
An Analysis of Service Quality using Importance Performance
Analysis and Gap Analysis at a Commercial Bank in Indonesia
Dedy Ansari Harahap
1,2
, Ratih Hurriyati
1
, Disman
1
, Vanessa Gaffar
1
, Dita Amanah
1,3
1
Universitas Pendidikan Indonesia, Bandung, Indonesia
2
Universitas Islam Sumatera Utara, Medan, Indonesia
3
Universitas Negeri Medan, Medan Indonesia
Keywords: Service Quality, Importance Performance Analysis, Gap Analysis & Banking.
Abstract: Increasingly complex challenges in the banking industry and the rapid advancement of information
technology, encourage the banking industry to respond quickly to fulfill customer needs by providing safe
and quality banking products and services. This study aims to measure and determine the service quality of
PT. BNI (Persero) Tbk, USU Medan. This study is a descriptive quantitative research with the sample of 120
respondents and analyzed statistically using Importance Performance Analysis (IPA) and Gap Analysis
(GAP). The results showed the service quality with the IPA method was very good with the level of
performance is 80.40%, while the GAP method obtained from the whole instrument is -0.95, which indicates
that the service quality is good. This article provides guidelines that every bank must continuously improve
its service to customers thus customers feel satisfied and do not switch to another bank. Service quality is
important in order to attract customers become loyal to the bank.
1 INTRODUCTION
Banks are required to be more professional,
trustworthy in service and able to meet customer
desires quickly. An increasingly competitive banking
industry, not only competing with each other; but also
with non-banks and other financial institutions
(Kaynak & Kucukemiroglu, 1992;Hull, 2002). All
services and facilities provided by banks have a very
important role in measuring the level of quality of
banking services along with banking performance.
Intensification of competition in the financial services
industry to remain competitive, financial institutions
have provided a variety of financial services (Hinson,
Mohammed, & Mensah, 2006). All research was
carried out using SERVQUAL on the basis of five
dimensions namely; tangibility (physical facilities),
reliability, responsiveness, assurance, and empathy.
Quality of service is considered a critical measure
of organizational performance. This remains the most
important issue in the marketing literature in general
and the special service marketing literature (Jensen
and Markland, 1996).
Academic researchers (Hawes & Rao, 1985;
Hermmasi, Strong, & S. Taylor, 1994; Martilla &
James, 1977; Swinyard, 1980), advocate the use of
importance-performance analysis (IPA) as a
managerially relevant approach to the interpretation
of customer perceptions of services into strategic
application and organizational resources. There is a
precedent for using IPA to get a better understanding
of banking customers' perceptions of selected service
factors (Ennew, Reed, & Binks, 1993; Joseph,
McClure, & Joseph, 1999; Joseph & Stone, 2003;
Swinyard, 1980).
The reputable banking practitioners (Albro, 1999;
Motley, 1999), have recommended great adoption of
performance-interest grids (described in detail later in
this article) as heuristic decision tools that are useful
for guiding strategic analysis.
BNI USU Medan is the main branch office located
in the largest university area in North Sumatra located
in Medan. Customers are not only the society, but also
USU students, staff and lecturers who are making
transaction at this bank. This bank is very strategic
that can help every one of the surrounding their
business activities. This bank also holds the salary
accounts of all USU lecturers and staff, banks for
paying tuition fees for students, registration fees for
state university tests. This bank has experienced a lot
of renewal in the physical building in 2017-2018, so
Ansari Harahap, D., Hurriyati, R., Disman, ., Gaffar, V. and Amanah, D.
An Analysis of Service Quality using Importance Performance Analysis and Gap Analysis at a Commercial Banks in Indonesia.
DOI: 10.5220/0008437901610168
In Proceedings of the 4th Sriwijaya Economics, Accounting, and Business Conference (SEABC 2018), pages 161-168
ISBN: 978-989-758-387-2
Copyright
c
2019 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
161

it is known as a bank that has the best service, fast,
clean and comfortable room (IDLokasi, 2018).
