
Behaviour Therapy in Nature Environment, and the Application
in an Inclusive Education Curriculum
Melati Ismi Hapsari
1
, Roro Setyawati
2
1
Faculty of Teacher Training and Education, Universitas Muhammadiyah Purwokerto
2
Faculty of Psychology, Universitas Muhammadiyah Purwokerto
Keywords: Inclusive education, applied behavior analysis, school of nature
Abstract: This study examined an application of behavior therapy done in nature and open environment in an
inclusive education curriculum. This was a qualitative study, and descriptive method was used for analyzing
the data. It was provided by a depth interview and observation to the data sources (students, teachers and
therapists as informants, process of therapy, and documents). This study was done in one of schools of
nature that provided an inclusive education for early childhood with neurodevelopmental disorders. The
results showed that behaviour therapy in open environment, in that school of nature was delivered
comprehensively to all of child developmental needs, through 6 main programmes namely root programme
for sensory motor, stem programme for communication, leaf programme for social skills, flower programme
for self-help & daily activity, and fruit programme for pre/academic & talents. The second result showed
that the therapy was applied integrated with the curriculum in 3 settings, 1) individual therapy (focused on
root & stem programme), 2) group therapy (focused on root & leaf programme), 3) classical learning
activities (focused on leaf, flower, and fruit programme). The third result showed that the therapy was
appropriately based on applied behavior analysis approach. Targets of behavior were broken down into
small steps and many repeated opportunities were provided with abundant reinforcement.
1 INTRODUCTION
For the last decades Indonesian government has
concerned more seriously on the special needs
children through inclusive education policies. The
problem is that not all inclusive schools in Indonesia
are able to provide an adequate treatments at school.
Applied Behavior Analysis is one of therapies
for children with special needs, that familiar in
Indonesia. It has been proven as an effective method
for children with special needs, but in most cases in
Indonesia the therapy is set as an indoor activity in a
formal settings. Research shows that contact and
frequent experiences with nature have a major
impact on the healthy growth and development of a
child’s mind, body and spirit.
The research was done in one of schools of
nature that provides behaviour therapy integrated
with the inclusive education curriculum. The
purpose of this study was to examine an application
of behavior therapy done in nature and open
environment, in an inclusive education curriculum.
1.1 Children with Special Needs
Children with special needs is a term widely used in
the field of education in Indonesia, to mention they
who have barriers in their development. Meanwhile,
in the field of psychology and health, it is known as
neurodevelopmental disorders.
Neurodevelopmental disorders are a group of
conditions with onset in the developmental period.
The disorders typically manifest early in
development, often resulting from the implications
of personal, social, academic, or occupational
functioning. The classifications are: 1) Intellectual
Disability, 2) Communication Disorders, 3) Autism
Spectrum Disorder, 4) Attention Deficit /
Hyperactivity Disorder, 5) Specific Learning
Disorder (Reading, Written, Mathematics), 6) Motor
Disorders (included Cerebral Palsy) 7) Tic Disorders
(A tic Disorders, and 8) unspecified or other
Neurodevelopmental Disorders (DSM-V, 2013).
In everyday conversations among educational
and health practitioners, there is often inconsistency
450
Hapsari, M. and Setyawati, R.
Behavior Therapy in Nature Environment, and the Application in an Inclusive Education Curriculum.
DOI: 10.5220/0008590704500457
In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Psychology in Health, Educational, Social, and Organizational Settings (ICP-HESOS 2018) - Improving Mental Health and Harmony in
Global Community, pages 450-457
ISBN: 978-989-758-435-0
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

in using the term children with special needs. The
term of children with special needs is often attached
to the term of handicap, or disability.
The prevalence of special needs children tends to
increase every year, however Indonesia has a very
limited data. The reason is that the number of special
studies on this issue is still very low. There are
approximately 4.2 million children with special
needs in Indonesia, with an estimated prevalence in
the general population of 21.3% (2006 figures;
South-East Asia Regional Office–World Health
Organization, 2013).
