
The Effect of Guided Discovery Learning Strategy using Students’
Worksheet (LKS) to the Learning Outcomes on IPA Physics of
Grade VIII Students in SMP N 24 Padang
*
RachmatRizaldi, Edi Azwar, Nana Mardiana, Miftahul Husna, Sheila Fitriana
Universitas Islam Sumatera Utara, Medan, Indonesia
Keywords: Guided Discovery, LKS, Learning Outcomes
Abstract: The student’s achievement which is low on IPA Physics competency is predicted as the result of the less
effective of learning strategy used in learning process. One of learning strategies which is considered
effective is Guided Discovery Strategy using LKS. This research aims to know the effect of the strategy on
the learning outcomes on IPA Physics of Grade VIII students in SMP N 24 Padang. Research design used is
Quasi Experiment Research using Randomized Control Group Only Design. The population is all the Grade
VIII students in the academic year 2012/2013 except the VIII-A students as the excellence class. Purpose
Sampling Technique is used in defining the sample. Data are collected by using written test for cognitive
aspect, observation sheet for affective aspect, and scoring rubrics for psychomotor aspect. T-test of 0,05 is
used to analyse the data. The results show that the average scores of experiment class for cognitive aspect
are 70,5 and of control class 62,58; of class experiment on affective aspect 77,93 and of control class 70,45;
and, of experiment class for psychomotor aspect 77,13 and of control class 72.96. Hypothesis is tested using
t-test, which for cognitive aspect obtained t
count
=2,51, for affective aspect t
count
=7,69, and for psychomotor
aspect t
count
=4,27, and t
table
= 1,67 on the level of 0,05. It means that t
count
>t
table,
so Ho is rejected. The
conclusion of this research is that there is an effect of the implementation of Guided Discovery Strategy
using LKS to the learning outcomes on IPA Physics of Grade VIII students in SMP N 24 Padang
.
1 INTRODUCTION
Qualified Education is the vision of the government
for education aspect. Qualified education will also
produce a qualified output. The output can be seen
on the high level of academic and non academic
learning competencies. In the education aspect, the
quality of the graduates assesses based on the
compatibility of student’s ability as stated in the
curriculum. The curriculum implemented now in
Indonesia is Level of Educational Curriculum
(KTSP) which demands mastery learning based on
Minimum Mastery Criteria (KKM). The efforts done
in meeting the requirements of KTSP in increasing
qualification process and learning outcomes on IPA
Physics are increasing the qualification of the
teachers through upgrading sessions, maximalizing
the learning process in the class by providing
supportive tools such as learning materials
procurement, learning tools improvement, and also
learning facilities and infrastucture improvement.
Although many efforts have been done, the
achievement of learning outcome of Natural
Sciences (IPA) in SMP is still not optimal. This can
be based on the result of second semester Final Test
(UAS) on IPA of Grade VIII students in SMP N 24
Padang in academic year 2011/2012 which are
generally less than the KKM of the subject which is
75, as in Table 1 below
.
Table 1: The Average Scores of Second Semester Final
Test (UAS) of IPA of Grade VIII Students in SMP N 24
Padang
.
No Class Avera
g
e Score
1 VIIIA 65,80
2 VIIIB 55,75
3 VIIIC 58,48
4 VIIID 63,40
5 VIIIE 55,60
6 VIIIF 53,43
7 VIIIG 54,71
8 VIIIH 50,01
578
Rizaldi, R., Azwar, E., Mardiana, N., Husna, M. and Fitriana, S.
The Effect of Guided Discovery Learning Strategy using Students’ Worksheet (LKS) to the Learning Outcomes on IPA Physics of Grade VIII Students in SMP N 24 Padang.
DOI: 10.5220/0008890705780583
In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Multidisciplinary Research (ICMR 2018) - , pages 578-583
ISBN: 978-989-758-437-4
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

Based on Table 1, it can be seen that the
achievement of IPA competency of the students is
low. The average score of Final Test on IPA of the
students is under KKM, 75. The cause predicted is
there is uncentered-learning process to the students,
which results the low competency achievement of
the students.
The low basic competency achievement of the
students relates to the less of students involvement
in learning process. The less of involvement is
caused by unvaried learning strategy used. Therefore
the learning strategy implemented by the teacher
must be varied so the student desires to be active in
learning process especially Physics.
Based on the problems faced in learning Physics
above, a strategy in learning effectively to solve a
problem is needed. Learning strategy implemented
must be able to involve the students in every
learning activity. It can be realized if the teacher is
able to implement various learning strategies such as
expository, cooperative, and discovery learning
strategies.
Discovery Learning Strategy is a strategy which
strives the students to be able to assimilate a concept
or a principle. Students are able to observe, to
absorb, to understand, to categorise, to hypothesise,
to explain, to estimate, andto conclude, etc. The
strategy lets the students find out the solution or
experience the problem themselves. Teacheronly
guides and gives instruction.
The implementation of discovery strategy is the
way to teach which involves the students in a mental
activity through sharing idea process, discussing,
reading or trying out themselves, in order to make
the students to be able to learning by themselves
(Roestiya, 2008, p. 20). The implementation of
discovery strategy can assist the teachers in
increasing the involvement of the students in
learning process. Thus, the researcher is interested to
implement the discovery strategy in learning process
using Student’s Worksheet (LKS). LKS is papers
which contain a guidance for students to do
programmed activities (Depdiknas, 2008, p. 100)
The implementation of Guided Discovery
Strategy using LKS can direct the students’
activities in the class and also can make the students
pay more attention to the teacher’s explanation.
