
Chromoblastomycosis Case Study at Aceh Province Referral
Hospital: Study in 8 Cases for 7 Years
Reno Keumalazia Kamarlis
Departement of Anatomical Pathology, Medical Faculty, Zainoel Abidin Hospital, Syiah Kuala University, Banda Aceh,
Indonesia
Keywords : Chromoblastomycosis, Pathological Anatomy, Histopathology, Department Surgery, Department
Dermatology and Venereology
Abstract : Chromoblastomycosis is a chronic fungal infection that occurs in the skin and subcutaneous tissue caused
by dematiaceous fungi. This study uses a case study approach obtained from medical record data of patients
in the pathology anatomy laboratory of Dr. Zainoel Abidin Hospital, Aceh Province within 7 years (2012-
2018). Information was obtained that reported cases of chromoblastomycosis tend to increase, especially in
the last 2 years (2017-May 2018). During 2013 to 2015 there were no cases of chromoblastomycosis. The
dominant patients in the age group above 50 years (62.50%) and the age group 0-10 years as much as
25.00%. The number of male and female chromoblastomycosis sufferers is the same. Localization of
dominant lesions (50.00%) is found in the lower limbs (extremities). Specimens were received from the
Surgery Department (62.50%) and the Department Dermatology and Venereology (37.50%). The cases
obtained were predominantly given a clinical diagnosis as malignant tumors. Initial suspicion and
appropriate laboratory diagnosis will assist in initiation of therapy in the early stages and specific isolation
of the etiology of the agent can help prevent latent complications.
1. INTRODUCTION
Chromoblastomycosis is a chronic fungal infection
that occurs in the skin and subcutaneous tissue
caused by dematiaceous fungi (Mukesh et al, 2012).
Usually the infecting fungi are Fonsecaea Pedrosoi,
Cladophialophora carrionii and Phialophora
verrusoca (Pawel et al, 2014) (Padmanaban et al,
2016). The prevalence of this disease is reported
from humid and tropical subtropics, one of which is
Asia (Agarwal et al, 2017) (Bobba, 2014). Men are
often experience chromoblastomycosis disease than
women (Mariani et al, 2015).
Dermal lesions can be shaped like small nodules
until a large eruption resembling a papilla. Clinical
features that often appear in the area of the neck,
legs, lower limbs, face and arms. In the early stages
can appear papules, such as warts then enlarge to
form hypertrophic plaques. In the lesions also appear
plaque with a flat surface and grow slowly in the
middle and then after a few years, the lesions can be
thickened to 3cm. The nature of
Chromoblastomycosis lesions is polymorphic and
must be distinguished from several clinical
conditions (Queiroz et al, 2009).
Diagnosis that can be done is by observing
muriform cells in tissue and isolation and
identification of causative agents (Murthy, 2011).
The success of healing is influenced by the causative
agent, the clinical form and the severity experienced
by the patient. In general, patients who experience
chromobalstomycosis are treated with itraconazole,
terbinafine or a combination of both. It is important
to evaluate individual resistance to drugs. The
treatment process requires the direction of clinical
criteria, mycology and histopathology (Queiroz et al,
2009). The following in this study will be reported
cases of chromoblastomycosis at the Anatomy
Pathology Laboratory of the Hospital Public Service
Agency Dr. Zainoel Abidin Aceh Province
.
2. METHOD
This study uses medical record data at the Anatomy
Pathology Laboratory of the Hospital of the Dr.
Zainoel Abidin Hospital, Aceh Province within 6
Kamarlis, R.
Chromoblastomycosis Case Study at Aceh Province Referral Hospital: Study in 8 Cases for 7 Years.
DOI: 10.5220/0008789002050210
In Proceedings of the 2nd Syiah Kuala International Conference on Medicine and Health Sciences (SKIC-MHS 2018), pages 205-210
ISBN: 978-989-758-438-1
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
205

years (2012-2018). Descriptive data analysis by
describing cases then discussed. The data displayed
includes examination year, age group, gender,
specimen sender department, clinical diagnosis
established and microscopic examination results.
