
Antecedents of Employee Performance of Conventional Taxi Driver
in Medan
Anggia Sari Lubis and Sari Wulandari
Departement of Management, Faculty Economy, Universitas Muslim Nusantara Al-Washliyah, Medan, Indonesia
Keywords: Adversity Quotient, Work Stress, Employee Motivation, Job Performance, Taxi Company
Abstract: As an important source of human resource management, job performance is considered by most scholars
and practitioners a must for contemporary organisations and and become a topic that is often discussed. In
this vein, organisational members should and must provide the best quality of work for the organization to
achieve the goals of the organization Various scholars have emphasized the value of identifying and
understanding the factors contributing to job performance. The purpose of this research is therefore to
investigate the factors fostering job performance. We have developed a conceptual model and tested it with
an empirical study based on a sample of 253 participants from conventional taxi driver in Medan City. The
results reveal that adversity quotient and work stress have positive impacts on job performance.
Furthermore, employee motivation is an intervening variable from the effect between adversity quotient and
work stress to job performance. These findings offer a new framework for developing further studies on job
performance, as well as important practical implications for managers especially for conventional taxi
company .
1 INTRODUCTION
The presence of online taxi-based applications in
Medan City has resulted in the reduction of
conventional taxi passengers. This is because the
fare of online taxi-based applications is lower than
that of conventional taxi. In addition, passengers
using online applications are also provided with ease
in the process of booking a taxi as the passengers
can easily order a taxi by using the application on
the smartphone, and in just a few minutes waiting
time, the passengers have been picked up by taxi-
based online applications. The circumstances
described in the preceding paragraph lead to a
decrease in the performance of conventional taxi
drivers. Yet if the performance achieved by
conventional taxi driver is good, it will ultimately
contribute to the performance of the company.
Employees’ performance is influenced from internal
and external enviroment of people,such as locus of
control , tolerance for ambiguity, business strategy
and corporate culture, business environment and
changing in the economic conditions (Desmond,
2007).
Other research results show that employee
performance is also influenced by human resource
practice consisting of job security, organizational
support and physicological contract (Latorre, Guest,
Ramos, & Gracia, 2016). The Adversity Quotient
(AQ) means to measure people’s capacity to respond
to and surmount adversity (Stoltz, 1997). Workers
with a high Adversity Quotient will have lower job
stress. AQ concept can predict the power and
focused of a person and can be used to enhance the
effectiveness of teams, relationships, families,
communities, cultures, societies and organizations
(Phoolka & Kaur, 2012). Based on the problems
that occur in conventional taxi drivers in Medan
City, job stress is one of the factors causing the
reduction of employees’ performance. Based on the
results of research, one of the factors that cause
work stress is the extrinsic rewards satisfaction
(Elmadağ & Ellinger, 2017). Job stressors involving
a range of stakeholders, either internally (eg,
employees, suppliers, financial agencies) are directly
and indirectly related (through the feeling of
loneliness) to burnout (Fernet, Torrès, Austin, & St-
Pierre, 2016). Motivation of work has become a long
concept in determining high employee performance.
Employees' motivation representing a key factor that
determines their own objectives (Rusu & Avasilcai,
2014). The object of this research is the conventional
284
Lubis, A. and Wulandari, S.
Antecedents of Employee Performance of Conventional Taxi Driver in Medan.
DOI: 10.5220/0008884002840290
In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Multidisciplinary Research (ICMR 2018) - , pages 284-290
ISBN: 978-989-758-437-4
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

taxi drivers in Medan City. No less than 824
conventional taxi drivers from conventional taxi
companies are still active in Medan City. Based on
the above background, this research is intended to
find out the Antecedents of Employee Performance
on conventional taxi drivers in Medan City.
2 THEORETICAL FRAMEWORK
AND HYPOTHESES
Job performance can be referred as the duties and
responsibilities that are performed as part of an
individual's job assignments (Vigoda, 2000). It
reflects organizational performance (Wall et al.,
2004 and Gomez-Mejia, Balkin, & Cardy, 2007).
