
Polymorphism of Vitamin D Fok1 Receptor Gene in Patients with
Pulmonary Tuberculosis of Batak Ethnic
Debby Mirani Lubis,
Department of Physiology, Muhammadiyah University of North Sumatera, Gedung Arca No. 53, Medan, Indonesia
Keywords: Vitamin D polymorphism, Fok1 polymorphism, Fok1 Tuberculosis
Abstract: Tuberculosis (TB) is one of the infectious diseases that is still a health problem of the world, especially in
developing countries. The polymorphism of the vitamin D receptor gene (VDR) by some studies may affect
the workings of vitamin D. The polymorphism of this receptor gene causes a person to become more
susceptible to M. tuberculosis infection. This study aimed to determine polymorphism of Vitamin D Fok1
Receptor Gene in Patients with Pulmonary Tuberculosis of Batak Ethnic. A total of 42 patients who met the
inclusion and exclusion criteria were examined for vitamin D Fok1 receptor gene with PCR-RFLP and
analyzed by electrophoresis and the level of vitamin D was examined by ELISA. The results showed that 26
patients had Ff genotype (61,9%), 14 patients have FF genotype (33,3%), and two patients had ff genotype
(4,8%). The most common level of Vitamin D in FF genotype was optimal (64,3%), in Ff genotype was
optimal (53,8%), and ff genotype had the same percentatage of optimal and insufficiency level. Conclusion:
Based on this research, the most common polymorphism of vitamin D Fok1 receptor gene in Batak ethnic is
Ff genotype.
1 INTRODUCTION
TB disease is caused by infection with the bacteria
Mycobacterium tuberculosis (M. tuberculosis),
which was first discovered by Robert Koch in 1903
so that the first disease called Koch Pulmonum
(Chocano-Bedoya & Ronnenberg, 2009). Judging
from the year of the discovery of that germs, it can
be said to be very ironic, because up to now this
disease cannot be eradicated from all over the world,
even new problems arise such as the emergence of
cases of drug-resistant TBC (Multi Drug Resistance)
and TBC cases that accompanied HIV (Human
Immunodeficiency Virus).
Several studies have suggested that there is a
relationship between vitamin D levels and resistance
to TBC. Vitamin D can increase the synthesis of the
innate immune system components through the
Vitamin D receptor (VDR) complex with the active
form of vitamin D (1.25D3), one of which is
cathelicidin which has an important role in fighting
infection from Mycobacterium (Sutaria et al., 2014).
Vitamin D can work when binding to VDR.
The polymorphism of this VDR gene causes a
person to become more susceptible to M.
tuberculosis infection. Some of the vitamin D
vitamin receptor polymorphisms that have been
identified are TaqI, ApaI, BsmI, and FokI.
The polymorphism of the Fok1 VDR gene is
formed by the transition of C to T (ACG-ATG) at
the first and second translational initiation sites in
exon 2. If the translation starts from the first ATG
(individual T allele, written f), the VDR protein
synthesis has a maximum length (427 amino acids).
Conversely, if translation begins at the second ATG
site (individuals with C allele, written as F), then the
VDR protein deficits three amino acids at the
terminal. The shortening of these three amino acids
leads to shorter VDR proteins to be more
functionally active (Chocano-Bedoya &
Ronnenberg, 2009).
Some studies of these polymorphisms have
shown quite varied results, whereas ethnicity also
affects the types of polymorphisms associated with
TB infection. Studies in Turkey showed that only
BsmI variations that have an effect on susceptibility
to TB, this result are different from studies in West
African populations who reportted on variations of
ApaI that are significantly associated with TB,
whereas in Asian populations, the ff genotype of
Fok1 is related to TB, even in a South American
study it was found that none of these polymorphism
Lubis, D.
Polymorphism of Vitamin D Fok1 Receptor Gene in Patients with Pulmonary Tuberculosis of Batak Ethnic.
DOI: 10.5220/0008790600490052
In Proceedings of the 2nd Syiah Kuala International Conference on Medicine and Health Sciences (SKIC-MHS 2018), pages 49-52
ISBN: 978-989-758-438-1
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
49
types were significantly associated with TB
(Khalilullah et al., 2014). This suggests that further
study of vitamin D polymorphisms in certain ethnic
groups is warranted.