Based on data from the Indonesian National
Health Survey in 2012 (Ministry of Health of the
Republic of Indonesia, 2014) the percentage of
children with special needs in Indonesia was
81.81%, which was in primary school age and below
(Early Age). It was only 14.4% from the overall
number in educational institutions. Therefore, it
needs holistic and integrated handling steps through
integrated therapy with educational curriculum in
school, especially in primary education level.
1.2 Applied Behavior Analysis
Applied behavior analysis has been demonstrated to
be a treatment for children with autism based on
over 40 years of supportive evidence in improving
social behavior and communication, also in reducing
levels of problem behavior (Lovaas, 1987). The
evidence reviewed of applied behavior analysis
indicates there are high positive benefits on children
with autism and other neurodevelopmental disorders
(Howlin, Magiati, & Charman, 2009; Ortega, 2010 ;
Novak, McIntyre, Morgan, at all, 2013 ; Vivanti &
Dissanayake, 2014).
Applied behavior analysis has been referred to as
the treatment of choice for children with special
needs in some therapy center at hospital, special
education institutions, and inclusive schools in
Indonesia.
1.3 Benefit of Nature for Child’s
Development
Children need to be outside, they need to explore to
get many information and knowledge. Research
shows that contact and interact with nature regularly
have a major impact on the healthy growth of a
child’s mind, body and spirit.
Louv (2005) said that outdoor activities and
positive stimulation through playing in natural
environment during childhood can foster happier,
healthier, and more well-adjusted children.
It is important that children and young people are
outside and using all their senses to actively explore,
and make sense of their environment, so that they
could have a sense of independence.
Davis (2004) stated that reconnection with nature
is essential, for people's basic well-being.
Individuals will feel more secure psychologically,
thus it helps the work function of the nervous system
to be more optimal.
Therapy at school should be integrated with
academic activities, in a natural play environment
setting. Children with special needs should not have
to be placed exclusively in a special room, separated
from their peers and social environment.
2 METHOD
2.1 Design
This was a case study research using a qualitative
approach. Descriptive method was used for
analyzing the data. All of data resources were
collected by observation and depth interview, with
semi-structured guide.
2.2 Place and Time
This research has been conducted at Baturraden
School of nature, in Banyumas regency, Central
Java, Indonesia. Sekolah Alam Baturraden (known
as SABar), is one of schools in Indonesia that
implements inclusive education through nature as a
medium for learning practice, including as a
therapeutic setting. SABar developed therapy which
combines applied behavior analyses and nature
environment education approach.
The research data retrieval process has been
conducted for approximately two semesters, starting
from July 2017 until the end of June 2018.
2.3 Subjects
Participants of this study were 3 students with
special needs. They were selected based on certain
criteria which was based on theory or operational
constructs according to the purposes: 1) Student of
SABar in 4 to 6 years old (preschool level), 2) They,
who was diagnosed by registered clinical
Psychologist as a child with a kind of
Behavior Therapy in Nature Environment, and the Application in an Inclusive Education Curriculum
451
neurodevelopmental disorders, 3) They, who have
received the therapy at SABar for at least 1
academic year, 4) They, who have barriers in
behaviour development.
Those 3 participants were the primary data
sources in this study. The secondary data sources
were students who did not meet the criteria above,
students, teachers, therapists, principals, and all
supporting documents (curriculum, manual of the
therapy, and developmental progress report of
students).
3 RESULT
3.1 Students with Special Needs in
Baturraden School of Nature
There were 38 students in SABar (preschool and
elementary school), and 13 of them were children
with special needs. They were diagnosed by clinical
Psychologist as a child with neurodevelopmental
disorders.
