
Development of Learning Instruments based on Scientific Approach
to Low Animal Taxonomy Courses for Students of Biology Study
Program at FKIP UISU
Budianto and Pandu Prabowo Warsodirejo
Biology Education Department, Faculty of Teacher Training and Education Science, UISU, Medan
Keywords: Instrument Development, Assessment, Scientific Approach, Low Animal Taxonomy
Abstract: In achieving good learning outcomes, assessment of student learning outcomes should be supported by good
assessment of instruments as well. Assessment of student learning outcomes is designed to add information
for lecturers, students, and parents of students about the advantages and disadvantages of educational
development. Based on the results of the analysis, 3 out of 5 lecturers still find it difficult or even unable to
make a good assessment instrument and to see student learning outcomes. Many professors often like to
provide a possible assessment on the basis of many factors. The cause of the difficulties in making the
assessment instrument is that too many students need to be observed at one time, and it takes a considerable
amount of time to develop judgment instruments, and the aspects and attitudes of skills are difficult to
observe. This is in accordance with the findings in the field that the lecturers do not assess the student's
learning outcomes on an ongoing basis between aspects of attitude, knowledge, and skills. To overcome
this, the development of student learning achievement assessment instrument is done on the basis of
scientific approach as a reflection of curriculum of KKNI or national curriculum.
1 INTRODUCTION
Assessment is one of the eight national education
standards. Assessment has several principles in its
implementation. Principles of assessment of student
learning outcomes are described in the Regulation of
the Minister of Education and Culture of the
Republic of Indonesia No. 23 of 2016 on Education
Appraisal Standards. (Ministry of National
Education, 2006). Some of the principles described
are valid, objective, comprehensive, and sustainable.
Overall, the assessment of students' learning
outcomes is expected to include continuity of all
aspects of competence, namely attitude (affective),
knowledge (cognitive) and skills (psychomotor)
which not only measure the results or what is known
to the students but also the process or what the
student has done during the learning process. Aims
are to be made to improve students' understanding
based on clear procedures and criteria. (Frey et al:
2012)Assessment of student learning outcomes is
important. This assessment can help add information
on lecturers, parents, students and students
themselves about the advantages and disadvantages
of each individual. In the Attachment to the
Regulation of the Minister of Education and Culture
of the Republic of Indonesia Number 104 Year 2015
on Learning in Higher Education, Curriculum of
KKNI uses scientific approach or science-based
approach. Stages in the scientific approach is 5Ms
that is, observing, asking, gathering information,
reasoning / associating, and communicating. This is
suitable with Biology Study Program of Low
Veterinary Taxonomy as a subject that requires the
ability of thinking and the skills of the process of
science in learning it. Low Veterinary Taxonomy is
expected to foster curiosity as well as the ability and
skills of students in obtaining scientific products. To
find out the extent of students’ ability, lecturers can
make an assessment by making an assessment of
learning outcomes based on a scientific approach.
However, the results of the survey on the analysis of
the needs of the assessment instrument of student
learning outcomes in the Low Animal Taxonomy are
obtained from two Lecturers of Biology Study
Program. Of the two respondents, one expresses
difficulties in making an instrument of student
learning outcomes. This is consistent with the result
310
Budianto, . and Warsodirejo, P.
Development of Learning Instruments based on Scientific Approach to Low Animal Taxonomy Courses for Students of Biology Study Program at FKIP UISU.
DOI: 10.5220/0008884403100314
In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Multidisciplinary Research (ICMR 2018) - , pages 310-314
ISBN: 978-989-758-437-4
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

of the statement that only two respondents use the
skill aspect as an assessment of learning outcomes.
Factors that cause lecturers to have difficulty in
making the instrument of student learning outcomes
are too many students need to be examined at one
time, and it takes time in making the instrument of
student learning result assessment and attitude
aspect as well as skill aspect. Stages in the
assessment of student learning outcomes, are from
four respondents. One does not use scientific
approach stages and the other two only use a few
stages only. Of all the respondents, two lecturers of
Biology want an assessment instrument of student
learning outcomes of attitude aspects with self-
assessment techniques to be developed. The gap
between student learning outcomes based on what is
written in government regulations and ministerial
regulations with what is happening at campus,
requires the development of a valid and reliable
learning assessment instrument. Because the
assessment of learning outcomes must be continuous
between aspects of attitude, knowledge, and skills.
The researcher develops the students' learning
achievement instrument based on the scientific
approach on the study of Low Animal Taxonomy.
2 METHODOLOGY
The instrument development procedure is based on
research and development (ADDIS). Steps of the
ADDIE model are Analysis, Design, Development,
Implementation, and Evaluation. The ADDIE model
is the simplest model but covers overall
development. Here is an ADDIE model scheme.
