
Estimation of River Flood Discharge by using 2D Model
Akbar Rizaldi
1
, Idham Riyando Moe
2
, Mohammad Farid
3
and Herryan Kendra
4
1
Center for Water Resources Development, Institute for Research and Community Services, Institut Teknologi Bandung,
Jalan Ganesha No.10, Bandung 40132, Indonesia
2
Directorate General of Water Resources, Ministry of Public Works and Housing,
Jalan Pattimura No. 20, Kebayoran Baru, Jakarta Selatan 12110, Indonesia
3
Water Resources Engineering Research Group, Institut Teknologi Bandung,
Jalan Ganesha No.10, Bandung 40132, Indonesia
4
Aditya Engineering Consultant, Jl. Batu Permata 1 No. 2A Margacinta, Bandung 40286, Indonesia
Keywords: River Flood, Discharge, 2D Model.
Abstract: Flood disaster is still a problem in many countries in the world; therefore, it is also still important to study
about the flood. There have been many flood studies conducted by researchers. Modelling is one of the topics
of flood studies which is usually discussed. Two-dimensional (2D) model is commonly used in flood
modelling because it provides more information compared with one dimensional (1D) model. By doing flood
simulation using a 2D model, important information, particularly related to inundation area, can be obtained
so that the analysis in the flood study can be more comprehensive. In this study, 2D flood model is applied to
Bolango River in order to estimate its actual capacity. The modelling process is conducted by using rainfall
ground stations in a period of 2010-2017, land-use map data in 2015, and a digital elevation model (DEM) by
combining SRTM data and observed cross-section data. The boundary condition at the downstream is sea
water level and at the upstream is the flood discharge from Bone River. The model is verified by comparing
inundated area from simulation result with the observation data. The model result shows good agreement with
the observed data. Based on the result, the bank-full capacity of Bolango River is 189 m3/s, which is just 30%
of 25 years return period of flood discharge.
1 INTRODUCTION
River flood modelling is a tool for assessment,
evaluation, and prediction of river flood risk in
various scenarios (Alaghmand, et.al, 2012).
Hydraulic modelling can certainly provide reliable
and accurate results especially when the model can
exploit the extensive information provided nowadays
(Detrembleur, et.al, 2009). Not only extensive, the
information needed must be accurate and up-to-date.
Thus, the flood rapid assessment is very important to
provide a better accurate hydraulic or flood model
(Moe, et.al, 2018). There are many flood modelling
software was developed to help engineers design,
assess, and evaluate drainage system and provide
them to analyse it in 1-D, 2-D, and 3-Dimensional
model. 2D modelling is considered as a model that
has a better accuracy rate than the 1D modelling
(Gharbi, et.al, 2016; Yakti, et.al, 2018). And also, 2D
model has been considered as the best way to simulate
flood inundation due to its effectiveness and
efficiency (Farid, et.al, 2017). Several considerations
should be done to decide which model will be used in
the study, such as the complexity of river scheme, the
flow characteristic, the availability of observation
data, until the capacity of hardware that will be used
in flood modelling.
Flood is one of the most common natural disasters
in Indonesia. Likewise, the city of Gorontalo which
crossed by the Bolango River. The Bolango River has
experience with flooding almost every year and it is
more frequent in the last five years, such as in 2002,
2013, 2014, 2016, and 2017. This incident causes
harm not only to the material but also to the victims.
Flood on the Bolango River is caused by several
causes such as land-use changes due to the
urbanization, small river capacity, high sedimentation
accumulation, and climate change also contributed to
the causes of the flood in the Bolango River.
Several studies have been conducted to deal with
or to reduce the flood in Gorontalo City. Lihawa and
Rizaldi, A., Moe, I., Farid, M. and Kendra, H.
Estimation of River Flood Discharge by using 2D Model.
DOI: 10.5220/0008560301370143
In Proceedings of the 6th International Seminar on Ocean and Coastal Engineering, Environmental and Natural Disaster Management (ISOCEEN 2018), pages 137-143
ISBN: 978-989-758-455-8
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
137

Sutikno (2009) also reported that the problem of
sedimentation was one of the causes of the flood in
Gorontalo City . In 2012, Arifin et al. have conducted
research on flood disaster risk maps based on several
factors such as rainfall, geological conditions, soil
type, groundwater table, topography and land cover.
