
Analysis Towards Factors of Students’ Learning Difficulties at
Muhammadiyah Elementary Schools in Sayegan Sub-District
Vera Yuli Erviana
Ahmad Dahlan University, Yogyakarta, Indonesia.
Keywords: Learning Difficulties Factors, Elementary School Students
Abstract: This study aims to describe the internal factor and external factor that became the main cause of learning
difficulties in Muhammadiyah elementary school students in Seyegan Sub-District. This research was
quantitative research. The research sample was 156 students of Muhammadiyah Elementary Schools in
Seyegan Sub-District. Data collection techniques were questionnaires and documentation. Data analysis
technique was by descriptive statistics. The results of this study indicate that the internal factor is the main
cause of student learning difficulties, i.e. the health level of the hearing and seeing senses is 16.30%. As for
the external factor, the relationship between students and parents is 14.68%. Both of these factors are highly
correlated so that these two factors must be constructed in order to reduce elementary school students' learning
difficulties.
1 INTRODUCTION
In Indonesia, learning difficulties are suspected to be
the main cause of students’ low achievement
(Basiran, 2012). PISA 2012 measured the
understanding of 15 years-old students in the fields of
mathematics, reading, and science, in which
Indonesia has a low rank among 65 participating
countries. Mathematics (score: 375) is ranked 64,
reading (Score: 396) is ranked 61, and science (score:
382) is ranked 64 (Dublin, 2012). As quoted by
(Darma, 2014), 31.1% of Indonesian students are
below the literacy level 1, 37.6% are at literacy level
1, 24.8% are at literacy level 2, 6.1% are at literacy
level 3, and only 0.4% are at the literacy level 4, and
no one has achieved the literacy level 5. This
indicates that the quality of Indonesian education,
especially in terms of literacy, is still very low
compared to other countries (Darma, 2014).
The NAEP (National Assessment of Educational
Progress) (2013) stated that in the measurement of
reading and mathematics skills in the United States,
4th-grade students who experience reading
difficulties are 69%, while in 8th grade is 60%. The
measurement of mathematics learning difficulties in
4th-grade students is 45% and in 8th grade is 65%.
This data showed that learning difficulties in 4th to
8th grades students have relatively high numbers
(Horowitz, 2014). Learning difficulties are one of the
obstacles that can prevent students from achieving
maximum performance. This is one of the
psychological disorders that includes disorder in
hearing, thinking, speaking, reading, writing,
spelling, or doing mathematical calculations
(Horowitz, 2014). The low learning outcomes
obtained by students indicate that the students have
learning difficulties.
Learning activities are the most basic activities.
Self-learning is an effort process that is carried out by
someone to obtain new behaviour change as a whole,
as a result of his/her own experience in interaction
with his/her environment (Slameto, 2015). This
means that the success or failure of educational goals
depends on how the learning process experienced by
students as learners. The learning success in school is
often seen from the students’ learning achievements.
(Anderson and Krathwohl, 2010) divided
students' knowledge dimensions into four
dimensions, which are factual knowledge, conceptual
knowledge, procedural knowledge, and
metacognitive knowledge. In order to understand the
students’ knowledge, the students need to be given
mathematical problems that must be solved. This is in
line with the opinion of (Soon, Lioe and McInnes,
2011)“the authors reflected that the short questions
posed to students helped to identify students'
difficulties and levels of conceptual understanding”.
Erviana, V.
Analysis Towards Factors of Students’ Learning Difficulties at Muhammadiyah Elementary Schools In Sayegan Sub-District.
DOI: 10.5220/0008410202210227
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Learning Innovation (ICLI 2018), pages 221-227
ISBN: 978-989-758-391-9
Copyright
c
2019 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
221

Learning difficulties are a situation where
students cannot learn properly due to certain obstacles
or disturbances in the learning process so that
students cannot achieve the expected learning
outcomes (Djamarah and Syaiful, 2011). (Horowitz,
2014) also mentioned that learning difficulties can be
diagnosed in the early days of schooling. 53% of
respondents think that learning difficulties can be
diagnosed when students are in 1st-4th grades, 23%
of respondents think that learning difficulties can be
diagnosed when students are at preschool, 76%
believe that learning difficulties are due to genetic
factors, while 43% think that learning difficulties are
related to IQ.