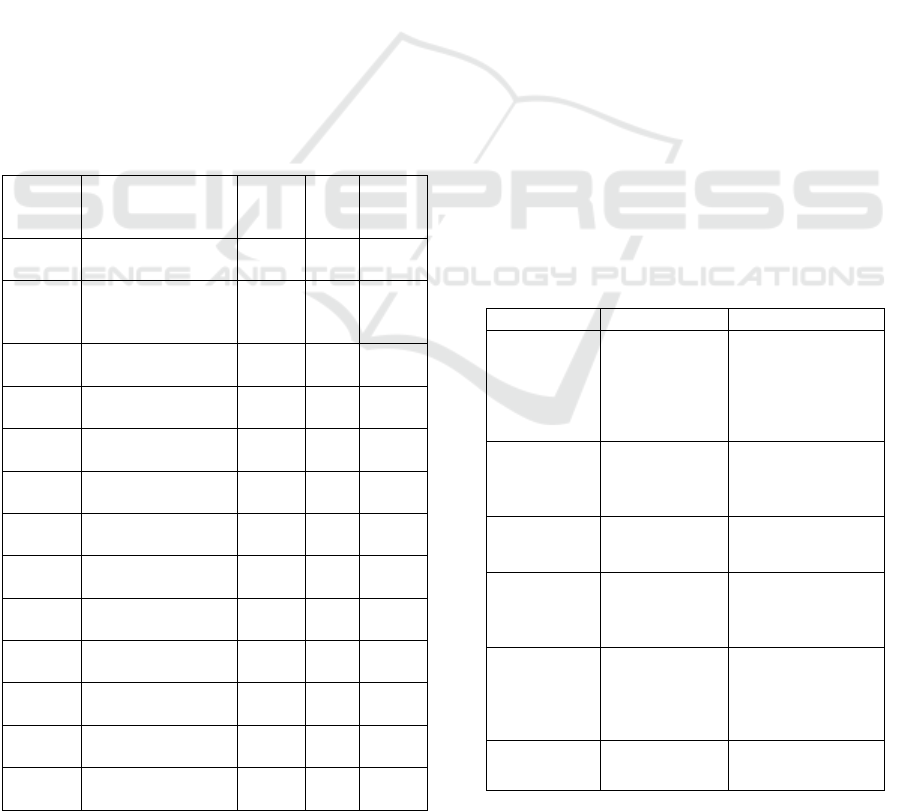
Table 1. Students with special needs in SABar.
Name
(initial)
Disorder Age
(years
old)
Sex Start
1. Dar Speech delay 6 Boy June
2017
2. Bin General
developmental
delay (brain cyst)
6 Boy June
2017
3. Fat ADHD 6 Boy June
2017
4. Sya ADHD 7 Boy March
2018
5. Ce Dyslexia 9 Girl Jan
2018
6. Key Deaf 7 Girl June
2017
7. Rif Down syndrome 8 Boy June
2014
8. Yu Cerebral Palsy 13 Girl June
2016
9. Ak ADD 8 Boy June
2016
10. Dn Disintegrative
disorde
r
13 Boy June
2013
11. Nn Down syndrome 17 Boy June
2013
12. Fen PDD-Nos 12 Boy Jan
2013
13. Fir Learning Disorder 10 Boy Jun
2015
3.2 General Overview of Baturraden
School of Nature and the Therapy
Sekolah Alam Baturraden (known as SABar) is a
School of Nature established by the year of 2011. It
is located in Nepenthes Forest at the base of Slamet
Mountain, at Banyumas regency. The school does
not use pretentious building. The classrooms are
made by bamboo and wood, called saung. Each
class consists of five to fifteen children, mentored by
2 teachers. Learning activities runs every Monday to
Friday from 07.30 to 12.00 for Preschool Class (age
2 for 6 years old) and 07.30 to 14.00 for Elementary
Class.
SABar had been developed a package of therapy
for their special students since 2011, and the manual
of the therapy was internally published for parents of
the students in 2013. The therapy was named as
SABar Green Therapy.