This article discusses the gaps in the literature by
analyzing the performance-importance of customer
perceptions of bank service. According to the authors,
the research on service quality using IPA and GAP
analysis is still a little done, so it is important to
analyze the performance-importance of customer
perceptions especially at BNI banks. The main focus
of this research is to identify gaps in service quality
between consumer expectations and perceptions at
BNI USU Medan. So that it can be a customer's
preference in considering the quality of service of a
bank in Medan in particular and Indonesia in general.
This study found that what consumers expect is
far more than their perceptions. The key to the
success of a bank is to remain competitive and
continually improve the quality of services to better
meet customer needs and provide superior services.
Banks must understand clearly and precisely
customer expectations, because customers compare
perceptions with expectations in assessing the quality
of bank services.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
Service quality is the result of an evaluation
process in which consumers compare expectations
with the reality of services perceived and accepted by
customers (Lai & Hitchcock, 2016). Service quality
can also distinguish between customer expectations
received and services perceived from a particular
place (Kuo, Wu, & Deng, 2009). Bitner (1990),
defines service quality as the customer's overall
impression of the inferiority/relative advantage of
service providers that is often considered the same as
the customer's overall attitude towards the company
(Parasuraman, Zeithaml, & Berry, 1988). Service
quality includes several points, one of which is the
attitude developed above all previous meetings with
service companies (Parasuraman, Zeithaml, & Berry,
1985; Parasuraman et al., 1988; Bitner, 1990).
Since its formulation, SERVQUAL has been used
in various service industries and various countries.
Some SERVQUAL-based writers have questioned
psychometric strengths and their uses. The principle
among these is that criticism depends on two scales
measuring perception and hope, when one scale
(simple perceptions or performance measures) will be
shorter, simpler and easier to understand and
ultimately more effective. The use of hope is
questioned by (Babakus & Mangold, 1992; Cronin &
Taylor, 1992), measuring the quality of services in
banks concludes that the disconfirmation approach
has little support both theoretically and empirically.
Teas (1994), questions the interpretation and
operationalization of expectations, and (Avkiran,
1999), notes the tendency to set higher expectations
than perceptions so as to make the gap between
perception and expectations inevitable. In addition,
for practical reasons the use of two scales and
negative-tone question items is both time-consuming
and too complex for most respondents (Avkiran,
1999).
Researchers have tried to develop conceptual
models to explain service quality and to measure
service quality perceived by consumers in different
industries (Seth, Deshmukh, & Vrat, 2005). The
SERVQUAL model has become the most extensive
and successful measurement of service quality used
in the twenty-first century (Tsoukatos & Rand, 2006).
A good operational example of a standard framework
for understanding service quality is the SERVQUAL
instrument developed by Parasuraman. The
researchers found five general dimensions with focus
group interviews that they labeled: reliability,
responsiveness, physical evidence, assurance and
empathy (Wong & Sohal, 2002). Service quality is an
important factor for success in the banking sector.
Thus, some bank managers emphasize various
dimensions of service quality (Glaveli, Petridou,
Liassides, & Spathis, 2006).
Most researchers support the quality of service as
a multidimensional construct such as tangibles,
responsiveness, reliability, empathy and assurance
(Parasuraman et al., 1985; Parasuraman et al., 1988;
Carman, 1990; Bitran & Lojo, 1993; Lewis, Orledge,
& Mitchell, 1994; Amin & Isa, 2008). Likewise in the
study, Harahap (2006), measures the quality of
services using 5 dimensions, namely; tangible,
reliability, responsiveness, assurance & empathy.
Generally, service quality has two main dimensions
(Grönroos, 1984; Parasuraman, Berry, & Zeithaml,
1991; Mcdougall & Levesque, 1994; Levesque,
Terrence; Mc Dougall, 1996). The first dimension is
called the core aspect of service (reliability), while the
second dimension is called the service process aspect
(tangibles, responsiveness, empathy and assurance).
More precisely, reliability is primarily related to
service outcomes, while physical evidence,
responsiveness, empathy and assurance are
associated with the release of services (Parasuraman
et al., 1991).
