
Management Commitment and Competencies of Asset
Administrators on Asset Management: A study in Government Units
of South Sumatera Province
Kartika Rachma Sari
1
, Didik Susetyo
2
, Inten Meutia
3
and Sa’adah Siddik
4
1
Department of Accounting, Sriwijaya State Polytechnic, Palembang , Indonesia
2
Department of Economic, Sriwijaya University, Palembang , Indonesia
3
Department of Accounting, Sriwijaya University, Palembang , Indonesia
2
Department of Accounting, Muhammaddiyah University, Palembang , Indonesia
Keywords: Management Commitment, Competencies of Asset Administrator, Asset Management.
Abstract: This study aims to analyze the influence of asset administrator competencies and management commitment
on asset management. The research was conducted on 50 Government Units in 4 city governments of South
Sumatera Province in 2017. The research data is primary data collected through a questionnaire. The
analytical tool is Partial Least Square (PLS); the determination of the sample is the head asset administrator
at each of the Government Units. The results of this research show that: (1) Management commitment has a
positive effect on asset management at Government Units in the city governments of South Sumatera
Province, (2) Competencies of asset administrators have positive effects on asset management at
Government Units in the city governments of South Sumatera Province. The implications of this study are
expected to contribute to help the heads of Government Units in South Sumatera Province to improve the
performance of asset management by performing a skilled asset administrator and management commitment
with the best of the assets.
1 INTRODUCTION
There are still many Local Government Financial
Reports (LCFR) which produce unqualified audit
opinions. There are only 252 (46.75%) of 539 LCFR
in 2016 (BPK, 2016). Asset still has the highest
percentage (30%) of the problems in the accounts on
the balance sheet that were presented not in
accordance with government accounting standards in
2015 (BPK, 2016). Many audit findings were found
which involved inequality in the management of
regional property and inadequate administration of
regional property.
Local governments must handle and utilize
public assets efficiently and effectively to optimize
the sources of regional revenues, including the
optimization and utilization of existing assets, as
referred to in law number 23 of 2014 concerning
regional governance. Public asset management must
be managed in order to cause these assets to be
developed as initial capital for local government to
strengthen their financial capabilities. To achieve
optimal benefits from an asset, good management of
the asset’s lifecycle is needed. Asset management is
a way of managing, planning, designing, and
monitoring the process of updating, acquiring,
maintaining, and disposal of all forms of technical
assets and infrastructure to support procurement of
public services. Management assets are a structured
and systematic process which cover the entire life of
a physical asset (AAMCoG, 2012)
The Indonesian Government has issued the
Regulation of Minister of Home Affairs Number 19
of 2016 concerning Technical Management of
Regional Assets which is used as a reference in
managing the assets. Local Governments should be
able to manage assets well, starting from needs
planning, budgeting, procurement, use, utilization,
Rachma Sari, K., Susetyo, D., Meutia, I. and Siddik, S.
Management Commitment and Competencies of Asset Administrator on Asset Management: Study in Government Units of South Sumatera Province.
DOI: 10.5220/0008444006850692
In Proceedings of the 4th Sriwijaya Economics, Accounting, and Business Conference (SEABC 2018), pages 685-692
ISBN: 978-989-758-387-2
Copyright
c
2019 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
685

administration, maintenance and security to their
supervision so that regional assets can provide
benefits and optimal contribution to the relevant
regional government.
Mardiasmo (2004) states that the strategic
objectives which must be achieved in the
management of assets include: (1) the creation of an
administrative order regarding regional wealth, (2)
the creation of efficiency and effectiveness in the
use of regional/local assets; (3) the safeguarding of
regional assets; (4) availability of accurate data/
information regarding the amount of regional
wealth. The Department of Communities and Local
Government (2007) states that effective asset
management directly links with the efficiency
strategy and national improvement. It means that
better asset management improves better public
services and value for money.
These statements are in line with the research
conducted by (Bond, S & Dent, 1998) the
importance of efficient asset management for
financial reporting and asset management will
enhance the role in meeting community services
efficiently, which is reflected in the assessment and
reporting. Related studies which support the
importance of asset management are (Pekei &
Hadiwidjojo, 2014); (Shepherd, 2013); (Krisindarto,
2012); (White, 2012); (Jolicoeur & Barrett, 2005).
