
Performance Measurement Analysis with Balanced Scorecard
Method (Case Study of Sriwijaya University and Bina Darma
University Palembang)
Mariska Aprilya Putri
Universitas Sriwijaya, Palembang, Indonesia
Keywords: Performance measurement, Balanced Scorecard, customer perspective, perspective finance, internal
business process perspective and growth and learning perspective.
Abstract: This study aims to find out and describe the performance of Sriwijaya University and Bina Darma
University Palembang with the balanced scorecard method. This type of research is qualitative research.
This study is viewed from four perspectives of the Balanced Scorecard, namely the customer perspective,
financial perspective, internal business process perspective and learning and growth perspective. The data
used are primary data in the form of a questionnaire where the respondents of this study involved students,
employees and lecturers of Sriwijaya University and Palembang Bina Darma University. The results of this
study are measuring performance from a customer perspective and financial perspective showing a fairly
good performance, while the perspective of internal business processes and the perspective of growth and
learning each show good performance.
1 INTRODUCTION
Preliminary
The era of globalization has had an influence on
the growth and development of the business world,
including the education service industry. Education
is an important factor in the development of human
resources. Education is a factor that is directly
related to the ability and progress of society. This is
because education is able to shape people's mindset
in a better direction. The higher the level of
education of a society will indirectly encourage the
level of national development to be faster and more
directed towards the development that is aspired.
The level of public awareness of education
increases with the needs and development. People
are increasingly aware that in facing challenges in
the future by having higher abilities, knowledge and
education. The higher the community's awareness of
the level of education requires a place or educational
institution that can accommodate and fulfill the
community's interest in higher education and science
that can improve their quality and ability. Higher
education is a level of education after secondary
education which includes diploma programs,
undergraduate programs, master's programs,
doctoral programs, and professional programs and
specialist programs organized by universities based
on Indonesian national culture (Government
Regulation No. 4 of 2014). As experienced by profit
oriented companies, competition in running its
operations is also experienced by non-profit
universities. The competition includes the field of
service to stakeholders, quality of graduates, and
tuition fees. Therefore, universities need strategic
planning to maintain life, win competition, and
develop themselves.
Appropriate and effective performance
measurement comprehensively includes not only
from the financial aspects, but also includes non-
financial aspects. By adding a measure of non-
financial performance, such as customer satisfaction,
productivity and cost effectiveness processes, human
resources and information technology. Organizations
are encouraged to pay attention to and provide
services that are the real drivers to realize financial
performance. The concept of balancing effort and
attention to financial and non-financial performances
Aprilya Putri, M.
Performance Measurement Analysis with Balanced Scorecard Method (Case Study of Sriwijaya University and Bina Darma University Palembang).
DOI: 10.5220/0008439202670273
In Proceedings of the 4th Sriwijaya Economics, Accounting, and Business Conference (SEABC 2018), pages 267-273
ISBN: 978-989-758-387-2
Copyright
c
2019 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
267
known as the Balanced Scorecard concept (Mulyadi,
2007).
Based on the explanation above it appears that
for now the Balanced Scorecard is more complete
than the existing performance measurement (ratios)
because external factors (customer perspective) are
also included in the performance measurement. This
needs to be done especially for organizations or
service companies including hospitals and
universities. The same thing was done in a study that
measured the service performance of the Indonesian
Islamic University (UII) with the Balanced
Scorecard approach where the results of the study
stated that the financial perspective of UII had a
successful efficiency and effectiveness in the use of
funds and the remaining amount of funds for the
benefit of development (Susilo, 2007), from the
perspective of internal business processes resulting
in a positive relationship between innovation and
organizational performance (mediaty, 2000), another
study from a customer perspective states that
students are satisfied with university performance,
internal business process perspective where the
results of the research questionnaire show that the
process of service to students has been done well.
From a learning and growth perspective also shows
employee satisfaction with the University (Sukesti,
2010).
