
Method of Handling Aggressive Behavior of School-aged Children
with Holistic Approach in Medan
Wardiyah Daulay
1*
, Sri Eka Wah
y
uni
1
and Mahnum Lailan
1
1
Faculty of Nursing Universitas Sumatera Utara, Jl. Prof.Maas No. 03 Kampus USU, Medan, Indonesia
Keywords: Aggressive, School-aged children, Holistic approach
Abstract : Aggressiveness is a type of behavior aiming to harm other people, verbally or non-verbally,
physically or psychologically and directly or indirectly. Aggressiveness in school-aged children
is caused by social factors, personal characters and situational factors. The worst impact which
can take place if this aggressive behavior is not handled is the children can put their friends or
other kids in danger. This research aims to identify the influence of aggressiveness-handling
method with holistic approachwhich involves biological, psychological, socio-cultural and
spiritual dimension towards the aggressiveness of school-aged children.This research was
conducted in 2 Private Primary School in Medan. The samples were 60 people who were divided
into two groups, namely intervention group and control group. The instrument was made by the
researchers themselves based on literature review. Analysis result shows the children’s
aggressiveness score before holistic handling 11.40 and after it becomes 8.93 (2.47 in
difference). The change of the score shows significant decline, meaning that the aggressiveness
in school-agedchildren has declined. These data are supported with test result of t dependent, it
obtains p value 0.000 and alpha 0.05.This signifies that there is significant influence between
holistic handling and aggressive behavior of school-aged children.
1 INTRODUCTION
School is adetermining factor for children’s
personality development, in their way of thinking,
attitude and their behavior (Hurlock, 1986 in
Syamsu & Juntika, 2005). The development stage of
primary-school children sometimes are faced with
obstacles that they do inappropriate behavior which
harms themselves and other. One of the digressing
behaviors is aggressiveness.
The phenomena of aggressiveness in school-
aged children have increased nowadaysin Indonesia.
This is supported by the research result conducted
by Azizah (2013), that the scholars especially
primary-5 male students are aggressive. There are
49% boys who do physical aggressiveness, such as
hitting, kicking, grabbing others’ belongings and
attacking other people. 49% out of 14 students is 7
students. Then, there are these 7 students showing
aggressive physical behavior. Meanwhile, verbal
aggressiveness such as yelling in the class, scolding,
being angry out of no reason, ordering older people
and threatening friends, is shown by 70% students or
if it is compared with the number of the students
which is 14 students, then there are 10 students who
have verbal aggressive behavior.Prosperity of
Indonesian Children (YKAI) shows that there are
5% children doing aggressive behavior when a
conflict takes place. For instance, children will get
angry and do not want to apologize when doing a
mistake. Moreover, 21.6% children will repay by
behaving aggressively if there is any of their friends
who makes them angry because they consider that
aggressiveness is a common and ordinary thing.
(YKAI, 2010). Nursing holistic is giving care to
treatment for bio welfare-psychosocial and spiritual
individual, family and society (Ilit, 2016). This
holistic approach keeps on its principlethat nursing
treatment provided must pay attention to all
dimensions so that intervention given to this
Daulay, W., Wahyuni, S. and Lailan, M.
Method of Handling Aggressive Behavior of School-aged Children with Holistic Approach in Medan.
DOI: 10.5220/0008791502490254
In Proceedings of the 2nd Syiah Kuala International Conference on Medicine and Health Sciences (SKIC-MHS 2018), pages 249-254
ISBN: 978-989-758-438-1
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
249
research will refer to all dimensions. For
psychological dimension with emotion control such
as recognizing signs, situation,the effect and
aggressiveness alternative, In biological dimension,
a way to express anger constructively is provided.
The way is deep breathing practice and doing sports.
In socio-cultural dimension, it teaches the way to
express anger verbally, such as rejecting politely,
asking politely and expressing feelings in a fine way.
Meanwhile, for spiritual dimension, children will be
taught to do spiritual activity based on their belief.
2 RESEARCH METODHS
This research aims to see aggressive behavior in
school-aged children before and after treatment with
a holistic approach. The experiment research
designis done to two groups. The study was
conducted in two private primary schools in Medan.
