
A Mini Review: Phenolic Compounds in Diets for Managing Type II
Diabetes
Suryawati
1
, Firdausa Sarah
2
, Mulia Dewi Vera
3
, Vonna Azizah
4
, Sakdiah
5
1
Department of Pharmacology, Faculty of Medicine, Syiah Kuala University, Indonesia
2
Department of Internal Medicine, Faculty of Medicine, Syiah Kuala University, Indonesia
3
Department of Patology Anatomy, Faculty of Medicine, Syiah Kuala University, Indonesia
4
Department of Pharmacy, Faculty of Math and Science, Syiah Kuala University, Indonesia
5
Department of Biochemistry, Faculty of Medicine, Syiah Kuala University, Indonesia
Keywords: Diabetes Mellitus, Phenolic Compounds, Diet.
Abstract: Diet management help to prevent or reduce the progress of diabetes mellitus, one of metabolic disorder
potentially lead to serious complications such as retinopathy, nephropathy, heart and vascular diseases. This
mini review highlights the hypoglycemic effect of natural supplemented diets evaluated in animals and
humans. Several phenolic compounds from natural origins comprise of Mangifera indica, Peperomia
pellucida, Sesamum indicum, Passiflora edulis and Aegle marmelos are briefly described. Mode of action
observed in isolated phenolic compounds in improving diabetes are including free radical scavengers,
inhibition of glucose regulating enymes and disruptions expression of glucose transporter genes.
1 INTRODUCTION
1.1 Diabetes Mellitus
Diabetes mellitus is a metabolic disorder
characterized by chronic hyperglycemia caused by
absolute or relative insulin deficiency, and sometime
accompanied by insulin resistance (Robertson,
2004). DM drives the body to a condition in which
the cells are exposed to an increase of oxidative
stress. Conversely, it has been suggested that
oxidative stress lead to chronic complication in
which the level of oxidative stress in diabetic subject
is advance. Hyperglycemia is a widely known
etiology of enhanced free radical concentrations and
decreased antioxidant defense system (Ahmed,
2005).
Free radicals are singlet oxygen comprising
superoxide anion radical, hydroxyl, alkoxyl, peroxyl
radical, hydrogen peroxide, and lipid hydroperoxide.
These species are resulted from biochemical reaction
in the body or environmental exposure. Cells
injuries which lead to many diseases such as cancer,
diabetes mellitus, developed due to the action of free
radicals on PUFA, amino acids, or DNA (Nimse &
Pal, 2015).
Chronic hyperglycemia leads to toxic effects on
structure and function of organs, including β-cell in
pancreas. Islet cells of pancreas are among the
tissues that have the lowest level of antioxidant
defense. In chronic hyperglycemic state, reactive
oxygen species accumulate in an excess amount and
cause chronic oxidative stress in the islet cell. This
condition damages the cell progressively
(Robertson, 2004).
The pathophysiology of DM is complex and
multi factorials, including the interaction of genetic
and environmental factors. Three main
pathophysiology factors involve in development
DM, which are insulin resistance, decreased insulin
secretion and increased glucose production
(Polonsky & Burant, 2016).
Several biochemical pathways and mechanisms
on how hyperglycemia causes cell damage have
been explained in many studies which include
increased glycolysis, activation of sorbitol pathway,
glucose autoxidation, glycation (Ahmed, 2005),
hexosamine metabolism, protein kinase C activation,
and oxidative phosphorylation (Robertson, 2004).
Therapy is targeted to increase insulin production,
Suryawati, ., Sarah, F., Vera, M., Azizah, V. and Sakdiah, .
A Mini Review: Phenolic Compounds in Diets for Managing Type II Diabetes.
DOI: 10.5220/0008792600850091
In Proceedings of the 2nd Syiah Kuala International Conference on Medicine and Health Sciences (SKIC-MHS 2018), pages 85-91
ISBN: 978-989-758-438-1
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
85
decrease insulin resistance and stimulate cells
glucose uptake. Several key factors targeted for
combating diabetes are stimulator for insulin
secretion (glucagon like peptide, GLP), inhibitor for
GLP degradation (dipeptidyl peptidase), glucose
regulating enzymes (amylase, glucosidase, etc),
glucose transporter (GLUT 2, GLUT 4), and
activated receptor for gene expression (peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptor) (Tiwari, Thakur,
Kumar, Dey, & Kumar, 2014).
To achieve a controlled glucose level,
pharmacotherapy should be carried out with physical
activities and diet management. Physical activity to
reduces weight more than 5% was essential to
achieve normal HbA1c and nutrition management
was recommended strategy for type II diabetes
patients (Franz, Boucher, Rutten-Ramos, &
VanWormer, 2015)
1.2 Supplemented-diet
Enriched supplements with hypoglycemic agents
help to prevent risk of hyperglycemia and normalize
glucose level in diabetic patients. Diet for diabetic
could be modulated with fibre, vitamins and natural
antioxidants comes from plants (Radmila, Pavle,
Dean, & Ljupco, 2013). Mediteranian food consist
of fruits, leaves, oil etc show activity to neutralize
free radicals, inhibit inflammation, prevent glucose
absorption and lipid production (Alkhatib et al.,
2017). Several studies had shown efficacy of
compounding natural origin in diet to maintain
normal glucose level.