2 METHOD
This research is analytic research with cross-
sectional design. After getting ethical clearance, the
Subjects were collected at Helvetia, Amplas,
Teladan and Johor Health Center in Medan in
January 2016. The inclusion criteria of subjects were
patients (male or female) with Pulmonary TB
(category 1) aged 18 to 65 years old, with ethnic
Batak obtained from 2 previous generations
(grandparents, father-mother). Patients with immune
deficiencies such as HIV (examined with HIV rapid
test), Diabetes Mellitus (examined with a glucotest
device), history of organ transplants, impaired renal
function, impaired liver function, malignancy,
treatment with steroids, pregnancy and lactation,
extrapulmonary TB patients, taking vitamin D, and
Body Mass Index ≤ 18.5 were excluded. After
signed informed consent, blood samples were taken
as much as 3 cc for examined of FokI gene
polymorphism and vitamin D levels. The blood
samples were centrifuged directly then taken to an
integrated laboratory of Faculty of Medicine,
University of North Sumatera.
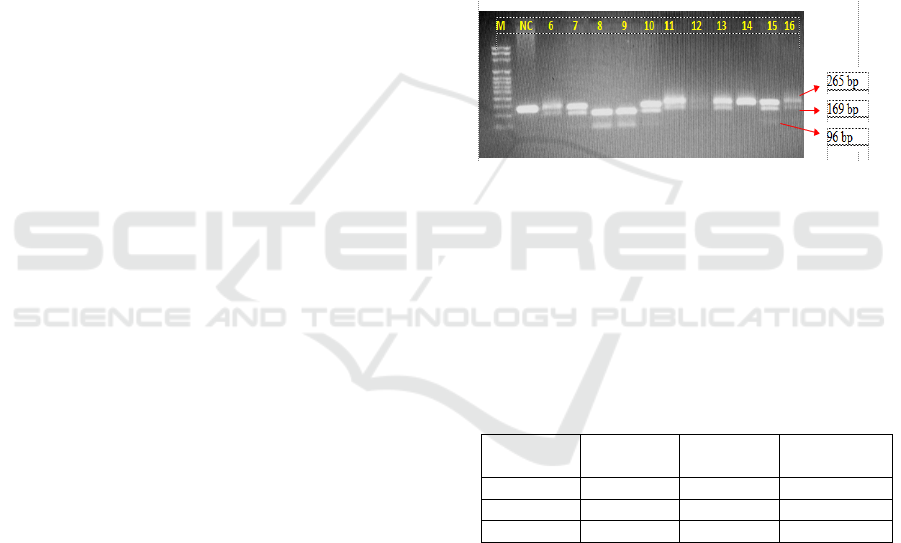
The polymorphism examined using PCR-RFLP
and analyzed with electrophoresis gel. On each gel is
given marker, positive control, and negative control.
The result of the tape was visualized on a UV
illuminator device. The resulting genotype depends
on the pattern of digestion. Homozygous FF for the
absence of a digested FokI side with a band of 265
bp; homozygous ff for a perfectly digested Fok1 into
196 bp and 69 bp and heterozygous Ff bands if there
are three bands (265 bp, 196 bp, and 69 bp).
The Levels of vitamin D (25OH) were examined
by ELISA kit (DIAsource®). The absorbance was
read at a wavelength of 450 nm.
3 RESULT
Subjects were 42 people; 27 men (62,5% and 32,5%
respectively). Subjects with the youngest age in this
study was 19 years old and the oldest 63 years old.
3.1. The Levels of Vitamin D
The vitamin D status is classified according to 3
levels; sufficiency (optimal) (30-100 ng/ml),
insufficiency (10-29 ng/ml) and deficiency (<10
ng/ml) (suggested reference values for adults from
ELISA kit brochure). There were 24 subjects
(57,1%) with optimal level, 15 subjects (35,7%)
with insufficiency and three subjects (7,1%) with
deficiency level.
3.2. The Polymorphism of VDR gen Fok1
The results showed that 26 patients have Ff
genotype (61,9%), 14 patients have FF genotype
(33,3%) and two patients have ff genotype (4,8%).
