
Analysis of the Factors Affecting the Capital Structure of a
Manufacturing Company Listed on the Indonesian Stock Exchange in
Moderation by Business Risk
*Puteri Anggi Lubis
1
, Iskandar Muda
2
, and Erlina
2
1
Department of Accounting, Faculty of Economics and Business,University of Sumatera Utara, Indonesia
2
Department of Magister of Accounting, Faculty of Economics and Business,University of Sumatera Utara, Indonesia
Keywords: Capital structure, sales growth, profitability, company growth, company size, business risk.
Abstract: This study aims to examine and analyze the factors that affect the capital structure of manufacturing
companies listed on the Indonesia Stock Exchange in moderation by business risk. The population of this
study are all manufacturing companies listed on the BEI in the period of 2012-2016. 42 companies and
simultaneously are used as a sample. The analysis of the data uses multiple linear regression with eviews
7software. The results showed that simultaneous factors of sales growth, profitability, corporate growth and
firm size significantly influence the capital structurevariable. Company growth and firm size have positive
but not significant effect on capital structure variable. Sales growth and profitability in moderation of
business risks are significant to the capital structure. Company growth and firm size in moderation of
business risk are insignificant to the capital structure.
1 INTRODUCTION
The capital structure has become one of the
important consideration factors in corporate finance.
The capital structure is strongly influenced by the
development of the stock market. The existence of
the stock market has given the company an
opportunity to increase its funding sources.
The company's capital needs can basically be
met from two sources, namely internal sources of the
company and external sources. Internal sources of
funds come from the company, namely Retained
Earnings. Retained Earnings are part of net income
after taxes that are not distributed to the owner of the
company, or any other profits reinvested in the
company. While the source of external funds is the
source of funds coming from outside the company.
External sources of funds can be debt and capital
from the owner of the company. The owners' capital
is obtained by issuing securities. With the issuance
of securities, the public can invest in the company.
The characteristics of a company can influence
the decision on the fulfillment of corporate resources
(Ozkan, 2001). Krisnan and Moyer (Krisnan and
Moyer,1996) in Omran (Omran,2009) studied
capital structure in industrialized countries,
whichdespite having similar economic
characteristics, differed in determining the capital
structure and the variables that influenced it. In the
United States, Japan, Italy, and Germany,
profitability, firm size and growth have proven to
significantly affect the capital structure of those
countries. In the United States, taxes are a
significant determinant.
The above results are not much different from
those of developing countries, such as India and
Indonesia. Bhaduri (Bhaduri,2002) in his research in
India found that the characteristics of companies
such as growth, free cash flow, firm size, product
type, and type of industry affect the company's
capital structure. In Indonesia, Yulianti
(Yulianti,2010) examines the significant variables
on capital structure is the company's characteristics
of profitability, liquidity, and size of the company.
The following will describe some of the reviews
of previous research related to this research:
Herlina (Herlina,2014) who examined the Effect
of Company Size, Profitability, Free Cash Flow
Against Capital Structure at Manufacturing
Companies in BEI. Dependent variable in this
research is Capital Structure whereas independent
variable is Company Size, Profitability and Free
570
Lubis, P., Muda, I. and Erlina, .
Analysis of the Factors Affecting the Capital Structure of a Manufacturing Company Listed on the Indonesian Stock Exchange in Moderation by Business Risk.
DOI: 10.5220/0008890605700577
In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Multidisciplinary Research (ICMR 2018) - , pages 570-577
ISBN: 978-989-758-437-4
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

Cash Flow with technique of Multiple Regression
Model. The results concluded that all independent
variables affect the capital structure.
Nugroho (Nugroho,2006) who examined the
Analysis of Factors Affecting Capital Structure of
Property Companies Go Public In JSE 1994-2004.
Dependent variable in this research is Capital
Structure while the independent variable is
Operating leverage, Liquidity, Asset Structure,
Growth, Price Earning Ratio, Profitability with
Multiple Regression Model technique. The result of
research concludes that Growth, and profitability
have positive effect to capital structure while
Operating Leverage, liquidity and STA have
negative influence.