3. CASE REPORT
Based on medical record data, the patient's reference
to the Anatomical Pathology Laboratory of the
Hospital Public Service Agency Dr. Zainoel Abidin
Aceh Province, found as many as 8 cases after the
examination was made diagnosis with
Chromoblastomycosis within 6 years (2012-2018),
as follows:
3.1 Case 1
Specimens from a male with an initial Ih 83 years
old were examined on May 3, 2012. Specimens were
sent from
Department Dermatology and Venereology.
Localization of complaints is in the Dorsum pedis
section with a differential diagnosis of
Chromoblastomycosis and eumycetoma.
3.2 Case 2
Specimens from a man with the initials Nc aged 67
years were examined on August 3, 2016. The
specimen was sent from the surgical department,
with a clinical diagnosis of a tumor os femur
malignant suspect.
3.3 Case 3
Specimens from a woman with an initial NFR of 9
years of age were examined on March 13, 2017.
Specimens were sent from the department of
Dermatology and Venereology. Localization of
complaints was in the part of the left arm with a
diagnosis of differential deep mycosis, Bacterielag
infection and TB cutis.
3.4 Case 4
Specimens from a woman with the initials Br 67
years old, were examined on August 7, 2017.
Specimens were sent from the surgical department.
Localization of complaints in the anterior thoracic
section with clinical diagnosis established is anterior
thoracic papilloma.
3.5 Case 5
Specimens from a man with the initials Sm, 55 years
old, were examined on November 14, 2017.
Specimens were sent from the surgical department.
Localization of complaints is at the side of the left
pedis with a clinical diagnosis established is a
malignant suspected skin tumor.
3.6 Case 6
Specimens from a woman with an initial Hm, 89
years old, were examined on February 9, 2018.
Specimens are sent from the
Department Dermatology
and Venereology
. Complaint localization is in the
cruris dextra with a differential diagnosis of
Chromomycosis, TB cutis, Blastomycosis,
Sporotricosis and Squamous cell carcinoma.
3.7 Case 7
Specimens from a man with initial Mh age 4 years
old, examined on May 16, 2018. Specimens were
sent from the surgical department, with a clinical
diagnosis of abscess at colli regio.
3.8 Case 8
Specimens from a woman with the initials Lb aged
27 years, were examined on May 17, 2018.
Specimens were sent from the surgical department,
with a clinical diagnosis is a malignant occipital
suspect tumor.
4. RESULT AND DISCUSSION
Based on the data collected, information was
obtained that reported cases of chromoblastomycosis
tend to increase, especially in the last 2 years (2017-
May 2018). Throughout 2013 to 2015 there were no
cases of chromoblastomycosis. These conditions
conclude that the discovery of chromoblastomycosis
cases tends to increase in the Anatomical Pathology
Laboratory of the Hospital Public Service Agency
Dr. Zainoel Abidin Hospital, Aceh Province.
The results of this study are in line with
Agarwal's (2017) study which stated that there was
an increase in the discovery of cases of
chromoblastomycosis between 2011-2016.