1.2.1 Mangifera indica
M. indica is tropical plants consumed for its tasteful
fruits. Leaves, stem bark and fruits are utilized for
their health benefits due to high content of vitamin A
and C, flavonoid and phenolic compounds. The
seeds of M. indica displayed an inhibitory activity
against alpha-amylase and glucosidase, two enzymes
involved in carbohydrate digestion. Additionally, it
prevented diabetes complication by interrupt alpha
reductase (Irondi, Oboh, & Akindahunsi). Leaves
extract suppress dipeptidyl peptidase- IV which
resulted in insulin secretion (Muthukumaran,
Srinivasan, Venkatesan, Ramachandran, &
Muruganathan).
Due its lowering effects on blood glucose level,
mangifera should be consumed routinely in daily life
based on scientific evidence. A study of diet
modulation using mangifera indica seeds conducted
by Irondi et al. (2016) . Seeds were dried and
grounded to produce kernell flour. The
administration of diet supplemented with 10-20% of
M. indica-kernell flour decreased fasting blood
glucose in streptozosin induced-diabetic rats, 3-fold
higher than diabetic rats received non-supplemented
food on day 21. Glycosilated haemoglobin value
was improved in treated rats at 6%, whereas diabetic
rats value was 10%. The kernell flour contained
flavonoid and phenolic acids, essential metabolites
for antihyperglycemic activity. Catechin, rutin,
quercetin, quercitrin, kaempferol, gallic acid, caffeic
acid, ellagic acid, and cholorogenic acid were
metabolites identified in mangifera seeds (Irondi et
al., 2016).
Consumption of diet containing catechin for 76
day decreased serum glucose in rats. In glucose
tolerance test, rats fed with catechin showed lowered
glucose amount after 120 minutes of glucose
feeding. Biomarkers for oxidative stress, albumin
and 8-hydroxy deoxyguanosine (8-OH dG) were less
excreted in urin showing catechin activity as
scavenger for free radicals (Igarashi, Honma,
Yoshinari, Nanjo, & Hara, 2007). Catechin was
observed to stimulated peroxisome proliferator
activated receptor (PPAR) γ, other key to treat
hyperglycemia (Shin et al., 2009).
There were numbers of studies reported that
using rutin 5-100 mg/kg in diabetic rats reduced
FBG and random glucose level. Rutin protected
neuron, kidney and liver from damage. It also
benefited on impairment of sexual function (Gullón,
Lú-Chau, Moreira, Lema, & Eibes, 2017). This
advantage might be correlated with its antioxidant
activity (Ghorbani, 2017).
Quercetin (15 mg/kg bw day) stimulated
endogenous antioxidant enzymes, superoxide
dismuthase (SOD), catalase and glutathione
peroxidase (GSP) in STZ-induceddiabetic rats
(Abdelmoaty, Ibrahim, Ahmed, & Abdelaziz, 2010).
The mechanism on how a flavonols like
quercetin works involving the formation of complex
with Cu that neutralizes hydroxyl radical, singlet
oxygen and hydrogen peroxide which cause
encountered oxidative stress in diabetes (Nimse &
Pal, 2015).
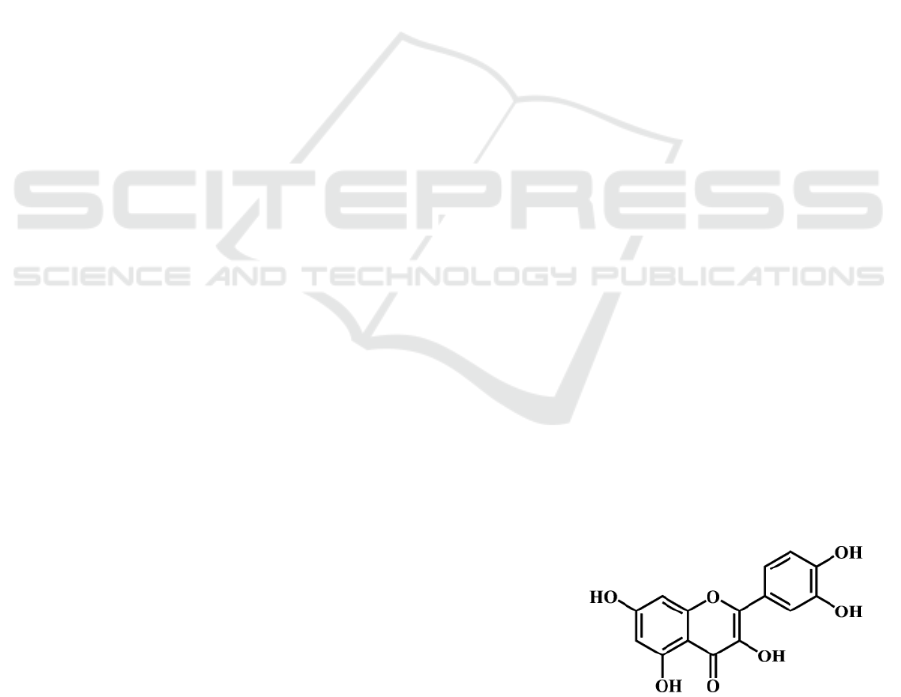
Figure 1. Quercetin
SKIC-MHS 2018 - The 2nd Syiah Kuala International Conference on Medicine and Health Sciences
86
Kaempferol given for 30 days at dose 5 and 10
mg/kg to STZ induced-diabetic rats benefit in
reducing glucose level and restoring neuron
conduction by neutralized oxidative stress. This
finding showed evidence that kaempferol enabled to
correct neuropathy as complication of chronic
hyperglycemia (Kishore, Kaur, & Singh, 2017)
1.2.2 Peperomia pellucida
P. pellucida in Indonesia, is known as kaca-kaca,
tumpangan air, rangu-rangu atau gofu goroho.