Saidi (Saidi,2004) who examined the Factors
Affecting the Capital Structure of Manufacturing
Companies Go Public in JSE 1997-2002. Dependent
variable in this research is Capital Structure whereas
independent variable is company size, business risk,
asset growth, profitability and ownership structure
with Multiple Regression technique. The result of
this research concludes that firm size, asset growth,
profiability and ownership structure have an effect
on capital structure while business risk has no
significant effect on capital structure.
Rachmawadani (Rachmawadani,2007) who
studied about Analyzing the Influence of Liquidity
Aspects, Business Risk, Profitability, and Sales
Growth on Capital Structure. Dependent variable in
this research is Capital Structure while the
independent variable is liquidity aspect, business
risk, profitability, and sales growth with Multiple
Regression and Chow Test technique. The result of
the research concludes that Liquidity, business risk,
profitability, and sales growth have positive and
significant effect to company's capital structure.
Taufan (Taufan,2009) who examined the Factors
affecting capital structure in manufacturing
companies listed on the Indonesia Stock Exchange
period 2005-2007. Dependent variable in this study
is the Capital Structure while the independent
variables are business risk, firm size, asset structure
and profitability with multiple regression techniques.
The result of the research conclude that business risk
and firm size have significant negative effect to
capital structure while asset structure and
profitability have positive and significant effect to
capital structure.
Werner R. Murhadi, (Werner R. Murhadi,2009)
who examined the Determinants of Capital
Structure: A Study In Southeast Asia. Dependent
variables in this study are Debt while the
independent variables are Profitability, Company
Size, Asset Tangibility, Corporate Growth and Non
Debt Tax Shield with multiple regression
techniques. The results conclude that the factors that
determine debt policy are profitability, firm size,
asset tangibility and growth rate.
Ng Chin Huat (Ng Chin Huat,2008) who
examined The Determinants Of Capital Structure:
Evidence From Selected ASEAN Countries.
Dependent variable in this research is Leverage
while the independent variables are Profitability,
Non Debt Tax Shield, Growth Opportunities, Firm
Size, GDP, Inflation with multiple regression
techniques. The results concluded that profitability
and growth of inverse relationship with leverage
while non-debt tax shield have a significant negative
impact on leverage. The size of the company
provides a significant positive relationship.
Gurcharan S, (Gurcharan S,2010) researched A
Review of Optimal Capital Structure. Dependent
variable in this research is Leverage while the
independent variables are Size, Bank - Size Of
Banking Industry, SKTMKT - Size Of Stock
Market, GDPRATE - GDP Growth Rate, and INF -
Annual Inflation Rate with multiple regression
techniques. The results conclude that Profitability
and growth opportunity show statistically significant
with inverse relationship with leverage. While non-
debt tax shield has a negative impact on leverage.
Company size shows a positive relationship.
Sashi Kumar, Kanesan (Sashi Kumar, Kanesan,
2009) studied Decision Selected ASEAN Countries.
Dependent variable in this research is Capital
Structure while the independent variable is Asset
Tangibility, Financial Flexibility, Liquidity,
Profitability, Size, Growth Growth, Inflation Rate
and Interest Rate with multiple regression technique.
The results concluded that Asset Tangibility did not
significantly affect the short-term debt ratio;
Masidonda (Masidonda,2013) examined the
Determinants Of Capital Structure and Impact
Capital Structure on Firm Value. Dependent variable
in this study is the Capital Structure while the
independent variable is CEO Ability, CEO of
Ownership Corporate Value with multiple regression
techniques. The results conclude that CEO's ability
and CEO ownership determine the capital structure
(LTDE), profitability and NDTS cash flow has no
effect. Furthermore, CEO ability, profitability,
NDTS and CEO ownership determine the capital
structure (LTDA), but cash flow has no effect. The
capital structure (LTDE and LTDA) determines the
value of the firm.
The hypothesis in this study are as follows: Sales
Growth, Profitability, Company Growth, Company
Analysis of the Factors Affecting the Capital Structure of a Manufacturing Company Listed on the Indonesian Stock Exchange in
Moderation by Business Risk
571
Size affect the Capital Structure moderated by
Business Risks in Companies Registered on the
Indonesia Stock Exchange.