Then in 2014, Sarwono et al. had done the assessment
of flood in the Province of Gorontalo to know the
conditions of the drainage system, hydrological
condition, and the rivers morphology. Utama et al. in
2015 reported that the Bolango River had large
sedimentation problems which had a large impact on
flooding. The aim of this study is utilizing the 2-
dimensional flood model to analyse Bolango river
capacity.
2 GOVERNING EQUATIONS
There are three types of approach models can be used
in flood modelling, one-dimensional, two-
dimensional, and three-dimensional. A one-
dimensional model is only considered flow in one
dimension (one-axis flow). Two and three-
dimensional modelling allows the numerical
simulation to expanse the flow from the river into
others axis respectively (Paudel, et.al, 2016; DHI,
2017).
2.1 One-dimensional Hydraulic Model
The equations are used in the numerical model is the
Saint Venant equations. The Saint Venant Equations
is consist of the continuity and the momentum
equations as given below.
Continuity
1
q
x
Q
t
A
(1)
Momentum
0
43
2
2
A
R
QgQn
x
h
gA
x
A
Q
t
Q
( 2 )
Where Q is discharge (m3 s-1), A is cross-
sectional area (m2), q1 is a distributed lateral inflow
or outflow along the x-axis from watercourse (m2 s-
1), n is Manning's roughness coefficient, α is
momentum distribution coefficient, g is acceleration
of gravity (m s-2), R is hydraulic radius (m), and h is
water level (m).
2.2 Two-dimensional Hydraulic Model
In the two-dimensional model, the equations are used
in the calculation process is same, St. Venant
equation. But, the equation will be derived into 2-
dimensional form to calculate flow characteristics in
2-dimensional. The Saint Venant equations are
written in the following form:
0
y
q
x
p
t
h
(3)
)(
1
22
22
2
xy
h
y
xx
h
x
w
hC
qpgp
x
gh
h
pq
y
h
p
xt
p
(4)
)(
1
22
22
2
xyyy
w
h
x
h
yhC
qpgq
y
gh
h
q
yh
pq
xt
p
(5)
Where x and y are the horizontal Cartesian
coordinates; h is the water depth; C(x,y) is Chézy
resistance (m1/2 s-1); ζ(x,y,t) is the water surface
elevation (m); g is the gravitational acceleration; ρw
is the density of water; τxy, τxx and τyy are the depth-
averaged turbulent stresses (kg m-1 s-2), and p(x,y,t),
q(x,y,t) are flux densities (m3 s-1 m-1) in x- and y-
directions.
2.3 Rainfall Run-off Model
The rainfall run-off model is used in this study is
lumped-sum rainfall run-off model by Nakayasu
model. This model is generated based on observations
of several rivers in Japan. The peak discharge can be
calculated by using the equation following:
𝑄
,,
,
(6)
Where C is the run-off coefficient from land use
of basin; Qp is the peak discharge (m3/s); R0 is the
unit rainfall (mm); A is the area of basin (km2), Tp is
the time of rain starts to peak discharge (hours); T0,3
the time needed for discharge decreasing to 30% of
the peak (hours)
trtgTp 8,0
(7)
tgtr 5,0
(8)
Time concentration can be calculated follows:
For L < 15 km
ISOCEEN 2018 - 6th International Seminar on Ocean and Coastal Engineering, Environmental and Natural Disaster Management
138
7,0
21,0 Ltg
(9)
For L ≥ 15 km
Ltg 058,04,0
(10)
Where tg is the time of concentration (hour); tr is
the effective time(hour); and L is the length of river
(km). The time needed to reduce the discharge from
peak discharge to 30% of peak discharge can be
calculated follow:
tgt .
3,0
(11)
tg
AL
25,0
47,0
(12)
Where α is the runoff coefficient. α = 2; for regular
basin, α = 1,5; for the rising part the hydrograph is
slow and falls rapidly, and α = 3; for the hydrograph
rises rapidly and falls slowly.
To make a hydrograph there is a rule to make
hydrograph like a Nakayasu hydrograph shape (see
Figure 1).