SERVQUAL was originally developed by
Parasuraman et al., (1985). This model consists of ten
components. SERVQUAL provides technology to
measure and manage service quality (SQ).
SEABC 2018 - 4th Sriwijaya Economics, Accounting, and Business Conference
162

SERVQUAL fills the gap between what customers
expect by SQ method and what they actually get. SQ
is presented as a multi-dimensional construction. In
the original formulation (Parasuraman et al., (1985),
identified ten components of SQ. In the 1988 work
this dimension was reduced to five dimensions:
tangible, reliability, responsiveness, assurance and
empathy.
Customer evaluation of bank service quality
involves the use of a variety of criteria that tend to
differ in importance based on individual needs and
preferences, with several criteria that clearly carry
more weight than others. While some criteria may be
important, only a few are most important.
Martilla & James (1977), developing simple
importance-performance techniques, the most
interesting features are the importance and
performance results can be illustrated graphically on
a two-dimensional grid. The four quadrants on the
grid can provide in-depth information about each of
the attributes tested. According to Ortinau, Bush,
Bush, & Twible (1989), each quadrant can be
described as follows: 1). Concentrate here; This is
where customers feel that certain attributes are very
important but their performance is not satisfactory, 2).
Keep up the good work; This is where
customers feel that certain attributes are very
important and they are satisfied with their
performance, 3). Low priority; Where customers are
not satisfied with the performance of certain attributes
but they do not consider it important, and 4). Possible
overkill; Customers are satisfied with the
performance of certain attributes but customers do not
consider it important.
Hermmasi et al., (1994), redeveloping the grid of
importance-performance, by drawing axes based on
their importance and overall performance rather than
based on the midpoint of the scale. Hermmasi et al.,
(1994), provides an alternative tool that is useful for
developing strategies because it provides a clearer
picture of the factors that are very important for
resource allocation. Research using importance-
performance measurement has been carried out in a
number of industries including food, housing and
education (Martilla & James, 1977; Joseph & Joseph,
1997) and in the banking industry (Joseph et al.,
1999).
Although many measures of service quality have
their supporters and critics, according to Hermmasi et
al., (1994), the method of importance-performance is
the most appropriate method for measuring service
quality in the banking industry. This method seems to
provide a useful and practical regulatory tool for
recognizing what is most important from the
customer's perspective, allowing bank managers to
ensure that the level of performance in the most
important areas is equal to the customer's perception.
3 RESEARCH METHOD
The sample was obtained through a questionnaire
distributed to customers who transacted at BNI USU
Medan. To get the right sampling frame, non
probability sampling was chosen as a sampling frame
that was more suitable for the purpose of this study.
Respondents were randomly selected from customers
who came during the transaction. Overall 130
questionnaires were distributed but only 120
questionnaires could be used. List of questions related
to customer expectations and the performance of bank
service quality. This research is a quantitative
descriptive research that is processed statistically by
the importance performance analysis (IPA) method
and gap analysis (GAP). Calculation of analysis used
version 22.00 Windows of the SPSS (Statistical
Packages for the Social Science) program.
4 RESULTS
Based on calculations from the results of the five-
dimensional SERVQUAL research namely; tangible,
responsiveness, reliability, assurance and empathy.
The measurement is done by calculating the
comparison between the reality of the service
received and the expectation of the desired service.