Research conducted by C.C. Wrenn and Reginald
Bell (Bennet, 1952) stated that the factors that cause
learning difficulties are difficulty in budgeting time,
unfamiliar standards of work, and slow reading
habits. Based on (Arief, 2012) the factors that cause
learning difficulties in physics are interest, talent,
motivation, intelligence, school facilities, teachers,
facilities or infrastructure and support, activities have
the same level, which is enough to cause physics
learning difficulties in students of Pilot International
Standard High School in Semarang City.
The results of research conducted by (Arief, 2012)
concerning Intelligence Profiles of Students with
Learning Difficulties in Gisikdrono Elementary
School Semarang, indicated that students with
learning difficulties have IQ scores that are at an
average level. The influence of internal factors on
students’ learning difficulties is also supported by the
results of research conducted by (Ariyati and Nurdini,
2013) about the Description of Learning Difficulties
and its Causes in Fungi Materials in Bawari Islamic
High School Pontianak and the Improvement Efforts.
From these studies concluded that the factors more
influential in causing students’ learning difficulties
are internal factors that are dominated by learning
habits and interests. While external factors that
influence learning difficulties are family and school
environment.
Learning difficulties in students can be caused by
several factors. There are two factors that cause
learning difficulties in students, i.e. internal and
external factors (Aunurrahman, 2008; Hakim, 2008;
Syah, 2015) Internal factors are factors within the
learners or individual. Whereas external factors that
cause learning difficulties are factors that exist
outside individual or students. Internal factors include
interest, attention, motivation, and learning habits.
While external factors include learning methods,
learning media, and learning resources. Then it can be
obtained questionnaire framework of the factors that
causing students’ learning difficulties as follows.
Students who experience learning difficulties
generally show the following symptoms: a) Learning
outcomes are lower than his/her group’s average; b)
Learning outcomes achieved today are lower than
before; c) Learning outcomes achieved are not
balanced with the efforts that have been made; d)
Slow in carrying out learning tasks; e) Demonstrate
unusual behaviour, such as ignorant with learning and
learning process, no regret when getting low scores;
f) Shows behaviour that deviates from the norm, such
as truant, skips classes; and g) Demonstrate emotional
symptoms that are less natural, easy to be offended,
being alone, acting aggressively, etc. (Sugiyanto,
2014).
The purpose of this research is to find out: 1)
students’ internal factor that becomes the main cause
of learning difficulties at Muhammadiyah
Elementary School in Seyegan Sub-District. 2) The
external factor that becomes the main cause of
learning difficulties at Muhammadiyah Elementary
School in Seyegan Sub-District. Analyses of
objectives to get an overview, declare, or report the
data empirically with enough parameters. Then the
conclusions are drawn from the data obtained in the
field.
2 METHOD
This research was quantitative research. Data
collection techniques were questionnaire and
interviews. Questionnaire made in accordance with
the framework then tested to students from 3rd to 5th
grade that consists of schools in Seyegan Sub-
District. The schools are Muhammadiyah Bolu
Elementary School, Muhammadiyah Gendol 4
Elementary School, Muhammadiyah Gendol 5
Elementary School, Muhammadiyah Gendol 7
Elementary School, and Muhammadiyah Kasuran
Elementary School. Respondents were 156 students.
Based on the respondent's answer, data analysis was
carried out using descriptive statistics.
3 RESULT AND DISCUSSION
Learning difficulties in students can be caused by
several factors. There are two factors that cause
learning difficulties in students, i.e. internal and
external factors (Aunurrahman, 2008; Hakim, 2008;
Syah, 2015). Internal factors are factors within the
ICLI 2018 - 2nd International Conference on Learning Innovation
222

learners or individual. Whereas external factors that
cause learning difficulties are factors that exist
outside individual or students. Internal factors include
interest, attention, motivation, and learning habits.