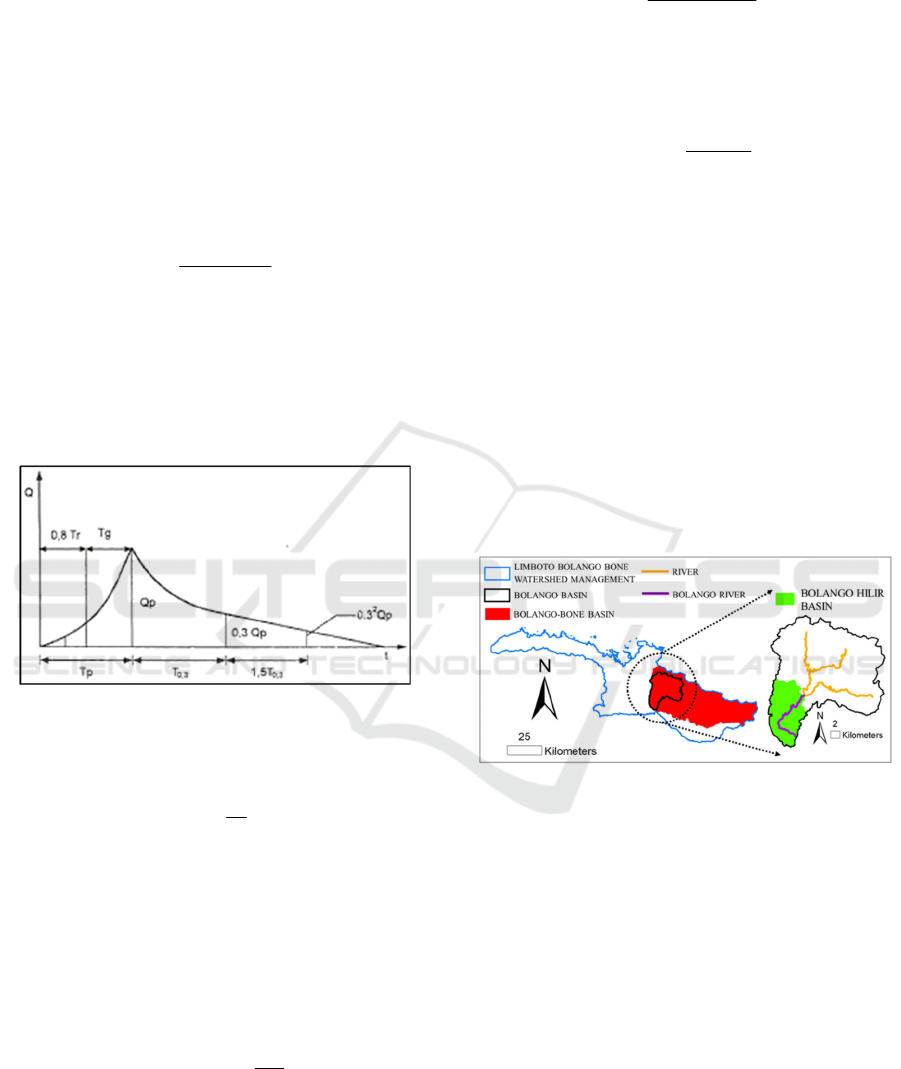
Figure 1: Nakayasu Hydrograph.
Unit hydrograph curves / rising limbs have the
following equation:
4,2
1
Tp
QpQa
(13)
𝑇 𝑇𝑝
Where Qa is run-off before reaching peak
discharge (m3/s); T is time (hour); Qp is peak
discharge (m3/s), and Tp is time peak (hours).
The decreasing limb has the following equation:
Curve down 1:
Tp ≤ t ≤ Tp + T
0,3
3,0
3,0.1
T
Tpt
QpQd
(14)
Curve down 2:
Tp + T0,3 ≤ t ≤ Tp + 1,5T0,3
3,0
5,1
3,0
5,0
3,0.2
T
TTpt
QpQd
(15)
Curve down 3:
Tp + 1,5T0,3 ≤ t
3,0
3,0
2
5,1
3,0.3
T
TTpt
QpQd
(16)
3 DESCRIPTION OF THE STUDY
AREA
This paper studies the use of 2-dimensional flood
modelling to assess the capacity of Bolango River.
The river flow through Gorontalo City (the south of
Gorontalo). The Bolango Basin has an area of 398
km2, with the longest river in that basin is Bolango
River. The length of Bolango river from upstream to
downstream is around 17 km. the main section of this
study, which is the river section to be observed in this
study is the downstream section (Pink line on Figure
2) which have a contact with Gorontalo City.