SABar green therapy was used to modified
several existing therapies, such as behaviour
therapy, play therapy, and art therapy. However, in
the development of the therapy, behavior therapy
had been chosen as the primary approach, which was
packed with nature as a medium and main learning
resource for children.
The concept of SABar’s therapy that used
behaviour therapy and nature setting, can be seen in
the Table 2.
Table 2. The concept of SABar’s therapy.
Programme Aspects Activities
Root
Sensory - Exploring
activities
(groping, and
squeezing)
- Standing &
walking barefoo
t
Stem Language &
Communication
- Speech training
(velum-muscle,
lip & mouth
exercises)
Leaf Social Skills - Initiating &
building social
interaction
Flower Self Help &
Daily Living
Activity
- Self-serving in
snack-time and
lunch
- Toilet Trainings
Fruit Pre-academic &
academic
- Knowing
alphabet, number,
colour, shape.
- worksheet
activities
Fruit Talents & Life
Skills
- Handicraft
- Painting
ICP-HESOS 2018 - International Conference on Psychology in Health, Educational, Social, and Organizational Settings
452

Therapy in SABar was generally divided into 3
parts namely: 1) Individual therapy; 2) Group
therapy; 3) Integrated therapy with classical
activities. Here is an overview of one-week course
of therapy that is imposed on a child aged 5 years
with Attention Deficit / Hyperactive Disorder
(ADHD) at SABar.
Table 3: Therapy programme for Ft (a child with ADHD,
5 years old).
Programm
e
Activities Place Typ
e
Sensory
Motor
Guided to :
1. Touching and
groping (grass,
rocks, soil, leaf,
dried leafs)
2. Squeezing
(leaf, dried leafs)
3. Standing
barefoot (pedestal
from grass, soil,
and gravel)
4. Walking
barefoot (pedestal
from grass, soil,
and gravel)
5. Picking-up
objects with
forefinger and
thumb (gravel,
resin seeds)
6. Walking on the
boardwalk (board
of treetrunk)
Schoolya
rd
Resin
forest
Gro
up
Following these
instruction :
1. Toss
2. Shake hand
3. Clapping
4. Hands Up
5. Open and Close
han
d
Schoolya
rd
Resin
forest
Indi
vid
ual
Communi
cation
1. Showing eye
contact
Following these
instructions :
2. Bubbling
(“ba..ba..ba..”,“c
a..ca..ca..”,
“lu..lu..lu..”)
3. Word
Immitation (
papa, mama,
kuda, makan,
minum, etc)
Saung
for
therapy
Indi
vid
ual
Social Eye contact
Greeting / say
Class
activit
y
Cla
ssic
hello
Smiling at friends
Shaking hand to
friends
Pla
y
in
g
to
g
ethe
r
(indoor
and
outdoor)
al
Self Help Having lunch /
snack
independently
Opening bottle
cap independently
Wearing and
taking-off bag &
shoes
independently
Toilet training
Putting the stuffs /
equipment in its
p
lace
Class
activity
(indoor /
saung))
Cla
ssic
al
Pra-
Academic
&
Academic
Learning alphabet
Learning number
Counting
Colouring
Doodling with
p
encil
Class
activity
(indoor /
saung)
Cla
ssic
al
Talents &
Creativit
y
Listening music Class
activit
y
Individual and group therapy were focused on
the Root program to strengthen the child's sensory
motor abilities, and on the Stem program to
strengthen communication skills (including speech
and language skills).
Individual therapy was performed indoors called
saung. Saung is wooden construction of
approximately 4x5 meters, shaped like a house with
4 stilts. Its walls, floors, and roofs are made of wood
with two large windows that are always open. Just
outside the window is the view of the green trees.
There are not many things in the room. There is only
one cupboard to put the equipment in, and one large
mirror mounted on one wall.
The room looks spacious, quiet, and comfortable.