An Analysis of Service Quality using Importance Performance Analysis and Gap Analysis at a Commercial Banks in Indonesia
163
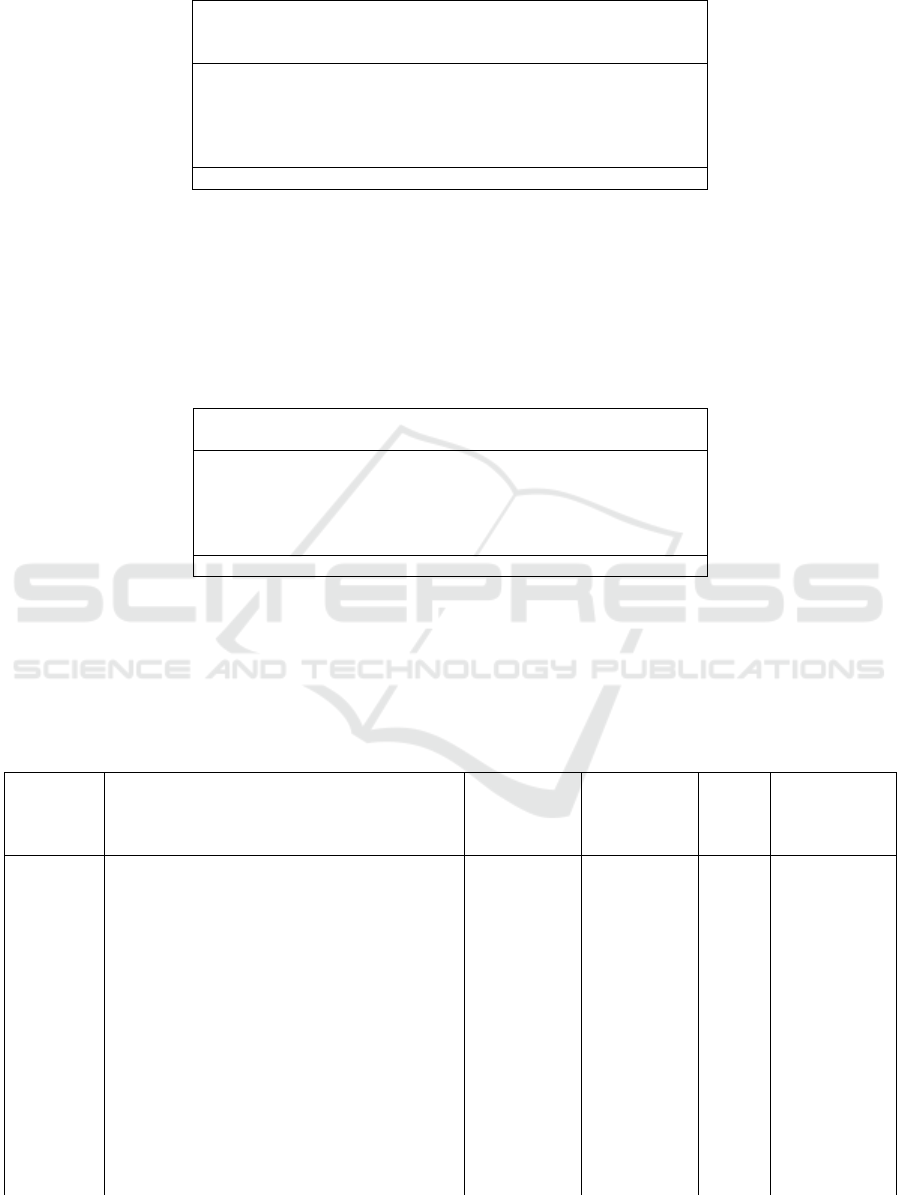
Table 1: Average Calculation of Suitability Level of Service Quality Dimensions
No
Dimensions
SERVQUAL
Average
Importance
Average
Performance
Level of
Conformity
(%)
1
Tangible
4,71
3,98
84,44%
2
Reliability
4,87
3,95
81,15%
3
Responsiveness
4,80
3,79
78,87%
4
Assurance
4,80
3,86
80,41%
5
Empathy
4,82
3,73
77,27%
Average
4,80
3,86
80,40%
Table 1. shows that the average of the five
SERVQUAL dimensions for service quality is
80.40%. While in each dimension is tangible 84.44%,
reliability 81.15%, responsiveness 78.87%, assurance
80.41% and empathy 77.27%. Based on the results of
the research data as a whole the quality of services
seen from the dimensions (reliability, responsiveness,
assurance, empathy & tangible) has the value of
conformity is very good according to the customer.