Performance within the organization is carried
out by all human resources within the organization,
by both leaders and employees. This is in line with
the research by (Cooper, 2006) who defined that
management commitment is to maintain and engage
in behaviours to help others achieve a goal.
(Simamora & Halim, 2013) stated that management
commitment is more critical in affecting asset
management. Top management must focus on its
employees with empowerment, involvement,
training, and appreciation to provide the best service
to beneficiaries. Employees will be given more
resources for training to improve asset management
skills when management is committed to improve
asset management. Chin et al. (2003) found that top
management commitment is the most important
factor for the successful implementation of ISO
9000. In line with this research, (Pheng & Teo,
2004) argued that top management commitment is
one of the elements reflecting TQM performance
measures. The commitment of top management
shown by the level of visibility and support in
implementing a total quality environment is very
important for the success of TQM implementation.
(Haupt & Whiteman, 2004); (Taylor & Wright,
2003); (Moorman, Niehoff, & Organ, 1993) argued
that commitment management has the potential to
influence organizational performance.
(Pate, Martin, & Robertson, 2003) stated that
competence provides a useful development
framework for those employees participating in a
program. He argued that competence can be seen
from two aspects. The first, competence, is a set of
specific attributes used in carrying out a job related
to the characteristics of high-performing employees
which can be learned through education, experience
or vocational training. This competence deals with
the behavior of particular individuals and how they
act in an organizational environment. The second,
competency, consists of a person's experience and
personality combined with job related factors that
stem from formal and informal organization. It
focuses on the interaction between the individual
and the job.
Yusuf (2013) suggested that knowledge about
asset management is needed for administrators in
utilizing assets to make asset management decisions
which benefit government operations. The
importance of an employee’s competence in an
organization is being able to support the
improvement of employee performance and
contribute to determining the future of the
organization (Wahyudi, 2014). In line with this,
(Qiao & Wang, 2009) suggested the critical
competencies for the success of middle managers in
China are team-building, communication,
coordination, execution and continual learning.
Some researchers have claimed that employees’
competencies provide an effective method for
predicting job performance (McClelland, 1973);
(Levenson, Van der Stede, & Cohen, 2006); (Darno,
2012).
Administrators of assets at the Regional
Government Organization are employees who work
in government agencies in Law Number 5 of 2014.
This concerns the State Civil Apparatus referred to
as the State Civil Apparatus that acts as a planner,
implementer, and supervisor of the implementation
of the general tasks of national governance and
development through the implementation of policies
and professional public services, free from political
intervention, and free from corruption, collusion and
nepotism.
In order to produce even high-quality asset
management, there is a need for reliable
management personnel. The audit board of the
Republic of Indonesia (BPK RI, 2016) found that the
problems in asset management occur partly because
the responsible officials/implementers are negligent
and not optimal in carrying out their duties and
SEABC 2018 - 4th Sriwijaya Economics, Accounting, and Business Conference
686
responsibilities according to their respective duties
and responsibilities, have not fully understood the
applicable provisions, and are weak in supervising
and controlling activities. Based on the background
above, it is interesting to test the influence of
management commitment and competencies of asset
administrators on asset management in Government
Units of South Sumatra Province.
2 METHOD
This research is quantitative research and was
conducted at 50 Government Units in the city
governments of South Sumatra Province which
consist of 4 city Governments, they are Palembang,
Pagar Alam, Prabumulih and Lubuk Linggau. The
population used in the study is the official
administration of local assets that have the authority
and play an active role in the management of assets
at Government Units in the city government of
South Sumatra Province. The sampling technique to
find the Government Units used in this research is
random sampling.
By using Stewardship Theory (Donaldson &
Davis, 1991), Asset Management as dependent
variable in this study is a way of managing,
planning, designing, and monitor the process of
acquiring, maintaining, updating, and disposal of all
forms of infrastructure and technical assets; to
support procurement of public services (AAMCoG,
2012). In this study, the writers evaluate the
performance of asset management’s procedure in
accordance with the Government’s Regulations.