Since it is located near the nature, there is only
occasionally heard the sound of children doing
activities in the schoolyard or surrounding resin
forest without any sound of vehicles. The air is so
cool and fresh with adequate sunlight.
Group therapy was performed by the child
together with other children with special needs,
guided by several therapists. One therapist was
responsible for 2 children. Group therapy was
carried out in open space. It focused on the
surrounding environment by maximizing the
potential of all the senses owned by the child.
The therapy programs of Leaf, Flower and Fruit
were implemented integrated with classical
activities. Here is an overview of the implementation
Behavior Therapy in Nature Environment, and the Application in an Inclusive Education Curriculum
453

of learning activities in SABar for pre-school age
children, including the implementation of therapy.
Table 4: Classical learning activities. (preschool class)
LEARNING ACTIVITIES TIME PLAC
E
I. Welcoming Activity
All teachers and therapists
welcome every child
enthusiastically, they greet
students warml
y
7 to 8 am Schoo
l yard
II. Opening Class & Morning
Promises
‐ Gathering with others,
opening prayers, and stating
commitment to rules at school
‐ Apperception activities with
li
g
ht conversation
8 to
8.30 am
Saung
III. Integrated Thematic
Activities
Example Activities at Week 25
EXPLORING SCHOOL
ENVIRONMENT
1.Fantasy gymnastics,
gymnastics that mimic the
movement of trees
2. Walking barefoot on gravel
pedestal and grass pedestal
3. Pulling out the weeds
FINDING HIBISCUS
1. Walking along into the
garden
2. Playing and working in a
group “finding hibiscus”
3. Picking some hibiscus
leaves and flowers
4. Counting them and finding
the appropriate number
BLOWING BUBBLES
1. Squeezing hibiscus leaves
into the bowl with water
2. Squeezing them until frothy
3. Making bubble with hand
from the hibiscus liquid
WORKSHEET ACTIVITY
1. Making a collage from
leaves and flowers of hibiscus
2. Writing down name and title
3. Spelling alphabet
8.30 to
11 am
Schoo
l yard,
garden
IV. Snack Time
children serve themselves
while eating, drinking, cleaning
u
p
the
g
arba
g
e and e
q
ui
p
ment
11 to
11.30 am
Saung
V. Closing
‐ Teacher summarizes, gives
feedback and compliment
‐ Sin
g
in
g
, and closin
g
p
ra
y
ers
11.30 to
12 am
Saung
3.3 The Procedure of Treatment for
Students with Special Needs
Before having the therapy, it had been explained
about the general description of therapy integrated
with learning in SABAR. Then, it will be explained
about the steps of behavioral therapy process applied
since the child entered the class for the first time.
Here is an overview of the therapeutic process
flow imposed on special needs children in SABAR
Figure 1: Process of therapy programme.
Assessment is the earliest stage which should be
done before the child gets therapy. Initial assessment
is conducted in a multidisciplinary manner by
teachers and therapists, as well as other related
professions namely Clinical Psychologist and
Paediatrician.
It is sometimes found that prospective students
had been already assessed and diagnosed previously
by psychologists, psychiatrists, or paediatricians
outside of school. However, preliminary assessment
still needs to be done.
Developmental assessment by multidisciplinary
may result in a firm diagnosis by the invited Clinical
Psychologist to school. Psychologists also provide a
record of recommendations on important matters
that must be considered or followed up by family
and school.
Psychological examination resulted from
psychologists, notes from pediatricians (or
psychiatrists if necessary), and assessment resulted
by teachers and therapists were then discussed
internally and then discussed by the school inclusion
curriculum team. The discussions produced the
child's primary needs in each aspect of development,
which were then broken down into behavioral
targets. Here is an example of a major
developmental requirement of a child named Bin
(initial) on baseline conditions and a list of
behavioral targets in every aspect of development.