Table 2: Average Gap Analysis Calculation of Service Quality Dimensions
No
Dimensions
SERVQUAL
Average
Importance
Average
Performance
GAP
(P-I)
1
Tangible
4,71
3,98
-0,73
2
Reliability
4,87
3,95
-0,92
3
Responsiveness
4,80
3,79
-1,02
4
Assurance
4,80
3,86
-0,94
5
Empathy
4,82
3,73
-1,10
Average
4,80
3,86
-0,95
Table 2. shows that the mean of the five
SERVQUAL dimensions for PI gap assessment is -
0.95. Whereas in each dimension are tangible -0.73,
reliability -0.92, responsiveness -1.02, assurance -
0.94 and empathy -1.10. Based on the results of the
research data as a whole the quality of services seen
from dimensions (reliability, responsiveness,
assurance, empathy & tangible) has a gap value that
is good according to the customer.
Table 3: Bank Service Quality Performance
Attribute
number
Attribute
Level of
Importance
(Yi)
Level of
Perfomance
( Xi)
Scores
Servqual
Performance
T1
The company has modern equipment
581
489
84.17
very good
T2
The physical facilities available are quite
interesting
551
466
84.57
very good
T3
Neat looking employee
548
506
92.34
very good
T4
Service-related materials (such as pamphlets
or brochures) appeal to customers
580
446
76.90
good
RL1
Companies always keep promises to do things
at certain times.
582
465
79.90
good
RL2
The company provides solutions if customers
face problems
586
474
80.89
very good
RL3
The company prioritizes service
587
485
82.62
very good
RL4
The company provides services and promises
to do so
586
473
80.72
very good
RL5
The company is responsive in solving
operational problems in banking transactions
582
474
81.44
very good
SEABC 2018 - 4th Sriwijaya Economics, Accounting, and Business Conference
164

RS1
Employees always explain well the questions
asked by customers
578
476
82.35
very good
RS2
Employees provide fast service to customers
577
445
77.12
good
RS3
Employees always strive to help customers
576
462
80.21
very good
RS4
Employees do not object to meeting each
customer's request
574
434
75.61
good
AS1
Customers trust employees
582
478
82.13
very good
AS2
Customers feel safe when making transactions
578
506
87.54
very good
AS3
Employees are always friendly to their
customers
572
404
70.63
good
AS4
Employees have more knowledge when
answering each customer's questions
571
463
81.09
very good
EM1
The company gives full attention to each
customer
576
445
77.26
good
EM2
The company always instills confidence in its
customers
575
473
82.26
very good
EM3
The company has employees who pay
attention to each customer
579
431
74.44
good
EM4
The company tries to attract customers
586
461
78.67
good
EM5
Employees understand the customer's specific
needs
577
426
73.83
good
Based on the results of respondents' evaluations of
BNI service quality performance attributes, in Table
3. the average is 80.30%. This illustrates that the
customer's assessment of BNI's service quality
performance is in very good criteria.
Importance-performance analysis in this study
was conducted on all respondents. From the data
using SPSS 22.00, the Cartesius diagram of IPA is
obtained for all customer respondents on the quality
of bank services, as follows:
Figure 1: Cartesian Diagram of Service Quality Dimensions
Kuadran I
Kuadran II
Kuadran III
Kuadran IV
An Analysis of Service Quality using Importance Performance Analysis and Gap Analysis at a Commercial Banks in Indonesia
165

Based on the figure 1 Cartesius Diagram on the
dimensions of service quality above can be explained
that:
Decision Making (IPA)
Quadrant I
Concentrate here
Attribute number : 4, 11, 20, 21, 22
Quadrant II
Keep up the good work
Attribute number : 1, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 14, 15
Quadrant III
Low priority
Attribute number : 12, 13, 16, 18
Quadrant IV
Possible overkill
Attribute number : 2, 3, 17, 19
Figure 1. shows that service quality has 5 (five)
attributes found in quadrant I (Concentrate Here). The
company prioritizes to focus on improving the
attributes in this quadrant, because the quality of
service performance is not satisfactory. 9 (nine)
attributes in Quadrant II (Keep Up The Good Work),
where it was concluded that customers were very
satisfied. Companies must maintain service quality
attributes in this quadrant II. 4 (four) attributes in
quadrant III (Low Priority), where attributes in this
quadrant are considered insignificant by the customer
and the service is not satisfactory. 4 (four) attributes
in quadrant IV (Possible Overkill), where customers
already feel satisfied with the performance of BNI
services.
