
Effect of Types and Application of Organic Ingredients against
Soybean Results (Glycine max (L.) Merrill) on Peat Planting Medium
Hapsoh, Isna Rahma Dini, Wawan and Nuranti
University of Riau Kampus Bina Widya Km 12,5 Simpang Baru Pekanbaru 28293, Indonesia
Keywords: Rice Straw, Soybean Litter, Spread, Immersed, Peat Medium.
Abstract: Soybeansare one of food crops thatgrow with shallow roots that can be cultivated on peat soil, but there are
still many obstacles, one of which is due to poor peat nutrients. Therefore, there needs to be an effort to
overcome it by providing organic material for plant waste that can help in increasing nutrients in peat soil.
The study aimed to determine the interaction and the best combination between the type organic matters and
application method to the yield of soybeans in peat soil. The study was conducted in the form of a trial using
a Completely Randomized Design (CRD) consisting of 2 factors and 3 replications. The first factor was the
provision of organic matter of rice straw, soybean litter, oil palm empty fruit bunches (OPEFB), and the
second factor was application byimmersing and spreading. The results showed that the components of yield
of soybean through application of rice straw with application spread and soy litter with immersed application
show high yields on the total number of pods per plant, number of pithy pods per plant, number of pithy seeds
per plant and seed weight dry per plant. Furthermore, the combination of OPEFB with two applications does
not show good effect on the yield parameters of soybean plants.
1 INTRODUCTION
The limitation of productive land causes agricultural
extensionleading to marginal lands. Peatlands are one
type of land that include criteria marginal land that
has the potential to be used as agricultural land. Riau
is one of the provinces that has extensive peatlands
and has enough potential to be developed as
agricultural land (Suwondo, 2002).
Damage to the peat ecosystem is resulted from
wrong land management and the selection of
commodities that are not in accordance with the
characteristics of peatland. Government Regulation
No 57 of 2016 concerning amendments to
Government Regulation No. 71 of 2014 concerning
the protection and management of peat ecosystems
article 23 paragraph 3 which reads the peat ecosystem
with a cultivation function declared to be damaged if
it meets the standard criteria for groundwater damage
on peat land more than 0.4 meters below the surface
of the peat at the point of arrangement. Therefore, it
is necessary to determine which plants are suitable for
cultivation on peat lands for the sake of the
sustainability of the peat ecosystem.
Soybean plants are included in the legume group
which has shallow roots and can be cultivated on peat
soil. The use of peatland as a growing medium for
legume plants turns out to meet many limiting factors
in its exploitation, such as poor nutrient and high
evaporation which causes peat soil to dry out like
charcoal so that the soil is no longer productive.
Therefore, there needs to be an effort to overcome the
problems found on peat soil, one of which is by
providing organic matter from plant waste. The role
of giving organic matter to the soil is related to
changes in soil properties, namely the physical,
biological, and chemical properties of the soil.
Rice straw, soybean litter and oil palm empty fruit
bunches (OPEFB) are organic materials of plant
waste that have good potential as a source of nutrients
for plants, energy sources for soil fauna and
microorganisms and as soil cover to maintain soil
temperature and humidity. Nevertheless organic
matter is often not utilized by farmers due to its
unknown function.
Composting organic matter such as
Lignocellulose-containing OPEFB requires a long
time. To overcome this, an alternative is needed that
can speed up the composting process. Huang et al.
(Huang et al.2009) stated that the use of
microorganism inoculants aims to accelerate
composting and improve the final product.
Hapsoh, ., Dini, I., Wawan, . and Nuranti, .
Effect of Types and Application of Organic Ingredients against Soybean Results (Glycine max (L.) Merrill) on Peat Planting medium.
DOI: 10.5220/0008883501590164
In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Multidisciplinary Research (ICMR 2018) - , pages 159-164
ISBN: 978-989-758-437-4
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
159

Microorganisms that can accelerate the
decomposition process are cellulolytic
microorganisms Azhari (Azhari, 2000). Cellulolytic
microorganisms are microorganisms that are able to
degrade cellulose enzymatically through the activity
of cellulase enzymes, one of which is bacteria.
In addition to organic matter which can affect the
nature of peat soil and the yield of soybean plants, the
way the application also influences it. Giving organic
matter to the soil can be done by mixing organic
matter into the soil and also as mulch (Pauza, 2016).