ICP-HESOS 2018 - International Conference on Psychology in Health, Educational, Social, and Organizational Settings
454

Bin is a 6 year old boy. Bin has got a Brain Cyst
since he was born, which caused general
developmental delay, although brain surgery had
been performed to him.
Table 5: Example of the target of student’s behavior.
As
p
ects Baseline Tar
g
et
(
first 3 months
)
Sensory
motor
‐ no response to
the sound or
touching
‐ grasping (with
guidance)
‐ leaning toward
a well-known
person
Responding to
exploration activity:
standing barefoot
(with guidance),
touching, groping
Following
instructions:
opening-closing hand,
tossing, clapping,
squeezing, shaking
han
d
, waving hands
Commu
nication
Crying
mumbling
(inadequate)
Following
instructions:
opening-closing
mouth, sticking tongue
out, gnashing teeth,
inflating the mouth,
blowing, smiling,
laughing, saying
words (e.g.mama,
p
a
p
a, mimi
)
Social
Skills
eye contact
(inadequate)
Adequate eye contact,
responding when
someone called his
name, answer greeting
Self-
help &
DLA
Unable wiping mouth, holding
a spoon, putting food
into the mouth,
holding a glass,
drinking and sucking
with a straw
Pre/Aca
demic
Unable Holding crayons and
markers, doodlin
g
Talents Unable Responding to the
music sound, moving
hands and fingers
(finger painting)
Different behavioral targets for each child are
based on developmental needs obtained from initial
assessment results. The next stage was to design
individual activities and group activities, which
became a means of achieving each target behavior.
Positive and negative reinforcement were applied
to achieve behavioral targets, and to maintain the
behavior achieved by the child, to be consistent. The
therapist in SABar did not use punishment for the
consequences.
The types of reinforcement used for each child
are different, depending on the child's interests and
needs, as well as the child's thinking ability.
Table 6. Example of the target of student’s behavior.
Response
Emer
g
ence
Reinforcement
None =====> No Reinforcement
Limited =====> Positive Reinforcement:
‐ Positive word (e.g.
yeeaaah, good, great,
amazing)
‐ Big smiling
‐ Holdin
g
child’s han
d
More
Adequate
=====> Positive Reinforcement:
‐ Positive word aloud
(e.g. yeeaaah, good,
great, amazing)
‐ Big smiling
‐ Tickling child’s
stomach
Behavior modification in this therapy also
applied token economy technique. Token economy
is aimed especially for target behavior on self-help
ability. Here is the process of applying token
economy in SABar.
Figure 2: Process of the token economy
Classical therapy guides, integrated with
classroom learning activities, were prepared by a
teacher based on some suggestions from the
therapists. The role of a therapist in classical therapy
is to accompany and set the child to achieve his or
her behavioral targets, especially social skills and
self-help.
Measurement of child development was done
continuously every day, inherent with the
implementation of therapy. The measurement sheet
Behavior Therapy in Nature Environment, and the Application in an Inclusive Education Curriculum
455

is a checklist, containing a list of behavioral and
rating targets in the rating scale range from 1 to 6,
with the following description: 1 = inadequate or
inappropriate at all ; 2 = very limited; 3 = the
development needs to be motivated ; 4 = sufficient
development; 5 = appropriate or adequate in an
optimal function ; 6 = excellent, consistent
development.
Home visit was done to every child, 1 every 3
month, or incidental visit whenever needed. Home
visit was done to see family support for child
development achievement.
The daily, weekly, and monthly assessment
process were then recorded into a child development
report once in three months and it would be
communicated with parents. If the child has
consistently achieved his or her behavioral targets,
then the behavioral target will be increased.
The initial and advanced behavioral targeting
process were conducted under supervision of clinical
psychologist, and paediatrician and psychiatric if
necessary. A clinical psychologist will reassess
children and do the counselling with parents on the
6th month.