5 DISCUSSION
Based on the results of research from the five
dimensions of SERVQUAL namely; tangible,
responsiveness, reliability, assurance and empathy.
Statistical techniques using the Importance
Performance Analysis (IPA) method show that the
level of bank service quality performance of 80.40%
is appropriate and very good, and Gap Analysis
(GAP) shows that the level of bank service quality
gap of -0.95 is good according customer. According
to Parasuraman et al., (1991), if the result of the gap
< -1 means good, and the result > -1 means that the
quality of the service provided is not good. In
principle, the data obtained through the SERVQUAL
instrument is used to calculate the gap score from the
average service quality dimensionon.
The In the Cartesian diagram shows the quality of
service is there 5 attributes (tangible4,
responsiveness2, empathy3, empathy4, empathy5) in
quadrant I, 9 attributes (tangible1, reliability1,
reliability2, reliability3, reliability4, reliability5,
responsiveness1, assurance1, assurance2) in quadrant
II, 4 attributes (responsiveness3, responsiveness4,
assurance3, empathy1) quadrant III and 4 attributes
(tangible2, tangible3, assurance4, empathy2)
quadrant IV.
Research with the analysis of "importance-
performance" carried out by (Martilla & James, 1977;
Ennew et al., 1993; Hermmasi et al., 1994; Slack,
1994), stated that customer assessment of the
performance of retail banks is compared with the
score of importance that they feel in the individual e-
SQ attribute. This result is also graphically illustrated
in a two-dimensional grid, which places the e-SQ
factor into one of four quadrants, namely;
"Concentrate here" (service area with a high level of
customer importance but a low level of performance);
"Keep up the good work" (areas with high importance
and strong levels of performance); "Low priority"
(service dimensions with a low level of importance
and performance); and "Possible overkill" (service
area with low importance but strong performance
level). Thus, this grid provides managers with
strategic tools that are useful for recognizing the most
important attributes from customer's perspective, and
challenging them to ensure high levels of
performance in areas considered critical by customers
(Martilla & James, 1977; Hermmasi et al., 1994;
Slack, 1994).
According to Buzzell & Gale (1987), Company
performance in the long run depends on the quality of
products and good services, a business can grow by
improving its quality, which leads to increased
market share and market expansion.
6 CONCLUSIONS
The SERVQUAL application has received a lot of
support and criticism. Overall, from bank services,
the gap approach to service quality and the IPA
SEABC 2018 - 4th Sriwijaya Economics, Accounting, and Business Conference
166

approach is conceptually interesting and
operationally useful.
A brief description of the 22 items in the tested
questionnaire provides a better understanding of gap
analysis, so that it can be concluded; 1) The level of
conformity through the Importance Performance
Analysis (IPA) method shows that BNI's service
quality performance is 80.40%. Means the service is
appropriate and customer assessment is very good. 2)
The level of gap through Gap Analysis (GAP) shows
that the level of BNI service quality gap is -0.95. This
is good according to customers. 3) Attributes that are
considered important and have excellent service
quality performance for bank customers are tangible,
reliability and assurance while responsiveness and
empathy are considered good by customers.
Customers expect high quality in service but
actual customer satisfaction is low. So this can be a
key for BNI to improve the quality of services. For
example, BNI is responsive in providing assistance to
customers. Concisely, this research contributes to
understanding important issues related to the quality
of bank services and provides some useful managerial
insights for bank.
REFERENCES
Albro, W. (1999). A strategy grid helps improve customer
service. Bank Marketing, 31(12), 36.