Leaves contained minerals, cardenolides, saponin,
alkaloid, tannin (Egwuche, Odetola, & Erukainure,
2011). A methanol extract showed the existence of
flavonoids and phenolic compounds and inhibit
oxidative reactions (Nirosa & Raman, 2012).
As nutrients in diets, a study conducted by
Hamzah et al showed the benefit of P. pellucida in
controlling diabetes. Fresh leaves were dried at room
temperature and processed to produce fine powder.
Diabetic animals induced by intraperitoneal alloxan
were fed with diet contained 10 and 20% of
Peperomia pellucida leaves. The glucose level was
measured after 28 days feeding and compared to the
negative and positive controls. The result showed
60% decrease in blood glucose level which was
close to positive control received glibenclamide. The
antioxidant activity was confirmed by the increase of
superoxide dismutase, CAT and GSH, the
endogenous antioxidants. Lipid peroxidation which
is abundant in diabetes was reduced. (Hamzah,
Odetola, Erukainure, & Oyagbemi, 2012).
.
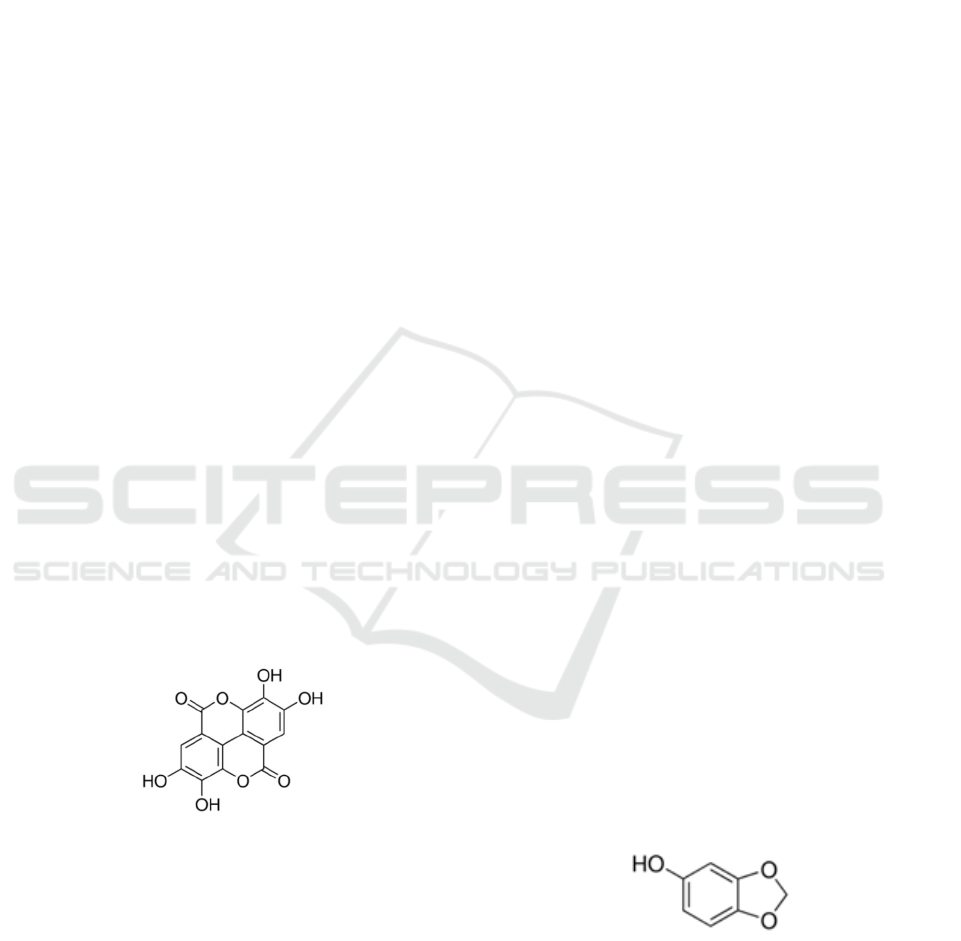
Figure 2. Ellagic acid
Susilawati et al succeeded to isolated ellagic acid, an
antihyperglicemic agent from peperomia pellucida
(Susilawati et al., 2017). In different study, ellagic
acid showed antioxidant activity in DPPH assay and
inhibitory activity of lipid peroxidation. As alpha-
amylase inhibitors, ellagic acid displayed a better
potency compared to rosiglitazone, glimepiride and
metformin (Mehta et al., 2017)
Ellagic acid tightly interacted with glycogen
phosphorilase, an enzyme that stimulate breakdown
of glycogen. The interaction cause the inhibition of
glucose production in hepar (Kyriakis et al., 2015).