Image Schema Model of ADDIE
Research is still underway at the design stage. After
conducting need analysis and literature study, the
researcher makes the instrument of student learning
achievement of three domains. For the affective
domain, the researcher creates a self-assessment
sheet based on eighteen values of the nation's
character by adapting the scientific approach and
Core Competency 1 and Core Competence 2. For the
cognitive domain, the researcher makes a structured
description based on factual, conceptual, procedural,
and metacognitive knowledge on matter of heat. For
the psychomotor domain, the researcher makes a
assessment sheet based on the scientific stage of the
scientific approach that is 5M, observing, asking,
gathering information, reasoning / associating, and
communicating. (Enger and Yager, 2000)
One instrument that can measure the ability of
good knowledge of students and the skills to carry
out activities authentically and scientifically is an
instrument in the form of items of activity that must
be done directly by students. Instrument is equipped
with assessment rubrics in accordance with the
components of scientific activity and assessment
guidelines. Assessment during the learning process
based on the 2013 curriculum is not separated from
the learning process and carried out applying the
scientific approach. Therefore the assessment of
achievement of the three domain of competence, is
also necessary done on students' abilities to carry out
scientific activities through the process learning with
a scientific approach. To measure the competency of
students in terms of knowledge and skills, tools are
needed for measurement to describe the scientific
activities. Instrument prepared by the lecturer to
measure students’ competency in general is in the
form of objective tests to measure the ability of
students in the mastery of material tested only. Skills
for conducting scientific activities cannot be
measured through objective questions developed.
Therefore measuring instrument is necessary to
know the knowledge of students, and to measure the
skills of students in doing scientific activities
authentically.
Authentic assessment is seen as the most
suitable model, complete, and objective, and has
been used in various countries and fields. Lowery
(2003), explains that school teachers in Texas
intensively are trained to have skills in composing
and applying authentic assessment instruments in
learning. Various types of instruments have been
developed by researchers, educators and education
practitioners.
3 RESULT
The result of the research consists of a self-
assessment sheet with check list, an assessment
instrument in the form of structured questions, and a
practical assessment sheet. Here is a grid of
assessment instruments developed by researchers.
Development of Learning Instruments based on Scientific Approach to Low Animal Taxonomy Courses for Students of Biology Study
Program at FKIP UISU
311
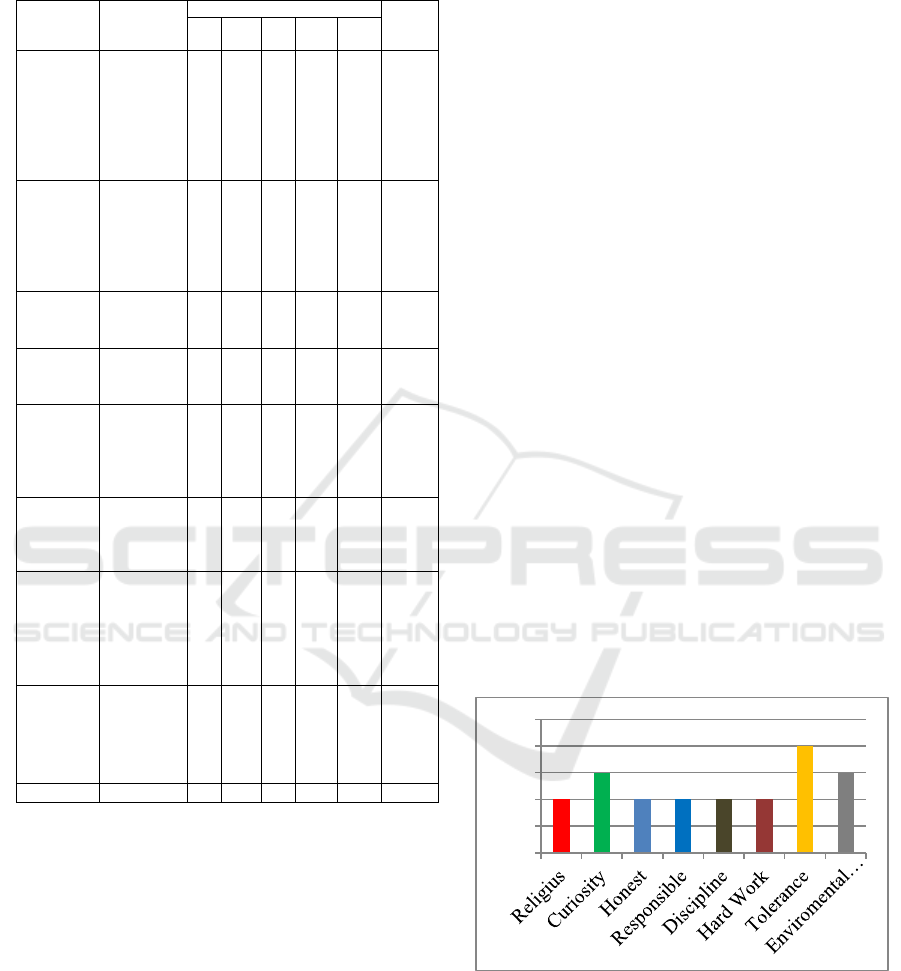
Table 3.1: Grid of the Assessment Instrument for
Students' Learning of Affective Range.