Amin, M., & Isa, Z. (2008). An examination of the
relationship between service quality perception and
customer satisfaction: A SEM approach towards
Malaysian Islamic banking. International Journal of
Islamic and Middle Eastern Finance and Management,
1(3), 191–209.
https://doi.org/10.1108/17538390810901131
Avkiran, N. K. (1999). Quality customer service demands
human contact. International Journal of Bank
Marketing, 17(2), 61–74.
https://doi.org/10.1108/02652329910258862
Babakus, E., & Mangold, W. G. (1992). Adapting the
SERVQUAL Scale to Hospital Services: An Empirical
Investigation. Health Services Research, 26(6), 767–
786. https://doi.org/January 17,1991
Bitner, M. J. (1990). Evaluating Service Encounters: The
Effects of Physical Surroundings and Employee
Responses. Journal of Marketing, 54(2), 69–82.
https://doi.org/10.2307/1251871
Bitran, G. R., & Lojo, M. (1993). A framework for
Analyzing Service Operations. European Management
Journal, 11(3), 271–282. https://doi.org/10.1016/0263-
2373(93)90053-K
Buzzell, R. D., & Gale, B. T. (1987). The PIMS Principles:
Linking Strategy and Performance. New York: Free
Press.
Carman, J. M. (1990). Consumer perceptions of service
quality: An assessment of the SERVQUAL dimensions.
Journal of Retailing, 66(1), 33–55.
Cronin, J. J., & Taylor, S. a. (1992). Measuring Quality : A
Reexamination and Extension. Journal of Marketing,
56(3), 55–68. https://doi.org/10.2307/1252296
Ennew, C. T., Reed, G. V., & Binks, M. R. (1993).
Importance‐Performance Analysis and the
Measurement of Service Quality. European Journal of
Marketing.
https://doi.org/10.1108/03090569310026402
Glaveli, N., Petridou, E., Liassides, C., & Spathis, C.
(2006). Bank service quality: Evidence from five
Balkan countries. Managing Service Quality, 16(4),
380–394. https://doi.org/10.1108/09604520610675711
Grönroos, C. (1984). A Service Quality Model and its
Marketing Implications. European Journal of
Marketing, 18(4), 36–44.
https://doi.org/10.1108/09574090910954864
Harahap, D. A. (2006). Hubungan Kualitas dan Loyalitas
Nasabah Jasa Perbankan PT. Bank Rakyat Indonesia
(Persero), Tbk Kota Medan. Program Pascasarjana
Syiah Kuala Banda Aceh.
https://doi.org/10.17605/OSF.IO/UGK4Z
Hawes, J. M., & Rao, C. P. (1985). Using importance-
performance analysis to develop health care marketing
strategies. Journal of Health Care Marketing, 5(4), 19–
25.
Hermmasi, M., Strong, K., & S. Taylor. (1994). Measuring
service quality for planning and analysis in service
firms. Journal of Applied Business Research, 10(4),
24–34.
Hinson, R., Mohammed, A., & Mensah, R. (2006).
Determinants of Ghanaian Bank Service Quality in a
Universal Banking Dispensation. Banks and Bank
Systems, 1(2), 69–81. Retrieved from
papers3://publication/uuid/FC81DFFC-21CE-4199-
BD5F-D9CB93A03B49
Hull, L. (2002). Foreign-owned banks : Implications for
New Zealand ’ s financial stability (No. DP2002/05).
New Zealand.
IDLokasi. (2018). Bank BNI Cabang USU Medan, Bank
BNI Di Jalan Dr Mansyur. Medan. Retrieved from
https://www.idlokasi.com/2018/02/06/bank-bni-
cabang-usu-medan/
Joseph, M., & Joseph, B. (1997). Service quality in
education : a student perspective. Quality Assurance in
Education, 5(1), 15–21.
https://doi.org/10.1080/0954412979839
Joseph, M., McClure, C., & Joseph, B. (1999). Service
quality in the banking sector : the impact of technology
on service delivery. International Journal of Bank
Marketing, 17(4), 182–191.
Joseph, M., & Stone, G. (2003). An empirical evaluation of
US bank customer perceptions of the impact of
technology on service delivery in the banking sector.