Formulation of the problem
From the description above, a formulation of the
problem in this research can be compiled, namely
"What is the performance of Higher Education in
this case Sriwijaya University and Bina Darma
University Palembang when viewed from a
customer perspective, financial perspective,
perspective of internal business processes and
learning and growth perspective?
Research purposes
Referring to the formulation of the above
problem, the purpose of this research is to find out
and describe the performance of Sriwijaya
University and Bina Darma University Palembang if
viewed from a customer perspective, financial
perspective, internal business process perspective
and learning and growth perspective.
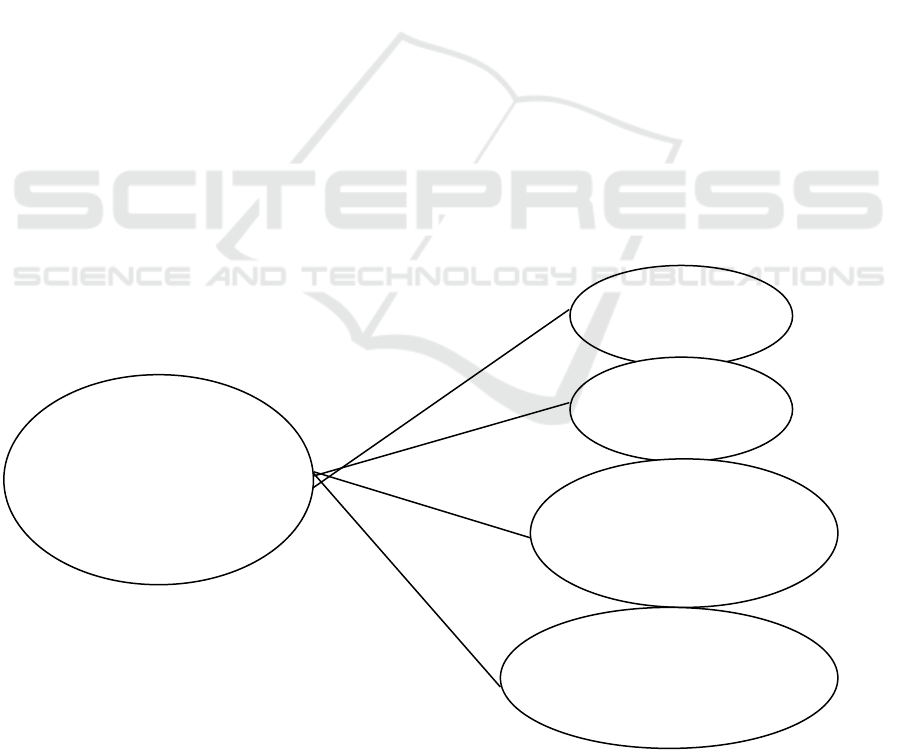
2 FRAMEWORK
Based on background and problem of this
research, the researcher describe the research
framework as seen in Figure 1 below.
Figure 1: Framework
Balanced Scorecard
of Universities at
Palembang
Financial
Perspective
Customer
Perspective
Business and
Internal Process
Perspective
Growth and Learning
Process Perspective
SEABC 2018 - 4th Sriwijaya Economics, Accounting, and Business Conference
268

3 MATERIAL AND METHOD
This research is a qualitative descriptive study
conducted on 2 (two) Universities: Sriwijaya
University as a State University and Palembang Bina
Darma University as a Private University. The
population of this study were Sriwjaya University
and Bina Darma University in Palembang, while the
samples used were: 1) students to measure
performance in customer perspectives, 2) university
employees both lecturers and education personnel to
measure performance on internal business process
perspective and growth perspective / learning.
This study uses primary data obtained directly
from data sources, namely data from interviews with
management / university employees, students and
questionnaire results. Besides that, secondary data is
also obtained indirectly from several journals. Data
collection techniques used in this study are through
interview methods and questionnaires. Each
questionnaire package consists of two parts that
must be answered by the respondent by following
the instructions contained in each section. The first
section contains questions relating to the
demographic data of respondents, including age, sex,
education, occupation and university name. The
second part is a statement relating to the views of
respondents on the four perspectives of balanced
scorecard.