Mulch has been reported to increase yield by creating
soil temperature and a favorable moisture regime
(Han and Ma, 1995). Mulch is a crop residue, plastic
sheet, or stone arrangement that is spread on the
ground. Mulch is the right strategy to reduce
evaporation, accelerate plant development, reduce
erosion and help control weeds. As a result of
reduced evaporation, mulch-treated soils improve
water conservation, especially in the soil at the top
(Godawatte and Silva, 2014). This study aims to
determine the interaction and determine the best
combination between the type and method of
application of organic matter to the yield of soybeans
in peat planting medium.
2 METHOD
This research was conducted at the Experimental
Garden of the Faculty of Agriculture, University of
Riau Campus Bina Widya Km 12.5 SimpangBaru
Village Panam, Tampan District, Pekanbaru, Riau.
This study lasted for 4 months starting from August
to November 2017.
The experiment was conducted experimentally
which was arranged in a completely randomized
design (CRD) factorial pattern consisting of 2 factors.
First factor: organic matter of plant waste (O),
namely: O1 (125 g-
1
medium rice straw), O2
(soybean litter 125 g-
1
medium), O3 (oil palm empty
fruit bunches (OPEFB) 125 g-
1
medium) and the
second factor: how to apply organic matter (C),
namely: C1 (immersed) and C2 (spread).
Parameters observed in this study were plant
height, number of productive branches, age of
flowering, total number of pods per plant, number of
potted pods per plant, number of empty pods per
plant, number of seeds per plant, and dry seed weight
of each plant.The data obtained were statistically
analyzed using statistical analysis system (SAS)
Version 9.1 program, then further testing was carried
out by duncan multiple distance test's new multipe
range test (DNMRT) at the level of 5%.
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
3.1 Plant Height, Number of
Productive Branches, Age of
Flower Emergence, Total Number
of Pods per Plant, Number of Pods
Containing Each Plant, Number of
Empty Pods per Plant, Number of
Seeds per Plant and Dry Seed
Weight of Each Plant
Table 1 shows that the treatment of organic matter,
the ways of application of organic matter and a
combination of both give different results not
significant to plant height, number of productive
branches and the age of flowering of soybean plants.
This is influenced by genetic factors such as the use
of the same variety and also the ability of soybean
plants to be symbiotic with Rhizobium to tether N2
from the air.
Zainal et al. (Zainal et al.2014) explained that
Nitrogen is an essential nutrient that is needed by
plants in quite a lot. Vegetative growth such as plant
height growth and formation of productive branches
formed are influenced by N availability. N nutrients
are needed by plants to produce protein and
chlorophyll and maintain photosynthetic efficiency,
so that the process of plant physiology runs well. The
number of productive branches produced is likely to
be a lot of flowers.
Flowering age or when the first flower emerges
from varieties planted at the same time and
environment the age of flowering in plants is also
almost the same. Research uses the same variety but
the organic material given as a different treatment by
means of application is also different, so it can be
expected that genetic factors predominantly affect the
age of flowering. Lakitan (Lakitan, 2007) states that
a flowering plant is also influenced by its variety.
Varieties play an important role in determining the
components of soybean products because to achieve
high productivity is very much determined by the
potential power yield of the superior varieties planted
(Irwan, 2006).
ICMR 2018 - International Conference on Multidisciplinary Research
160
Keterangan:
- TNP (Total number of pods),
- NPP (Number of pithy pods),
- NEP (Number of empty pods), - NSP (The number of
seeds is pithy), dan
- DSW (Dry seed weight).
A plant will give a different response to different
environments. The data in Table 2 provides
information about the role and function of the
treatment given. The data in Table 2 show that the
combination of organic matter of rice straw by means
of distributed application produces the total number
of pods per plant (93.67 pods), the number of seeds
per plant (91.33 pods), the number of seeds per plant
(195.00 seeds) and dry seedweight for each plant
18.36 g) highest compared to other combinations. It
is suspected that rice straw that is spread on the
surface of peat soil serves to protect the soil surface
from direct sunlight which can cause evaporation so
that the water content in the soil can be maintained
and the water needs for plants are fulfilled.
Comparison of planting medium after being given
organic matter by means of the application spread
shown in Figure 1.