Rated
Aspect
Indicator
Affective sta
g
e Amo
unt
A
1
A2 A
3
A4 A5
Religion
Students
perform
actions
based on
religious
teachings
embraced
2,1
7
2
Curiosity
Students
perfect
the
knowledg
e they
have
4,7
,8
3
Honesty
Students
show the
wor
k
13,
20
2
Responsi
bility
Students
complete
the tas
k
5,1
8
2
Discipline
Students
fulfil their
duties
with
coherence
3,6 2
Hard
Work
Students
do their
job
seriously
9,1
9
2
Tolerance
Students
hear the
opinions
of others
1,
1
0,
1
1,
1
2
4
Envirome
ntal Care
Students
initiate
environm
ental
awareness
1
4,
1
5,
1
6
3
Amount
4 4 3 3 6 20
The following aspects are assessed on the lattice of
student learning outcomes in the cognitive domain :
1. Factual:
has the following indicators:
a. students mention one of Avertebrate phylum and
its species example
b. students mention the tools used to observe
species from protozoan phyla
c. students explain the process of vegetative
propagation from one of the invertebrate phylum
2. Conceptual:
has the following indicators:
a. students explain the species life cycle of
invertebrate phyla
b. students explain the negative impact that aquatic
species can inflict on humans
c. students can explain the basic sequence of
classification levels of taxon
d. students explain the special features of each
phylum of invertebrates
e. students explain the function or usefulness of
every phylum for human life
f. students describe the characteristics of each class
of every invertebrate phyla
3. Procedural:
has the following indicators:
a. students sort the procedure of field practice work
b. students sort the process of observing the sample
species of each phylum in the laboratory.
4. Metacognitive:
has the following indicators:
Students complete a chassis study and pour it into a
paper report prepared by each group.
In the process of assessing student learning
outcomes in the cognitive domain the assessment
process Bloom's Taxonomy C1 to C6 is used.
Instrument has 20 item test questions and is divided
into:
C1 : 5 items
C2 : 1 item
C3 : 6 items
C4 : 5 items
C5 : 2 items
C6 : 1 item
Student learning outcome assessment instruments
are still in the development stage towards validation
and reliability tests. In the lattice of assessment
instrument Learning Outcomes of Affective Domain
students have several aspects, namely:
1. Religion with indicators that students take actions
based on the teachings of their religion.
2. Curiosity with indicators that students perfect
0,00
1,00
2,00
3,00
4,00
5,00
ICMR 2018 - International Conference on Multidisciplinary Research
312

their knowledge 3. Honesty with indicators that
students show the work based on what is done
4. Responsibility, students complete tasks that
should be done 5. Discipline, students fulfil the task
coherently 6. Hard Work, students do their work
seriously 7. Tolerance, students hear other people's
opinions 8. Caring for the Environment, students
initiate concern for the environment. As an example
of one aspect of the scientific stage in the
Psychomotor realm instrument is the stage of
gathering information. At this stage we can use the
assessed aspects as follows: a) Instruments / tools
used to collect data. b) Validity of information
collected. c) processing linkages between various
types of facts or concepts or theories. From these 3
aspects we can take a number of indicators, namely
1) students can use the right tools in making
measurements, 2) students operate the tool
repeatedly to get valid results 3) students construct
the interrelationship between collected taxonomy of
invertebrates
4 ANALYSIS
From the result of the Wilcoxon Signed Ranks Test,
it is analyzed that the alpha value of both groups are
less than 0.05. The Test Statistics shows that the
alpha value at Asymp.Sig. (2-tailed) of group A
(social class) is .001, and the alpha value of group B
(physics class) is .000. This result means that the
hypothesis is rejected. In other words, there is
significant difference of the students’ score before
and after the short course. Based on the score before
and after the short course of both groups, it is
analyzed that the score of the students in group A
(social class) increases up to 31.5 %, and the score
of the students in group B (physical class) also
increases up to 28.2 %. The assessment
instrument that is made is intended for the students
of Biology Education Study Program of Low
Animals Taxonomy. Instrument development is
done by Research and Development method of
ADDIE model (Analysis, Design, Development,
Implementation, and Evaluation). This research
results in an assessment instrument of learning result
of student’s attitude aspect, in the form of self
assessment sheet with check list based on basic
competence 1.1 one instrument of student learning
result of knowledge aspect in the form of structured
description test based on basic competence 2.1, and
one instrument of student learning result assessment
aspect practical engineering test skills with
checklists based on basic competencies 3.2.