The sample was taken by purposive sampling with a
sample of 60 people, divided into 2 groups: the
intervention group and the control group. The
instruments used are made by researchers based on
literature review. The instrument has been tested for
validity and reliability. Results of testing the validity
of the instrument to 3 (three) expert mental nursing
with a CVI value of 0.9. The instrument was also
tested for reliability in public elementary schools as
many as 40 students with a result of 0.88. The study
was conducted after obtaining approval from the
Ethics Committee of the Faculty of Nursing, North
Sumatra University. Data are analyzed using t test.
3 RESEARCH RESULT
The result shows that school-aged children who
behave aggressively are mostly males (88%), with
mostly 11 years-old (38%) and majority of
Bataknese (48%). The characteristics of the 60
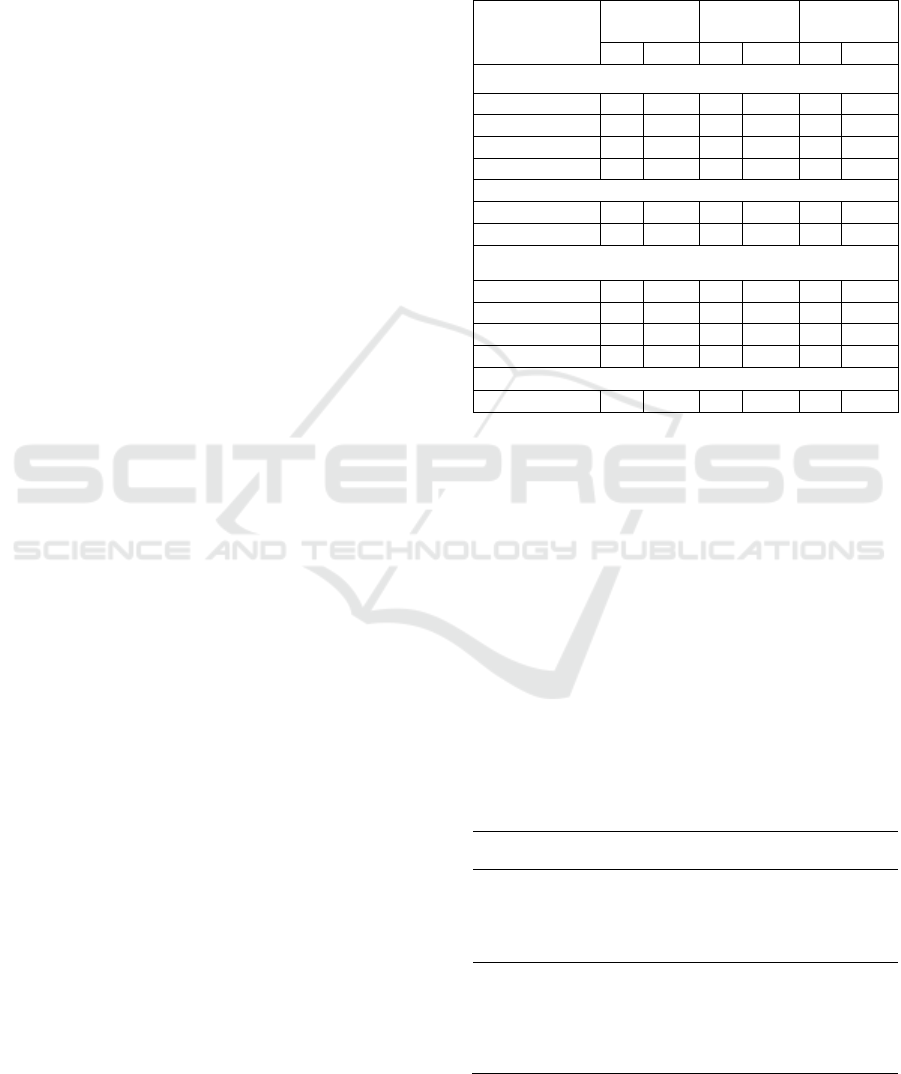
students can be seen in this following Tabel 1:
Table 1. Characteristics of School-Aged Children who
Have Aggressiveness in Intervention Group and Control
Group(n = 60)
Characteristic
Interventi
on Grou
p
Control
Grou
p
Total
F (%) F (%) f (%)
Age
9 yea
r
2 7 4 13 6 10
10 yea
r
9 30 8 27 17 28
11
y
ea
r
12 40 11 37 23 38
12
y
ea
r
7 23 7 23 14 24
Sex
Male 28 93 25 83 53 88
Female 2 7 5 17 7 22
Tribe
Bataknese 4 47 15 50 29 48
Acehnese 5 17 5 17 10 17
Javanese 7 23 7 23 14 23
Mala
y
4 13 3 10 7 12
Religion
Isla
m
30 100 30 100 60 100
Aggressiveness in school-aged children before the
holistic treatment is conducted in the intervention
group and control by comparing the mean score. The
difference in mean score of before the intervention is
0.1 and after the intervention, the score turns into a
mean score difference of -2.27. To see the difference
between the children’s aggressiveness between
intervention and control groups, independent t test is
conducted. Theresult is p-value 0.939 before
treatment and after treatment, value is 0.014. This
value isbetween the intervention and control groups,
which can be seen in Table 2.
