1)
naively egocentric, (2) having social relation with
things and people that is still simple and primitive, (3)
physical and spiritual unity is a must, and (4) having
physiognomy lifestyle.
In the table 5 we can look about score
development Social Emotional Children. Social and
Emotional Children with knowledge parent about it
development will influence each child. It is very
important to future. According to Santrock (2007),
childhood is an important and precious phase; a phase
of formation in somebody's life (a noble and
malleable phase of human life). Because of this
childhood is often dubbed as the golden age for
education. It is a fundamental phase in which a
person's personality or social-emotion has the biggest
chance to shape.
Development in the social-emotional ability of
Children in B-class kindergarten in Malang Regency
is clearly observable from their willingness to have
interactions either with friends of the same age or
with adults, such as playing with friends without
discriminating, appreciating others, and daring to
invite others to play together; the ability to show their
confidence and independence, such as asking
questions, making simple decisions, telling stories in
front of friends, cleaning up themselves (taking baths)
and putting on clothes on their own; the ability to
express proper emotion, such as when they are sad,
angry or happy; the ability to show discipline, such as
throwing trashes in the cans, return their toys to the
proper places and being at school on time; the ability
to be responsible and environment-caring, such as
doing their assignments and taking care of things
either belonging to them or belonging to others.
This development cannot be separated from the
parents' role. They are the main agent that can
influence how these children will be in the future.
They will always play this role from the childhood,
post-school, up to the point where their
sons/daughters live their own lives apart from the
parents. Children get the view of life rules, morals and
social norms from their parents. Their good and/or
bad come(s) from the parents.
Parenting efficacy is a cognitive element on which
parents' treatments to their children are based. These
treatments are what will influence the children's life
in the future. By having parenting efficacy parents
ICLI 2018 - 2nd International Conference on Learning Innovation
82

will have the confidence that they are capable of
conducting effective parenting. Some research in
Coleman and Karraker (2003) also show that mothers
with high levels of parenting efficacy have good and
positive ways in providing what the child needs, have
positive interactions with the child, can help the child
when facing problems, and can play the role of a
mother well.
4 CONCLUSIONS
Research shows that there are positive and significant
effects of parenting efficacy on children's social-
emotional development. The higher it is results in
better social-emotional development on the children.
It can be seen from the significance value 0.00<0.05
and the coefficient of determination at 48.5%.
REFERENCES
Berndt, T. J. (1997a) Child Development. 2nd Editio.
William C Brown Communications.
Berndt, T. J. (1997b) ‘Exploring the effects of friendship
quality on social development’, in Bukowski, W. M.,
Newcomb, A. F., and Hartup, W. W. (eds) The company
they keep: Friendship in childhood and adolescence.
Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, pp. 346–365.
Coleman, P. K. and Karraker, K. H. (2003) ‘Maternal self‐
efficacy beliefs, competence in parenting, and toddlers’
behavior and developmental status’, Infant Mental
Health Journal: Official Publication of The World
Association for Infant Mental Health, 24(2), pp. 126–
148.
Coolahan, K. et al. (2000) ‘Preschool peer interactions and
readiness to learn: Relationships between classroom
peer play and learning behaviors and conduct’, Journal
of Educational Psychology, 92(3), p. 458.
Dabrowska, A. and Pisula, E. (2010) ‘Parenting stress and
coping styles in mothers and fathers of pre‐school
children with autism and Down syndrome’, Journal of
Intellectual Disability Research, 54(3), pp. 266–280.
Gardner, H. (1983) Frames of Mind: The Theory of
Multiple Intelligences. New York, USA: Basic Books,
Inc.
Goleman, D. (1995) Emotional Intelligence. Jakarta:
Gramedia Pustaka utama.
Hurlock, H. (2003) Psikologi Perkembangan. Jakarta:
Erlangga.
Jeynes, W. H. (2003) ‘A meta-analysis: The effects of
parental involvement on minority children’s academic
achievement’, Education and urban society, 35(2), pp.
202–218.
Kartono, K. (2000) Hygiene Mental. Jakarta: CV. Mandar
Maju.
Kazdin, A. E. (1987) Child Psychotherapy: Development
and Identifying Effective Treatments. New York:
Pergamon.
Mashar, R. (2011) Emosi Anak Usia Dini dan Strategi
Pengembangan. Jakarta: Kencana.
Santrock, J. W. (2007) Psikologi Pendidikan. Edited by Tri
Wibowo B.S. Jakarta: Kencana.
Singarimbun, M. and Effendi, S. (2009) Metode penelitian
survai. Jakarta: LP3ES.
Trunzo, A. C. (2006) Engagement Parenting Skills, and
Parent-Child Relation as Mediators of The
Relationship between Parental Self-Efficacy and
Treatment Outcomes for Children with Conduct
Problems. University of Pittsburgh.
Williams, H. and Monsma, E. V. (2006) ‘Assessment of
gross motor development’, in Bracken, B. A. and
Nagle, R. J. (eds) Psychoeducational Assessment of
Preschool Children. 4th editio. Hillsdale, NJ.:
Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, pp. 397–433.
The Effect of Parenting Efficacy on the Social-Emotional Development of Children in B-Class Kindergarten
83