Adversity quotient is a concept of intelligence raised
by Paul G. Stoltz to measure how a person's
responses to a problem or obstacle to be utilized as
an opportunity. Adversity quotient emphasizes the
element of adversity as a determinant of one's
success. Adversity quotient informs individuals
about their ability to deal with adversity and the
ability to overcome them, to forecast capable and
incapable individual to cope with adversity, to
predict those who will be able and who will fail to
achieve expectations of performance and potential ,
and predict individuals who will surrender and who
will survive in the face of adversity. Stoltz (2000) in
Phoolka (2012) states that a person who has the
ability to survive and continue to struggle with
perseverance, full of motivation, enthusiasm,
ambitious, keeping the spirit when faced with a
problematic life is seen as a figure that has a high
Adversity quotient, meanwhile a person who
surrenders easily, to fate, and becomespessimistic
and has a tendency to be negative when faced with a
difficulty is seen as individual who has low levels of
Adversity quotient. Stoltz (2000) in Shen (2014)
proposes several factors necessary to change the
failure into an opportunity: competitiveness,
productivity, creativity, motivation, risk,
perseverance, learning, embrace change, and
perseverance. Indicators of adversity quotient
variables include the ability to control difficulties
(control), the ability of individuals to identify the
emergence of difficulties (origin), the ability of
individuals to face difficulties and not to repeat
(reach) and to know the duration of facing adversity
(endurance) (CORE). According to Phoolka & Kaur
(2012) Adversity Quotient can be used to predict
employee performance, motivation, creativity, and
productivity of an employee within a company.
Baron and Greenberd in Mardiana (2002),
defines stress as emotional and psychological
reactions that occur in situations where individual
goals get blocked and cannot cope with them.
According to Ramzan (2013), work stress affects job
satisfaction of an employee that ultimately affects
the performance of employees as a whole. From the
description above it can be concluded that the
occurrence of work stress is due to an imbalance
poinst between employee personality characteristics
and characteristics of aspects of work and this can
occur in all conditions of work. Indicators of work
stress that can be used as a reference to know the
stress caused by work, include Roles in the
organization, Workload, career development,
Relations in Work, and Structure and Climate of
Organizations.
Munandar (Munandar, 2009) states that
motivation is a process which needs to encourage a
person to carry out a series of activities to achieve
his goals. While in a large dictionary of Indonesian
(KBBI) motivation is the impulse that arises in a
person consciously or unconsciously to perform an
action with a specific purpose. Motivation of work is
the incentive and desire that is in man to carry out
his job duties well (Umar, 2013). Motivation of
work is an impulse that exists within a person to
carry out his duties well so that his goals are
achieved. Indicators of work motivation in this study
uses the theory of Herzberg in Slamet (2007):
Relationship with colleagues and superiors, Work
environment, Opportunity to increase knowledge
and skills and Provision of benefits.
Figure 1: Conceptual model and hypotheses.
2.1 Effect of Adversity Quotient on
Employee Performance
AQ is something in addition of IQ and EQ that
shares some commonalities with hardiness and
resilience. Adversity Quotient is a form of
intelligence that backs the success of someone who
in this case is a conventional taxi driver in the face
of challenges in the event of difficulties such as
difficulty to get passengers which is a necessity
because the level of income that will be obtained by
conventional taxi drivers depends on the number of
Antecedents of Employee Performance of Conventional Taxi Driver in Medan
285

passengers they serve. According to Phoolka & Kaur
(2012) Adversity Quotient can be used to predict
employee performance, motivation, creativity,
productivity of an employee within a company.
H1: There is a direct positive effect of adversity
quotient on the performance of conventional taxi
drivers in Medan City.
H2: There is an indirect positive influence of
adversity quotient on the performance of
conventional taxi drivers in Medan City.
2.2 Effect of Job Stress on Employee
Performance
Situational constraints can affect the performance,
satisfaction, and stress experienced by employee.
(Lapidus, Roberts, & Chonko, 1997). Based on the
research that is conducted by Wani (2013) it is stated
that there is a significant influence in work stress on
employee work motivation. Research conducted by
Awadh et al (2015) shows a result that as much as
44.8% work stress variables can explain the effect
on employee performance. Indicators for measuring
job stress include organizational roles, workload,
career development, relationships in work and
organizational structure and climate.
H3. There is a direct positive effect of job stress
on the performance of conventional taxi drivers in
Medan City.
H4. There is an indirect effect of job stress on the
performance of conventional taxi drivers in Medan
City.
2.3 Effect of Employee Motivation on
Job Performance
Munandar (2009) states that motivation is a process
by which there is a need to encourage a person to
carry out a series of activities to achieve the goals.