From this theory, it is made into a research
questionnaire frame that contained in table 1. It is in
the form of 45 items of yes or no questions, 20
questions related to internal factors such as body
organs, health level of the hearing and seeing senses,
the success rate in learning the material, attitude
towards learning, level of attention in learning, talent
in learning, and motivation in learning. There are also
25 questions related to external factors such as
relationship between students and parents,
relationship between students and teachers,
relationship between students and employees/staff,
the way of teachers’ presentation, activities in the
community, relationship between students and peers,
home atmosphere, school curriculum, school
environment, school facilities and infrastructure, and
weather conditions and study time used by students.
As explained earlier, this research will describe
the internal and external factor that is the main cause
of students’ learning difficulties of Muhammadiyah
Elementary Schools in Sayegan Sub-District using
the questionnaire distribution method. Questionnaires
were distributed to 156 respondents. Each respondent
will fill in a questionnaire containing 45 questions.
The results of this questionnaire are got all the data
including the data that shows the main factors of
student learning difficulties as follows:
3.1 Internal Factors Causing Students’
Learning Difficulties
Learning difficulties in students can be caused by
several factors. Internal factors are factors within the
learners or individual (Volman, Van Schendel and
Jongmans, 2006). There are questionnaire results of
questions number one to twenty about internal
factors. This internal factor contains several
indicators, including the fitness level of the body
organs, the health level of the hearing and seeing
senses, the level of success in learning the material,
attitudes towards learning, the level of attention to
learning, talent in learning, motivation in learning. In
table 1 is the result of responses related to internal
factors that cause students’ learning difficulties.
Table 1 explains the total questions answered by
the respondents and the most sequence of the
indicators contained in the questionnaire frame. There
is one indicator for several questions such as the
fitness level of body organs is found in questions
number one to three; the health level of the hearing
and seeing senses is in questions number four to six;
the level of success in learning the material is found
in questions number seven and eight; attitudes toward
learning are found in numbers nine to eleven; the
level of attention to learning is found in questions
number twelve to fourteen; talent in learning is found
in questions number fifteen to seventeen; motivation
in learning is found in the number eighteen to twenty.
Then from the explanation above, the results of the
questionnaire can be classified can see in Table 2.
Table 1: Questionnaire result of internal factors causing
students’ learning difficulties.
Sequence
Item No
Total
Indicator
1
18
140
Motivation in learning
2
8
139
The level of success in
learning the material
3
7
138
The level of success in
learning the material
4
6
135
The health level of the
hearing and seeing
senses
5
16
132
Talent in learning
6
20
132
Motivation in learning
7
11
129
Attitude towards
learning
8
3
128
The fitness level of
body organs
9
14
126
Level of attention to
learning
10
10
124
Attitude towards
learning
11
5
123
The health level of the
hearing and seeing
senses
12
4
122
The health level of the
hearing and seeing
senses
13
13
121
Level of attention to
learning
14
17
120
Talent in learning
15
15
116
Talent in learning
16
9
114
Attitude towards
learning
17
12
101
Level of attention to
learning
18
1
86
The fitness level of
body organs
19
2
64
The fitness level of
body organs
20
19
42
Motivation in learning
Analysis Towards Factors of Students’ Learning Difficulties at Muhammadiyah Elementary Schools In Sayegan Sub-District
223

Table 2: Classification of questionnaire results of internal factors causing students’ learning difficulties.
Table 2 contains the sequence of the number of
respondents' answers to each question. This is used to
determine the most of learning difficulty factors from
the study results. The results of the research on the
main internal factors that caused the students’
learning difficulties in elementary schools in Sayegan
Sub-District are: 1) The health level of the hearing
and seeing senses is 16,30%; 2) Talent in learning
15,78%; 3) Attitude towards learning 15,74%; 4) The
level of attention to learning is 14,92%; 5) Motivation
in learning 13,46%; 6) Fitness level of body organs is
11,92%; 7) The level of success in learning the
material is 11,88%.