Figure 2: Bolango River Basin Location.
4 MATERIALS AND METHODS
4.1 Elevation Data
The elevation data used in this study comes from the
National Aeronautics and Space Administration
(NASA) from the United States. The elevation data
used in this study has a level of 30 meters resolution.
From the elevation data, it is known that the
downstream area (Gorontalo City) has a flat height
with an elevation of about 1 to 8 meters above the
mean sea level (Mean Sea Level). This situation can
be seen in Figure 3. While the situation in the
mountains has a very high and steep slope between
1300-1500 m above the average surface of sea water.
Estimation of River Flood Discharge by using 2D Model
139

The mountainous altitude situation in the upstream
city of Gorontalo can also be seen in Figure 3.
Figure 3: Elevation Data of Bolango Basin.
4.2 Land Use Data
The Gorontalo City is filled with shops and
government centres as shown in Figure 4 below,
where land use is filled with urban areas in 2015. It
can be seen also in Figure 4 that the state of land use
in the upstream part of Gorontalo is still a forest area
and open land both in 2009 and 2015. However,
changes in land use from rice fields or open land to
urban areas will have a great opportunity to occur as
shown in Figure 4. This also means that the situation
of increasing urbanization will still be possible in the
future.
Figure 4: Land use Change.
4.3 Cross-section Data
The cross-section data used in this study is data
derived from the study of Balai Besar Wilayah Sungai
Sulawesi II. In Figure 5 below, is an example of a
cross section measured by the BWS Sulawesi II
Team. This cross-section data will be used as the
initial initiation input for the inundation flood model
to find out the parts that can be passed by the water in
this downstream Bolango River.
Figure 5: Example of Cross Section Bolango River.
4.4 Rain Gauge Data
Based on the spatial analysis of rain gauges from 9
stations, there are only 4 stations that have an
influence on the Bolago River Basin, namely Alale
Station, Longalo Station, Dulamayo Station, and
Boidu Bolango Station. So that the rain gauge is used
as a frequency analysis of the return period (Tr).
There are 4 out of 9 rain gauge with a daily
temporal distribution on the target area that has a
series of rain data that is quite good and uniform.
Namely Dulamayo, Longalo, Boidu, and Alale. Also,
there is a water level station (see Figure 6) to calibrate
the rainfall-runoff model.
Figure 6: Rain Gauge and Water Level Station.
The calculation of the return period of rainfall
based on the average area of rainfall data in Bolango
Basin. The maximum daily rainfall from each year
can be seen in Table 1.
ISOCEEN 2018 - 6th International Seminar on Ocean and Coastal Engineering, Environmental and Natural Disaster Management
140

Table 1: Maximum Rainfall Data.
No Years R
24
Max
1 2010 55.7
2 2011 47.8
3 2012 57.8
4 2013 52.4
5 2014 65.7
6 2015 52.7
7 2016 76.6
8 2017 62.4
Then the rain calculation is done again using the
Gumbel distribution. From the calculations that have
been made, the following values are generated.
Table 2: Return Period of Rain.
Return
Period
Probability Rainfall (mm)
2 0.5 57
5 0.8 69
10 0.9 76
25 0.96 86
50 0.98 93
100 0.99 100
200 0.995 107
1000 0.999 123
4.5 Flow Data
Flow data were generated by Nakayasu rainfall-
runoff model as described in the previous section. The
relationship of rainfall and flow recorded in the
calculation of the amount of discharge that affects the
flooded unit in the study area. The flow hydrograph
was calculated after the Nakayasu model was
calibrated by observation data at Talaga Water Level
Station. The calculated hydrograph flow can be seen
in Figure 7
Figure 7: Flow Hydrograph.
5 SIMULATION AND RESULT
We use the 1-D hydraulic model, then coupling it
with a 2-D model to do flood simulation. Before we
do flood simulation we should calibrate the flood
model with observation data. This is the important
stage because to get the exact capacity of Bolango
River we should make sure that the model we will use
in flood modelling represents the actual condition of
the river. Then we do the calibration process and we
can see the result follow Figure 8.
Figure 8: Calibration Result.