Administration of 10 mg/kg BW ellagic acid with 10
mg/kg BW pioglitazone showed more potent effect
as hypoglycemic agents compared to a single agent
use in diabetic rats. The combination influenced
positively on gene expression for GLUT 4 and
PPAR gamma (Nankar & Doble, 2017).
1.2.3 Sesamum Indicum
In in vitro study, butanol extract of black sesame
inhibited alpha glucosidase higher than inhibitory
against alpha amylase with activity superior
compared to acarbose, a standard drug.
Phytochemical screening identified glycosides,
tannin, terpenoids and steroids (Amutha &
Godavari).
Clinical trials revealed that sesamum seeds
stimulated the activity of enzymatic antioxidants,
such as SOD, as well as non-enzymatic antioxidants,
vitamin E (Vittori Gouveia, Cardoso, de Oliveira,
Rosa, & Moreira, 2016).
Akanya, Isa, Adeyemi, and Ossamulu (2015)
showed that 10%- 20% sesame seed in diet lowered
blood glucose about 35-37%. Zhou, Lin, Abbasi, and
Zheng (2016) found that black sesame contained
more phenolic acid compared to white sesame,
whereas flavonoid found to be more in white sesame
rather than in black sesame. The existence of
phenolic and flavonoid was correlated with the
antioxidant activity. Sesamol, sesamin and
sesamolin were lignant identified in a large amount
in black sesame which explained its superior
antioxidant activity (oxygen radical absorbance
capacity (ORAC) value :132.33 µmol TE/g).
Sesamin decreased blood glucose level and
stimulated cardiac function in STZ induced diabetes
rats after given orally 100 and 200 mg/kg for 4 week
(Thuy et al., 2017). Since hydroxyl functional group
is important to react with radicals, sesamin and
sesamolin with 4 OH showed more potent activity
against free radical compared to sesamol that only
pose 2 OH group (Jeng & Hou, 2005).
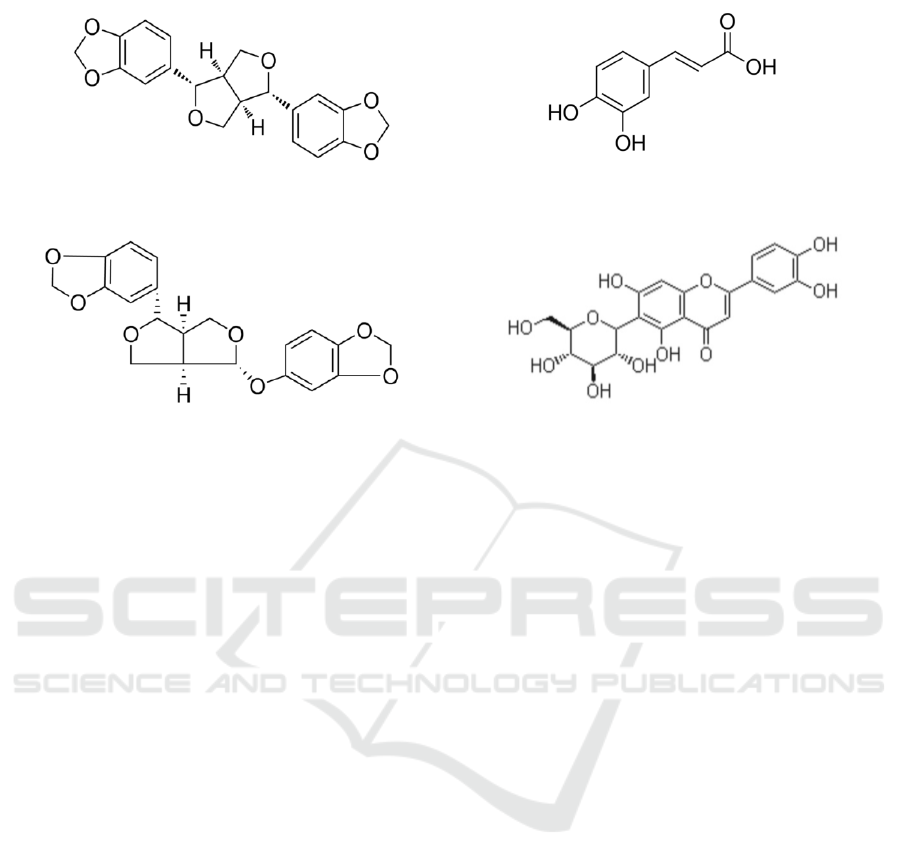
Figure 3. Sesamol
A Mini Review: Phenolic Compounds in Diets for Managing Type II Diabetes
87
S
e
s
a
m
i
n
Figure 4. Sesamolin
1.2.4 Passiflora edulis
Feeding 0.5–25 mg/kg of pectin from P. edulis to
alloxan induced-diabetic rats reduced blood glucose
(Silva et al., 2011). Extract of P. edulis peel were
given at dose 250 and 500 mg/kg to diabetic rats
induced by STZ for15 days. The result showed a
controlled blood glucose level with an increase of
SOD level which reflected its antioxidant effect.