Therefore, it can be concluded that the main
internal factor that causin students' learning
difficulties is the health level of the hearing and
seeing senses of 16.30%. This is how the sensing
conditions (sensory modalities) are functioning
partially or intensified without any obstacles,
coordination of sensory modalities will affect
information processing because these conditions are
closely related to the functioning of the human brain
system, and also the existence of these sensory
modalities will also affect perception, imagery,
symbolizing, and learning concepts. Overall it will
affect verbal and non-verbal abilities in the learning
process.
However, there is a consensus about the
characteristics and learning processes typical of
students with learning difficulties. Generally, they are
regarded as inactive and inefficient learners, are often
off-task, and are easily distracted. They often are
unable to integrate prior knowledge and their own
experiences into what they are learning. These factors
combined with learned helplessness and
accompanying socio-emotional problems often result
in the development of poor self-esteem and
expectation of non-performance in academic areas
(Van Kraayenoord, 1998; Ashman and Elkins, 2004).
Without appropriate teaching and accommodations,
these students consistently fail or underachieve at the
secondary school level. This educational, social and
personal disadvantage resulting from school failure
may include unemployment, poverty, delinquency,
and poor physical, emotional and mental health
(Weare, 2000) In addition, the health of hearing sense
is very important to improve the quality of human
resources. The Ministry of Health of the Republic of
Indonesia has made a National Strategy plan for
overcoming hearing loss and deafness, which is
adjusted to Law no. 36 of 2009 concerning health. In
addition, there are still many obstacles in the
discovery of hearing loss cases in Indonesia and other
developing countries due to lack of knowledge,
information, attention, and public awareness about
the importance of finding cases of hearing loss early
on.
3.2 External Factors Causing Students’
Learning Difficulties
Learning difficulties in students can be caused by
several factors. According to (Aunurrahman, 2008;
Hakim, 2008; Syah, 2015) there are two factors that
cause learning difficulties in students, i.e. internal and
external factors. Whereas external factors that cause
learning difficulties are factors that exist outside
individual or students. While external factors include
learning methods, learning media, and learning
resources. Then it can be obtained questionnaire
framework of the factors that causing students’
learning difficulties as follows. The results of the
questionnaire number 21 to 45 about external factors.
This external factors contain several indicators,
among others: the relationship between students and
parents, the relationship between students and
teachers, the relationship between students and
employees/staff, the way of teachers’ presentation,
activities in the community, the relationship between
students and peers, home atmosphere, school
No
Indicator
Questionnaire Number
Total Questions
%
Sequence
1
The fitness level of body organs
1,2,3
3
11,92
6
2
The health level of the hearing and seeing senses
4,5,6
3
16,30
1
3
The level of success in learning the material
7,8
2
11,88
7
4
Attitude towards learning
9,10,11
3
15,74
3
5
Level of attention to learning
12,13,14
3
14,92
4
6
Talent in learning
15,16,17
3
15,78
2
7
Motivation in learning
18,19,20
3
13,46
5
ICLI 2018 - 2nd International Conference on Learning Innovation
224
curriculum, school environment, school facilities and
infrastructure, weather conditions and study time
used by students. In table 3 is the result of responses
related to external factors that cause students’
learning difficulties.