Figure 8 (left) the result of a simulation of
inundation floods due to flooding on the Bolango
River with Q25. The left one is the simulated flood
situation with Q25 using the measurement data of the
original cross section. The right picture is the most
disaster-prone zone map. This map of disaster-prone
zones comes from Arifin et al (2016). We can see that
the comparison between simulation and observation
has a fairly close relationship. We get some calibrated
parameters data, Manning's roughness coefficient (n)
for river bed is 0,03 – 0,6 and for floodplain,
Manning's roughness coefficient (n) is around 0,4.
That is, this flood model is quite well calibrated.
After the calibration process, the current capacity
of the Bolango River bankfull can be evaluated. For
the information, the results of the model calibration in
this study use a return period flow (Q25). Then, we
carried out several numerical simulation scenarios to
testing the inundation flood model by using Q25 as
input for the model. This scenario is to reduce the Q25
discharge by 0.7 times, 0.5 times, 0.32 times, 0.31
times and 0.3 times. The graph of each discharge
scenario can be seen in Figure 9. Each scenario will
be numerically tested using a flood inundation model.
Estimation of River Flood Discharge by using 2D Model
141
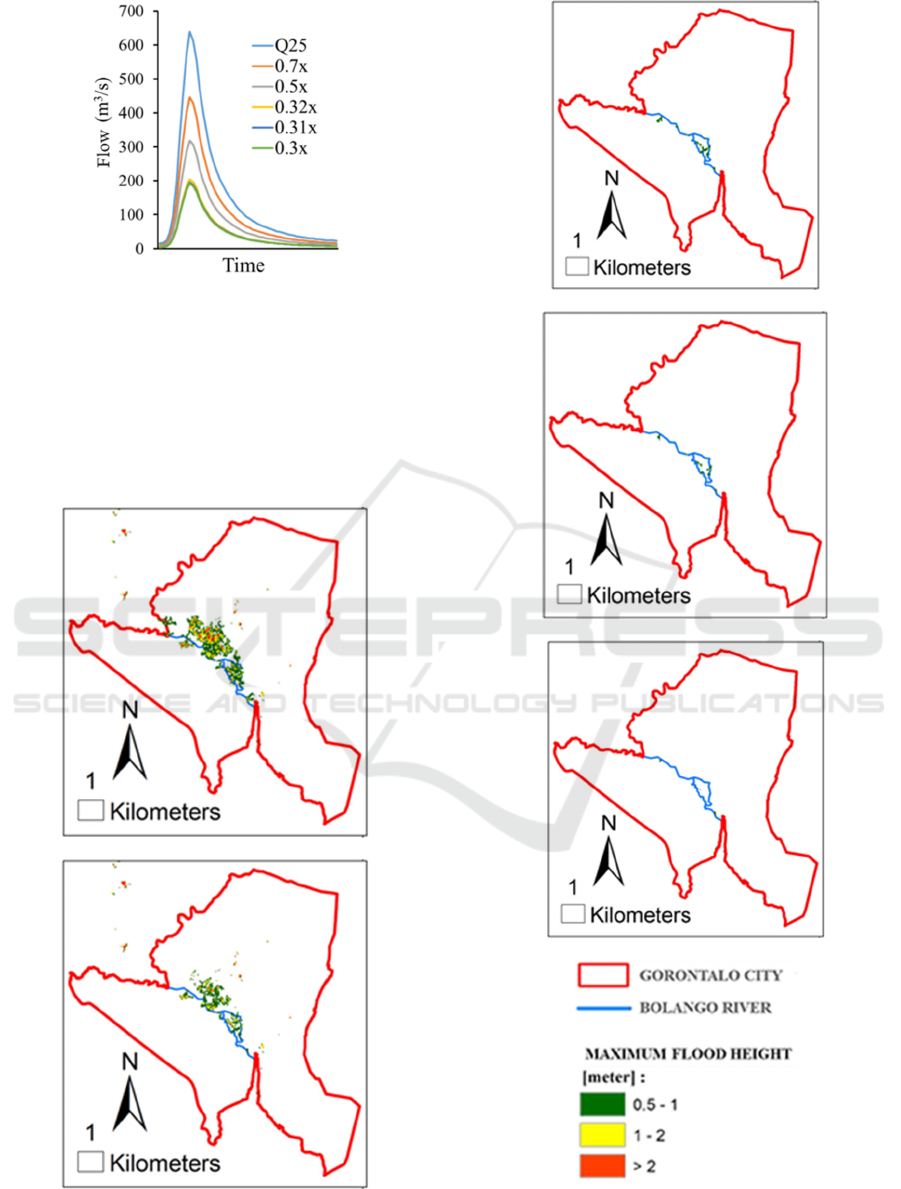
Figure 9: Flow Scenario to Evaluate the river capacity.