The measurement scale is an agreement that is
used as a reference to determine the length of the
short interval in the measuring instrument, so that
the measuring instrument when used in the
measurement will produce quantitative data. The
measuring instrument used in the study is called the
research instrument (Sugiyono, 2010).
The university performance measurement scale
uses an interval questionnaire in a Likert scale.
Likert scale is one way to determine the score by
giving questions to respondents and choosing one of
the answers. Likert scale is designed to examine how
strongly subjects are satisfied or dissatisfied with
statements on a 5-point scale. The score intervals
used in the research Likert scale for the 4 balanced
scorecard perspectives are as follows:
Table 1: Scale of Questionnaire Measurement
Scale
Category
5
Very satisfied
4-4,9
Satisfied
3-3,9
Quite satisfied
2-2,9
Dissatisfied
1 -1,9
Very dissatisfied
Data collection methods, described based on 4
perspectives as follows:
1) Financial perspective, the author distributes
questionnaires that contain statements about sources
of income, allocation of income, and income growth.
The author refers to value for money that is
measuring economic level, efficiency and
effectiveness of university financial management.
Questionnaires were distributed to the university's
finance department.
2) Customer perspective, the method taken by
distributing questionnaires about student satisfaction
level of student satisfaction and expectations of
students as consumers of educational services.
3) Perspective of internal business processes,
internal business performance measurement has
indicators of facilities and infrastructure, work
process and satisfaction both lecturers and university
employees.
4) Perspective of growth and learning, measurement
of growth and learning performance has indicators
of facilities and infrastructure, opportunities for self-
development, innovation and working atmosphere
both lecturers and university employees.
4 RESULT AND DISCUSSION
Data Results and Analysis
Customer Perspective
The customer perspective is the first order
because the main purpose of the college is to serve
the community and provide facilities in the field of
education. The performance of the customer
perspective aims to see customer satisfaction,
namely, students on services provided by the
campus.
Performance Measurement Analysis with Balanced Scorecard Method (Case Study of Sriwijaya University and Bina Darma University