Table 2. Difference Analysis of Children’s Aggressiveness
between Intervention Group and Control (N=60)
Children’s
Aggressiveness
Mean SD SE P
value
Before Holistic
Treatment
- Intervention Group
- Control Group
Mean in Difference
11.40
11.33
0.1
3.539
3.198
0.646
0.584
0.939
After Holistic
Treatment
- Intervention Group
- Control Group
Mean in Difference
8.93
11.20
-2.27
3.648
3.305
0.666
0.603
0.014
SKIC-MHS 2018 - The 2nd Syiah Kuala International Conference on Medicine and Health Sciences
250

The difference in mean scores before and after on
intervention group as is much as 2.47 and the control
group’s difference in mean score is 12:13. To see the
difference ofchildren’s aggressiveness before and
after between intervention and control group, t
dependent test is performed. The result obtained is
p-value of 0.005 on the intervention group and 0.442
on the control group, which can be seen in Table 3.
Table 3. Analysis of Children’s Aggressiveness Difference
Before and After Holistic Treatment (N=60)
Children’s
Aggressiveness
Mean SD SE P
value
Intervention
Group
- Before
- After
The difference
in mean
11.40
8.93
2.47
3.539
3.648
0.646
0.666
0.005
Control Group
- Before
- After
The difference
in mean
11.33
11.20
0.13
3.198
3.305
0.584
0.603
0.442
The analysis shows a score of children’s aggressive
before holistic treatment 11:40 and thereafter
become 8.93 (the difference of the score is 2.47).
The score change shows a significant decrease,
meaning that there is a decrease in aggressive
behavior in school-aged children. This data is
supported by the results obtained dependent t-test p
value 0.000; alpha of 0.05. This value indicates that
there is a significant effect between holistic
treatment and aggressive behavior of school-aged
children.
This holistic treatment consists of several
sessions. The first session is for the psychological
dimension. In this session, children are taught to
manage emotions with psychological self-
adjustment capability, in which individuals are able
to identify, recognize and able to manage it.
Managing emotions is an act to regulate the
thoughts, feelings, passion of anger in an appropriate
and positive manner and socially-accepted as well. It
is expected to prevent something bad or prevent
them from harming themselves and others. After
being given an intervention, children begin to get to
know and manage their emotions.
According to Goleman (1997), recognizing the
emotion of anger is the ability to identify feelings of
anger when anger arises, so that one is not controlled
by anger. Someone who has the ability to recognize
emotion of anger can react appropriately against
rising anger at the right time. Recognizing the
emotion of anger can be done by identifying the
early signs that comes with anger.
In addition, a person can also be more sensitive
to recognize the emotion of anger by identifying
situations or things which become the triggerof
anger (Hershorn, 2005). The lack of ability to
recognize emotion of anger can make individual
unable to control his emotions and react
inappropriately and excessively. Incapacity to
recognize the emotion of anger also results in
confusion in identifying the exact emotions he is
experiencing, so the person often reacts
inappropriately to emotional situations (Goleman,
1997).