Additionally, histophalogy evaluation revealed the
organ protective effects (Kandandapani, Balaraman,
& Ahamed, 2015)
Peel flour was also tested in 43 diabetic
respondents. Each volunteer consumed 30 g/day for
two months. The result showed a decrease in blood
blucose (de Queiroz et al., 2012). Supplemented diet
with 30% of peel-fluor of Passiflora edulis prevented
insulin resistance in mice induced by 8 week-
administration of 10% fructose. The study identified
two phenolics compounds, caffeic acid and
isoorientin (Goss et al., 2018).
Caffeic acid affected the expression of genes
including glucose transporter 2(Glut 2), insulin 1
(Ins 1) and some proteins played roles in increasing
insulin production (Bhattacharya, Oksbjerg, Young,
& Jeppesen, 2014). Caffeic acid is one of
hydroxycinnamates that scavenge free radicals by
giving its hydroxyl hydrogen to inhibit cells
destruction (Nimse & Pal, 2015).
Figure 5. Caffeicacid
Figure 6. Isoorientin
In a study using murine and human adipocyte, it was
revealed the mode of action how isorientin worked
as antidiabetic agent which affected insulin signal
transduction. Normally, insulin binds to insulin
receptor (IR) which then caused phosphorylationof
the receptor, followed by activation of
phosphatidylinositol 3 kinase (PI3K). PI3K
phosphorylate protein kinase B resulted in a
movement of glucose transporter (GLUT 4) to
membrane to start glucose absorption. Isoorientin
stimulated phosphorylation important protein IR,
PI3K and protein kinase B (Alonso-Castro, Zapata-
Bustos, Gómez-Espinoza, & Salazar-Olivo, 2012).
1.2.5 Aegle Marmelos
A. marmelos, known as maja in Indonesia, is
classified into Rutaceae. In a clinical study,
consumption of Aegle Marmelos Correa leaf 20
g/100 mL reduce fasting blood glucose and HbA1c
about 20%, observed after 4 weeks. The leaves
contained aegelin 2, scopoletin and sitosterol
(Nigam & Nambiar, 2018).
Identification using UHPLC-PDA showed the
presence of aegeline (alkaloid), umbelliferone,
scopoletin, marmesinin, 8-hydroxypsoralen,
angelicin and marmelosin (simultaneous, avula).
Phenolic compounds identified using RP-HPLC
analyses were gallic acid (GA), p-coumaric acid (p-
CA), vanillic acid (VA), p-hydroxy benzoic acid (p-
HBA), syringic acid (SA), ferulic acid (FA) and
chlorogenic acid (ChA) (Wali, Gupta, Mallick,
Guleria, & Sharma, 2015)
SKIC-MHS 2018 - The 2nd Syiah Kuala International Conference on Medicine and Health Sciences
88

GA and p-CA restored glucose regulation
indicated by decreased glucose level and HbA1c and
inclined insulin. Degeneration of neuron function in
brain of diabetic rats was improved by affecting
expression of protein Bax and Bcl-2 (abd moneim,
gallic acid).
In vivo study on streptozosin-induced diabetic
rats, given 100 mg/kg b.w of p-CA, showed the
suppression of stimulant enzymes in
gluconeogenesis along with improvement of serum
lipids contributed for hiperglicemia. Administration
of p-CA disrupted expression of protein GLUT 2
(Amalan, Vijayakumar, Indumathi, &
Ramakrishnan, 2016) which facilitate glucose
transportation across cell membrane and stimulate
insulin secretion (Thorens, 2015).
Diabetic rats treated with GA (20 mg/kg b.wt.
per day) and p-CA (40 mg/kg b.wt. per day) for 6
weeks displayed the hepatoprotective effects
reflected by the controlled level of alanin transferase
and aspartate aminotransferase (Moneim, El-Twab,
Ashour, & Yousef, 2016) . GA and p-CA affected
expression of tumour necrosis factor (TNFα) and
PPAR γ (Abdel-Moneim, El-Twab, Yousef, Reheim,
& Ashour, 2018). TNFα is a cytokine known to
induced insulin resistance and found overproduced
in adipocytes. Inhibition of its gene expression was
believed to induce insulin sensitivity (Moller,
2000).