At the end of the semester, therapists, teachers,
and principals carried out the evaluation process to
improve the quality of inclusion programs in the
future.
4 DISCUSSION
Serving the mandate of inclusive education is not
easy, it takes a rigorous commitment, as well as
strong multidisciplinary cooperation.
An effective inclusive education is more than a
philosophy and more than a willingness to create a
supportive environment. Teaching inclusively is a
complex challenge and is most likely to stem from a
coordinated, whole-school approach (McMillan &
Jarvis, 2013)
SABar has shown this strong commitment for 7
years, from 2011 until now. Principals
(kindergartens and primary school), teachers, and
therapists, are able to work together and strongly
committed to provide an effective inclusive
education, including with involving a clinical
psychologists and pediatricians, also parents and
families.
At the beginning the primary vision of SABar
was giving treatment and acceptance to every special
child as well as other children without any specific
obstacles. This vision is in line with the principle of
Unconditional Positive Regard in the guidance and
therapy approach for children with special needs
(Hallahan, 2001).
In most cases, therapy is addressed as an indoor
verbal activity in which the relationship between
therapist and client stands at its centre. Therapy in
SABar for children with special needs uses a
different approach. Nature environment is used not
only as a therapeutic setting but also as a medium
and a partner in the process. The therapy uses nature
and other various objects in an open environment.
Reconnection with nature is essential, for
people's basic well-being. Individuals will feel more
secure psychologically, thus it helps to optimize the
work function of the nervous system (Davis, 2004).
Louv (2005) stated that outdoor activities and
positive stimulation through playing in natural
environment during childhood, can foster happier,
healthier, and more well-adjusted children. Kuo &
Taylor (2004) in their study concluded that children
with attention deficit disorder (ADD) showed a
greater ability to focus immediately after spending
time in nature.
The best results will be obtained when teachers
are able to integrate learning in the natural
environment with classroom learning strategies. Kuo
& Taylor (2004) in their study concluded that
children with attention deficit disorder (ADD)
showed a greater ability to focus immediately after
spending time in nature.
Nature has the power to help children grow and
develop optimally, including those with barriers or
developmental disorders.
The therapy in SABar is an intervention for
children with special needs that uses a variety of
behavioral strategies to teach developmentally
appropriate and prerequisite skills. It is very
compatible with the character of Applied Behavior
Analysis (ABA) approach.
All skills of children behaviour were broken
down into small steps or components, and learners
were provided many repeated opportunities to learn
and practice skills in a variety of settings, with
abundant positive reinforcement (Kazdin, 2012).
The ABA therapy is generally given in a closed
room, individually between a child and therapist,
with various instructions that seem stiff. This can be
an obstacle for clients and children who tend to feel
bored quickly, awkward and uncomfortable with
formal room settings.
The therapy at SABar applied ABA that was
combined with nature objects and open environment.
While many empirical results show that ABA is
a therapy generally chosen to handle children with
special needs, there is still a critical about ABA
ICP-HESOS 2018 - International Conference on Psychology in Health, Educational, Social, and Organizational Settings
456

therapy. Germansky (2013) said that ABA involved
a lot of repetition that is tough on the children.
There are ways of manipulating the environment so
that kids are more naturalistically learning a lot of
positive behaviour skills. Children are more able to
generalize skills learned in a naturalistic situation
beyond the therapy sessions, therapist should take
them out into the world with them.
A first key component of ABA is behavioral
(Baer, et al, 1968; Newman et al., 2003). Applied
Behavior Analysis is the systematic, controlled, and
empirical investigation of socially important
behavior using empirically validated research-based
and socially acceptable practices (Cooper, et al.,
2007, Newman et al., 2003).
The therapy at SABar provided observable and
measurable studies about child’s responses
individually. Data were collected in an ongoing
manner. In teaching situations, repeated
measurement assisted in monitoring progress over
time.