In two sessions, school-aged children are taught
to practice deep breathing. Deep breathing relaxation
can reduce tension and give you peace. Deep
breathing relaxation stimulates the body to release
opioids endogenous, namely endorphins and
enkephalins. The release of endorphins can
strengthen the immune system, keeping the brain
cells of young, anti-aging, lowering aggressiveness
in human relationships, improving moral and
creativity (Smeltzer& Bare, 2002). Supporting
research is the research conducted by Sumirta (2013)
on deep breathing relaxation to control client’s anger
with violent behavior. The result of the study reports
that deep breathing relaxation has a significant
influence on the control of anger.
On the third session,scholars are taught how to
prevent verbal aggressiveness in a way that is
expressing anger, asking for and refusing properly.
Verbal way is also called assertive behavior.
Assertive behavior is expressing ideas, wishes,
desires, disapproval directly to the child. The
purpose of assertive behavior is to communicate
something in the atmosphere of mutual trust
(Novianti, 2010). Aggressive behavior is one of the
non-assertive behaviors. Assertive training is one of
the ways in Anger Management which aims to
remove the feelings, thoughts and beliefs which
cause anger as well to other people (Reilly,
Shopshire, Durazzo & Campbell, 2002).
Assertive communication is one skill which can
be learned by individuals. Assertive is one way to
cope with aggressive behavior. Assertive teaches
how to communicate by paying attention to the
principle of respecting other people,. Individuals are
also taught to express feelings honestly and care for
other people (Larkin, 2005).
At the fourth session, spiritual way is taught to
control anger. Spiritual approach is conducted by
doing spiritual activities. Spiritual is associated with
Method of Handling Aggressive Behavior of School-aged Children with Holistic Approach in Medan
251

belief in such things as: nature, science, religion or
higher power that helps people achieve goals of life.
It covers morals, values and ethics of a person.
Therapy which can be done is the therapy of
motivating children to conduct spiritual activities.
Spiritual activities undertaken are to motivate
children to perform religious activities, improve the
relationship with themselves, other people and the
environment. Children are encouraged to
improvedoing religious activities such as prayer or
other religious activities. Based on previous
research, a lot of spiritual activities are doneby
people. One of them is meditation which can lessen
the the individual’s anger. Meditation is one therapy
conducted in the Anger Management Program which
aims to train individuals to control and overcome the
upset experienced (Borland, 1981). Beside
meditation, spiritual activity others can be taught is
by praying and sholat.
Religious activities such as praying and sholat
prayer, is a positive activity that can raise
expectations and a positive impact and improve the
healing process in individuals (Gore, 2013). Results
of previous studies have also shown that prayer is
one of the coping mechanisms which are often used.
It is usually effective because praying makes a
person uncomfortable, getting directions or
guidelines as well as to strengthen the powers of the
individual (Gore, 2013).
Schools are advised to apply method of
aggressiveness handling in schools throughSchool
Health Program and also train the tutors such as
teachers and family, especially mothers so that they
are able to conduct this handling method
independently at home and school.
4 RESEARCH DISCUSSION
Aggressive behavior is considered as a type of
behavior aiming to hurt other people, verbally or
non-verbally, physically or psychologically and
directly or indirectly (Anantasari, 2006). Baron (in
Dayakisni & Hudaniah, 2009) states that
aggressiveness is individual’s behavioraiming to
hurt or harm other individuals do not wish the
behavior to exist. This definition covers four
behavior factors, namely aiming to hurt or harm, the
individual becoming the suspect, the individual
becoming the victim and victim’s unwillingnessin
accepting the suspect’s behavior.
Betty Neuman (inMarriner-Tomey, 1994) sees
human (client) as a whole which its parts influence
one another and interact dynamically. The parts
cover physiological, psychological, socio-cultural
and spiritual. Kozier (1995) states that in holistic, all
organism lives are seen as interactions.Any
disturbance on one part will disturb a system wholly.