Throughout 1955-2016 found 169 cases of
chromoblastomycosis in India, where in the period
2011-2015 found 81 cases. In addition, in 2016 until
May there were 25 cases
SKIC-MHS 2018 - The 2nd Syiah Kuala International Conference on Medicine and Health Sciences
206
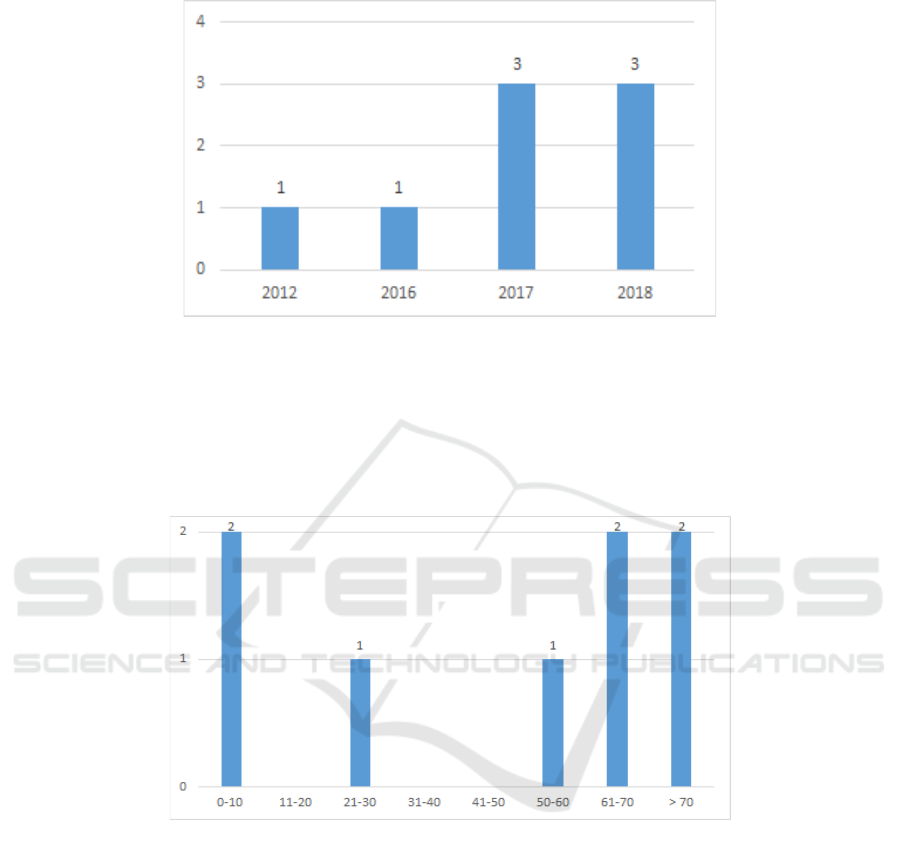
Figure 1. Distribution of specimen examinations of patients with a
diagnosis of chromoblastomycosis at the Anatomical Pathology
Laboratory of the Hospital Public Service Agency Dr. Zainoel Abidin
Aceh Province in 2012-2018
Figure 2. Distribution of age groups (in years) of patients with a diagnosis of
chromoblastomycosis at the Anatomical Pathology Laboratory of the
Hospital Public Service Agency Dr. Zainoel Abidin Aceh Province in 2012-
2018.
Chromoblastomycosis patients are dominant in
the age group above 50 years, as many as 5 cases
(62.50%). The age group of 0-10 years is the age
group where this case is found to be the second
largest, namely as many as 2 cases or 25.00%. The
information above shows that young age groups
(children) and parents are the most common age
group where chromoblastomycosis is found.
This phenomenon is not in line with Sarangi's
research (2017) which states that
chromoblastomycosis cases tend to be found more in
the age range of 21-35 years (45.4%) than 11 cases.
Research Agarwal (2017) also found that those who
stated that chromoblastomycosis cases were more
prevalent in the age range of 31-50 years (35%).
Based on gender, it was found that the number of
male and female chromoblastomycosis sufferers was
the same, where in each sex there were 4 cases
(50.00%). This condition shows that in 8 cases that
have been found there has not been a tendency for
Chromoblastomycosis Case Study at Aceh Province Referral Hospital: Study in 8 Cases for 7 Years
207

this case to be dominant in one sex only.
Localization of the dominant lesion (50.00%) was
found in the lower limb (extremity) area, where 1
case (12.50%) was in the thigh section and 3 other
cases in the pedis and cruris area (37.50%). The
neck, back of the head, upper extremities and chest
area were found in 1 case each.
Research conducted by Agarwal (2017) found
that 81.10% of patients were men so they had a
higher risk than women at 4.2: 1. The study
conducted by Sarangi (2017) also found that men
were more predominantly suffering from this disease
with a risk of 1.4: 1 compared to women. Based on
research conducted by Pawel et al (2014) states that
infection can occur in all parts of the body. The legs
and shin are the dominant parts of the body. This is
in line with the results obtained in this study that
found dominant lesions in the lower limbs (inferior
extremities).