The independent variables are management
commitment and competencies of asset
administrators. Management commitment in this
study carries a strong belief and support from
management to carry out and implement asset
management policies in accordance with established
regulations so that the objective of implementing
these policies can be achieved for the benefit of the
organization (Cooper, 2006); (Tan, C. and Hamzah,
2008); (Caroline, Harriet, & Anne, 2016). We used
the dimensions studied by (Tan, C. and Hamzah,
2008) which are quality goals, priority, efforts,
involvement, resource allocation and attitude to
change. The competencies of asset administrators
are the technical ability in asset management
through the dimension of knowledge, skill and work
attitude. (Boyatzis, 2008); (Qiao & Wang, 2009);
(Yusuf, 2013). The Conceptual Research framework
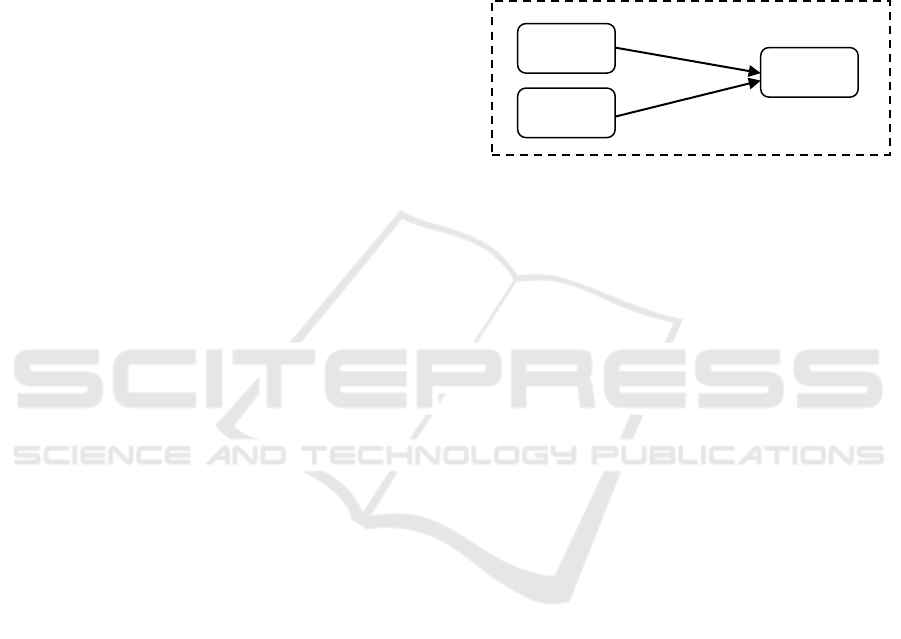
image is seen in figure 1.
The required research data are primary data
collected through questionnaires by providing a
written set of questions. The analytical tool used is
Partial Least Square with the aim to determine the
effect of the relationship between latent variables. In
this study the writers want to know the influence of
Management Commitment and the competencies of
asset administrators on asset management in
Government Units of South Sumatra Province.
Figure 1: Conceptual Research Framework.
3 RESULT AND DISCUSSION
The full model of SEM equation using the Smart
PLS 3.0 program is obtained by two models, namely
the standardized model (PLS Algorithm) and the t-
values model (Bootstrapping), each model is shown
in the following figure.
There are two steps in the measurement model.
They are the convergence validity and discriminant
validity. factor loading, and average variance
extracted (AVE) which were computed to get
convergence validity. Based on Figure 2 the range of
loading factor (0,629 to 0,949) is more than 0,6 (≥
0,6). All latent constructs demonstrate adequate
convergence validity.