While in a large dictionary of Indonesian (KBBI)
motivation is the impulse that arises in a person
consciously or unconsciously to perform an action
with a specific purpose. Motivation of work is the
incentive and desire that is in man to carry out his
duties well (Umar, 2013). Motivation of work is an
impulse that exists within a person to carry out his
duties well so that his goals are achieved. Indicators
of employee motivation in this study uses the theory
of Herzberg in Slamet (2007): Relationship with
colleagues and manager, Work environment,
Opportunity to increase knowledge and skills and
Provision of benefits.
H5: There is a direct positive effect of employee
motivation on the performance of conventional taxi
drivers in Medan City.
2.4 Methodology
The research uses questionnaire (quantitative
research) in order to measure the influence of
adversity quotient, job stres, employee motivation
and job performance. The questionnaire is from
(Phoolka&Kaur,2012) in regard to the statements
used in the adversity quotient measurement.
Questionnaires benefited from the studies of
(Lapidus, Roberts, & Chonko, 1997) in regard to the
statements are used in job stres measurement.
Questionnaires benefited from the studies of
(Onanda,2015) in regard to the statements are used
in the employee motivation measurement. And
Questionnaire benefited from the studies of (Ali
Ahmad & Tang, 2017) in regard to the statements
are used in job performance measurement.
Adversity quotient is measured with 12 statements,
job stres with 14 statements, employee motivation
with 12 statement. and job performance with 15
statements. A five-point Likert-type scale is used for
all statements in this section.
2.4.1 Data Collection and Sample
The present study is carried out on taxi driver in
Medan. Questionnaires are delivered to 4 taxi
companies in Medan with sample size of 265
Respondents selected with convenience sampling.
2.4.2 Data Screening and Analysis
Path Analysis (Path Analysis) (Sugiyono ,2007)
show the development of linear regression analysis.
Regression analysis is a special form of path
analysis. Path analysis is used to illustrate and test
the model of relationship on the variables in the
form of cause and effect. The path model is a
diagram of independent, intermediate and dependent
variables. Pattern relationship is shown by using
arrows. Single arrows show a causal relationship
between exogenous variables or intermediaries with
one or more dependent variables. The arrows also
connect the error (variable residue) with all
endogenous variables respectively.
There are two dependent variables in the model:
Y1 and Y2. Consequently, there are two dependent
equations: Equation 1 showing the overall Work
Motivation (Y1) relationship with two variables (X1,
X2), and the second two equations showing the
ICMR 2018 - International Conference on Multidisciplinary Research
286
performance relationship (Y2) with three variables
(X1, X2, Y1).
Regression Equation:
Y1 = b1X1+b2X2+e1
Y2 = b1X1+b2X2+b3Y1+e2
Remarks:
Y1 = dependent variable (employee motivation)
Y2 = dependent variable (performance of
conventional taxi driver)
b1 = regression coefficient of adversity quotient
b2 = regression coefficient of work stres
X1 = independent variable (adversity quotient)
X2 = independent variable (work stres)
e = Factors beyond Effect generated from the above
path model can be written as follows:
a. Direct Effect
i. effect of adversity quotient on job performance
X1 Y2 = ρy2x1
ii. effect of adversity quotient on employee motivation
X1 Y1 = ρy1x1
iii.effect of work stres on job performance
X2 Y2 = ρy2x2
iv. effect of eork stres on employee omtivation
X2 Y1 = ρy1x2
b. Indirect Effect
i. The effect of adversity quotient variable on performance
through employee motivation
X1 Y1 Y2 = (ρy2x1) x (ρy2y1)
ii. The effect of work stress variable on performance
through employee motivation
X2 Y1 Y2 = (ρy2x2) x (ρy2y1)
c. Total Effect
i. The influence of adversity quotient variable on performance
employee motivation
X1 Y1 Y2 = ρy2x1 + ( ρy2x1) x (ρy2x1)
ii. The effect of work stress variable on performance
through employee motivation
X2 Y1 Y2 = ρy2x2 + (ρy2x2) x (ρy2y1)
3 RESULT AND ANALYSIS
3.1 Reliability and Validity
First, this research applies item analysis to measure
the relevance of each questionnaire item. The results
show that the research variables (i.e. adversity
quotient, job stress employee motivation, and job
performance) are appropriate. Second, exploratory
factor analysis is employed and questionnaire items
which have not reached the standard for factor
selection are deleted.