In other words, if there is any part distracted, other
parts will get its effect overall. Erikson, Tomlin and
Swain (inMarriner-Tomey, 1994) also state about
holism, which sees a human as a whole individual
who consists of a lot of sub-systems which are
dependent to one another and unable to be
separated.This is related with generic issues and
spiritual control. Body, mind, emotions and spirit are
the core which is dynamic. Influencing and
controlling one another. The interaction of this
various sub-systems cannot be separated, which
eventually produce holism.Holistic is related with
wellness which is believed to have effect towards
human’s health status. Anspaugh (inKozier, 1995)
signifies that to reach health and wealth, there are
five dimensions which are related and dependent one
another. These dimensions are also had by each
individual, namely biological, psychological, socio-
cultural and spiritual dimension.
Holistic approach method, in lessening the
aggressiveness, is started with biological dimension,
which is giving deep breathing technique.
Handoyo’s (2005) states that before given deep
breathing technique, the respondents who are able to
control violence behavior are only 6 people (15.4%)
while those who are unable with it are 33 people
(84.6%). After the therapy, the numbers of
respondents who were unable decreased into 3
people (7.7%) while the ones who were able
increased into 36 people (92.3%). Deep breathing
relaxation technique does not only calm the
respondents down physically but also their mind.
Research conducted by Kustamti& Widodo (2008)
also signifies that there is the influence of the
relaxation technique which relates to the aggressive
patients. One of the techniques is deep breathing
relaxation and that research concludes that the
influence indeed exists. It happens also with
Zelianti’s research result which obtains p value
0,000 and that the research result signifies that it has
the influence to change, before and after the deep
breathing relaxation technique.
Socio-cultural approach is given by conducting
verbal practice. Verbal practice is conducted
bytraining the skills of asking something politely,
declining a request and expressing feelings.
Moreover, the children are also taught to give
compliments, complain due to disagreement, strive
for personal rights, give advice to others, solve
problems and collaborate with others (MqQuaid,
2000).The children will also be taught how to
SKIC-MHS 2018 - The 2nd Syiah Kuala International Conference on Medicine and Health Sciences
252

habituate effective words which can minimalize the
aggressiveness, such as ‘sorry’, ‘thank you’ and
‘please’. Apologizing, expressing gratitude and
saying sorry are local absorptivity from Indonesian
culture which should be maintained (Shiradj, 2013).
Psychological approach is conducted through
emotion managing by doing actions which can
control mind, feelings and anger in effective,
positive and socially-accepted so it can prevent
anything bad happening or harm themselves and
others. There are some aspects of managing
emotions, such as identifying anger. According to
Goleman (1997), identifying anger means an ability
to identify anger when the anger takes over so a
person is not controlled by anger. A person who has
the ability to identify anger can react to the anger
effectively and in the right time. Identifying anger
can be done by recognizing early signs which come
along the anger, such as fast-beating pulse, fast-
beating heart, stiff jaw, strained muscles, feeling hot
in all over the body, making a fist, walking back-
and-forth, being restless, talking faster or
considering to rage violently or committing revenge,
etc.
Moreover, a person can be more sensitive to
recognize anger by identifying situations or any
matters which can trigger the anger(Hershorn,
2005).Lack of the ability to recognize can cause a
person unable to control his/her emotions and make
him/her react inappropriately and exaggeratedly.
Inability in recognizing anger also affect to
confusion in identifying emotions felt by the person
so he/she often reacts improperly towards emotional
situations (Goleman, 1997).Someone who can
control his anger will not let the anger dominates
him. He can control his emotions and keep the
balance of the emotions so the anger will get out of
control and happen in high intensity (Goleman,
1997).
Easing the anger is the ability to calm oneself
after being angry. According to Tice (in Goleman,
1997), one of the effective strategiescommonly done
to ease the anger is going somewherealone. The
other alternative is having an errand far away from
home. Someone will face difficulty to ease his anger
if his mind is till full of anger. How small the
thought about the anger is can trigger bigger anger.
To stop the thought of anger, we can do it
bydistracting attention from the trigger of the anger.
Spiritual approach covers spiritual activities.
