
Improving Student Learning Quality Through Jigsaw Cooperative
Learning Methods in Communication Theory Courses
Elva Ronaning Roem and Sarmiati
Communication Studies Program, Faculty of Social and Political Sciences, Andalas University, Padang, Indonesia
Keywords: Jigsaw Learning Method, Effective Communication, Learning Quality.
Abstract: Action research is a classroom research that uses a cycle of planning, action, observation, and reflection. The
main problem addressed in this study is the low creativity of students in class discussion in the application of
Student Centered Learning in the Communication Theory course. Generally, this research aims to improve
student learning in the Communication Science Study Program of the Faculty of Social and Political Science
of Universitas Andalas using a Jigsaw Cooperative Learning model. Action Research was carried out in two
ways with discussion material that had been prepared before the class and with students prepared discussion
material for presentation in front of the class to be listened to by other students, which provides creativity
space for them to conduct class presentations. The data collection tool used consisted of course materials
(Papers and Power points), evaluations (tests and non-tests), and observations. The subjects studied were all
second-semester students (2017/2018 academic year) of Communication Science Study Program who took
Communication Theory courses. The results showed that using the Jigsaw model learning approach student
learning outcomes each cycle resulted in a significant change. Before implementing the Jigsaw model almost
all of the students were assessed as not good enough but in the process of discussing the presentations the
student performance improved. From observations, students were able to show their creativity in discussions
in front of the class. The discussion group consisted of 5 students who divided one topic between them. The
implementation of the Jigsaw model learning approach could ultimately improve student learning outcomes
in the presentation of lecture material every week. Students could apply effective communication skills to
speak in the class and express their opinions and thoughts on the materials of the week in the Communication
Theory course.
1 INTRODUCTION
The duties of lecturers set out in the Tri Dharma
Perguruan Tinggi, include teaching and learning and
require use of good and effective learning methods.
The lecturer should act as a facilitator creating a
situation that allows students to learn and as a
learning manager in charge of creating learning
activities that allow students to achieve optimal
learning goals. The problems and experiences that the
authors still face as a lecturer in Communication
Science in Universitas Andalas are with the second-
semester students. When the authors taught several
times and delivered a course review every week, all
students who took this course tended avoid asking
questions or even discussing them. It led to a passive
class atmosphere.
It also seemed that students were not confident
and ashamed if they answered questions. Students
also felt afraid to ask questions which eventually led
them to becoming the focus of jokes by other students
in the class.
Communication is a central human activity. In our
daily lives we are never separated from
communication activities. Watzlawick has said that
humans need communication (Watzlawick,
Weakland, and Fisch, 1974). Thus, learning and
understanding communication theory will help
students see things related to the activities in their
surroundings. Therefore, to achieve the teaching
objectives of the communication theory course, it is
not appropriate if learning is only carried out with a
lecture method which is unlikely to provide direct
experience to students.
Communication theory courses are the subjects
that should emphasise the use of communication. In
fact, since almost all classroom activities are part of
the communication process, it was decided, based on
Roem, E. and Sarmiati, .
Improving Student Learning Quality Through Jigsaw Cooperative Learning Methods on Communication Theory Courses.
DOI: 10.5220/0008678800290033
In Improving Educational Quality Toward International Standard (ICED-QA 2018), pages 29-33
ISBN: 978-989-758-392-6
Copyright
c
2019 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
29

the results of discussions with teammates for this
course, it is necessary to undertake action research to
improve learning outcomes, generate student
creativity and ideas that are fun for students, through
use of Jigsaw cooperative learning. This would also
build personal and group responsibility and change
the learning method used by lecturers. The lecturer
would not be the only source of learning (teacher
centered) but peers could also become a source of
knowledge. Because of these factors, the author
designed and conducted this research with the title of
Improving Student Learning Quality Through Jigsaw
Cooperative Learning Methods in Communication
Theory Courses.