3.2 Multiple Regression Analysis
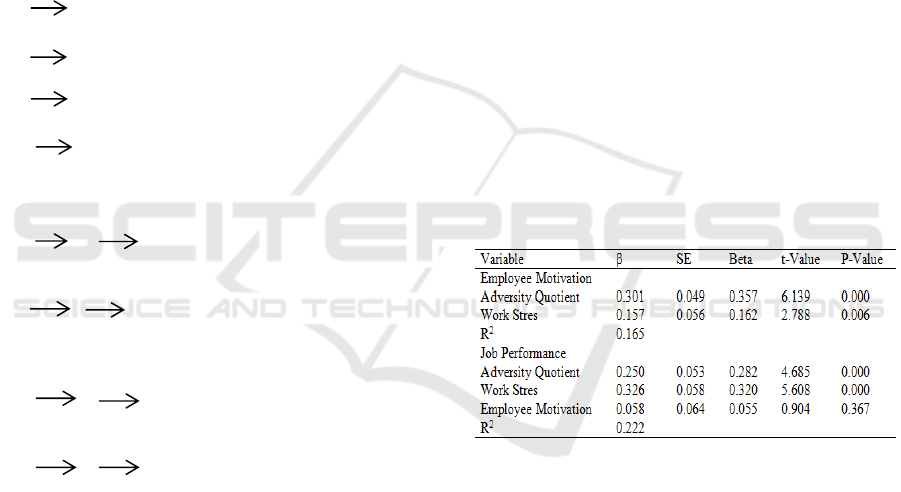
The multiple-regression analysis for adversity
quotient and job stres on employee motivation; and
adversity quotient, job stres and employee
motivation on job performance, are shown in Table
I. The b values for adversity quotient and job stres
on job performance are 0.267 and 0.335,
respectively. The β values for adversity quotient, job
stres and employee motivation on job performance
are 0.363 and 0.530, respectively. The β values for
adversity quotient, job stres and employee
performance on job performance are 0.250, 0.326,
and 0.058, respectively. The variables show a
positive significant relation between adversity
quotient and job stres. And only employee
motivation shows a positive but not significant
relation . The adjusted R2 are 0.213, and 0.165,
respectively. The explained variation for all
variables are not high. Therefore, it means that
adversity quotient and job stres will not have
significant effects on job performance; adversity
quotient, job stres and employee motivation will not
not have significant effects on job performance
either.
Table I: The Multiple Regression Analysis.
Based on the Table I The model is Y1 =
30,7878 + 0,301 X1 + 0,175 X2 (where y is
employee motivation, X1 is adversity quotient, X2 is
job stres). Adversity quotient shows a positive
significant relation. And job stres shows a positive
but not significant relation. The adjusted R
2
is 0.165
and the explained variation for all variables is not
high. Therefore, it means that adversity quotient and
job stres will have a positive and not significant
effects on job performance.
The second model is Y2 = 57,381 + 0,250 X1 +
0,326 X2 + 0,058Y1 + e2. (where y is job
performance, X1 is adversity quotient, X2 is job
stres and Y1 is employee motivation). Adversity
quotient and work stres show a positive significant
relation. And employee motivation shows a positive
but not significant relation. The adjusted R
2
is 0.222
Antecedents of Employee Performance of Conventional Taxi Driver in Medan
287

and the explained variation for all variables is not
high. Therefore, it means that adversity quotient and
job stres and employee motivation will have a
positive and not significant effects on job
performance.
3.3 Testing the Intervening Effects of
Employee Motivation
The multiple-regression analysis for adversity
quotientm work stres and employee motivation on
job performance is shown in Table I. As indicated in
these tables, the β value, Beta value, t-value and all
other values achieve a positive level. Based on
Tables I, it is found that the standardized coefficient
of adversity quotient, work stres and employee
motivation on job performance is 0.282, 0.320 and
0.055. The path coefficient for employee motivation
on job performance decreases from 0.058 to 0.055,
showing that employee motivation is an intervening
variable on job performance. Furthermore, this
implies that the influence of adversity quotient and
work stres on job performance during the process
will partially affect employee motivation and then in
turn, will affect the job performance.
3.4 Path Analysis
Path analysis (PATH Analysis) in this research can
be described as in the following figures:
Figure 2: Path Analysis Result.
The direct, indirect and total effect can be seen
in Table 2 below:
Table 2: Direct, Indirect, Total Effect.