Specimens received by the Anatomical
Pathology Laboratory of the Hospital Public Service
Agency Dr. Zainoel Abidin, the dominant province
of Aceh, came from the Surgical Section with 5
cases (62.50%). Three other cases (37.50%) were
sent from the
Dermatology and Venereology. Clinical
diagnosis sent from the Department of Dermatology
and Venereology is clinically diagnosed with
chromoblastomycosis or cases of deep mycosis.
Cases obtained from the dominant surgical
department were given a clinical diagnosis with
malignant tumors (4 malignancies) (80.00%) and 1
case (20.00%) were abscesses.
The term 'chromoblastomycosis' is exclusively
used for typical fungal lesions resulting in 'sclerotic'
bodies caused by dematiaceous fungi in the
'phaeohyphomycosis' group. The agents that cause
this disease are Fonsecea, Cladosporium, and
Rhinocladiella species. Most cases are limited to
localized disorders of the skin and subcutaneous
tissue. Initial suspicion and appropriate laboratory
diagnosis will assist in initiation of therapy in the
early stages and specific isolation of the etiology of
the agent can help prevent latent complications
(Chavan SS and Reddy P, 2013).
The histopathological features are described
below:
Case 1
Microscopic examination results showed that
preparations of tissue without epithelial lining were
seen in groups of glandular structures of round oval
shape with cuboidal epithelial linings, basophil
spherical nuclei, fine chromatin,
cytoplasmaeosinophilyl. The stroma consists of
collagen connective tissue, as it appears
multinucleated giant cells and lymphocyte cells.
There is no sign of malignancy in the preparation, so
it can be concluded to support a
chromoblastomycosis.
Case 2
Based on the results of microscopic examination
performed, tissue preparations with layered sterile
epithelial linings with hyperkeratosis, acantosis,
hypergranulosis, intact basal membrane appear. Intra
epithelium appears pseudohorncyst. The sub
epithelium consists of fibromycsoid connective
tissue with a lymphocyte cell, multinucleated giant
cell, PMN cells, neutrophils and a golden brown
pigment. There is no sign of malignancy in this
preparation, so it can be concluded that
chromoblastomycosis.
Case 3
Based on the results of microscopic examination
carried out, it was found that tissue preparations
from specimen 3 with epithelial linings lay flat
within normal limits. Sub epithelials appear
granulomatous-granulomatous consisting of
epithelioid cells, histiocytes and multinucleated
giant cells between fibromycsoid connective tissue.
In some places a brownish pigment appears. There is
no sign of malignancy in this preparation, it can be
concluded as chromoblastomycosis.
Case 4
Based on the results of microscopic examination,
tissue preparations with layered epithelial lining, sub
epithelial appearance, granulomatous features
consisting of epitheloid cells, multinucleated giant
cells, lymphocytes and a brownish pigment between
fibromycsoid connective tissue were seen. There is
no sign of malignancy in the preparation, it can be
concluded a chromoblastomycosis.
Case 5
Based on the results of microscopic examination
performed, tissue preparations with layered sterile
epithelial linings that experience hyperkeratosis are
obtained. Sub epithelials appear to group
lymphocytic inflammatory cells, epithelial cells and
multinucleated giant cells accompanied by copper
bodies; between fibromycsoid connective tissue.