MC
CA
AM
Management Commitment and Competencies of Asset Administrator on Asset Management: Study in Government Units of South Sumatera
Province
687
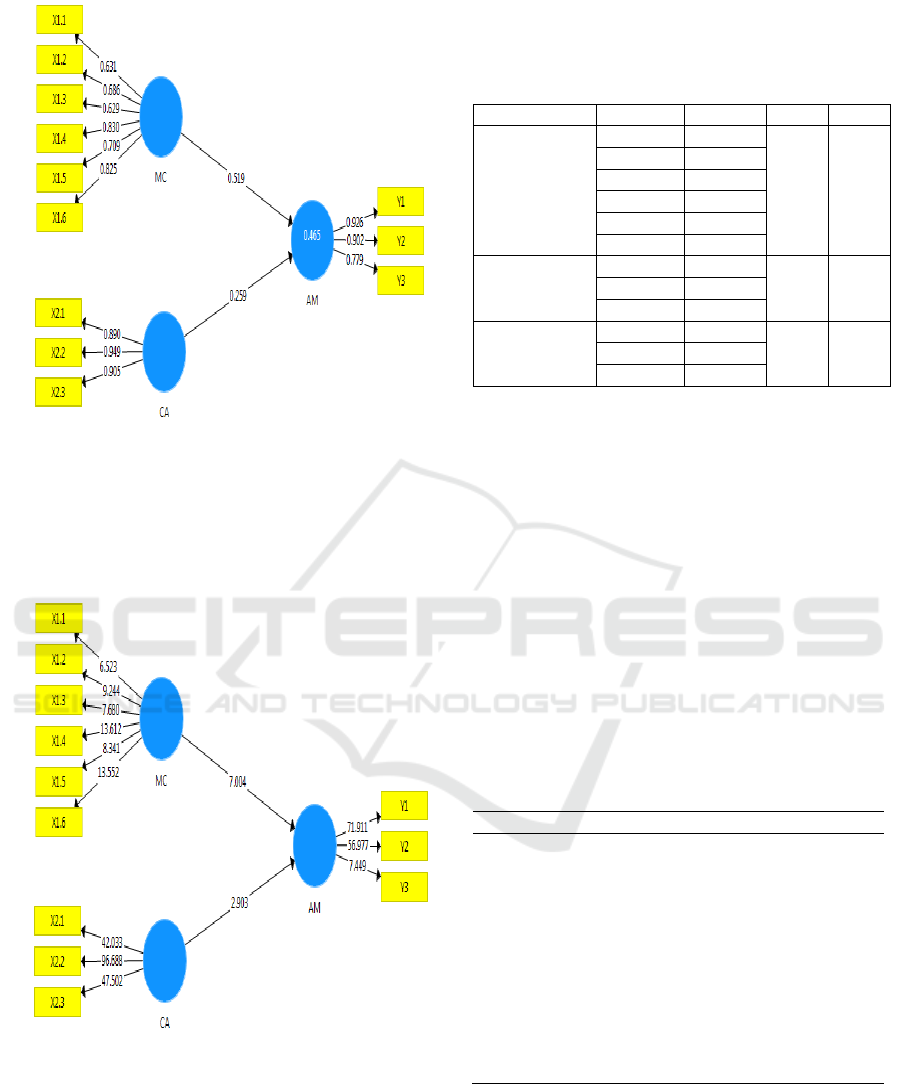
Figure 2: Algorithm Model
Figure 3: Bootstrapping Model shows that the
value of t-statistic for the correlation among
indicators are considered valid where t-statistic > t-
table (1.96). All latent constructs demonstrate
adequate convergence validity.
Figure 3: Bootstrapping Model
From Table 1, AVE values in range from 0,522
to 0,838, meanwhile the CR value for the latent
variable (0,866 to 0,939) was above Hair et al (2010)
threshold value of 0,7, suggesting significant
homogeneity. It means that the indicators are
considered valid. The loading factor is a correlation
between indicators and their construct. The higher
the correlation, the better the level of validity is.
Table 1: Convergence Validity
Indicator
Loading
CR
AVE
Management
Commitment
X1.1
0,631
0,866
0,522
X1.2
0,686
X1.3
0,629
X1.4
0,830
X1.5
0,709
X1.6
0,825
Competencies
Asset
Administrator
X2.1
0,890
0,939
0,838
X2.2
0,949
X2.3
0,905
Asset
Management
Y1
0,926
0,904
0,759
Y2
0,902
Y3
0,779
Discriminant validity is used to prove that latent
constructs predict the size of the construct is better
than the size of the other constructs. Discriminant
validity was tested by analyzing the cross-loading
value for each variable in which the construct being
measured is greater than the other constructs.
Discriminant validity can be seen through the value
of cross-loading, as seen in Table 2. Table 2 shows
that the indicator of each variable has resulted in
discriminant validity. This can be seen from the
value of the management commitment (MC)
competencies of asset administrator (CA) and asset
management (AM) that have cross load values
greater than other cross loading values, it means that
all variables have met the discriminant validity.
Table 2: Convergence Validity
Indicator
MC
CA
AM
X1.1
0,631
0,355
0,420
X1.2
0,686
0,349
0,409
X1.3
0,629
0,369
0,464
X1.4
0,830
0,364
0,525
X1.5
0,709
0,244
0,405
X1.6
0,825
0,371
0,536
X2.1
0,481
0,890
0,446
X2.2
0,446
0,949
0,503
X2.3
0,378
0,905
0,437
Y1
0,617
0,488
0,926
Y2
0,611
0,487
0,902
Y3
0,421
0,321
0,779
The following is the results of the R-Square
analysis in Table 3. It can be seen that R-Square
shows that the value of R-Square (R²) for construct
asset management (AM) is 46.5 or 46,5%. It belongs
to moderate model based on opinion of Chin (1998).