Figure 1: Analyzed bands with electrophoresis gel.
3.3. The Polymorphism and Levels of
Vitamin D
The most common level of Vitamin D in FF
genotype was optimal (64,3%), in Ff genotype was
optimal (53,8%), and ff genotype had the same
percentage of optimal and insufficiency level.
Table 1: The polymorphism and levels of vitamin D
Polymorp
hism
Optimal
(n)
Insufficie
ncy(n)
Deficiency
(n)
FF
9
4
1
Ff
14
10
2
ff
1
1
0
4 DISCUSSION
The majority of epidemiologic studies found vitamin
D status less susceptible to tuberculosis but different
from this study where the majority of TB patients
had optimal vitamin D status. These different results
are likely to be influenced by many factors, one of
which is the ethnic factor which from several
previous studies can show different results in
different ethnic populations (Rashedi et al 2015,
Salahuddin et al, 2013; Siswanto et al, 2009; Sutaria
et al 2014)
SKIC-MHS 2018 - The 2nd Syiah Kuala International Conference on Medicine and Health Sciences
50

In the distribution of Fok1 VDR gene
polymorphism, the most common genotype was
heterozygous (Ff) whereas homozygous ff subjects
were found in 2 patients. The same is true of
research conducted by Sinaga et al. in Indonesia on
Batak ethnic (Sinaga et al., 2014) and Sharma et al.
in India in Chhattisgarth ethnic (Sharma et al.,
2011). However, these results are different from
those of other studies conducted in West Africa
(Bornman et al., 2004), India (Selvaraj et al, 2003),
South Africa (Babb et al, 2007), England (Martineu
et al, 2011) and Iran (Rashedi et al, 2015), which
shows the most commonly encountered genotype is
the FF type. A meta-analysis by Gao et al. (2010)
which states that the ff genotype has risk
susceptibility to TB that is clearly different from the
results obtained in this study because the genotype ff
only found in 2 subjects. Ethnic factors are likely to
affect the distribution of polymorphism genotypes in
each population.
Table 2: Comparison of FokI genotype in TB Patients
from Various Population Studies.
Researcher
(year)
Country
(ethnic)
FF(%)
Ff(%)
ff(%)
Selvaraj
(2003)
India
65
30
5
Bornman
(2004)
West Africa
62
33,2
4,8
Babb
(2007)
South Africa
58
37
6
Martineu
(2011)
England
47
40
13
Sharma
(2011)
India/
(Chattisgarth)
44
48
0,07
Sinaga
(2014)
Indonesia
(Batak)
35,5
55,3
9,2
Rashedi
(2015)
Iran
52,4
39,3
8,3
In terms of theory, subjects with an allele F
should be stronger than the f alleles, so subjects with
ff genotype would be more susceptible to
tuberculosis, but this is not the case in this study
because the genotype ff is very few and the genotype
that has the F allele is susceptible also to
tuberculosis. The possibility of Batak tribe is a few
who have ff genotype and no previous studies are
sufficient to compare the frequency of this genotype.
In addition to this study, there is only one more
study that also studied polymorphism of VDR FokI
gene on Batak tribe that is research by Sinaga et al.
(2014) which also shows a proportion distribution
similar to this study.
5 CONCLUSIONS
Most subjects showed the optimal status of vitamin
D levels. The polymorphisms of Fok1 VDR gene in
Lung TB patients of Batak ethnic encountered in
this study are the heterozygous Ff genotype and the
least of which is the ff genotype. Ethnic factors may
affect a person's susceptibility and correlation to
tuberculosis, so it is necessary to conduct similar
research on different ethnicities with a large number
of samples from this study.
REFERENCES
Babb, C., Merweb, L., Beyersc, N., Pheiffera, C., Walzla,
G., Duncand, K., Heldena, P., Hoala, E.G., 2007.
Vitamin D receptor gene polymorphisms and sputum
conversion time in pulmonary tuberculosis patients.
Elsevier. 87: 295–302.
Bornman, L., Campbell, S.J., Fielding, K., Bah, B., Sillah,
J., Gustafson, P., Manneh, K., Lisse, I., Allen, A.,
Sirugo, G., Sylla, A., Aaby, P., McAdam, K., Bah-
Sow, O., Bennett, Lienhardt, C., Hill, A.V., 2004.