In a study evaluating phenolic compounds as
antidiabetic agents showed that glucose was
maximally absorbed into cells when VA was
applied. In diabetic rats given 30 mg/kg bw of VA
for 3 weeks the glucose and insulin level were
decreased showing activity against insulin resistance
(Chang et al., 2015).
SA improved hyperglycemia by inhibiting
formation of glycoprotein, a complex of protein and
carbohydrate. In diabetic organism, the unutilized
glucose was bonded to protein. The administration
of SA 50 mg/kg bw in alloxan induced diabetic rats
for 30 days effectively normalized the amount of
glycoprotein including hexose, hexosamine, fucose
and sialic acid Muthukumaran et al. (2013).
Narasimhan, Chinnaiyan, and Karundevi (2015)
found that FA countered expression of GLUT 2 by
inhibiting the binding of GLUT 2 transcription
factors with their promotors. The transcription
factors including sterol response element–binding
protein (SREBP)-1c and Hepatocyte nuclear factor
(HNF). These molecules made complex with
promotor at specific site which then induced
expression of gene for GLUT 2. Hiperglycemia
stimulate the interaction of SREBP)-1c with
promotor (Im et al., 2005)
2 CONCLUSIONS
In diabetes mellitus treatment, supplemented diet is
essential to provide active agents which play roles in
inhibiting glucose absorption, stimulating insulin
production and increasing cells glucose uptake.
REFERENCES
Abdel-Moneim, A., El-Twab, S. M. A., Yousef, A. I.,
Reheim, E. S. A., & Ashour, M. B. (2018).
Modulation of hyperglycemia and dyslipidemia in
experimental type 2 diabetes by gallic acid and p-
coumaric acid: The role of adipocytokines and PPARγ.
Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy, 105, 1091-1097.
Abdelmoaty, M. A., Ibrahim, M., Ahmed, N., &
Abdelaziz, M. (2010). Confirmatory studies on the
antioxidant and antidiabetic effect of quercetin in rats.
Indian Journal of Clinical Biochemistry, 25(2), 188-
192.
Ahmed, R. G. (2005). The physiological and biochemical
effects of diabetes on the balance between oxidative
stress and antioxidant defense system. Medical
Journal of Islamic World Academy of Sciences, 15(1),
31-42.
Akanya, H., Isa, U., Adeyemi, H., & Ossamulu, I. (2015).
Effect of Sesamum indicum (Linn) seeds
supplemented diets on blood glucose, lipid profiles
and serum levels of enzymes in alloxan induced
diabetic rats. J. Appl. Life Sci. Int, 2, 134-144.
Alkhatib, A., Tsang, C., Tiss, A., Bahorun, T., Arefanian,
H., Barake, R., . . . Tuomilehto, J. (2017). Functional
Foods and Lifestyle Approaches for Diabetes
Prevention and Management. Nutrients, 9(12), 1310.
Alonso-Castro, A. J., Zapata-Bustos, R., Gómez-Espinoza,
G., & Salazar-Olivo, L. A. (2012). Isoorientin reverts
TNF-α-induced insulin resistance in adipocytes
activating the insulin signaling pathway.
Endocrinology, 153(11), 5222-5230.
Amalan, V., Vijayakumar, N., Indumathi, D., &
Ramakrishnan, A. (2016). Antidiabetic and
antihyperlipidemic activity of p-coumaric acid in
diabetic rats, role of pancreatic GLUT 2: In vivo
approach. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy, 84, 230-
236.
Amutha, K., & Godavari, A. (2016). In-Vitro-Antidiabetic
Activity of N-Butanol Extract Of Sesamum Indicum.
In-Vitro, 9(4).
Bhattacharya, S., Oksbjerg, N., Young, J., & Jeppesen, P.
(2014). Caffeic acid, naringenin and quercetin enhance
glucose‐stimulated insulin secretion and glucose
sensitivity in INS‐1E cells. Diabetes, Obesity and
Metabolism, 16(7), 602-612.
Chang, W.-C., Wu, J. S.-B., Chen, C.-W., Kuo, P.-L.,
Chien, H.-M., Wang, Y.-T., & Shen, S.-C. (2015).
Protective effect of vanillic acid against
hyperinsulinemia, hyperglycemia and hyperlipidemia
A Mini Review: Phenolic Compounds in Diets for Managing Type II Diabetes
89

via alleviating hepatic insulin resistance and
inflammation in high-fat diet (HFD)-fed rats.
Nutrients, 7(12), 9946-9959.
De Queiroz, M. d. S. R., Janebro, D. I., da Cunha, M. A.