Palembang)
269
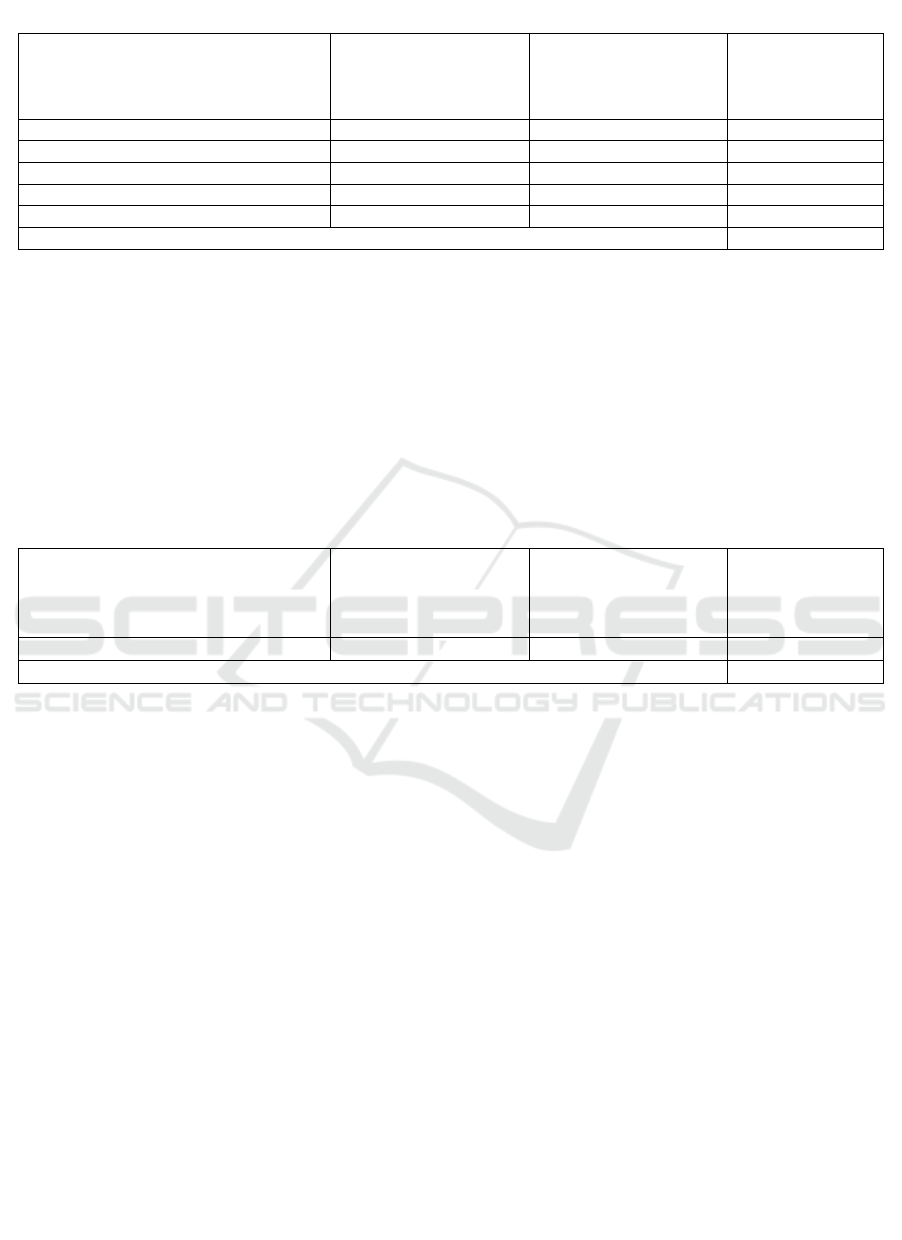
Table 2: Customer Perspective Performance (Variables of Sriwijaya University and Bina Darma University)
Variable
Universitas Sriwijaya
Universitas
Bina Darma
Mean
Tangibles
4,00
3,93
3,97
Reliability
4,05
4,01
4,03
Responsiveness
3,88
3,89
3,89
Assurance
4,02
3,83
3,92
Emphaty
3,79
3,90
3,84
The average value of the customer perspective variable
3,93
Customer satisfaction measures how satisfied
customers are in this case Unsri and Bidar
University students are satisfied with the facilities /
infrastructure, educational products and services of
the university. Customer perspective performance
has an average value of 3.93 which is in the good
category.
Financial Perspective
The financial perspective on universities is an
important perspective to support the perspectives of
others. This is what distinguishes balanced scorecard
from business sector organizations with balanced
scorecards in universities. Questionnaires were
given to employees of Unsri's finance department
and Bina Darma University to be answered and the
results of the questions were answered through the
table below:
Table 3: Financial Perspective Performance (Variables of Sriwijaya University and Bina Darma University)
Variable
Universitas Sriwijaya
Universitas
Bina Darma
Mean
Financial
3,63
3,57
3,60
The average value of the customer perspective variable
3,93
Business and Internal Process
Perspectives
In the perspective of internal business processes
is measured from three aspects, namely facilities and
infrastructure, work processes and satisfaction.
Facilities and infrastructure include the issue of
availability of office stationery, data and information
and a computerized system to support the work of
both lecturers and employees in providing services
to students. The process aspect consists of the
Service Operational Standards (SOP) of employees
and lecturers in carrying out their work whether they
have met the prescribed standards, whether the work
has been completed on time. Aspects of work
satisfaction include satisfaction received by both
employees and lecturers in carrying out their duties
and functions, the existence of rewards and
punishments at work, the existence of career
enhancements that are influenced by the sincerity of
attitude in work. The results of the measurement
scale perspective of internal business processes can
be seen from table 4. below this.