2 METHODOLOGY
2.1 Research Design
The data used in this research are secondary data
involving the financial statements of manufacturing
companies listed in Indonesia Stock Exchange in
period 2012 - 2016 for data analysis. Data were
obtained from the website of Indonesia Stock
Exchange (www.idx.co.id) and Indonesian Capital
Market Directory (ICMD). Eviews 7Software was
used.
2.2 Population and Sample
The population used in this study is a manufacturing
company listed on the Indonesia Stock Exchange in
2012 - 2016. The criteria that must be met by the
sample in this study are as follows:
1. The company is listed on BEI in 2011 until
2015 and is not in the delisting process
during the study period.
2. The Company publishes complete financial
statements with no negative retained
earnings during the 2011-2015 observation
period.
2.3 Instrument
The instrument that is used to collect the data in this
researchis documentation method. The type of data
used in this study is secondary data, namely the
company's annual financial statements that have
been audited by independent auditors in all
companies, fundamental data, closing price of shares
during the period of 2012 to 2016. The data sources
were obtained from the Indonesia Stock Exchange
(www. idx.co.id) and Indonesia Capital Market
Institute (www.ticmi.co.id) an educational institution
that organizes education and training as well as the
capital market profession certification exams.
2.4 Data Collection and Analysis
Data analysis Method performed in this study is
multiple linear regression models. Data are
processed using Eviews 7 software.
Table 1: Methods Data analysis.
No Criteria Amount Accumulation
1
Manufacturing
company listed on
the Stock
Exchange in 2012-
2016
141
2
Manufacturing
companies that
carry out 2012-
2016 delisting
from the IDX
(20) 121
3
Has a negative
earnings balance
during the
observation period
(
2012-2016
)
(69) 52
4
Does not publish
financial
statements in full
(10) 42
Total sample
companies during the
stud
y
p
eriod
42
2.5 Data Normality Test
In this study, the normality test for residuals uses the
Jarque-Bera (J-B) test. In this study, the level of
significance used is α = 0.05. The basis for decision-
making is to look at the probability numbers of J-B
statistics, with the following conditions.
If the probability value p is 0.05, then the
assumption of normality is met.
If the probability is <0.05, then the assumption of
normality is not met.
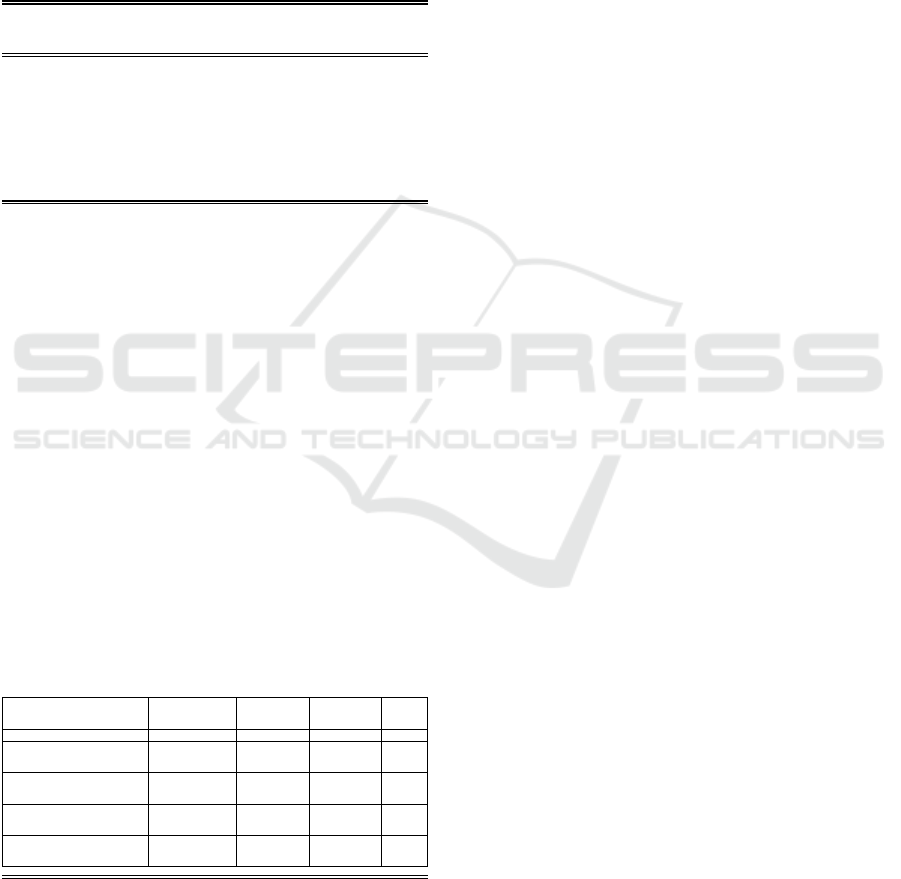
Figure 1: Test of Normality with Jarque-Bera Test.