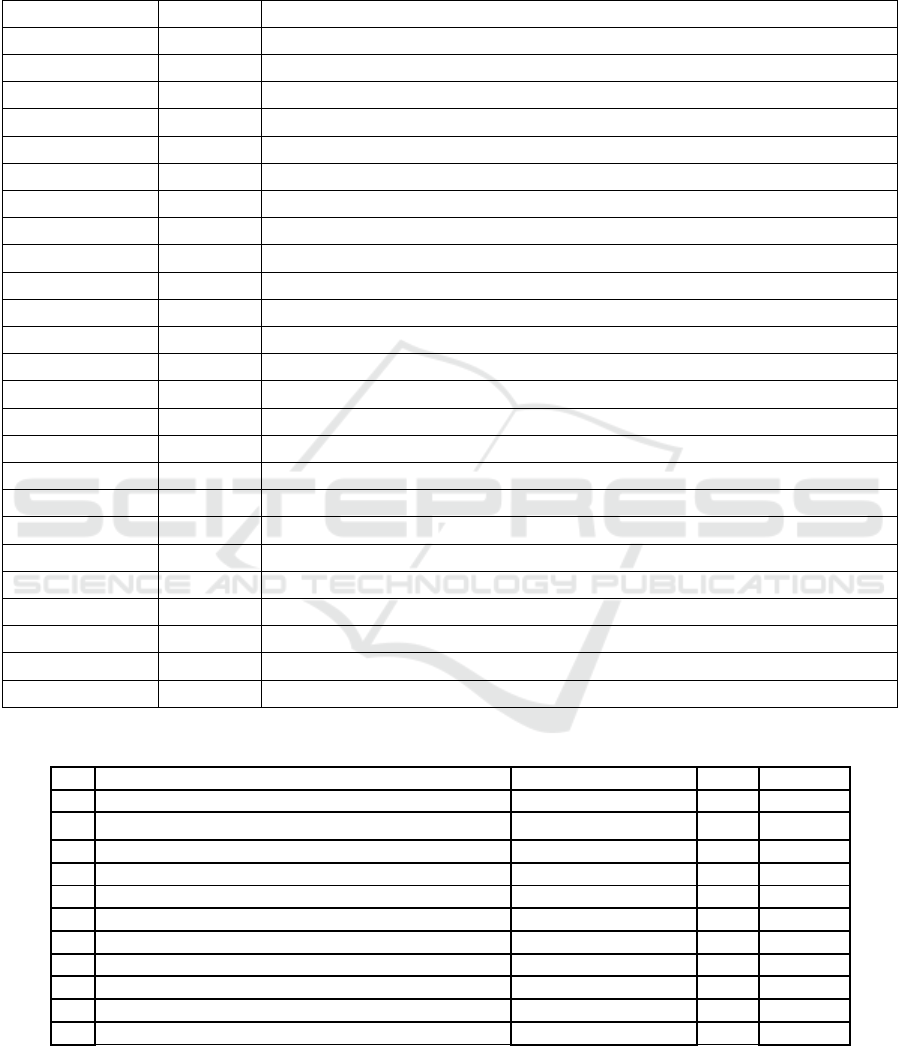
Table 3. Questionnaire Result of External Factors Causing Students’ Learning Difficulties
Table 4. Classification of Questionnaire Results of External Factors Causing Students’ Learning Difficulties
Item Number
Total
Indicator
21
137
The relationship between students and parents
22
135
The relationship between students and parents
23
134
The relationship between students and parents
24
131
The relationship between students and teachers
25
131
The relationship between students and teachers
26
129
The relationship between students and employees/staff
27
128
The relationship between students and employees/staff
28
127
The way of teachers’ presentation
29
126
The way of teachers’ presentation
30
124
The way of teachers’ presentation
31
121
Activities in the community
32
115
Activities in the community
33
114
The relationship between students and peers
34
112
The relationship between students and peers
35
112
Home atmosphere
36
110
Home atmosphere
37
101
School curriculum
38
100
School curriculum
39
97
School environment
40
92
School environment
41
91
School facilities and infrastructure
42
82
School facilities and infrastructure
43
80
School facilities and infrastructure
44
73
Weather conditions and study time used by students
45
64
Weather conditions and study time used by students
No
Indicator
Questionnaire Number
%
Sequence
1
The relationship between students and parents
21,22,23
14,68
1
2
The relationship between students and teachers
24,25
9,47
3
3
The relationship between students and employees/staff
26,27
9,29
4
4
The way of teachers’ presentation
28,29,30
13,63
2
5
Activities in the community
31,32
8,53
6
6
The relationship between students and peers
33,34
8,17
7
7
Home atmosphere
35,36
8,03
8
8
School curriculum
37,38
7,27
9
9
School environment
39,40
6,83
10
10
School facilities and infrastructure
41,42,43
9,15
5
11
Weather conditions and study time used by students
44,45
4,95
11
Analysis Towards Factors of Students’ Learning Difficulties at Muhammadiyah Elementary Schools In Sayegan Sub-District
225

There is one indicator for several questions such
as the relationship between students and parents is
found in questions number 21 to 23; the relationship
between students and teachers is found in questions
number 24 and 25; relationship between students and
employees/staff is found in questions number 26 and
27; The way teachers' presentation is in questions
number 28 to 30; activities in the community are
found in questions 31 and 32; relationship between
students and peers is found in questions 33 and 34;
the home atmosphere is in the questions number 35
and 36; the school curriculum is found in questions
number 37 and 38; the school environment is found
in questions number 39 and 40; school facilities and
infrastructure are found in questions number 41 to 43;
weather conditions and study time used by students
are found in questions number 44 and 45. Therefore,
from the explanation above the results of the
questionnaire can be classified as in table 4.