Spiritual is associated with belief in such things as:
nature, science, religion or higher power which helps
people achieve their goals of life. It includes morals,
values and ethics of a person. Therapy which can be
done is the therapy of motivating children to conduct
spiritual activities.
5 CONCLUSIONS
Schools are advised to apply method of
aggressiveness handling in schools throughSchool
Health Program and also train the tutors such as
teachers and family, especially mothers so that they
are able to conduct this handling method
independently at home and school.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The author would like to thank the Ministry of
Research and Technology Higher Education of the
Republic of Indonesia, Prof. Dr. Runtung, SH,
M.Hum as the Rector of University of North
Sumatera.
REFERENCES
Anantasari. (2006). Menyikapi perilaku agresif
anak. Yogyakarta: Kanisius
Azizah, D., M. (2013). Mengurangi perilaku agresif
melalui layanan klasikal menggunakan
teknik sosiodrama pada siswa kelas V di
SD Negeri Pegirikan 03 Kabupaten Tegal.
Downloaded on 27 September 2015, from
http://lib.unnes.ac.id/17874/1/1301409046.
pdf
Baron, R. A., & Byrne, D. (2005). Psikologi sosial
edisi kesepuluh jilid 2. Jakarta: Erlangga
Borland (1981). Learning From Conflict. Accessed
http://psychologicalselfhelp.org/Chapter7.p
dfon 3 October 2016
Dayakisni, T., & Hudaniah. (2009). Psikologi sosial
edisi revisi. Malang: UMM Press
Gunarsa, S.D., & Gunarsa, Y.S.D. (2010). Psikologi
perkembangan anak dan remaja. Jakarta:
PT BPK Gunung Mulia
Gore (2013). Spiritual Care: Nurses Roles.
Unpublished.
Judarwanto. (2005). Psikologi anak. Surabaya: Fadil
Cipta
Handoyo, A. (2005).
PanduanPraktisAplikasiolehNafas
2.Jakarta :Elex Media Komputindo
Krahe, B. (2005). Perilaku agresif. Yogyakarta:
Pustaka Pelajar
Larkin (2005). Anger Management. Accessed from
http://www.raminader.com/PDFs%20Uploa
ded/Wellness%20
Method of Handling Aggressive Behavior of School-aged Children with Holistic Approach in Medan
253

%20Anger%20Management.pdfon 3
October 2016
Novianti (2010). Pengaruh Latihan Assertif terhadap
Perilaku Agresif Anak Usia Sekolah.
Tesis UI. Unpublished.
Nuryanti, L. (2008). Psikologi anak. Jakarta: PT
Indeks
Priyatno, D. (2008). Mandiri belajar SPSS untuk
analisis data dan uji statistik. Jakarta:
Mediakom
Rymm, S. (2003). Mendidik dan menerapkan
disiplin pada anak prasekolah: pola asuh
anak masa kini. Jakarta: PT Gramedia
Pustaka Utama
Syahadat, Y.M. (2013). Pelatihan regulasi emosi
untuk menurunkan perilaku agresif pada
anak. Downloadedon 12 October 2015,
fromjournal.uad.ac.id
Taylor, S.E., Peplau, L.A., Sears, D.O. (2009).
Psikologi sosial (edisi kedua belas).
Jakarta: Kencana Prenada Media Group
Wong, D.L. (2008). Buku ajar keperawatan
pediatrik wong edisi 6. Jakarta:
EGC
Yusuf, S. (2012). Psikologi perkembangan anak &
remaja. Bandung: Remaja Rosdakarya
Yusuf, S., & Nurihsan, J. (2005). Psikologi
perkembangan anak dan remaja. Bandung:
Remaja Rosdakarya
Yusuf, S., & Nurihsan, J. (2010). Landasan
bimbingan konseling. Bandung: PT Remaja
Rosdakarya
Yusuf, S., & Sugandhi, N.M. (2013). Perkembangan
peserta didik. Jakarta: PT RajaGrafindo
Persada
Zulkifli, L. (2005). Psikologi perkembangan.
Bandung: PT Remaja Rosdakarya
SKIC-MHS 2018 - The 2nd Syiah Kuala International Conference on Medicine and Health Sciences
254