2 METHOD
2.1 Jigsaw Method
Jigsaw method is a type of cooperative learning that
encourages students to be active and help each other
in mastering lecture material and gain understanding
(Evcim and İpek, 2013; Hong et.al, 2012). Aronson
first developed the jigsaw method. In this study
students were put into small groups consisting of 4-6
people. Each group was given information that
addressed one of the topics of the course.
In the implementation of jigsaw cooperative
learning, students work in two different groups, in
their own groups and in expert groups. A group of
students that has the same information is known as
the expert group. In this group, each student discusses
and looks for the best way to explain that part of the
information to their original group members. Then all
students in this expert group returned to their original
group, and each of them explains the information to
their group friends.
2.2 The Basics of the Jigsaw Method
The Jigsaw method, as well as other group learning
processes, is an effective way to vary the atmosphere
of class discussion. Assuming that discussion
requires arrangements to control the class as a whole,
and the procedures used in the cooperative phase can
give students more time to think, respond and help
each other.
2.3 Elements of the Jigsaw Method
Jigsaw learning is more than learning in groups. Basic
elements of learning that are carried out include (1)
"Make it easy for students to learn using something
"useful" such as facts, skills, values, concepts, and
how to live in harmony with each other” (2)
Knowledge, values and skills are recognized by those
who are competent in assessing (Garcia et.al, 2017;
Tewksbury, 1995; The Foundation Coalition, 2001).
According to Anita Lie, the Jigsaw method, along
with other group-based learning, contains interrelated
elements, including:
1. Positive Interdependence.
It does not mean that students depend entirely on
other students. If students rely on others without
giving or being depended on by others it cannot
be called positive interdependence. Johnson at the
University of Minnesota, Shlomo Sharan (Sharan,
1999) at Tel Aviv University, and Robert E.
Slavin (Slavin, 1980) at John Hopkins, have
become researchers and practitioners who
develop Cooperative Learning as a learning model
that can improve student achievement while
honing student interpersonal intelligence and
create an atmosphere that encourages students to
feel a mutual need. This feeling is called positive
interdependence. This interdependence can be
achieved through the use of goals, tasks, materials
or learning resources, roles, and gifts.
2. Individual Accountability.
The jigsaw model requires individual
accountability as it involves measuring the
understanding of each group member and is gives
feedback about the learning achievements of the
members, so they know which partners who need
help. Unlike in traditional groups where
individual accountability is often overlooked so
that a few members may do most of the tasks, in
the jigsaw model students are responsible for the
tasks carried out by each member.
3. Face to Face Interaction.
Cooperative interaction requires all members of
the learning group to be face-to-face so that they
can dialogue not only with lecturers but also with
peers. Students often find it easier to learn from
peers than from lecturers.
4. Social Skill.
This element requires students to be provided by
a variety of social skills, such as leadership,
decisions making, trust building, management
communication, and conflict skills. Other social
skills such as tolerance, politeness to peer,
criticizing the ideas, daring to maintain a logical
mindset, not dominating others, being
ICED-QA 2018 - International Conference On Education Development And Quality Assurance
30

independent, and various other qualities that are
useful in establishing interpersonal relationships
are not only assumed but intentionally taught.
5. Group Processing.
This process occurs when each group member
evaluates the extent to which they interacted
effectively to achieve a common goal. The group
needs to discuss the behavior of cooperative and
uncooperative members and decide which
behavioral decisions must be changed or
maintained. This encourages the creation of a
learning community where learning outcomes are
obtained from the results of collaboration with
other people in the form of sharing of individuals,
between groups and between those who know and
do not know.
3 RESULT AND DISCUSSION
The classroom action research was carried out by the
Communication Science Study Program of
Universitas Andalas to second-semester students
every week from February to the end of May in 2
cycles. Each cycle was 2 x 60 minutes (1 x Meeting).