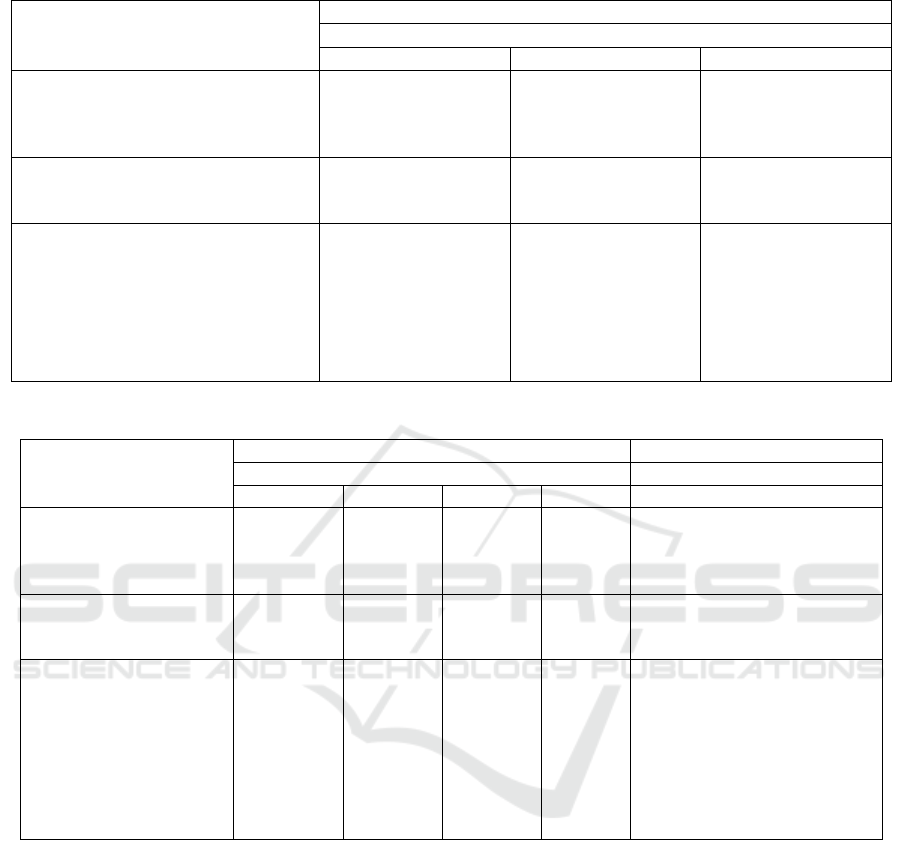
Table 1: Growth of soybean plants after being given several organic ingredients and their application ways.
Treatment
Soybean Plant Growth
Plant height Number of Productive Branches Flowers appear
(Cm) (Branch) (Dap)
Organic material (O)
Rice straw (O1)
Soybean litter (O2)
OPEFB (O3)
56,67
55,50
58,67
6,00
6,33
5,67
41,17
41,17
40,67
Application method (C)
Immersed (C1)
Spread (C2)
55,00
58,00
5,89
6,11
41,33
40,67
Organic ingredients & application ways
O1C1
O1C2
O2C1
O2C2
O3C1
O3C2
55,67
56,67
50,00
61,00
59,33
58,00
5,67
6,33
7,00
5,67
5,00
6,33
41,33
41,00
41,67
40,67
41,00
40,33
Table 2: Components of yield and yield of soybean plants after being given organic matter and the application method.
Treatment
Components of Results for each Plant The results of each plant
TNPNPPNEPNSP DSW
(Pod) (Pod) (Pod) (Seed) (g)
Organic material (O)
Rice straw (O1)
Soybean litter (O2)
OPEFB (O3)
80,83
77,83
65,83
78,67
75,50
64,33
2,16
2,33
1,50
162,83
156,00
124,67
15,86
14,88
12,10
Application method (C)
Immersed (C1)
Spread (C2)
76,67
73,00
73,89
71,78
2,78
1,22
145,44
150,22
13,85
14,71
Organic ingredients &
application ways
O1C1
O1C2
O2C1
O2C2
O3C1
O3C2
68,00
93,67
93,00
62,67
69,00
62,67
66,00
91,33
89,33
61,67
66,33
62,33
2,00
2,33
3,67
1,00
2,67
0,33
130,67
195,00
179,00
133,00
126,67
122,67
13,36
18,36
16,03
13,73
12,16
12,03
Effect of Types and Application of Organic Ingredients against Soybean Results (Glycine max (L.) Merrill) on Peat Planting medium
161

Figure 1: medium of application of rice straw spread (a), soybean litter application medium spread (b),the media planted the
OPEFB application is spread (c).
The provision of organic matter to the planting
medium gives an influence on the yield and yield
components of soybean. Figure 1 shows the
difference in soil surface given organic matter with
the application spread.