Note that according to Figure 1, the probability
value of J-B statistic is 0.138355. Because the
probability value p, ie 0.138355, is greater than the
level of significance, ie 0.05, the assumption of
normality is met.
0
4
8
12
16
20
24
28
-2.5 -2.0 -1.5 -1.0 -0.5 0.0 0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5
Series: Residuals
Sample 1 210
Observations 210
Mean 5.96e-16
Median 0.096871
Maximum 2.375562
Minimum -2.354440
Std. Dev. 0.809685
Skewness -0.335987
Kurtosis 3.023437
Jarque-Bera 3.955860
Probability 0.138355
ICMR 2018 - International Conference on Multidisciplinary Research
572

3 RESULT
3.1 Descriptive Statistics
Table 2: Descriptive Statistics Of Profitability, Corporate
Growth, Company Size, Capital Structure, Sales Growth,
and Business Risk.
Variabl
e
Min Max Mean Std.D
eviati
on
Capital
Structu
re
0.01581 5.29829 0.88068 0.817
18
Sales
Develo
p
ment
-0.94 0.90176
6
0.0453 0.225
3
Profita
b
ilit
y
-9.47785 0.90177 -0.08452 1.064
87
Compa
ny
Develo
p
ment
-6.91892 0.94804 0.07250 0.514
90
Compa
n
y
Size
5.402 17.604 14.609 1.840
31
Busine
ss Ris
k
-0.24754 1.03144 0.13724 0.166
37
Source: Results of software Eviews 7
3.2 Classic Assumption Test
3.2.1 Multicollinearity Test
In this study, symptoms of multicolinearity can be
seen from the correlation values between variables
contained in the correlation matrix. (Ghozali, 2013,
p.105) states if the inter-independent variables is a
fairly high correlation, i.e. above 0.9, then the
multico-linearityexists. Multicollinearity test results
are presented in Table 3.
Table3: Multi co linearity Testwith Matrix Correlation.
X1 X2 X3 X4
X1 1.000000 -0.139871 0.153375 0.500706
X2 -0.139871 1.000000 -0.004117 0.019434
X3 0.153375 -0.004117 1.000000 -0.046477
X4 0.500706 0.019434 -0.046477 1.000000
Source: Eviews 7 Software Results
3.2.2 Autocorrelation Test
Assumptions about residual independence (non-
autocorrelation) can be tested using the Durbin-
Watson test Field (Field, 2009, p. 220). The
statistical value of the Durbin-Watson test ranges
between 0 and 4. Field (Field, 2009, p. 220)states as
follows.
The statistical value of the Durbin-Watson test
that is smaller than 1 or greater than 3 indicates an
autocorrelation.Field (Field, 2009, p.220-221) states
as follows.
Table 4: Autocorrelation Test with Durbin-Watson Test.
Log
likelihood
-253.1428 Hannan-
Quinn
criter.
2.490719
Durbin-
Watson stat
2.049199
Source: Software Eviews 7 Results
According to Table 3, the value of the Durbin-
Watson statistic is 2.049199. Note that since the
Durbin-Watson statistic value lies between 1 and 3,
ie 1<2.049199<3, then non-autocorrelation
assumptions are met. In other words, there are no
symptoms of high autocorrelation in residuals.