SKIC-MHS 2018 - The 2nd Syiah Kuala International Conference on Medicine and Health Sciences
208
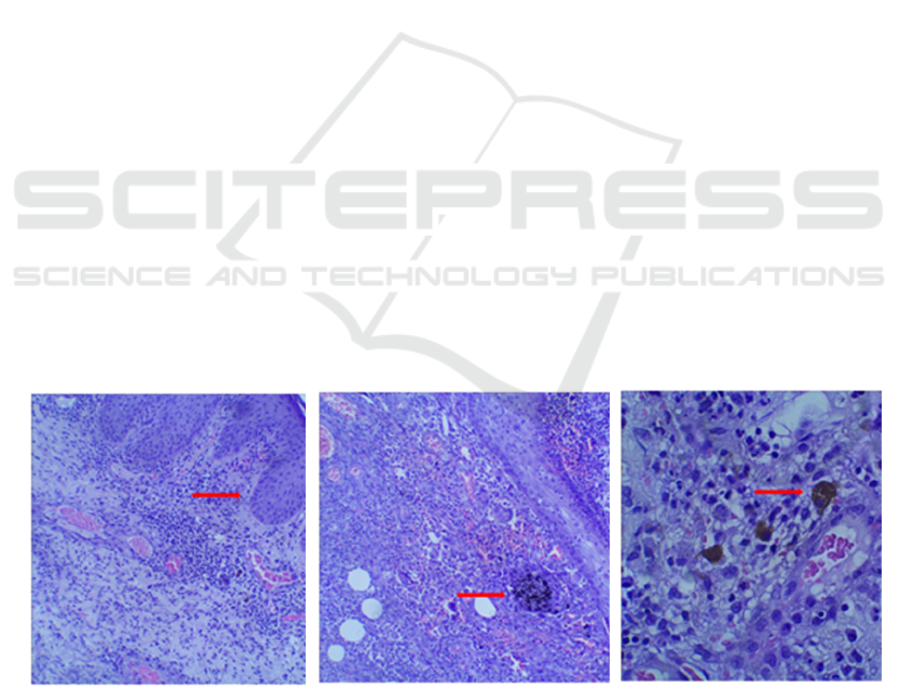
There is no sign of malignancy in this preparation.
So that can be concluded is chromoblastomycosis.
Case 6
Based on the results of microscopic examination
carried out, obtained tissue preparations with
epithelial coating layered within normal limits. The
local sub epithelial cells appear lymphocytic
inflammatory cells, epithelioid cells and brownish
pigments between fibromycsoid tissues. There is no
sign of malignancy in the preparation, it can be
concluded to support chromoblastomycosis.
Case 7
Based on the results of microscopic examination
carried out, obtained tissue preparations with sub
epithelial layered epithelial coating, fibromycsoid
tissue with an inflammatory cell PMN, neutrophils
and lymphocytes appear. In some places epitheloid
cells, multinucleated giant cells and copper bodies
are seen. There is no sign of malignancy in the
preparation, it can be concluded as
chromoblastomycosis with secondary infection.
Case 8
Based on the results of microscopic examination
carried out, obtained tissue preparations with
epithelial coating layered within normal limits. The
sub epithelial consists of fibromycsoid tissue with
the distribution of inflammatory cells of PMN,
neutrophils and lymphocytes. Found groups of
epithelioid and multinucleated giant cell and copper
bodies. There is no sign of malignancy, so it can be
concluded as chromoblastomycosis.
Many cases are not diagnosed cytologically
because of a lack of clinical suspicion that is
undiagnosed. In the preparation often found mixed
inflammatory cells and scattered fungal sclerotic
bodies. The sclerotic bodies look orange to reddish
brown round to polyhedral, about the size of red
cells (approximately 5-8 mm), show mature thick
wall (just like outer border of copper penny), and
characteristic intracellular septations (Chavan SS
and Reddy P , 2013).
Histopathologic examination with hematoxylin
eosin (HE) staining on chromoblastomycosis will
show inflammatory granuloma in the form of
pseudoepiteliomatous epidermal hyperplasia with
parakeratosis, spongiosis, and extensive dermal
infiltrate consisting of numerous epithelioid
histiocytes. Another component of infiltrates is the
presence of multinucleated giant cells in which there
are sclerotic bodies, neutrophils, lymphocytes,
plasma cells, and eosinophils.