International Journal of Retail & Distribution
Management, 31(4), 190–202.
https://doi.org/10.1108/09590550310469185
Kaynak, E., & Kucukemiroglu, O. (1992). Bank and
Product Selection : Hongkong. International Journal of
An Analysis of Service Quality using Importance Performance Analysis and Gap Analysis at a Commercial Banks in Indonesia
167

Bank Marketing, 10(1), 3–16.
Kuo, Y. F., Wu, C. M., & Deng, W. J. (2009). The
relationships among service quality, perceived value,
customer satisfaction, and post-purchase intention in
mobile value-added services. Computers in Human
Behavior, 25(4), 887–896.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2009.03.003
Lai, I. K. W., & Hitchcock, M. (2016). A comparison of
service quality attributes for stand-alone and resort-
based luxury hotels in Macau: 3-Dimensional
importance-performance analysis. Tourism
Management, 55, 139–159.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tourman.2016.01.007
Levesque, Terrence; Mc Dougall, G. H. G. (1996).
Determinants of customer satisfaction in retail banking.
International Journal of Bank Marketing , 14(7), 12–
20. Retrieved from
http://www.emeraldinsight.com/doi/pdfplus/10.1108/0
2652329610151340
Lewis, B. R., Orledge, J., & Mitchell, V.-W. (1994).
Service Quality: Students’ Assessment of Banks and
Building Societies. International Journal of Bank
Marketing, 12(4), 3–12.
Martilla, J. A., & James, J. C. (1977). Importance-
Performance Analysis. Journal of Marketing, 41(1),
77–79.
Mcdougall, G. H. G., & Levesque, T. J. (1994). A Revised
View of Service Quality Dimensions A Revised View
of Service Quality Dimensions : An Empirical
Investigation. Journal of Professional Services
Marketing, 11(1), 189–201.
https://doi.org/10.1300/J090v11n01
Motley, L. B. (1999). Customer surveys that work. Bank
Marketing, 31(12), 40.
Ortinau, D. J., Bush, A. J., Bush, R. P., & Twible, J. L.
(1989). The Use of Importance-Performance Analysis
for Improving the Quality of Marketing Education:
Interpreting Faculty-Course Evaluations. Journal of
Marketing Education, 11(2), 78–86.
Parasuraman, A., Berry, L. L., & Zeithaml, V. A. (1991).
Refinement and Reassessment of the SERVQUAL
scale. Journal of Retailing, 67(4), 420–450.
Parasuraman, A., Zeithaml, V. A., & Berry, L. L. (1985). A
Conceptual Model of Service Quality and Its
Implications for Future Research. The Journal of
Marketing, 49(4), 41–50.
Parasuraman, A., Zeithaml, V. A., & Berry, L. L. (1988).
SERQUAL: A Multiple-Item Scale for Measuring
Consumer Perceptions of Service Quality. Journal of
Retailing, 64(1), 12–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0148-
2963(99)00084-3
Seth, N., Deshmukh, S. G., & Vrat, P. (2005). Service
quality models: a review. International Journal of
Quality & Reliability Management (Vol. 22).
https://doi.org/10.1108/02656710510625211
Slack, N. (1994). The Importance‐Performance Matrix as a
Determinant of Improvement Priority. International
Journal of Operations & Production Management,
14(5), 59–75.
https://doi.org/10.1108/01443579410056803
Swinyard, W. R. (1980). Strategy development with
importance/performance analysis. Journal of Bank
Research, 10(4), 228–234.
Teas, K. R. (1994). Expectations as a comparison standard
in measuring service quality : An assess ... Journal of
Marketing, 58(1), 132–139.
Tsoukatos, E., & Rand, G. K. (2006). Path analysis of
perceived service quality, satisfaction and loyalty in
Greek insurance. Managing Service Quality, 16(5),
501–519. https://doi.org/10.1108/09604520610686746
Wong, A., & Sohal, A. (2002). Customers’ perspectives on
service quality and relationship quality in retail
encounters. Managing Service Quality: An
International Journal, 12(6), 424–433.
https://doi.org/10.1108/09604520210451902
SEABC 2018 - 4th Sriwijaya Economics, Accounting, and Business Conference
168