3.2.3 Heteroscedasticity Test
Detection of the presence or absence of
heteroskedastisitas can be done with Breusch-Pagan
test Gujarati, Gio and Elly(Gujarati, 2003; Gio and
Elly, 2015). The following test results Breusch-
Pagan.
Tabel 5: Heteroskedasticity Test: Breusch-Pagan-Godfrey.
F-statistic 1.705653 Prob. F(4,205) 0.1500
Obs*R-squared 6.763906 Prob. Chi-
Square(4)
0.1489
Source: Results of software Eviews 7
The value of Prob Obs * R-Squared is 0.1489>
0.05, which means there is no heteroscedasticity.
3.2.4 Test (F Test)
F test aims to examine the effect of independent
variables simultaneously or simultaneously to the
dependent variable. Based on Table 6, the value of
Prob is known. (F-statistics),ie 0.0004585 <0,05, it
can be concluded that all independent variableslike
sales growth, profitability, corporate growth, and
company size simultaneously, have a significant
effect on capital structure variable.
Analysis of the Factors Affecting the Capital Structure of a Manufacturing Company Listed on the Indonesian Stock Exchange in
Moderation by Business Risk
573

3.2.5 The Panel Data Regression
Equationand Partial Effect
Significance Test (t Test)
Based on Table 6, we obtain the panel data
regression equation as follows.
Y = 0,081 + 0,075X
1
+ 0,111X
2
+ 0,009X
3
+ 0,033X
4
+ e (1)
Based on Table 6, it is known:
1. The coefficient value of independent variable
of sales growth is 0,081, that is positive value.
The value can be interpreted as variable of
sales growth have positive effect to capital
structure variable. It is known that the Prob
value of the sales growth variable is 0.0161, ie
<0.05, then the sales growth variables have a
significant (statistically) effect on the capital
structure variable, at the 5% significance level.
2. The coefficient value of the profitability free
variable is 0.111, which is positive. The value
can be interpreted profitability variables which
have a positive effect on capital structure
variable. It is known that Prob value of
profitability variable is 0,0013, that is <0,05,
profitability variable has significant effect
(statistically) to capital structure variable, at
5% significance level.
3. The coefficient value of the growth-free
variable is 0.009, which is positive. The value
can be interpreted by company growth variable
have positive effect to capital structure
variable. The value of Prob of the variable
growth of the firm is 0.8384, that is> 0.05, then
the variable of company growth has no
significant effect (statistically) on the variable
of capital structure, at the 5% significance
level.
4. The coefficient value of the independent
variable of firm size is 0.033 is positive. The
value can be interpreted firm size variables
have a positive effect on capital structure
variables. It is known that Prob value of firm
size variable is 0,2646, that is> 0,05, hence
firm size variable has no significant effect
(statistically) to capital structure variable, at
5% significance level.
3.2.6 Moderation Significance Test
The following test results of business risk
significance in moderating the influence of sales
growth, profitability, corporate growth, and firm size
on capital structure using interaction test.
Table 7: Test of Business Risk Significance in Moderating
The influence of sales growth on capital structure.
De
p
endent Variable: Y
Method: Least S
q
uares
Date: 01/24/18 Time: 22:19
Sample: 1 210
Included observations: 210
Variable Coefficient Std. Erro
r
t
-Statistic Prob.
X1 -0.003484 0.049758 -0.070017 0.9442
Z -0.084347 0.054707 -1.541801 0.1247
INTERACTION
_
ZX1-0.037828 0.017999 -2.101654 0.0368
C -0.452432 0.139876 -3.234515 0.0014
Source: Results of Eviews 7software
Based on Table 7, we obtain the moderation
equation of interaction test as follows.
Y = -0.45-0,0034X_1-0,0843Z-0,037X_1 Z (2)
The value of Prob of the interaction_ZX1 is
0.0368 <0.05, then the business risk is significant in
moderating the effect of sales growth on the capital
structure.
Table 8: Test of Business Risk Significance in Moderating
Effect of profitability on capital structure.
Dependent Variable: Y
Method: Least S
q
uares
Date: 01/24/18 Time: 22:22
Sample: 1 210
Included observations: 210
Variable Coefficient Std. Erro
r
t
-Statistic Prob.