Figure 3. Histopathological features of specimen examination of patients with a diagnosis of chromoblastomycosis
at the Anatomical Pathology Laboratory of the Hospital Public Service Agency Dr. Zainoel Abidin Hospital, Aceh
Province in 2012-2018 (A) pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia of per capplasia (B) Pigmented sclerotic bodies
(Medlar bodies or Copper bodies)
A B B
Chromoblastomycosis Case Study at Aceh Province Referral Hospital: Study in 8 Cases for 7 Years
209

Fungal species that cause chromoblastomycosis
cannot be distinguished from histopathological
examination so that identification of tissue culture is
needed. Macroscopically, the results of tissue culture
from fungi generally give a similar picture, namely
blackish colonies. Microscopic identification of
culture depends on the presence of different types of
sporulation. Accurate differentiation of various fungi
is difficult to do (Mariani et al, 2015).
5. CONCLUSION
Based on medical record data of patients at the
Anatomy Pathology Laboratory of Dr. Zainoel
Abidin, Nanggroe Aceh Province, has 8 cases of
chromoblastomycosis throughout 2012-2018.
Chromoblastomycosis cases tend to increase in the
last 2 years (2016-2018). Most sufferers in the
elderly and young with localization of dominant
lesions in the extremities. Gender there is no
difference in this case study. Specimens received
predominantly from the Surgery and
Dermatology and
Venereology Department. Clinical diagnosis of
dominant malignant tumors (malignancy). Initial
suspicion and appropriate laboratory diagnosis will
assist in initiation of therapy in the early stages and
specific isolation of the etiology of the agent can
help prevent latent complications.
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
Anatomical Pathology Laboratory Hospital Public
Service Agency Dr. Zainoel Abidin Hospital,
Nanggroe Aceh Darussalam Province
REFERENCES
Agarwal R, Singh G, Ghosh A, Verma KK, Pandey M,
Xess I (2017) Chromoblastomycosis in India: Review
of 169 cases. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 11 (8): e0005534.
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal. pntd.0005534
Mariani V Lasut, Rita S Tanamal, Grace M Kapantow
(2015) Kasus Kromoblastikosis Pada Seorang
Perempuan. Jurnal Biomedik (JBM), Vol 7 No 1 hal
62-69
Paweł M Krzyściak, Małgorzata Pindycka-
Piaszczyńska, Michał Piaszczyński (2014)
Chromoblastomycosis. Journal Postepy Dermatol
Alergol, Vol 31 No 5 hal 310-321 doi:
10.5114/pdia.2014.40949
Queiroz-Telles F, Esterre P, Perez-Blanco M, Vitale
RG, Salgado CG, Bonifaz A (2009)
Chromoblastomycosis: an overview ofclinical
manifestations, diagnosis and treatment. Journal Med
Mycol¸Vol 47 No 1 hal 3-15 doi:
10.1080/13693780802538001
Sarangi G, Dash M, Paty BP, Mohapatra D, Majhi S,
Chayani N (2017) A study on Chromoblastomycosis
in a tertiary care hospital of eastern Odisha. J Med Soc
31:201-204
Chavan SS, Reddy P (2013) Cytological diagnosis of
chromoblastomycosis. J Cytol 30:276-277
Mukesh M Sharma, Rabindra NMisra, NageswariR
Gandham, Savita V Jadhav, Gupta N (2012)
Chromoblastomycosis of the Face: A Rare Case
Report form the District of Western Maharashtra,
India. Journal of Clinical and Diagnostic Research
Vol 6 issue 5 page 899-901
Bobba S (2014) Case Study: Chromoblastomycosis. J
Trop Dis 2: 143. doi: 10.4172/2329-891X.1000143
Padmanaban K Govindraman, Marimuthu V, Senthil G
(2016) Chromoblastomycosis:a case report with
literature review. International Journal or Research in
Dermatology Vol 2 issue 4 page 135-138 doi:
http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-
4529.IntJResDermatol20164075
Murthy R and Swain JP (2011) Concurrent mycetoma and
chromomycosis. Indian Journal of Medical
Microbiology vol 29 no 4 page 437-439
SKIC-MHS 2018 - The 2nd Syiah Kuala International Conference on Medicine and Health Sciences
210