Based on calculations on Table 2, the calculation
of indirect effect is obtained from multiplication of
direct performance coefficient AQ to employee
motivation, with influence of employee motivation
to performance (0,465x0,359) = 0,166935. The same
calculation is also for work stress variable. The total
effect is gained by summing up the direct and
indirect effects. Based on the results it is seen that
the values of both direct and indirect impact of
adverity quotient and work stres on job performance,
adversity quotient and work stres possess significant
influence on job performance. Therefore, if a
company would like to enhance job performance, it
has not only to improve the employee motivation but
also to manage the adversity quotient and work stres
for employee so that it is possible to effectively
enhance overall performance.
3.5 Discussion and Implication
The results of this study indicate that adversity
quotient and work stres are significantly affect the
employee motivation and job performance.
According to the result of the multiple regression
analysis (Table I), there is a significant positive
effect between adversity quotient and work stres
with employee motivation and job performance.
Moreover, the factors of adversity quotient show a
significantly positive affect with employee
motivation and job performance. This means that if
the adversity quotient and work stres are superior, it
can significantly enhance employee motivation and
organizational performance. This study further
shows that the β value of adversity quotient is more
than the work stres, particularly shown in Table I.
This implies that the adversity quotient can
effectively enhance employee motivation and job
performance compared to work stres. Thus there
should be an endeavor to attract and encourage their
employees to participate in facing the adversity
situation and work stres situation, as well as enhance
their employee motivation and job performance,
particularly adversity quotient. For example, AQ can
be useful to predict performance, motivation,
empowerment, creativity, productivity, learning,
energy, hope, happiness, vitality, emotional health,
physical health, persistence, resilience, attitude,
longevity and response to change.
(Phoolka&Kaur,2012). Furthermore, a firm should
allow their employees to have the ability to face the
adversity situation, solve problems, and to have the
ability to face the work stres situation.
Based on the results of the path analysis, it is
found that adversity quotient and work stres possess
direct influence to enhance job performance;
moreover, employee motivation is also indirectly
ICMR 2018 - International Conference on Multidisciplinary Research
288

interrelated in terms of enhancing job performance.
This shows that a taxi driver possesses better
management in the adversity quotient and work
stres. Dr. Stoltz in (Phoolka&Kaur,2012) shows that
team conducting research with sales employees of
SBC Telecommunication finds that sales persons
with high AQ scores sells more than those with low
AQ. In another study conducted at Deloitte and
Touche, the team finds that AQ of top performers
exceeds the AQ of low performers by 17 points
which indicate AQ can be a measure of employee
performance. By giving AQ training to the
employees, AQ of the employees can be improved.
Companies like SunTrust measures the AQ of every
applicant before hiring him/her.
4 CONCLUSION
Despite of the belief that adversity quotient and
work stres decrease the job performance and
employee motivation increases job performance,
researchers have attempted very little theoretical
work on the development of relationships among
adversity quotient, work stres, employee
motivation, and job performance. As such, this study
investigates the affect among adversity quotient,
work stres, employee motivation and job
performance. The results indicate that employee
motivation is not an important intervening variable
on employee(in this research a taxi driver). A
research done in Malaysia recommends that there is
a need for employers to restructure the methodology
for training employees on soft-skills (Ibrahim,
Boerhannoeddin, & Kazeem Kayode, 2017).
Another research related to job performance
states that High commitment HR practices are
related to employee performance through the
mediating effect of perceived organizational support,
a fulfilled psychological contract and job security, as
key features of the employment relationship, and job
satisfaction (Latorre et al., 2016). Another variable
that affects job performance is customer orientation
(Boles, Babin, Brashear, & Brooks, 2001). Job
performance is a behaviour that is consistent with
organizational objectives and is generally assessed
on the basis of employees’ achievement of these
objectives. Participative leadership, instrumental
leadership, satisfaction with supervisor, turnover
intentions, and work effort are variables that affect
job performance (Mulki, Caemmerer, & Heggde,
2015).
This research applies a convenience sampling
method and obtains enough number of respondents.
Therefore, it is suggested that future researchers
should apply another sampling method to collect
more responses to increase the generalizability. On
the other hand, a regression analysis method is
applied to simplify the research framework and to
investigate the affects among adversity quotient,
work stres, employee motivation and job
performance. Hence, it might be more difficult to
explain the overall model of this research. It is
suggested that future researchers should apply the
structural equation model to further verify the model
in order to simplify the elaboration of the research
structure.