5 CONCLUSION
Development of a Scientific Approach Based
Assessment Instrument on the Material of Low
Animal Taxonomy using the ADDIE model includes
5 processes, namely Analysis, Design, Development,
Implementation, and Evaluation. These five stages
must be sequentially carried out continuously in the
instrument development process in the Low Animal
Taxonomy course. The Low Animal Taxonomy
course itself consists of 9 phyla where this course is
one of the courses in Biology Study Program that
meets the requirements to be chosen as a scientific
approach media. This course is chosen because it
fulfils the requirements for the criteria for the 3
aspects of assessment: attitude, normative, and skill
assessment. The results of the development of an
instrument are one instrument assesses student
learning outcomes in the form of structured
description based on basic competencies in the class,
and an instrument for evaluating student learning
outcomes in technical practice tests in the
laboratory. From the results of the assessment and
development, 8 aspects of the points are assessed
and instruments are obtained amounted to 20 points
per indicator.
RECOMMENDATION
With the development of assessment instruments
based on 3 aspects Affective, Cognitive, and
Psychomotor, it is expected that each lecturer will be
able to develop an assessment instrument based on
the ability of each lecturer. Adjusting to the courses
can enable them to more easily analyze the learning
outcomes obtained by students. Indicators of each
aspect must be considered, as well as the questions
used in the instrument must be in accordance with
the taxonomy of blooms C1 to C6. and levels A1 to
A5. Instrument validation is also needed to ensure
that the instruments used can be measured for their
validity and reliability.
Types of data used in this research development
are quantitative and qualitative. Quantitative data are
obtained from the score from questionnaire
responses from teachers, and test data validity and
reliability. Qualitative data are obtained from
responses and suggestions provided by validation
experts and teachers as practitioners. Development
research is equipped with the use of research
instruments. Instruments are in the form of a
validation sheet by the team material expert and
product design and questionnaire of teacher’s
responses to assessment instruments based on the
Development of Learning Instruments based on Scientific Approach to Low Animal Taxonomy Courses for Students of Biology Study
Program at FKIP UISU
313

scientific payload approach in animal and plant sub-
themes in home environment. In the limited test data
obtained from the teacher's response is a score.
Questionnaire score is analyzed by first making
interval table. Interval distance is calculated by use
of the following formula (Ridwan, 2010): interval =
(highest score - lowest score) / number of interval
and classes after obtaining interval distance. The
classification is determined for the following
teacher’s responses:
9.77 - 12.00: very decent
7.51 - 9.76: feasible
5.26 - 7.50: quite decent
3.00 - 5.25: not feasible
In addition to the teacher's response, data on the
limited test are also obtained from student learning
outcomes used to determine validity and reliability.
Validity and reliability are obtained by using the
product-moment correlation formula (Arikunto,
1999). In the trial of students, the ability of students
to carry out scientific activities can be analyzed
using percentage calculation techniques using the
formula:
Average value = (score obtained / maximum
score) x 100 (Arikunto:2016)
REFERENCES
Arikunto, S. 1999. Prosedur Penelitian (Suatu Pendekatan
Praktek), PT Rineka Cipta: Jakarta.
Branch, Robert Maribe. 2009. Instructional Design: The
ADDIE Approach. Athens.Springer.
Enger ,K.S., Yager,E., dan Robert. 2000. Assesing Student
Understanding In Science. Corwin Press, INC:
California.
Fatonah, S., Suyata, P., Prasetyo, Z. K., 2013, Developing
an Authentic Assessment Model in Elementary
SchoolScience Teaching, Journal of Education and
Practice, Vol.4, No.13, 1-13.
Faizal. 2014. Sukses Mengawal Kurikulum 2013 di SD
(Teori & Aplikasi). Diandra Kreatif. Yogyakarta.
Frey, B. B., Schmitt, V. L., Allen, J. P.,2012, Defining
Authentic Classroom Assessment, Practical
Assessment, Research & Evaluation, Vol 17, No 2, 1–
18.
Lowery, N. V., 2003, Assessment Insights from the
Classroom, Biology Educator, Vol. 13, No. 1, 15–21.
ICMR 2018 - International Conference on Multidisciplinary Research
314