5 CONCLUSION
Behaviour therapy in open environment, in
Baturraden school of nature was delivered
comprehensively to all of child developmental
needs, through 6 main programmes namely root
programme for sensory motor, stem programme for
communication, leaf programme for social skills,
flower programme for self-help & daily activity, and
fruit programme for pre/academic & talents.
The therapy was applied integrated with the
curriculum in 3 settings, 1) individual therapy, 2)
group therapy, 3) classical learning activities. The
therapy was appropriately based on applied behavior
analysis approach. Targets of behavior were broken
down into small steps and many repeated
opportunities were provided with abundant
reinforcement.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work is dedicated to the amazing team
(teachers, therapist, and students) at Baturraden
school of nature, where we learn a lot about the
meaning of gratitude and struggle. We also express
our deep appreciation to our family, and also to
Universitas Muhammadiyah Purwokerto.
REFERENCES
Baer, D. M., Wolf, M. M., & Risley, T. R., 1968. Some
Current Dimensions of Applied Behavior Analysis.
Journal of Applied Behavior Analysis, 1,91-97.
Cooper, J. O., Heron, T. E., & Heward, W. L., 2007.
Applied Behavior Analysis. Upper Saddle River, NJ:
Pearson Education, Inc.
Davis, J. 1998., The Transpersonal Dimensions of
Eco
-
psychology: Nature, Nonduality, and Spiritual
Practice. The Humanistic Psychologist, 26(1–3), 60–
100
Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders
(DSM-V)., 1994. New York : American Psychiatric
Association.
Eldevik S, Hastings R.P, Hughes J.C, Jahr E, Eikeseth S,
and Cross S., 2010. Using Participant Data to Extend
the Evidence Base for Intensive Behavioral
Intervention for Children With Autism. American
Journal on Intellectual and Developmental Disabilities
115:5, 381-405.
Howlin P, Magiati I, and Charman T., 2009. Systematic
Review of Early Intensive Behavioral Interventions for
Children With Autism. American Journal on
Intellectual and Developmental Disabilities. Vol. 114,
No. 1, pp. 23-41.
Kazdin, A.E. 2012. Behavior Modification in Applied
Settings: Seventh Edition. Long Grove, Illinois :
waveland, press. Inc.
Kuo, F.E., & Faber Taylor, A., 2004. A potential natural
treatment for Attention-Deficit / Hyperactivity
Disorder: Evidence from a national study. American
Journal of Public Health, 94, 1580-1586
Louv, Richard., 2008. Last Child in the Woods: Saving
Our Children From Nature-Deficit Disorder. Chapel
Hill, NC : Algonquin Books of Chapel Hill,
McMillan, J.M., Jarvis, J.M., 2013. Mental Health and
Students with Disabilities: A Review of Literature.
Australian Journal of Guidance and Counseling.
Volume 23, Issue 2 December 2013 , pp. 236-251
Newman, B., Reeve, K. F., Reeve,S. A., & Ryan, C. S.,
2003. Behaviorspeak. New York: Free Press.
Novak I, McIntyre S, Morgan C, Campbel L, Dark L,
Morton L, Stumbles E, Wilson S.A, Goldsmith S.,
2013. A Systematic Review of Intervention for
Children with Cerebral Palsy : State of The Evidence.
Journal of Developmental Medicine & Child
Neurology. Vol 55. Pp 877-878
Ortega J.V., 2010. Applied behavior analytic intervention
for autism in early childhood: Meta-analysis, meta-
regression and dose–response meta-analysis of
multiple outcomes. Clinical Psychology Review. Vol
30, Issue 4, pp 387-399
Vivanti G, Dissanayake C., 2016. Outcome for Children
Receiving the Early Start Denver Model before and
after 48 Months. Journal of Autism and
Developmental Disorders. Vol.46, Issue 7, pp 2441–
2449
Behavior Therapy in Nature Environment, and the Application in an Inclusive Education Curriculum
457