Variable management commitment (MC) and
SEABC 2018 - 4th Sriwijaya Economics, Accounting, and Business Conference
688

competencies of asset administrator (CA) are able to
explain variable asset management (AM) equal to
46,5% while 53,5% is explained by other variables.
Table 3: R.Square Analysis
R Square
R Square Adjusted
AM
0,465
0,454
Hypothesis testing can be done by analyzing the
value of path coefficients after the bootstrapping
process. To see hypothesis testing done by
comparing t-statistic value with t-table value. The
hypothesis is accepted if the value of t-statistic > t-
table (1.96), but if the value of t-statistic < t-table
(1.96) then the hypothesis be rejected. In addition, to
test that the hypothesis can be done by analyzing the
significance of p-value compared with the error rate
set in this research is one-tailed test with alpha 5%
(0.05). The p-values < 0.05 then the hypothesis is
accepted, however, if p-values > 0.05, then the
hypothesis can be rejected. The results of path
coefficients analysis are presented in Table 4.
Table 4: The Result of Path Coefficients Analysis
Variable
Original
Sample
t-
Statistic
p-
Value
CA > AM
0,259
2,903
0,004
MC > AM
0,519
7,004
0,000
Table 4 described the analysis research
hypothesis testing. The hypotheses are:
H1: Management commitment (MC) has a positive
effect on asset management (AM) at
Government Units in the city governments of
South Sumatra Province.
H2: Competencies of asset administrator (CA) has a
positive effect on asset management (AM)
Government Units in the city governments of
South Sumatra Province.
The explanation of the results of hypothesis
testing based on Table 4 is as follows. The first
Hypothesis states that variable management
commitment (MC) has a positive effect on asset
management (AM) at Government Units in the city
governments of South Sumatra Province. Table 4
describes that MC testing with AM has a t-statistic
value of 7,004 greater than the value of t-table at
alpha 5% of 1,96. Thus, it can be said that the
hypothesis is accepted. The value of p-values
between MC and AM of 0.000 indicates a significant
level at alpha 0.05 (5%). It means that Management
Commitment (MC) has a significant effect on Asset
Management (AM). Meanwhile, to analyze the
direction of the relationship variable is by looking at
the path coefficient value (original samples) between
the variables of management commitment (MC)
with asset management (AM) of 0.519 with a
positive direction.
Thus, it can be concluded that the variables of
management commitment (MC) have a significant
positive effect on asset management (AM) at
Government Units in the city governments of South
Sumatra Province. It means that the first hypothesis
is accepted. This is in line with the research by
(Cooper, 2006) that defined management
commitment is to maintain and engage in behaviors
that can help others achieve a goal. He found that
senior management commitment played a primary
role in shaping employee behaviors and a secondary
role by shaping lower management behavior that
acts in turn on employee behavior.
Other researchers that clarify the relationship
between management commitment and performance
are (Tan, C. and Hamzah, 2008), (Pheng & Teo,
2004); (Taylor & Wright, 2003), Chin et al. (2003).
In an effort to improve the performance of asset
management, it is expected that management must
fully understand and support the management of
assets and actively participate in its implementation ,
rather than delegate it.
The second hypothesis states that the Variable
Competencies of Administrator (CA) have a positive
effect on Asset Management (AM) at Government
Units (OPD) in the city governments of South
Sumatra Province. Table 4 shows that the test CA
with AM has a value of 2,903 t-statistic greater than
t-table at alpha 5% by 1.96. Thus, it can be said that
the hypothesis is accepted. The value of p-values
between CA and AM of 0,004 indicates a significant
level in alpha 0.05 (5%), which means competencies
of administrator (CA) has a significant effect on
asset management (AM)). The direction of the
relationship of variables is analyzed by looking at
the value of path coefficient (original sample)
between competencies of administrator variable
(CA) with asset management (AM) of 0.259 with
positive direction.