Vitamin D receptor polymorphisms and susceptibility
to tuberculosis in West Africa: A Case-Control and
Family Study. The Journal of Infectious Diseases.
190:1631–41.
Chocano-Bedoya, P., Ronnenberg, A.G., 2009. Vitamin D
and tuberculosis. Nutrition Reviews. Vol. 67(5):289–
93.
Gao, L., Tao, Y., Zhang, L., Jin, Q., 2010. Vitamin D
receptor genetic polymorphisms and tuberculosis:
updated systematic review and meta-analysis.
International Journal of Tuberculosis Lung Disease.
14(1):15–23.
Khalilullah, S.A., Harapan, Hasan, N.A., Winardi, W.,
Ichsan, Mulyadi, 2014. Host genome polymorphisms
and tuberculosis infection: What we have to say?.
Egyptian Journal of Chest Diseases and Tuberculosis.
63,173–85.
Martineau, A.R., Timms, P.M., Bothamley, G.H., Hanifa,
Y., Islam, K., Claxton, A.P., Packe, G.E., Moore-
Gillon, J.C., Darmalingam, M., Davidson, R.N.,
Milburn, H.J., Baker, L.V., Barker, R.D., Woodward,
N.J., Venton, T.R., Barnes, K.E., Mullett, C.J.,
Coussens, A.K., Rutterford, C.M., Mein, C.A., Davies,
G.R., Wilkinson, R.J., Nikolayevskyy, V.,
Drobniewski, F.A., Eldridge, S.M., Griffi, C.J., 2011.
High-dose vitamin D3 during intensive-phase
antimicrobial treatment of pulmonary tuberculosis: a
double-blind randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 377:
242-50.
Rashedi, J., Asgharzadeh, M., Moaddab, S.R., Sahebi, L.,
Khalili, M., Mazani, M., Abdolalizadeh, J., 2015.
Vitamin D receptor gene polymorphism and
vitamin D plasma concentration: correlation with
Polymorphism of Vitamin D Fok1 Receptor Gene in Patients with Pulmonary Tuberculosis of Batak Ethnic
51

susceptibility to tuberkulosis. Advanced
Pharmaceutical Bulletin. 5;1-5.
Salahuddin, N., Ali, F., Hasan, Z., Rao, N., Aqeel, M.,
Mahmood, F., 2013. Vitamin D accelerates clinical
recovery from tuberculosis: results of the SUCCINCT
Study [Supplementary Cholecalciferol in recovery
from tuberculosis]. A randomized, placebo-controlled,
clinical trial of vitamin D supplementation in patients
with pulmonary tuberculosis. BMC Infectious Disease.
13-22
Sharma P.R., Singh, S., Jena, M., Mishra, G., Prakash, R.,,
Das, P.K., Bamezai, R.N.K., Tiwari, P.K., 2011.
Coding and non-coding polymorphisms in VDR gene
and susceptibility to pulmonary tuberculosis in tribes,
castes and Muslims of Central India. Infection,
Genetics and Evolution. 11;1456–61.
Sinaga, B.Y.M., Amin, M., Siregar, Y., Sarumpaet, S.M.,
2014. Correlation between vitamin D receptor gene
FOK-I and BSMI polymorphisms and the
susceptibility to pulmonary tuberculosis in an
Indonesian Batak-ethnic population. Acta Medica
Indonesia. 2014; (46): 275-82
Siswanto, Sumarno, Jane, Y., Widayanti, O.A., Muktiati,
N.S., 2009. Pengobatan Suportif Vitamin D
Mempercepat Konversi Sputum dan Perbaikan
Gambaran Radiologis Penderita Tuberkulosis. Jurnal
Kedokteran Brawijaya. Vol. XXV; 128-32
Sutaria, N., Liu, C.T., Chen, T.C., 2014. Vitamin D status,
receptor gene polymorphisms, and supplementation on
tuberculosis: A systematic review of case-control
studies and randomized controlled trials. Journal of
Clinical & Translational Endocrinology. 2014; 151-60
SKIC-MHS 2018 - The 2nd Syiah Kuala International Conference on Medicine and Health Sciences
52