L., dos Santos Medeiros, J., Sabaa-Srur, A. U.,
Margareth de Fatima, F., & Dos Santos, S. C. (2012).
Effect of the yellow passion fruit peel flour (Passiflora
edulis f. flavicarpa deg.) in insulin sensitivity in type 2
diabetes mellitus patients. Nutrition journal, 11(1), 89.
Egwuche, R., Odetola, A., & Erukainure, O. (2011).
Preliminary investigation into the chemical properties
of Peperomia pellucida L. Research Journal of
Phytochemistry, 5(1), 48-53.
Franz, M. J., Boucher, J. L., Rutten-Ramos, S., &
VanWormer, J. J. (2015). Lifestyle weight-loss
intervention outcomes in overweight and obese adults
with type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-
analysis of randomized clinical trials. Journal of the
Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics, 115(9), 1447-
1463.
Ghorbani, A. (2017). Mechanisms of antidiabetic effects
of flavonoid rutin. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy,
96, 305-312.
Goss, M., Nunes, M., Machado, I., Merlin, L., Macedo,
N., Silva, A., . . . Santin, J. (2018). Peel flour of
Passiflora edulis Var. Flavicarpa supplementation
prevents the insulin resistance and hepatic steatosis
induced by low-fructose-diet in young rats.
Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy, 102, 848-854.
Gullón, B., Lú-Chau, T. A., Moreira, M. T., Lema, J. M.,
& Eibes, G. (2017). Rutin: a review on extraction,
identification and purification methods, biological
activities and approaches to enhance its
bioavailability. Trends in Food Science & Technology,
67, 220-235.
Hamzah, R. U., Odetola, A. A., Erukainure, O. L., &
Oyagbemi, A. A. (2012). Peperomia pellucida in diets
modulates hyperglyceamia, oxidative stress and
dyslipidemia in diabetic rats. Journal of Acute
Disease, 1(2), 135-140.
Igarashi, K., Honma, K., Yoshinari, O., Nanjo, F., & Hara,
Y. (2007). Effects of dietary catechins on glucose
tolerance, blood pressure and oxidative status in Goto-
Kakizaki rats. Journal of nutritional science and
vitaminology, 53(6), 496-500.
Im, S.-S., Kang, S.-Y., Kim, S.-Y., Kim, H.-i., Kim, J.-W.,
Kim, K.-S., & Ahn, Y.-H. (2005). Glucose-stimulated
upregulation of GLUT2 gene is mediated by sterol
response element–binding protein-1c in the
hepatocytes. Diabetes, 54(6), 1684-1691.
Irondi, E. A., Oboh, G., & Akindahunsi, A. A. (2016).
Antidiabetic effects of Mangifera indica Kernel Flour‐
supplemented diet in streptozotocin‐induced type 2
diabetes in rats. Food science & nutrition, 4(6), 828-
839.
Jeng, K., & Hou, R. (2005). Sesamin and sesamolin:
nature's therapeutic lignans. Current Enzyme
Inhibition, 1(1), 11-20.
Kandandapani, S., Balaraman, A. K., & Ahamed, H. N.
(2015). Extracts of passion fruit peel and seed of
Passiflora edulis (Passifloraceae) attenuate oxidative
stress in diabetic rats. Chinese Journal of Natural
Medicines, 13(9), 680-686. doi:
https://doi.org/10.1016/S1875-5364(15)30066-2
Kishore, L., Kaur, N., & Singh, R. (2017). Effect of
Kaempferol isolated from seeds of Eruca sativa on
changes of pain sensitivity in Streptozotocin-induced
diabetic neuropathy. Inflammopharmacology, 1-11.
Kyriakis, E., Stravodimos, G. A., Kantsadi, A. L.,
Chatzileontiadou, D. S., Skamnaki, V. T., & Leonidas,
D. D. (2015). Natural flavonoids as antidiabetic
agents. The binding of gallic and ellagic acids to
glycogen phosphorylase b. FEBS letters, 589(15),
1787-1794.
Mehta, V., Verma, P., Sharma, N., Sharma, A., Thakur,
A., & Malairaman, U. (2017). Quercetin, ascorbic
acid, caffeine and ellagic acid are more efficient than
rosiglitazone, metformin and glimepiride in interfering
with pathways leading to the development of
neurological complications associated with diabetes: A
comparative in-vitro study. Bulletin of Faculty of
Pharmacy, Cairo University, 55(1), 115-121.
Moller, D. E. (2000). Potential role of TNF-α in the
pathogenesis of insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes.
Trends in Endocrinology & Metabolism, 11(6), 212-
217.
Moneim, A. A., El-Twab, S. M. A., Ashour, M. B., &
Yousef, A. I. (2016). Hepato-renal protective effects
of gallic acid and p-coumaric acid in
nicotinamide/streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats.
International Journal of Bioassays, 5(6), 4641-4649.
Muthukumaran, J., Srinivasan, S., Venkatesan, R. S.,
Ramachandran, V., & Muruganathan, U. (2013).