During the implementation of the research the
researcher was assisted by a peer observer from the
Communication Science Study Program who
observed the learning process, and assisted in
collecting data. This research was a classroom action
research with an emphasis on improving the quality
of learning processes and practices and focuses on the
use of Jigsaw Cooperative learning method as a way
to develop students' abilities or improve their ability
to think about Communication Theory.
Two cycles as described in the model adapted
from Slavin (1995) were used. Each cycle in this
study consisted of four components of primary
activities: (a) planning; (b) acting; (c) observing (d)
reflecting. The four components of these main
activities operate continuously with some
modifications in the planning component. The
planned actions in each cycle consists of the
following:
3.1 Planning
The researcher and colleague who form one team in
the Communication Theory course discussed the
material, learning activities and evaluation tools and
prepared teaching aids/ instruments and observation
guidelines.
3.2 Action Implementation.
In implementation, researcher’s action steps
according to the lesson plan as follows:
Initial activities: Apperception, explanation of
learning objectives and provision of material.
Core activities: Class presentations, group
division, Implementation of Jigsaw
Cooperative Learning: weekly course material
for selected students and their team who came
to in front of the class. The implementation of
observation assessment, Class presentations
from the results of student discussion, both
concluding and equating perceptions
continued with evaluation.
Final activities: Giving rewards, reaffirming
the main/important matters,
improvement/enrichment, and closing.
3.3 Observation
Observation was done during the activities in the
class. Observations include both student and lecturer
activities and used observation sheets. The researcher
and colleague in the team observed the impact of the
implementation, whether it went according to plan
and what obstacles were faced by students. Data
collection techniques during learning activities
involved observing, documenting, and active learning
discussion practices.
Observation is carried out using an instrument of
affective and psychomotor performance, to measure
the indicators of work, efficiency, and involvement of
students in the learning process.
Active learning discussions were encouraged by
explaining about how students must be able to speak
and be active in front of the class in material
discussion groups. Assessment was given on student
activity and interest level of material and presentation
slides. This was done to measure the ability and skills
of students in understanding the communication
theory material.
The material for each presentation was taken from
the material contained in the semester learning plan
(RPS). Assessment was performed to identify
students' abilities before being given Jigsaw tasks
and at the same time to determine the level of each
student to form cooperative groups.
Improving Student Learning Quality Through Jigsaw Cooperative Learning Methods on Communication Theory Courses
31
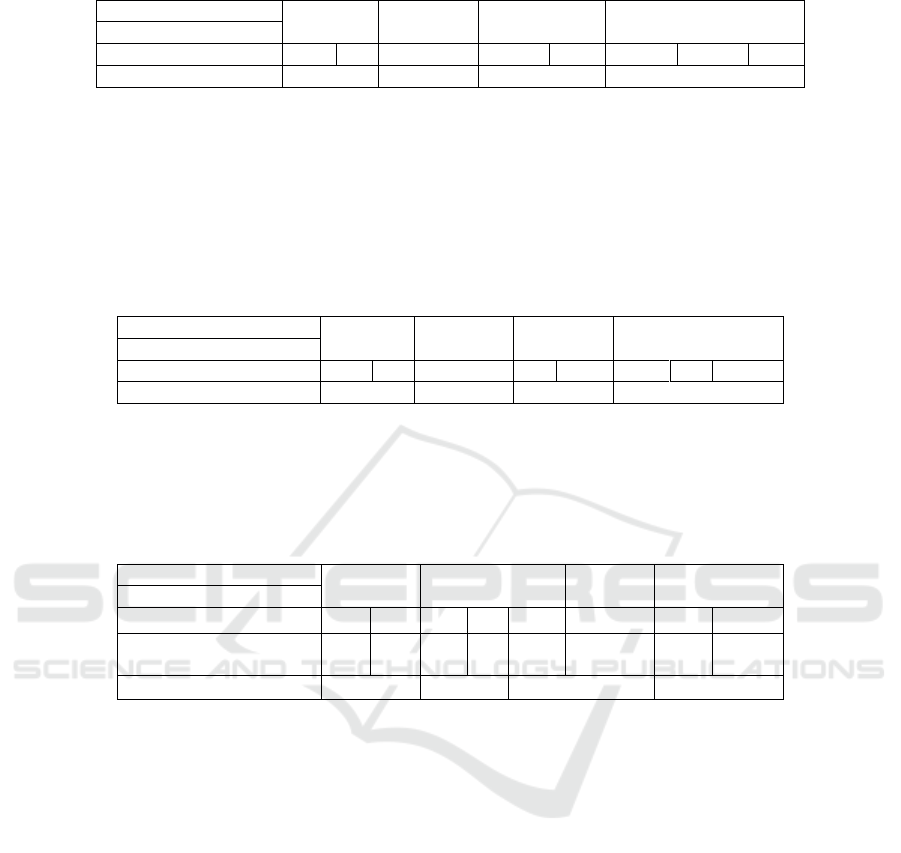
Table 1: Learning Acquisition from The First Cycle.