Thus, it can be concluded that the competencies
of administrator (CA) variable has a significant
positive effect on asset management (AM). It means
that the second hypothesis is accepted, which is in
line with research conducted by Sedarmayanti
(2007) that the organizational goals can be achieved
because of the efforts of the actors found in the
organization. Competence is a fundamental
characteristic possessed by someone who has a
direct influence or can predict good performance. In
this case there is a close relationship between
employee competencies and institutional
performance. In other words, if the employee's
competence is good, then it is likely that
organizational performance is also good. Employee
Management Commitment and Competencies of Asset Administrator on Asset Management: Study in Government Units of South Sumatera
Province
689

competence will be better if you have high
knowledge, established skills and a good work
attitude.
Other research which clarifies the relationship
between competencies and performance are (Qiao &
Wang, 2009); (Ryan, Emmerling, & Spencer, 2009);
(Boyatzis, 2008); (Levenson et al., 2006); Dainty
(2004). In an effort to improve the performance of
asset management, it is expected that the
management of assets can be given adequate training
to improve performance in asset management.
3.1 The influence of management
commitment on asset management
at Government Units in the city
governments of South Sumatra
Province.
(Cooper, 2006) stated that management
commitment is defined as maintaining and engaging
in behavior that helps others achieve a goal.
Management Commitment is direct management
participation in important aspects and programs of
an organization and must be driven by the power of
desire to improve the quality of all organizations’
businesses. Top management has the power and
motivation to influence a change. Leadership that is
shown in the top management commitment and
supported by all members of the organization will
change towards a better direction.
In line with (Tan, C. and Hamzah, 2008) top
management commitment towards quality
management, it is generally perceived as one of the
key factors in determining its success. The research
conducted by (Munaim, 2012) found the existence
of management commitment in the implementation
of technical regulation of asset management is a
contributing factor to the implementation of good
asset management policies in each OPD to the
Government of West Nusa Tenggara Province. In
line with the results of research by Chin et al.
(2003), (Simamora & Halim, 2013) also stated that
management commitment factors are more critical to
affect asset management. Management commitment
is needed in overcoming problems related to asset
management. This is indicated by the information
obtained indicating that of managers who do not pay
attention to asset issues makes asset management a
complicated matter.
Other studies that support the results of this study
are (Caroline et al., 2016); (Javed, 2015);
(Abomaleh & Zahari, 2014); (Namada, Aosa,
Awino, & Wainaina, 2014); (Yousaf, 2006); (Taylor
& Wright, 2003); (Pheng & Teo, 2004); Samson et
al. (1999).
3.2 The influence of Asset
Administrator’s Competencies on
Asset Management at Government
Units in the city governments of
South Sumatra Province.
Implementation of asset management requires
asset administrators with adequate competencies.
The competencies possessed by the asset
administrator will determine the ability of the
organization in achieving the objectives of asset
management. According to Yusuf (2013), the key to
successful management of regional property is the
availability of competent employees in the
management of regional property. It is necessary to
have competent employees who have knowledge
about regional assets, skills in managing regional
assets, and attitudes towards managing local assets.
Knowledge about asset management will be very
helpful in making asset management decisions that
provide space for administrators to empower/utilize
an asset for the benefit of government operations
(Yusuf, 2013)
(Darno, 2012) found empirical evidence of the
influence of the ability of human resources on the
quality of local asset reports. According to
(Supriyadi, 2008), improving the quality of human
resources that carry out inventory and management
of regional property needs to be pursued in the form
of education, training, or technical guidance. With
this kind of activity, it is expected that the quality of
asset administrators will increase and impact upon
the quality of asset management.
The results of this study are in line with the
research conducted by (Wahyudi, 2014) that
competence shows skills and knowledge
characterized by professionalism. Competency
enhancement is certainly supported by the level of
the employee’s education, specialization (skills),
work experience and work attitude. (Zaim, Yaşar, &
Ünal, 2013) analyzed the effects of individual
competencies on performance in the services
industries in Turkey. He found that competencies
have a positive relationship to individual
performance. Furthermore, core competencies have
the most significant effect on individual
performance. In line with (Zaim et al., 2013) and
(Wahyudi, 2014), asset management competencies
are the most significant factor, when it comes to
asset management performance.