The performance of business and internal process
perspectives from the table above shows that the
performance of Unsri and Bina Darma University
Palembang has an average value of 4.00 and is
categorized as good. Good performance of lecturers
and staff will support the attitude and form of
responsive services that encourage satisfaction with
customers, namely students.
SEABC 2018 - 4th Sriwijaya Economics, Accounting, and Business Conference
270
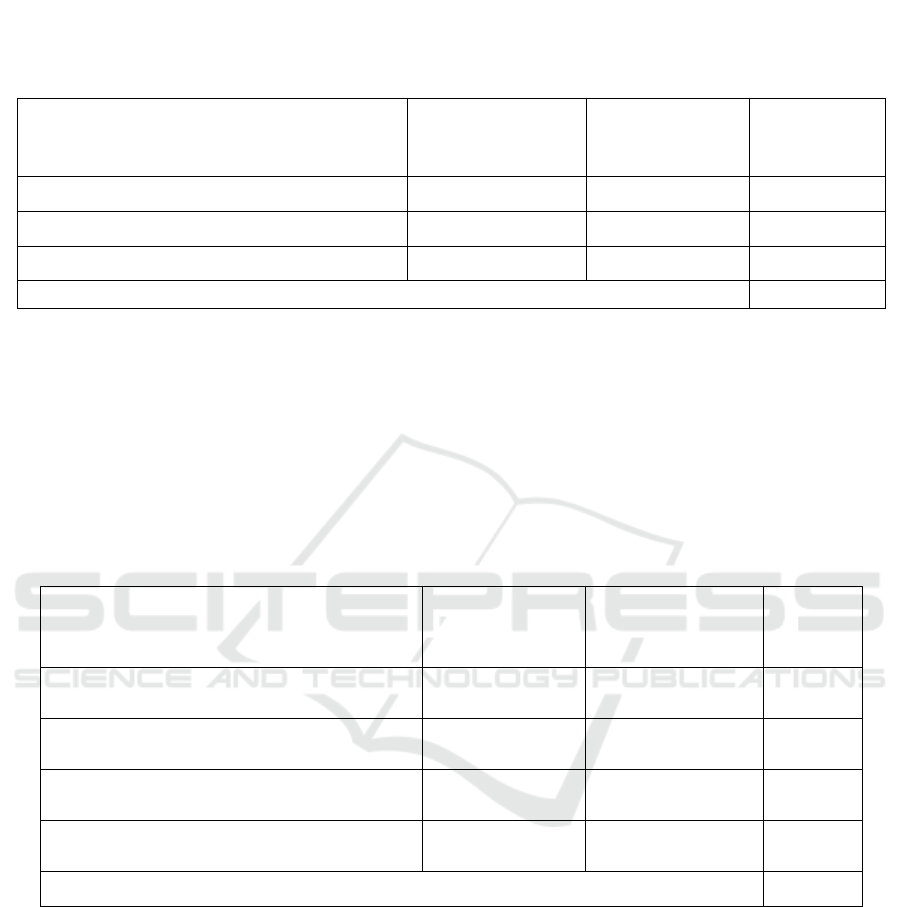
Table 4: Business and Internal Process Perspective Performance (Variables of Sriwijaya University and Bina Darma
University)
Variable
Universitas Sriwijaya
Universitas Bina
Darma
Mean
Facilities and infrastructure
3,92
3,88
3,90
Process
3,97
3,95
3,96
Job satisfaction
4,15
4,11
4,13
The average value of the customer perspective variable
4,00
Growth and Learning Perspectives
The measurement on the performance of the
growth and learning perspective aims to find out
how the organization can continue to improve and
add value to its customers and stakeholders. To
measure this performance, 4 aspects are used
including facilities and infrastructure, opportunities
for self-development, innovation and the atmosphere
at work. The results of the calculation of the
measurement scale from the performance of this
growth and learning perspective can be seen in table
5.