Cycle
Grades
Cognitive
Affective
Psychomotor
Assessment area
I.Theory of Paradigm
80
60
50
7
47
10
46
11
Number of Students
57
57
57
57
From the data obtained it was seen that the
implementation of learning in each cycle varied
greatly, especially in the shortcomings/weaknesses.
In the first cycle, only 20 students of the 57 showed
ability to work intelligently and creatively in
conducting interesting class discussions. The rest of
the students (37 students) were passive in class
discussions, as indicated by the cognitive, affective,
to psychomotor assessments. It was considered
necessary to improve in the second cycle both the
lecturer directives, and the students’ understanding of
the topic, provide motivation, guide the discussion
and improve understanding of the material as all these
were evident weaknesses in this cycle.
Table 2: Acquisition of The First Cycle.
Cycle
Grades
Cognitive
Affective
Psychomotor
Assessments
I. Theory of Paradigm
80
60
50
7
47
10
46
11
Total of Student
57
57
57
57
In the second cycle, achievement of the class showed
a very significant improvement in the cognitive
evaluation and observations of affective and
psychomotor student behavior. The average
achievement increased from 80 to 85 and 60 to 68. (in
cycles 1 and II) meaning that students had mastered
the subject matter and had fulfilled the achievements
of the works.
Table 3: Learning Acquisition in The Second Cycle
Cycle
Grades
Cognitive
Affective
Psychomotoric
Assessments
I. Theory of Paradigm
80
60
50
7
47
10
46
11
II. Theoretical
Tradition
85
68
54
3
50
17
47
10
Total of Student
57
57
57
57
From the assessment of each cycle, we can conclude
that there was an improvement compared to the
previous cycle, both in learning achievement
measured through tests and observations during the
activity. The improvement between the initial
condition and first cycle especially on the average
grade the observation results was under 50%
(effective 47% and psychomotor 46%). Cooperative
learning is a new method; students were not used to
implementing it because they only had experience
with traditional methods so they lacked to answer or
give opinions.
The development between first and second cycles
was encouraging both in the evaluation and from the
observations. The average achievement grade result
was 100% while the result of the average observation
of student who was not passive was 60%, with
cognitive factors 7%, affective factor 10%,
psychomotor 11%. The low grade of some students is
due to the lack of courage of students to express their
opinions, while the improvements of observation
result have proved the lecturers were mastering the
classroom situation. In the second cycle, this is shown
in teaching and learning activities.
The table, clearly shows that each cycle resulted
in very significant changes and developments so that
it can be said that the indicators in the improvement
of learning have been reached. The application of
cooperative learning improved the learning outcomes
of the second-semester students of Communication
Science Study Program Universitas Andalas;
Academic Year 2017 / 2018. The following
conclusions can be drawn:
1. The Jigsaw cooperative learning approach could
stimulate students' creative thinking in solving
problems they faced. Students could remember all
forms of behavior, so that learning outcomes were
improved.