X2 0.308515 0.089385 3.451538 0.0007
Z 0.170551 0.064766 2.633333 0.0091
INTERACTION
_
ZX20.070242 0.028105 2.499299 0.0132
C 0.308264 0.219250 1.405992 0.1612
Source: Results of software Eviews 7
Based on Table 8, we obtain the moderation
equation of interaction test as follows.
Y = 0,3082 + 0,3085X_2 + 0,1705Z + 0,0702X_2 Z
(3)
The value of Prob of interaction_ZX2 is 0.0132
<0.05, then the business risk is significant in
ICMR 2018 - International Conference on Multidisciplinary Research
574
moderating the effect of profitability on the capital
structure.
Table 9: Test of Business Risk Significance in Moderating
Influence of company growth on growth of capital
structure.
De
p
endent Variable: Y
Method: Least Squares
Date: 01/24/18 Time: 22:23
Sam
p
le: 1 210
Included observations: 210
Variable Coefficient Std. Erro
r
t
-Statistic Prob.
X3 0.103922 0.100717 1.031817 0.3034
Z 0.082189 0.074373 1.105091 0.2704
INTERACTION
_
ZX3 0.026273 0.028402 0.925066 0.3560
C -0.141654 0.246257 -0.575227 0.5658
Source: Results of software Eviews 7
Based on Table 9, we obtain the moderation
equation of interaction test as follows.
Y = -0.141 + 0.1039X_3 + 0,0821Z + 0,0262X_3 Z
(4)
The probability of Prob value of interaction_ZX3
is 0.3560> 0.05, then business risk is not significant
in moderating the influence of firm growth on
capital structure.
Table 10: Test of Business Risk Significance in
Moderating The influence of firm size on capital structure.
De
p
endent Variable: Y
Method: Least S
q
uares
Date: 01/24/18 Time: 22:23
Sam
p
le: 1 210
Included observations: 210
Variable Coefficient Std. Erro
r
t
-Statistic Prob.
X4 0.083723 0.041797 2.003085 0.0465
Z 0.024084 0.048024 0.501498 0.6166
INTERACTION
_
ZX4 0.004211 0.015460 0.272354 0.7856
C -0.227974 0.132378 -1.722146 0.0865
Source: Results of software Eviews 7
Based on Table 10, we obtain the moderation
equation of interaction test as follows.
Y = -0,227 + 0,083X_4 + 0,024Z + 0,004X_4 Z (5)
The probability of Prob value of interaction_ZX4
is 0.7586> 0.05, then business risk is not significant
in moderating the effect of firm size on capital
structure.
4 ANALYSIS
4.1 Effect of Sales Growth on Capital
Structure
The coefficient value of the free variable of sales
growth is 0.076 is positive to the variable of capital
structure. Known value Prob of variable sales
growth is 0,0150, that is <0,05, hence variable of
sales growth have significant effect to capital
structure variable.
This research is supported by Ni Made Novione
and Made Rusmala (Ni Made Novione and Made
Rusmala,2016) who state that sales growth has a
positive and significant effect on capital structure.
Sales growth will affect changes in capital structure.
This positive value of the coefficient regression
indicates that the increased sales growth will be
followed by increased capital structure and vice
versa. And the research of Rahmawardani
(Rahmawardani,2007) states that Sales growth has a
positive and significant effect.
4.2 Effect of Profitability on Capital
Structure
The coefficient value of the profitability free
variable is 0.121 is positive to the capital structure
variable. Known Prob value of the profitability
variable is 0.0034, ie <0.05, then the profitability
variable significantly influence the variable of
capital structure.
The research supported by Seftianne
(Seftianne,2011) and Rahmawardani
(Rahmawardani,2007) get profitability result which
have a significant positive effect to capital structure.
The results showed that the higher the profitability
of the company, the higher the capital structure is.
Profitability positively affects the capital structure
because the company does an expansion that it
requires a lot of funds to encourage increased profits
in the future.
Analysis of the Factors Affecting the Capital Structure of a Manufacturing Company Listed on the Indonesian Stock Exchange in
Moderation by Business Risk
575

4.3 Effect of Corporate Growth on
Capital Structure
The coefficient value of the growth-free variable of
firm is 0,009.This is positive value of capital
structure variable. Known Prob value of variable
growth of company is 0,8384, that is> 0,05, hence
variable growth of company have no significant
effect to variable of capital structure.