The performance of the growth and learning
perspective has an average value of 4.03 which
shows the value of this perspective variable is good.
Table 5: Growth and Learning Perspective Performance (Variables of Sriwijaya University and Bina Darma University)
Variable
Universitas
Sriwijaya
Universitas Bina
Darma
Mean
Facilities and Infrastructure
4,08
4,07
4,08
Self Development Opportunities
3,94
4,05
4,00
Innovation
4,14
4,05
4,09
The atmosphere in work
4,04
3,88
3,96
The average value of the customer perspective variable
4,03
5 CONCLUSION
Performance of Sriwijaya University and
Bina Darma University Palembang from
a Customer Perspective
The results of the measurement of Balanced
Scorecard performance analysis on customer aspects
at Sriwijaya University and Bina Darma University
Palembang showed quite satisfying performance.
The performance of Sriwijaya University
and Bina Darma University Palembang
from the Financial Perspective
The results of the measurement of the Balanced
Scorecard performance analysis on financial aspects
at Sriwijaya University and Bina Darma University
Palembang showed a fairly good performance.
Performance Measurement Analysis with Balanced Scorecard Method (Case Study of Sriwijaya University and Bina Darma University
Palembang)
271

Performance of Sriwijaya University and
Bina Darma University Palembang from
Business and Internal Process
Perspectives
The results of the Balanced Scorecard
performance analysis measurements from the
perspective of business and internal processes at
Sriwijaya University and Bina Darma University
Palembang show good performance.
Performance of Sriwijaya University and
Bina Darma University Palembang from
the Growth and Learning Process
Perspective
The results of the Balanced Scorecard
performance analysis measurement on the
perspective of growth and learning at the University
of Sriwijaya and Palembang Bina Darma University
showed good performance.
REFERENCES
Agung, A. A. G., & Irna Yuniar. (2014). Indicator Design
and Implementation of Lecturer Performance
Assessment in Information Systems. National Seminar
on Indonesian Information Systems - SESINDO (pp.
11–17).
Ahmad, S. (2015). A balanced scorecard approach to
recruitment in higher education institutions., 17–39.
Al-Hosaini, F. F., & Sofian, S. (2015). A Review of the
Balanced Scorecard Framework in Higher Education
Institutions (HEIs). International Review of
Management and Marketing, 5 (1), 26–35.
Al-Zwyalif, I. M. (2012). The Possibility of Implementing
the Balanced Scorecard in Jordanian Private
Universities. International Business Research, 5 (11),
113–120. https://doi.org/10.5539/ibr.v5n11p113
Ambras, A., & Tamosiunas, T. (2010). The
Implementation of the Balanced Scorecard System in
the Strategic Management of Social Sciences Faculty,
1 (1) Social Sciences, 5-18.
Bash, E. (2015). Performance Measurement Analysis
Using the Balance ScoreCard (Bsc) Method in
Sidoarjo Cv Mch. PhD Proposal, 1.
https://doi.org/10.1017/CBO9781107415324.004
Cancino, C. A., Farias, A. D., & Coronado, F. C. (2016).
Implementation of a Balanced Scorecard in a Non-
Profit Educational Foundation Implementación De Un
Cuadro De Mando Integral En Una Fundación
Educacional, 9 (October).
Chen, S.-H. (2010). Establishment and comparison of the
balanced scorecard for profit and non-profit
organizations. African Journal of Business
Management, 4 (14), 3005–3012.
https://doi.org/10.1177/0899764012443312
Ciptani, M. K. (2004). Balanced Scorecard as
Measurement of Future Performance: An Introduction.
Journal of Accounting and Finance, 2, 21–35.
https://doi.org/10.9744/jak.2.1.pp. 21-35
Colquitt, Lepine, W. (2011). Work management.
Performance Management / Wibowo-Jakarta:
Rajawali Press, (p. 179).
Deshpande, B. (2015). Application of Balanced Score
Card in Higher Education with special emphasis in a
Business School. International Conference on
Technology and Business Management, 201-2014.