2. The role of lecturers in the learning of
communication theory courses using the Jigsaw
cooperative learning approach is as a facilitator
and learning resource that can guide students and
ICED-QA 2018 - International Conference On Education Development And Quality Assurance
32

direct them to find solutions related to the
problems they face.
3. Confidence and creative thinking skills are the
necessary needs for students to use the Jigsaw
cooperative learning approach more successfully.
4. Problems in learning by using the Jigsaw
cooperative learning approach can be overcome
jointly between students and lecturers until the
most appropriate solution is finally found.
5. The results showed that by using the Jigsaw
cooperative learning approach, student learning
outcomes in each cycle experienced a significant
improvement. The learning outcomes of the
second-semester students of Communication
Science, degree of understanding of the
discussion material about the Paradigm of
Communication Theory and the Theoretical
Tradition as indicated by grades 80 and 60.
Students who scored 80, cognitive average 54 %
an increase from 50%, while affective scores rose
from 47% to 50%, and psychomotor aspects from
46% to 47%. Meanwhile, students who scored 60
had an average increase that varied in both cycles.
Cognitive factors decreased from 7% to 3%.
Affective factors rose from 10% to 17%, and
psychomotor aspects decreased from 11% to 10%.
6. The application of cooperative learning approach
with the Jigsaw model ultimately improved the
learning outcomes of the second-semester
students of Communication Science Study
Program, Faculty Social Political Science at
Universitas Andalas.
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
Thank you very much to the students in the second
semester of 2017. Thanks for the good cooperation,
the end of this research can be done. Thanks also to
LP3M, Communication Science Study Program
Pasca Sarjna, and their lecturers.
REFERENCES
Change, W.W. Norton, New York.
Hüseyin Evcim, Ömer Faruk İpek. Effects of Jigsaw II on
Academic Achievement in English Prep Classes.
Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences. Volume 70,
2013. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbspro.2013.01.236.
Jon-Chao Hong, Ming-Yueh Hwang, Ker-Ping Tam, Yi-
Hsuan Lai, Li-Chun Liu. Effects of cognitive style on
digital jigsaw puzzle performance: A GridWare
analysis. Computers in Human Behavior. Volume 28,
Issue 3. 2012. Pages 920-928.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2011.12.012.
Garcia, Alejandro, Jesus Abrego, Reguenes Robert Using
the Jigsaw Method for Meaningful Learning to Enhance
Learning and Rentention in an Educational Leadership
Graduate School Course. Global Journal of Human-
Social Science: G Linguistics & Education, Volume 17
Issue 5, 2017.
Tewksbury, B. J. 1995. Specific strategies for using the
“jigsaw” technique for working in groups in non-
lecturebased courses. Journal of Geological Education,
43, 322-326. Retrievable from:
http://d32ogoqmya1dw8.cloudfront.net/files/nagt/jge/a
bstracts/using_jigsaw_method.pdf
The Foundation Coalition. (2001). Positive
Interdependence, Individual Accountability, Promotive
Interaction: Three Pillars of Cooperative Learning.
Retrievable from: Best Practices for Teaching S-E
Synthesis with Case Studies
http://www.foundationcoalition.org/home/
keycomponents/collaborative_learning.html
Sharan, S., ed. 1999. Handbook of cooperative learning
methods, (2
nd
edition), Westport, CT: Praeger.
Slavin, R. (1980). Cooperative Learning. Review of
Educational Research, 50(2), 315-342. Retrieved from
http://www.jstor.org/stable/1170149
Slavin, R.E. (1995). Cooperative learning: Theory,
research, and practice (2nd Ed.). Boston: Allyn &
Bacon
Improving Student Learning Quality Through Jigsaw Cooperative Learning Methods on Communication Theory Courses
33