The results of the research on the main external
factors that causing students’ learning difficulties in
elementary schools in Sayegan Sub-District are: 1)
Relationship between students and parents is 14,68%;
2) The way of teachers’ presentation is 13,63%; 3)
The relationship between students and teachers is
9,47%; 4) Relationship between students and
employees/staff is 9,29%; 5) School facilities and
infrastructure is 9,15%; 6) activities in the community
is 8,53%; 7) Relationship between students and peers
is 8,17%; 8) Home atmosphere is 8,03%; 9) School
curriculum is 7,27%; 10) School environment is
6,83%; 11) Weather conditions and study time used
by students is 4,95%.
So it can be concluded that the main external
factor that causes learning difficulties for students of
Muhammadiyah Elementary Schools in Seyegan
Sub-District is the relationship between students and
parents by 14.68%. Parents as home tutors also play
an important role in overcoming children's learning
difficulties in addition to the teacher's role in the
school.
Factors the can cause problems that come from the
family area). the attitude of parents who isolate, do
not trust, unfair and do not want to accept their
children, b). broken home, divorce, bickering, c).
Authoritarian education, too weak and spoiled
children, d). Parents do not know their children's
abilities, personality traits, interests, talents, etc.
(Slameto, 2015).
These internal and external factors can influence
the students’ learning difficulties of Muhammadiyah
Elementary School in Seyegan Sub-District. So every
aspect above must be considered again, thus students
can minimize learning difficulties in every lesson. It
means that students can gain knowledge well without
any difficulties.
This research is similar to the research conducted
by (Watson, 2005) that there seem to be a number of
ways to change the outcomes for these students.
There is an urgent need for a national definition of
learning difficulties to be established. This is a
political imperative: it would allow the group to be
recognized as having special needs, allow real levels
of prevalence to be established, and help give
improved access to funding and appropriate
programmes. Special education knowledge and skills
should also be mandatory for all secondary teachers
including pre-service and practicing teachers.
Appropriate and extensive professional development,
that is relevant to teacher’s needs, should be available
and delivered by service providers with proven track
records. Courses should include appropriate teaching
practices, including mentoring, accommodations,
assessment and curriculum modification. Secondary
school structures and policies also need to be revised.
It is not sufficient to have inclusive policies if these
are undermined by other stakeholder policies, or at
the school level, by lack of teaching expertise and
understanding or by the school organization itself.
School structure should complement and support
good classroom practice that works effectively for the
benefit of all students. Finally, schools should be
involved in active community building in which the
values of respect, caring, collaboration and
cooperation are central elements. This combined with
good pedagogy and a strong, committed, positive
leadership should allow students with learning
difficulties to not only achieve their academic
potential but to thrive at school.
There are internal and external factors that must
be overcome when become learning barriers or cause
learning difficulties, especially the dominant ones.
This effort must be supported by students, families,
teachers, principals, related educational institutions,
the community, and the country.