The organic matter of rice straw by means of
spread (Figure 1.a) gives higher yields, this is because
the organic matter of rice straw spread on the soil
surface is able to cover the soil perfectly compared to
organic soybean litter and OPEFB. This condition is
caused by the organic matter of soybean litter being
spread on the surface of peat soil (Figure 1.b) unable
to cover the soil properly due to soybean litter
exposed to sunlight and rainwater which are easily
weathered and wrinkled so that the soil surface is
more open. This condition causes excessive
evaporation of peat soil is still happening, this is no
different from the provision of OPEFB. Tie and Lim
(Tie and Lim, 1992) state that peat has irreversible
drying properties which means that once there is
excessive dryness the nature of peat colloids will
become damaged so that the peat cannot return to
hold water. Peat which is already dry changes its
properties like charcoal and can no longer absorb
nutrients (Chotimah, 2002).
Subhan and Sumana (Subhan and Sumana, 1994)
in Marliah et al. (Marliah et al.2011) stated, the use of
organic mulch such as straw will provide a good
growth environment for plants because it can reduce
evaporation, prevent direct sunlight from excessive
exposure to soil and moisture can be maintained so
that plants can absorb nutrients and water properly.
Besides that the organic material of rice straw which
has been chopped and then spread on the ground
surface is very strong to hold water compared to other
organic materials. Irfany et al. (Irfany et al.2016)
states that high soil moisture indicates that the water
contained in the soil is also high so that the need for
water for plants can be fulfilled. The availability of
enough water to meet the water needs of plants is very
important. If the availability of ground water is less
for the plants as a result of water as photosynthetic
raw material, the transportation of the nutrient will be
hampered so that it will affect the production
produced (Felania, 2017).
Water capacity is less available causing plant
development to be disrupted so that the formation of
pods and filling of pods will be inhibited. In addition
to water, nutrients also affect the development of
soybean plants. Comparison of the total number of
pods and the number of seeds pithy after being given
organic matter and the application method are shown
in Figures 2 and 3.
Figures 2 and 3 show a comparison of the total
number of pods and the number of seeds of p plants
per soybean in each treatment. The provision of rice
straw with the spread application (O1C2) showed the
highest total number of pods and number of pithy
seeds followed by the provision of soybean porridge
with the Immersed application. The provision of
soybean litter organic material (O2C1) in Immersed
shows high yields after the combination of organic
matter of rice straw with the application spread over
other treatments.
a b c
ICMR 2018 - International Conference on Multidisciplinary Research
162

Figure 3: Pithy seed:immersed rice straw (O
1
C
1
), spread rice straw (O
1
C
2
),immersed soy litter (O
2
C
1
), spread soy litter (O
2
C
2
),
immersed OPEFB (O
3
C
1
), and spread OPEFB (O
3
C
2
).
The data in Table 2 shows that the combination of
organic matter of soybean litter by means of
application is immersed to produce the total number
of pods per plant (93.00 pods), number of pithy pods
per plant (89.33 pods), number of pithy seeds per
plant (179.00 seeds ) and the highest dry seed weight
per plant (16.06 g) compared to the treatment of rice
straw in immersed, soybean litter was spread and the
OPEFB was immersed or spread. This condition is
due to the embedded soy litter containing high
nutrients, especially N and easily decomposed. This
condition causes the soaked soy litter to provide more
nutrients and faster than other treatments.
Nitrogen acts as a constituent of chlorophyll and
chlorophyll which controls the ability of plants to
carry out photosynthesis (Setyanti et al., 2013).
Photosynthesis results will be translocated by the
plant to the branch of the plant.
The data in Table 2 shows the number of empty
pods produced by each crop, namely the average of
2-3 planted pods. The lowest number of empty pods
is in the OPEFB growing medium. Although the total
number of pods produced is small, but when
associated with total pods, the application of OPEFB
is still less able to show high yields, this is suspected
when the pods are blocked due to water and nutrients
needed by the plants are not available.
Formation of pods, seed formation and increase in
soybean seed weight are influenced by the availability
of water and nutrients, if water and nutrients are less
available it can cause the formation of pithy seeds to
be disturbed so that the seeds produced are few. This
condition is not different from the provision of
OPEFB organic matter.
The combination of OPEFB which was applied in
the method of Immersed (O3C1) or spread (O3C2)
did not show a tendency for high yields even though
the vegetative phase showed the same growth but in
the generative phase showed differences in results.
This is because the organic matter of OPEFB contains
high lignin which causes the duration of decomposed
organic matter compared to other organic materials.
The length of decomposed organic OPEFB
organic matter causes nutrients available in the soil to
be used by soil organisms as energy to remodel
organic matter that causes nutrients needed by plants
less available. Whereas the Immersed organic matter
of OPEFB is not able to cover the soil perfectly and
is very weak in holding water which can cause high
evaporation of peat soils can occur.