REFERENCES
Ahmed,Ashfaq, Dr. Muhammad Ramzan. Effects of Job
Stress on Employees Job Performance A Study on
Banking Sector of Pakistan. IOSR Journal of Business
and Management (IOSR-JBM) e-ISSN: 2278-487X, p-
ISSN: 2319-7668. Volume 11, Issue 6 (Jul. - Aug.
2013), PP 61-68
Ali Ahmad, B., & Tang, N. (2017). Transformative HR
practices and employee task performance in high-tech
firms: The role of employee adaptivity. Journal of
Organizational Change Management, 30(5), 710-724.
doi: 10.1108/JOCM-02-2016-0030
Awadh, Alharbi Mohammad. 2013. Organizational
Corporate Culture on Employee Performance.
International Review of Management and
Business Research.Vol. 2 Issue. 1.
Boles, J. S., Babin, B. J., Brashear, T. G., & Brooks, C.
(2001). An examination of the relationships between
retail work environments, salesperson selling
orientation-customer orientation and job performance.
Journal of Marketing Theory and Practice, 9(3), 1-13.
Desmond, Y. (2007). Antecedents of budgetary
participation: enhancing employees' job performance.
Managerial Auditing Journal, 22(5), 533-548. doi:
10.1108/02686900710750793
Elmadağ, A. B., & Ellinger, A. E. (2017). Alleviating job
stress to improve service employee work affect: the
influence of rewarding. Service Business. doi:
10.1007/s11628-017-0340-y
Fernet, C., Torrès, O., Austin, S., & St-Pierre, J. (2016).
The psychological costs of owning and managing an
SME: Linking job stressors, occupational loneliness,
entrepreneurial orientation, and burnout. Burnout
Research, 3(2), 45-53. doi:
10.1016/j.burn.2016.03.002
Ibrahim, R., Boerhannoeddin, A., & Kazeem Kayode, B.
(2017). Organizational culture and development:
Testing the structural path of factors affecting
employees’ work performance in an organization. Asia
Pacific Management Review, 22(2), 104-111. doi:
10.1016/j.apmrv.2016.10.002
Antecedents of Employee Performance of Conventional Taxi Driver in Medan
289

Lapidus, R. S., Roberts, J. A., & Chonko, L. B. (1997).
Stressors, leadership substitutes, and relations with
supervision among industrial salespeople. Industrial
Marketing Management, 26(3), 255-269. doi:
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0019-8501(96)00093-4
Latorre, F., Guest, D., Ramos, J., & Gracia, F. J. (2016).
High commitment HR practices, the employment
relationship and job performance: A test of a
mediation model. European Management Journal,
34(4), 328-337. doi: 10.1016/j.emj.2016.05.005
Mbarak Ibtisam, Lucy Gichinga and Dr. Anwar Hood
Ahmed. Effects of Workplace Stress on Employee
Performance in the County Governments in Kenya: A
Case Study of Kilifi County Government.
International Journal of Scientific and Research
Publications ISSN 2250-3153, Volume 5, Issue 10,
October 2015
Mulki, J. P., Caemmerer, B., & Heggde, G. S. (2015).
Leadership style, salesperson's work effort and job
performance: the influence of power distance. Journal
of Personal Selling & Sales Management, 35(1), 3-22.
doi: 10.1080/08853134.2014.958157
Phoolka, Er. Shivinder , Dr. Navjot Kaur. ADVERSITY
QUOTIENT: A New Paradigm in Management to
Explore. The International Journal`s Research Journal
of Social Science and Management ISSN 2251-1571
Volume:02 Number: 07, November 2012
Rusu, G., & Avasilcai, S. (2014). Linking Human
Resources Motivation to Organizational Climate.
Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences, 124, 51-
58. doi: 10.1016/j.sbspro.2014.02.459
Shen, Chao-Ying. The Relative Study of Gender Roles,
and Job Stress and Adversity Quotient . The Journal of
Global Business Management Volume 10 * Number 1
* April 2014 issue.
Stoltz, P. G. 2007. Adversity Quotient @ Work (Alih
Bahasa: Drs. Alexander Sindoro). Batam:
Interaksara
ICMR 2018 - International Conference on Multidisciplinary Research
290