4 CONCLUSION
Based on the results of the research described above,
the main internal factor that causes students’ learning
difficulties in elementary schools in Sayegan Sub-
District is the health level of the hearing and seeing
senses by 16.30% and the main external factor that
causes students’ learning difficulties in elementary
schools in Sayegan Sub-District is a relationship
between students and parents by 14.68%. Therefore,
the recommended aspect to be considered more in
ICLI 2018 - 2nd International Conference on Learning Innovation
226

order to overcome learning difficulties is the internal
factor of the level of success in learning the material
and external factors of the relationship between
students and parents. Therefore, for teachers and
parties involved in learning must pay more attention
to internal and external factors that can affect
students' learning difficulties. This is in order to
students can learn without difficulty because aspects
that lead to students’ learning difficulties has been
already prevented and minimized.
REFERENCES
Anderson, L. W. and Krathwohl, D. R. (2010) Kerangka
landasan untuk pembelajaran, pengajaran, dan
asesmen. Yogyakarta: Pustaka Belajar.
Arief, M. K. (2012) ‘Identifikasi Kesulitan Belajar Fisika
pada Siswa RSBI: Studi Kasus di RSMABI Se Kota
Semarang’, Unnes Physics Education Journal, 2012(1),
pp. 2–10.
Ariyati, E. and Nurdini, A. (2013) ‘Deskripsi Kesulitan
Belajar dan Faktor Penyebabnya pada Materi Fungi di
SMA Islam Bawari Pontianak dan Upaya
Perbaikannya’, Jurnal Pendidikan dan Pembelajaran,
2(9).
Ashman, A. and Elkins, J. (2004) Educating children with
diverse abilities. Pearson Education Australia.
Aunurrahman, A. (2008) Belajar dan Pembelajaran.
Bandung: Alfabeta.
Basiran, B. (2012) ‘Faktor yang Mempengaruhi Kesulitan
dalam Belajar’, Jurnal Edukasi, pp. 1–18.
Bennet, M. (1952) Problems of Self-Discovery and Self-
Direction. New York: McGraw-Hill.
Darma, S. (2014) ‘Membangun Bangsa Melalui Literasi:
Apa, Mengapa, dan Bagaimana’, in Seminar Nasional
BK-PGSD Universitas Ahmad Dahlan. Yogyakarta:
Universitas Ahmad Dahlan.
Djamarah, D. and Syaiful, B. (2011) Psikologi belajar.
Jakarta: Rineka Cipta.
Dublin, T. M. C. (2012) ‘Entrepreneurship Skills for
Growth-Orientated Businesses Institute of Technology
Report for the Workshop on Skills Development for
SMEs and Entrepreneurship’. Copenhagen: OECD.
Hakim, T. (2008) Belajar Secara Efektif. Jakarta: Rineka
Cipta.
Horowitz, C. K. (2014) The State of Learning Disabilities.
3rd ed. New York: National Center for Learning
Disabilities.
Van Kraayenoord, F. (1998) Responding to students with
severe and persistent literacy difficulties in secondary
schools. Brisbane: University of Queensland.
Slameto, S. (2015) Belajar dan Faktor-faktor yang
Mempengaruhi. Jakarta: Rineka Cipta.
Soon, W., Lioe, L. T. and McInnes, B. (2011)
‘Understanding the difficulties faced by engineering
undergraduates in learning mathematical modelling’,
International Journal of Mathematical Education in
Science and Technology, 42(8), pp. 1023–1039.
Sugiyanto, S. (2014) Psikologi Pendidikan Diagnosis
Kesulitan Belajar (DKB). Yogyakarta: Universitas
Negeri Yogyakarta.
Syah, M. (2015) Psikologi Belajar. Jakarta: Rajagrafindo
Persada.
Volman, M. J. M., Van Schendel, B. M. and Jongmans, M.
J. (2006) ‘Handwriting difficulties in primary school
children: A search for underlying mechanisms’,
American Journal of Occupational Therapy, 60(4), pp.
451–460.
Watson, J. A. (2005) ‘Mainstreamed students with learning
difficulties: Failing and underachieving in the
secondary school’, Australian Journal of Learning
Disabilities, 10(2), pp. 43–49.
Weare, K. (2000) Promoting mental, emotional and social
health. London: Routledge.
Analysis Towards Factors of Students’ Learning Difficulties at Muhammadiyah Elementary Schools In Sayegan Sub-District
227