Figure 2: Total pods per soybean plant:immersed rice straw (O
1
C
1
), spread rice straw (O
1
C
2
),immersed soy litter (O
2
C
1
),
spread soy litter (O
2
C
2
), immersed OPEFB (O
3
C
1
), and spread OPEFB (O
3
C
2
).
Effect of Types and Application of Organic Ingredients against Soybean Results (Glycine max (L.) Merrill) on Peat Planting medium
163

Insufficient nutrients and water can inhibit the
formation of pods and fill pods so that the yield and
yield components of soybean plants decrease.
4 CONCLUSIONS
The provision of various organic materials and the
application method gives no different results on
growth parameters such as plant height, number of
productive branches and age of flowering, but on the
yield components of soybean plants through the
provision of rice straw with application spread and
soy litter with immersed applications tend to show
high yields on the total number of pods per plant,
number of pithy pods per plant, number of pithy seeds
per plant and dry seed weight of each plant.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
Thank you the Ministry of Higher Education. The
research is done through the Competency Grant
Research which has funded this research.
REFERENCES
Azhari. 2000. Effect of the Use of Cellulolytic
Microorganisms on Composting of Oil Palm Empty
Fruit Bunches. Thesis. University of Northern Sumatra.
Field.
Chotimah, H. E. N. C. 2002. Utilization of Peatlands for
Agricultural Plants. Paper. IPB Postgraduate Program.
Bogor.
Felania, C. 2017. Character of air against the growth of
green beans (Phaseolus radiatus L.). Proceedings of the
National Seminar on Biology and Biology Education,
Department of Biological Education, Faculty of
Mathematics and Natural Sciences, Yogyakarta State
University. 131-138.
Godawatte and Silva. 2014. Effect of Mulch on Soil
Properties, Growth and Yield of Chili (Capsicum
annuum L.) Exposed to Temperature Stress due to
Global Warming. Journal of Engineering and
Technology of the Open University of Sri Lanka
(JETOUSL). 2(2): 15 -28.
Han, Y. O And Q. H. Han. 1995. Effect of wheat straw
mulch on the growth, develo pment and yield of maize.
Acta Agric. Boreali-sinica, 10(1): 106-111.
Huang, H. L, G. M. Zeng, R. Q. Jiang, X. Z. Yuan, M. Yu,
D. L. Huang, J. C. Zhang and C. L. Feng. 2009.
Fluorescence spectroscopy characteristics of humic
acid by inoculating white-rot fungus during different
phases of agricultural waste composting. J. Cent. South
Univ. Technol. 16: 440-443.
Irfany, A., M. Nawawi and T. Islami. (2016). Giving mulch
of rice straw and green fertilizer Crotalaria juncea L.
In the field and yield of maize tambin kretek. Journal of
Plant Production. 4 (6): 454-461.
Irwan, A. W. 2006. Cultivation of Soybean (Glycine max
(L.) Merril). Thesis. Padjadjaran University. Bandung.
Lakitan B. 2007. Basics of Plant Physiology. Raja
Grafindo Persada. Jakarta.
Marliah, A., Nurhayati and D. Suliwati. 2011. Effect of
organic fertilizer and organic mulch on growth and
yield of soybean (Glycine max (L.) Merrill). Floratek
Journal. 6 (2): 192-201.
Pauza, N. M. 2016. Effect of tillage systems and application
of bagasse mulch on carbon biomass of soil
microorganisms (c-mic) on the 5th year of sugarcane
(Saccharum officinarum L.) planting area. Thesis.
University of Lampung. Bandar Lampung.
Government Regulation of the Republic of Indonesia
Number 57 Year 2016 concerning Amendments to
Government Regulations Number 71 of 2014 in 2014
concerning Protection and Management of Peat
Ecosystems. Jakarta.
Setyanti, Y. H., S. Anwar and W. Slamet. 2013.
Photosynthetic characteristics and forage phosphate
uptake of alfafa (Medicago sativa) at different nitrogen
cutting and fertilizing heights. Animal Agriculture
Journal, 2 (1): 86-96.
Suwondo. 2002. Composition and diversity of soil
microartropods as bioindicator of biological
characteristics on peat soil. Thesis. University of Riau,
Pekanbaru.
Tie, Y.L., dan J.S. Lim. 1992. Dalam:Tropical Peat,
Proceedings of the International Symposium on
Tropical Peatland, Kuching. Malaysia. hal. 107-113.
Zainal, M., A. Nugroho and N. E. Suminarti. 2014. Growth
response and yield of soybean (Glycine max (L.) Merill)
at various levels of N fertilization and chicken manure.
Journal of Plant Production. 2 (6):
484-490.
ICMR 2018 - International Conference on Multidisciplinary Research
164