SEABC 2018 - 4th Sriwijaya Economics, Accounting, and Business Conference
690

4 CONCLUSIONS
Based on the results of this study, it can be
concluded as follows: 1) Management commitment
has a significant positive effect on asset management
at Government Units in the city governments of
South Sumatra Province, meaning that Management
Commitment has a strong influence on the
optimization of asset management. 2) the
competencies of an asset administrator have a
positive influence on asset management, it means
that competencies of asset administrators are needed
to assist the asset management to be carried out
optimally at Government Units in the city
governments of South Sumatra Province.
This research has been conducted on the
influence of management commitment and
competencies of asset administrators on asset
management. However, there are still some
limitations in this study to be an input for further
researchers especially on optimizing asset
management. The limitations in this study are as
follows : 1) The scope of this study is only limited to
4 city governments of South Sumatra Province,
while there are 17 cities/districts in South Sumatra
Province which were not included in this study; 2)
two variables that influence asset management in
this study are able to explain equal to 46,5%, while
53,5% is explained by other variables, thus, there is
still less exploration of other factors that affect asset
management; 3) The sample used in this study is
only limited to the head of Asset Administrator, so
that the information obtained is only limited to the
perception of the head of asset administrator in
Government Units .
In order to get better results, further researchers
are expected to do, as follows: 1) It is expected to
expand the research area to whole cities and districts
in this province. 2) To add the number of variables
that influenced asset management. 3) To include all
of the officials of asset management in Government
Units.
5 REFERENCES
AAMCoG. (2012). Pedoman Sistem Terpadu Pengelolaan
Aset yang Strategis (Vol. IS: 978-0-).
Abomaleh, A., & Zahari, I. (2014). The impact of
management commitment to service quality and
customer satisfaction : A Review of Saudi Arabia
public service sector, 3(1), 1–9.
Bond, S & Dent, P. (1998). Efficient management of
public sector assets The call for correct evaluation
criteria and techniques. Journal of Property Valuation
and Investment, 16(4), 369–385.
Boyatzis, R. E. (2008). Competencies in the 21st century,
27(1), 5–12.
https://doi.org/10.1108/02621710810840730
Caroline, N., Harriet, K., & Anne, N. (2016). Top
management commitment for successful small and
medium-enterprises ( SMEs ): A hoax or a reality ?,
12(4), 259–267.
https://doi.org/10.19044/esj.2016.v12n4p259
Cooper, D. (2006). The Impact of Management ’ s
Commitment on Employee Behavior : A Field Study.
American Society of Safety Engineers, 1(317), 7–14.
Darno. (n.d.). Analisis Pengaruh Kemampuan Sumber
Daya Manusia dan Pemanfaatan Teknologi Informasi
Terhadap Kualitas Laporan Barang Kuasa Pengguna
(Studi pada Satuan Kerja di Wilayah Kerja KPPB
Malang).
Donaldson, L., & Davis, J. H. (1991). Stewardship Theory
or Agency Theory: Australian Journal of
Management, 16(June 1991), 49–66.
https://doi.org/10.1177/031289629101600103
Haupt, T. C., & Whiteman, D. E. (2004). Inhibiting factors
of implementing total quality management on
construction sites. The TQM Magazine, 16(3), 166–
173. https://doi.org/10.1108/09544780410532891
Javed, S. (2015). Impact of Top Management
Commitment on Quality Management. International
Journal of Scientific and Research Publication, 5(8),
1–5.
Jolicoeur, P. W., & Barrett, J. T. (2005). Coming of age:
Strategic asset management in the municipal sector.
Journal of Facilities Management, 3(1), 41–52.
https://doi.org/10.1108/14725960510808383
Krisindarto, A. (2012). Pengelolaan Aset Tanah Milik
Pemerintah Kota Semarang. Jurnal Pembangunan
Wilayah & Kota, 8(4), 403–411.
Levenson, A. R., Van der Stede, W. A., & Cohen, S. G.
(2006). Measuring the Relationship Between
Managerial Competencies and Performance. Journal
of Management, 32(3), 360–380.
https://doi.org/10.1177/0149206305280789
McClelland, D. C. (1973). Testing for competence rather
than for “intelligence”. The American Psychologist,
28(1), 1–14. https://doi.org/10.1037/h0034092
Moorman, R. H., Niehoff, B. P., & Organ, D. W. (1993).
Treating employees fairly and organizational
citizenship behavior: Sorting the effects of job
satisfaction, organizational commitment, and
procedural justice. Employee Responsibilities and
Rights Journal, 6(3), 209–225.
https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01419445
Munaim. (2012). Kebijakan Pengelolaan Barang Milik
Daerah pada Pemerintah Provinsi Nusa Tenggara
Barat.