The research supported by Liem et al (Liem et
al.2013) obtained the result of growth which has no
significant positive effect on capital structure. The
results of this study do not support the results of
research conducted by Wahidahwati
(Wahidahwati,2002) which shows that the growth of
the company proved to negatively affect the capital
structure.
4.4 Effect of Company Size on Capital
Structure
The coefficient value of the independent variable of
firm size is 0,036 is positive value to capital
structure variable. Known Prob value of variable
size of company is 0,2365, that is> 0,05, hence firm
size variables have no significant effect to capital
structure variable.
This shows that the size of a large company does
not guarantee the survival of the company or the
smooth operation of the company. Thus the size of
the company does not guarantee the interest of
investors or creditors in investing funds to the
company. The results support the research conducted
by Firnanti (Firnanti,2010) and Hapsari
(Hapsari,2010), but they are different from research
conducted by Sari (Sari,2013) and Finky
(Finky,2013) which states that firm size variables
have positive and significant influence on capital
structure.
4.5 The Influence of Business Risk as
Moderating Variableof Variable
Structure of Capital
From the results of the tests conducted can be seen
that the business risk variables used as moderating
variables show significant when it is used with the
growth of sales and profitability. The results are not
significantly indicated on the use of company
growth and firm size. Firms with high risk levels
tend to avoid additional funding through foreign
capital compared to firms with low risk levels. It
will also increase the likelihood of bankruptcy.
5 CONCLUSIONS
5.1 Conclusion
This study was conducted to examine whether sales
growth, profitability, corporate growth and firm size,
affect the capital structure listed on the Indonesia
Stock Exchange moderated by business risk. The
sample of research is 42 companies listed on BEI
during period 2012-2016.
Based on the result of research, it can be
concluded that:
1. All independent variables: sales growth,
profitability, company growth, and company
size, able to influence/ explain the structure of
capital simultaneously or together equal to
7.7%, the rest of 92.3% influenced by other
factors.
2. All independent variables: sales growth,
profitability, corporate growth, and company
size, simultaneously, have a significant effect
on capital structure variables.
3. Sales growth has a positive and significant
effect on capital structure variable.
4. Profitability has positive and significant effect
on capital structure variable.
5. The growth of the company has a positive, but
not significant effect on the variable of capital
structure.
6. The size of the company has a positive, but not
significant effect on the sales growth variable.
7. Business risk is able to moderate the effect of
sales growth on capital structure.
8. Business risk is able to moderate the effect of
profitability on capital structure.
9. Business risk is not able to moderate the
influence of corporate growth on capital
structure.
10. Business risk is not able to moderate the effect
of firm size on capital structure
5.2 Limitations of Research
Limitations of this study are the sample of this study
which are only taken from manufacturing companies
listed on the Indonesia Stock Exchange (BEI) 5-year
period of 2012 - 2016. This causes the results of the
study which cannot be generalized to other types of
companies listed on the Indonesia Stock Exchange.
ICMR 2018 - International Conference on Multidisciplinary Research
576

REFERENCES
Bhaduri. 2002.The Characteristics of CompaniesSuch as
Growth, FreeCash Flow, FirmSize, ProductType, and
Type of IndustryAffect the Company'sCapitalStructure.
India
Brigham, E.F dan Gapenski, Louis C. 1996. Intermediate
Finance Management. Harbor Drive : The Dryden
Press.
Brigham Eugine F. dan Joel F. Huston 2006. Dasar-Dasar
Manajemen Keuangan. Jakarta: Penerbit Salemba
Empat.
Field. 2009. Autocorrelationstatistical value of the
Durbin-Watson. 220.
Field. 2009. Autocorrelation statistical value of the
Durbin-Watson. 220-221.
Ghozali. 2013. Correlation Matrix. 105.
Gujarati, Damodar N. 2003. Gio and Elly, 2015.
Ekonometrika Dasar. Jakarta : Penerbit Erlangga.