Syringic acid, a novel natural phenolic acid,
normalizes hyperglycemia with special reference to
glycoprotein components in experimental diabetic rats.
Journal of Acute Disease, 2(4), 304-309.
Nankar, R. P., & Doble, M. (2017). Hybrid drug
combination: Anti-diabetic treatment of type 2 diabetic
Wistar rats with combination of ellagic acid and
pioglitazone. Phytomedicine, 37, 4-9.
Narasimhan, A., Chinnaiyan, M., & Karundevi, B. (2015).
Ferulic acid regulates hepatic GLUT2 gene expression
in high fat and fructose-induced type-2 diabetic adult
male rat. European journal of pharmacology, 761,
391-397.
Nigam, V., & Nambiar, V. S. (2018). Aegle Marmelos
Leaf Juice As A Complementary Therapy To Control
Type 2 Diabetes-Randomised Controlled Trial In
Gujarat, India. Advances in Integrative Medicine.
Nimse, S. B., & Pal, D. (2015). Free radicals, natural
antioxidants, and their reaction mechanisms. Rsc
Advances, 5(35), 27986-28006.
Nirosa, A., & Raman, P. (2012). Isolation of Chemical
Compounds From Methanol Extract of Peperomia
pellucida: Fak Sains dan Teknol Univ Malaysia
Trengg.
Polonsky, K. S., & Burant, C. F. (2016). Type 2 Diabetes
Mellitus. In S. Melmed, K. S. Polonsky, P. R. Larsen
& H. M. Kronenberg (Eds.), Williams Textbook of
SKIC-MHS 2018 - The 2nd Syiah Kuala International Conference on Medicine and Health Sciences
90

Endocrinology (pp. 1386-1450). Philadelphia: Elsevier
Health Sciences.
Radmila, C.-N., Pavle, S., Dean, J., & Ljupco, A. (2013).
The influence of nutrition (diet treatment) in
streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Macedonian
Veterinary Review, 36(1), 41-47.
Robertson, R. P. (2004). Chronic Oxidative Stress as a
Central Mechanism for Glucose Toxicity in Pancreatic
Islet Beta Cells in Diabetes. Journal of Biological
Chemistry, 279(41), 42351-42354. doi:
10.1074/jbc.R400019200
Shin, D. W., Kim, S. N., Lee, S. M., Lee, W., Song, M. J.,
Park, S. M., . . . Hong, J.-H. (2009). (−)-Catechin
promotes adipocyte differentiation in human bone
marrow mesenchymal stem cells through PPARγ
transactivation. Biochemical pharmacology, 77(1),
125-133.
Silva, D. C., Freitas, A. L., Pessoa, C. D., Paula, R. C.,
Mesquita, J. X., Leal, L. K., . . . Viana, G. S. (2011).
Pectin from Passiflora edulis shows anti-inflammatory
action as well as hypoglycemic and
hypotriglyceridemic properties in diabetic rats.
Journal of medicinal food, 14(10), 1118-1126.
Susilawati, Y., Nugraha, R., Krishnan, J., Muhtadi, A.,
Sutardjo, S., & Supratman, U. (2017). A New
Antidiabetic Compound 8, 9-dimethoxy Ellagic Acid
from Sasaladaan (Peperomia pellucida L. Kunth).
Research Journal of Pharmaceutical Biological And
Chemical Sciences, 8, 269-274.
Thorens, B. (2015). GLUT2, glucose sensing and glucose
homeostasis. Diabetologia, 58(2), 221-232.
Thuy, T. D., Phan, N. N., Wang, C.-Y., Yu, H.-G., Wang,
S.-Y., Huang, P.-L., . . . Lin, Y.-C. (2017). Novel
therapeutic effects of sesamin on diabetes-induced
cardiac dysfunction. Molecular medicine reports,
15(5), 2949-2956.
Tiwari, N., Thakur, A., Kumar, V., Dey, A., & Kumar, V.
(2014). Therapeutic targets for diabetes mellitus: an
update. Clinical Pharmacology & Biopharmaceutics,
3(1), 1-10.
Vittori Gouveia, L. d. A., Cardoso, C. A., de Oliveira, G.
M. M., Rosa, G., & Moreira, A. S. B. (2016). Effects
of the Intake of sesame seeds (Sesamum indicum L.)
and derivatives on oxidative stress: A systematic
review. Journal of medicinal food, 19(4), 337-345.
Wali, A., Gupta, M., Mallick, S., Guleria, S., & Sharma,
M. (2015). Antioxidant potential and phenol profile of
Bael leaf (Aegle marmelos). Indian Journal of
Agricultural Biochemistry, 28(2), 138-142.
Zhou, L., Lin, X., Abbasi, A. M., & Zheng, B. (2016).
Phytochemical contents and antioxidant and
antiproliferative activities of selected black and white
sesame seeds. BioMed research international, 2016.
A Mini Review: Phenolic Compounds in Diets for Managing Type II Diabetes
91