The flow hydrograph from each scenario are used
as input for the inundation flood model. Inundation
flood situation of each discharge scenario in Figure 9
can be seen from the inundation simulation results in
Figure 10. For the record, the simulation of
inundation results presented is the maximum
inundation height in each simulation scenario.
(i)
(ii)
(iii)
(iv)
(v)
Figure 10: Flood Simulation Results: (i) 0,7 X ; (ii) 0,5 X ;
(iii) 0,32 X ;(iv) 0,31 X ; and (v) 0,3 X.
ISOCEEN 2018 - 6th International Seminar on Ocean and Coastal Engineering, Environmental and Natural Disaster Management
142

From Figure 10 above we can see that with a
discharge scenario of 0.3 from Q25 there is hardly
any more inundation in the target area of the study
area. That is, from the results of numerical
simulations carried out, peak discharge with 189 m3/s
is a bankfull capacity for the current Bolango River.
This also means that bankfull capacity for the
Bolango River is 30% of Q25. And that is below the
value of flow with a return period 2-year. This
bankfull capacity might decrease when the
accumulation of sedimentation in the Bolango River
increases following the time.
6 CONCLUSION
In this study, the inundation floods model of Bolango
River was constructed. Simulation results of flood
inundation from the flood inundation model have
been compared with inundation observations data and
have a fairly close relationship between the two. From
that conclusion, the model has been calibrated and
can be used to produce a flood inundation simulation.
Based on the results of numerical simulations, the
average maximum peak discharge capacity of the
Bolango River downstream is 189 m3/s. This peak
discharge situation is 30% of the Q25 return period
flow. That is the amount of discharge that can be
drained by the Bolango River without any inundated
area along the river. The situation of the maximum
discharge that can be traversed by the water in the
downstream Bolango River will become smaller in
capacity when considering the accumulation of
sedimentation that might increase in the future.
REFERENCES
B. P. Yakti, M. B. Adityawan, M. Farid, Y. Suryadi, J.
Nugroho, and I. K. Hadihardaja, 2018. MATEC Web of
Conferences, 147, 03009.
B. Sarwono, Sutikno, U. Lasminto, K. A. Utama, and A.
Zainuri, 2014. Prosiding Seminar Nasional Aplikasi
Teknologi Prasarana Wilayah (ATPW), ISSN 2301-
6752.
DHI, 2017. MIKE 21 & MIKE 3 Flow Model FM
Hydrodynamic and Transport Module Scientific
Documentation, MIKE DHI.
F. Lihawa and Sutikno, 2009. IJG Vol. 41 No. 2, 103-122,
ISSN 0024-9521.
I. Arifin Yayu and M. Kasim, 2012. Program Studi
Geografi Fakultas Matematika dan IPA, Universitas
Negeri Gorontalo.
I. R. Moe, A. Rizaldi, M. Farid, A. S. Moerwanto, and A.
A. Kuntoro, 2018. MATEC Web of Conferences, 229,
04011.
K. A. Utama and R. Husnan, 2015. Fakultas Teknik
Universitas Negeri Gorontalo.
M. Farid, A. Marlina, and M. S. B. Kusuma, 2017. AIP
Conference Proceedings, vol. 1903(1), 100009.
M. Gharbi, A. Soualmia, D. Dartus, and L. Masbernat,
2016. J. Mater. Environ. Sci., 7 (8), 3017-3026.
M. Paudel, S. B. Roman, and J. Prichard, 2016. Wood
Rodger Inc., Sacramento, CA.
S. Alaghmand, R. Abdullah, and I. Abustan, 2012. Int. J.
Hydrology Science and Technology, Vol. 2, No. 3.
S. Detrembleur, B. J. Dewals, P. Archambeau, S. Erpicum,
and A. Pirotton, 2009. Associ. Sci. Tech. Eau. Environ.
7, 23-29.
Estimation of River Flood Discharge by using 2D Model
143