Gurcharan S. 2010. A Review of Optimal Capital
Structure Determinant Of. Journal Economic
Hapsari, Laksmi Indri. 2010. AnalisisFaktor-Faktor Yang
Mempengaruhi Struktur Modal Perusahaan
Manufaktur Di Bursa Efek Indonesia Periode 2006-
2008 Studi Kasus Pada Sektor Automotive And Allied
Product. Skripsi: Universitas Diponegoro Semarang.
Indahningrum, Rizka Putri dan Ratih Handayani. 2009.
Pengaruh Ukuran Perusahaan, Kepemilikan
Institusional, Dividen, Pertumbuhan Perusahaan, Free
Cash Flow dan Profitabilitas Terhadap Kebijakan
Utang Perusahaan. Jurnal Bisnis dan Akuntansi. Vol
11, No. 3. Hlm 189-207.
Jensen, M. Dan W.H. Meckling. 1976, Theory of the firm:
Managerial Bihavior, Agency Cost and Ownership
Structure. Jurnal of Financial Economic.No. 3. Hlm.
305-360.
Liem, dkk. 2013 Faktor-Faktor yang Mempengaruhi
Struktur Modal Kerja pada Industri Cunsomer Goods
yang Terdaftar di BEI periode 2007-2011. Jurnal
Ekonomi dan Bisnis.
Masidonda. 2013. Determinants Of Capital Structure and
Impact Capital Structure on Firm Value. Journal
Business and Economics
Myers, Steward, C. Dan Nicholas S. Majluf. 1984.
Corporate Financing Decision When Firm Have
Investment Information That Investor Do Not. Journal
of Financial Economics. Vol. 13, hlm. 187-220.
Ng Chin Huat. 2008. The Determinants Of Capital
Structure: Evidence From Selected ASEAN Countries.
Journal Business and Economic.
Nugroho. 2006. Analisis Faktor-Faktor yang
Mempengaruhi Struktur Modal Perusahaan Property
yang Go Public Di BEJ Tahun 1994-2004. Jurnal
Ekonomi dan Bisnis.
Ozkan, 2001. Krisnan and Moyer. 1996. in Omran. 2009.
CapitalStructure in IndustrializedCountrieswhich,
DespiteHavingSimilarEconomicCharacteristics,
Differed in Determining the CapitalStructure and the
Variables that Influenced it. In the United States,
Japan, Italy, and Germany.United States.
Rahmawardani. 2007. Menganalisis Pengaruh Aspek
Likuiditas, Risiko Bisnis, Profitabilitas, dan
Pertumbuhan Penjualan Terhadap Struktur Modal.
Jurnal Ekonomi dan Bisnis.
Saidi. 2004. Faktor-Faktor yang
MempengaruhiStrukturModalpada Perusahaan
Manufaktur yang Go Publicdi BEJ Tahun 1997-2002.
Jurnal Ekonomi dan Bisnis.
Salehi, Mahdi., Nazanin Bashiri Manesh. 2012. A Study Of
The Roles Of Firm And Country On Specific
Determinates In Capital Structure: Iranian Evidence.
Interntional Management Review. 8 (2): 51-85.
Sugiyono. 2012. Metodologi Penelitian Bisnis. Bandung:
Alfabeta.
Taufan. 2009. Faktor-faktor yang
MempengaruhiStrukturModal pada
PerusahaanManufaktur yang Terdaftar di Bursa Efek
Indonesia Periode 2005-2007. Skripsi.
Wahidahwati.2002.Pengaruh Kepemilikan Manajerial dan
Kepemilikian Institusional pada Kebijakan Hutang
Perusahaan: Sebuah Perspektif Theory Agency. The
Indonesian Journal of Accounting Research 5 (1).
Werner R, Murhadi. 2009. Determinants of Capital
Structure: A Study In Southeast Asia.
Yulianti.2010. Capital Structure is the Company's
Characteristics of Profitability, Liquidity, and Size of
the Company. Jurnal Bisnis Dan Akuntansi.
www.idx.co.id
www.ticmi.co.id
Analysis of the Factors Affecting the Capital Structure of a Manufacturing Company Listed on the Indonesian Stock Exchange in
Moderation by Business Risk
577