Namada, J. M., Aosa, E., Awino, Z., & Wainaina, G.
(2014). Management Participation and Firm
Performance, (March), 113–122.
Pate, J., Martin, G., & Robertson, M. (2003). Accrediting
competencies: a case of Scottish vocational
qualifications. Journal of European Industrial
Management Commitment and Competencies of Asset Administrator on Asset Management: Study in Government Units of South Sumatera
Province
691

Training, 27(2/3/4), 169–176.
https://doi.org/10.1108/03090590310468976
Pekei, B., & Hadiwidjojo, D. (2014). The Effectiveness Of
Local Asset Management ( A Study On The
Government Of Jayapura ), 3(3), 16–26.
Pheng, L. S., & Teo, J. A. (2004). Implementing total
quality management in construction firms. Journal of
Management in Engineering, 20(1), 8–15.
https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)0742-
597X(2004)20:1(8)
Qiao, J., & Wang, W. (2009). Managerial competencies
for middle managers: some empirical findings from
China. Journal of European Industrial Training,
33(1), 69–81.
https://doi.org/10.1108/03090590910924388
RI, I. I. B. (n.d.). IHPS I Tahun 2016.
Ryan, G., Emmerling, R. J., & Spencer, L. M. (2009).
Distinguishing high‐performing European executives.
Journal of Management Development, 28(9), 859–
875. https://doi.org/10.1108/02621710910987692
Shepherd, E. (2013). Why are records in the public sector
organizational assets? Records Management Journal,
16(1), 6–12. https:
//doi.org/http://dx.doi.org/10.1108/MRR-09-2015-
0216
Simamora, R., & Halim, A. (2013). Faktor-Faktor yang
Mempengaruhi Pengelolaan Aset Pasca Pemekaran
Wilayah di Kabupaten Tapanuli Selatan. Jurnal
Ekonomi Dan Bisnis, 13(September), 29–43.
Tan, C. and Hamzah, A. (2008). Top Management
Commitment Towards Quality Management, 1–13.
Taylor, W. A., & Wright, G. H. (2003). The impact of
senior managers’ commitment on the success of TQM
programmes. International Journal of Manpower,
24(5), 535–550.
https://doi.org/10.1108/01437720310491071
W. Supriyadi. (2008). Evaluasi Proses Inventarisasi
Barang Milik Daerah di dalam pengelolaan barang
milik daerah di Pemerintah Kabupaten Lampung Barat
dalam mendukung pengelolaan barang milik daerah
yang efektif dan efisien.
Wahyudi, F. (2014). Peran Kompetensi Dalam
Meningkatkan Kinerja Pegawai Bagian Sosial
Sekretariat Daerah Kabupaten Kutai Timur Firman
Wahyudi, 3(2), 186–197.
White, A. D. (2012). A review of UK public sector real
estate asset management. Journal of Corporate Real
Estate International Journal of Operations &
Production Management Iss International Journal of
Manpower, 14(7), 94–104. Retrieved from
http://dx.doi.org/10.1108/14630011211261696%5
Yousaf, N. (2006). Impact of Organizational Culture on
TQM Program, 1–11.
Zaim, H., Yaşar, M. F., & Ünal, Ö. F. (2013). Analyzing
the Effects of Individual Competencies on
Performance: a Field Study in Services Industries in
Turkey. Journal of Global Strategic Management,
2(7), 67–67.
https://doi.org/10.20460/JGSM.2013715668
Badan Pemeriksa Keuangan (BPK RI). 2015. Ihtisar
Hasil Pemeriksaan Semester Satu dan Dua Tahun
2014, Indonesia.
Peraturan Pemerintah No. 27 Tahun 2014 tentang
Pengelolaan Barang Milik Daerah
Peraturan Menteri Dalam Negeri Nomor 19 Tahun 2016
tentang Pedoman Teknis Pengelolaan Barang Milik
Daerah
Undang-undang Nomor 23 Tahun 2014 tentang
Pemerintahan Daerah
Undang-undang Nomor 5 Tahun 2014 tentang Aparatur
Sipil Negara
SEABC 2018 - 4th Sriwijaya Economics, Accounting, and Business Conference
692