Retrieved from
http://www.ictbm.org/ictbm15/ICTBM15CD/pdf/D51
07-final.pdf
Evangeline, S., & Anastacio, L. (2016). Balanced
scorecard model for Paulinian educational institutions,
8 (1), 69–89.
Fathoni, & Kesuma, I. S. (2011). Hospital Performance
Evaluation Analysis Using the Balanced Scorecard
(Case Study of "Abc" Houses). Journal of Information
Systems, 3 (1), 2085–1588. Retrieved from
http://ejournal.unsri.ac.id/index.php/jsi/index
Ferina, I. S. (2012). Perspective Balanced Scorecard
Performance Analysis at the Hospital Public Service
Agency in Palembang.
H, N. S. (2016). Measuring Employee Performance
Indexes by Implementing the Balanced Scorecard
Method (Case Study: University X), 13 (1), 53–57.
Imelda R H N. (2004). Implementation of the Balanced
Scorecard in Public Organizations. Journal of
Accounting and Finance, 6 (Gaspersz 2003), 106–122.
Karathanos, D., & Karathanos, P. (2005). Applying the
Balanced Scorecard to Education. Journal of
Education for Business, 80 (4), 222-230.
https://doi.org/10.3200/joeb.80.4.222-230
Kettunen, J. (2010). Strategy process in higher education.
Journal of Institutional Research, 15 (1), 16–27.
Mahmudi. (2010). Public Sector Performance
Management. Jakarta: STIE YKPN.
Mahmudi, A. A., Surarso, B., & Subagio, A. (2014).
Combination of Balanced Scorecard and Objective
Matrix for Higher Education Performance
Assessment, 1, 1–10.
Mahsun, M. (2009). Public Sector Performance
Measurement. Yogyakarta: BPFE.
Maskur. (2004). Performance Measurement with the
Balanced Scorecard Approach (Case Study at Dr.
Kariadi Hospital Semarang). Diponegoro.
Mayrina, H., Kristianto, D., & Suharno. (2016). Analysis
of Application of Management Performance
Measurement Systems at PT Duta Indonesia Djaya
Based on Balanced Scorecard, 12 (Chilcot), 138–149.
Niven, P. R. (2008). The Balanced Scorecard Step by Step
for Government and Non Profit Agencies. New Jersey:
Juhon Wiley and Sons. Retrieved from
http://hanin.web.id/ebook/management/Balanced
Scorecard Step-by-Step for Government and Nonprofit
Agencies.pdf
SEABC 2018 - 4th Sriwijaya Economics, Accounting, and Business Conference
272

Norton, D. P., & Kaplan, R. S. (2000). Balanced
Scorecard: Setting a Strategy into Action. (P. R. Y.
Pasla, Ed.). Jakarta: Erlangga.
Paliszkiewicz, J., & Klepacki, B. (2015). The application
of the balanced scorecard (BSC) in the higher
education setting of a Polish university. Online Journal
of Applied Knowledge Management, 3 (1), 151–164.
Pramono, J. (2014). Analysis of Measurement of
Performance of Surakarta 6 Public Vocational Schools
with the Balanced Scorecard Approach. Echo, 1335–
1355.
Purwawinata, A. (2014). Design of Balanced Scorecard as
Performance Evaluation at RSUD Dokter Mohammad
Saleh Kota Probolinggo (Balanced Scorecard Design
as Performance Assessment at The General Hospital
Dr. Mohammad Saleh Probolinggo).
Putri, A., & Danto, W. (2011). Balanced Scorecard as a
Measure Tool for Higher Education Performance (It
Telkom), (February 2011).
Rahardjo, S. N., Si, M., & Undip, F. E. (2013).
Application of the Balanced Scorecard Method as a
Measurement of Performance Assessment in, 2 (2), 1–
31.
Performance Measurement Analysis with Balanced Scorecard Method (Case Study of Sriwijaya University and Bina Darma University
Palembang)
273