Students must work on their own ways to find out a
concept by answering the question in the LKS given.
Through the strategy students are trained to learn
more themselves. (Suherman, 2003: 214). Teacher
gives a general problem to the students to be solved.
The student starts to solve the problem by observing
a complex or specific example to get a general
principle.
Learning process using discovery strategy must
pay attention to the knowledge of prerequisites had
by the students before doing discovery
(Siryosubroto, 1997, p. 199-200). Using correct
steps the teacher can assist the students to discover
the result as expected.
The goal of this research is to know the effect of
guided discovery learning strategy using LKS on the
learning achievement of IPA Physics of VIII
students in SMP N 24 Padang. Subject of lesson
discussed is the materials of second semester of VIII
students about vibration, frequency, and sound
.
2 RESEARCH METHOD
The research method used is Quasi Experiment
Research with Randomized Control Group only
Design. See Table 2 below
.
Table 2: Method Framework.
Class Pretest Treatment Postest
Experiment - X T
2
Control - - T
2
The X in the table is the treatment given to the
experiment class that is the implementation of
Guided Discovery Strategy using LKS. T2 is the
final test given to the experiment class and control
class in the final of the learning process
.
Population is generalizational area which
consists of object or subject which has certain
quality and characteristics which stated by the
research to be learnt. Population of this research is
all the Grade VIII students registered in academic
year 2012/2013 except VIIIA students which is the
excellence students. See Table 3 below
.
Table 3: The amount of VIII students in SMP N 24
Padang in academic year 2012/2013.
No Class Amount
1 VIIIA 31
2 VIIIB 29
3 VIIIC 29
4 VIIID 30
5 VIIIE 30
6 VIIIF 31
7 VIIIG 29
8 VIIIH 30
Total amount 239
The Effect of Guided Discovery Learning Strategy using Students’ Worksheet (LKS) to the Learning Outcomes on IPA Physics of Grade
VIII Students in SMP N 24 Padang
579

Sample is part of population taken as data source
and represents the population. Sample is taken by
using Purposive Sampling Technique. Purposive
Sampling Technique is a sampling technique based
on some goals and considerations (Sudjana, 2002, p.
168).
A research has variable. Research variable is an
object or activity which has certain variation stated
by the researhers to be learnt and then to be
concluded. Research variables consist of free
variable, bound and control variables. This research
has the implementation of Guided Discovery
Strategy using LKS as free variable, and student
learning outcome on cognitive, affective and
psychomotor aspects as bound variable, and teacher,
learning materials, curriculum, and equal time
allocation as control variable.
A research results data or information obtained
by using intruments. The instruments used in this
research are written test for cognitive aspect,
observation sheet for affective aspect, and scoring
rubrics for psychomotor aspect. For cognitive
aspect, before taking the data, the instrument of the
test is tried out first, then is analysed to obtain valid
test tools, reliability, to get difficulty level, and also
to get good distinguishing power of the questions.
Validity process is need to be done to know the
test quality in the relation to the thing must be
measured. A question is valid if has been measured
the things to be measured (Arikunto, 2009: 57).
Reliability is the accuracy of a tes if it is tested on
the same object (Arikunto, 2009: 100). For
determining the reliability of a test, Kuder
Richaderson (KR-20) equation below can be
implemented
.
2
11
)(
1
1
nS
MnM
n
n
r
(1)
M =
∑
(2)
r11 in the equation is the intrument of reliability,
n number of questions, M mean, N test participants,
and S deviation standard.
Reviewed for difficulties level, a good question
is not a too easy or too difficult questions (Arikunto,
2009: 208). The difficult or easy of a question is
shown by the difficulty level of the question. It can
be counted using the following equation
.
s
J
B
P
(3)
P in the equation 3 is the proportion of correct
answers or difficulties level. B is the total amount of
participants answer correctly, and Js is total amount
of participants.
A good question also can differenciate students
of high group or low group (Arikunto, 2009: 211).
The number showing the amout of distinguishing
power is called discrimination index or D which can
be counted by the following formula
.
B
B
A
A
J
B
J
B
D
(4)
D, in the equation, is distinguishing index, B
A
the
total amount of high group participants answer
correctly, B
B
total amount of low group participants
answer correctly, J
A
total amount of high group
participants, and J
B
total amount of low group
participants.
On the research procedure, how the research
steps managed to be a procedure beginning with the
planning or activity preparation done for research is
elaborated. The steps are arranging the research
schedule and research materials, defining population
and sample, preparing Lesson Plans (RPP) for
experiment class and control class, and preparing
research instruments and LKS. Research steps are
done based on RPP. On the final steps, the activities
of analysing the data obtained from the two classes,
concluding the result obtained from the two sample
classes, and concluding the result obtained in line
with data analysis technique used are done.
Data of this research are the achievement of the
students on 3 aspects; cognitive aspect which
assessed from the final test result, affective and
psychomotor aspects from observation result of
students attitude along the learning process. Then,
data obtained are analysed. Data analysis aims to test
the validitiy of hypothesis proposed in the research.
The normality and homogeneity of the data are
tested first. Normal and homogeneous distributed
data will be tested its hypothesis uses two average
equality test
.
Normality test aims to know whether the sample
comes from the population which normally or not
distributed. Thus, Liliefors test which consist of
some steps are used. First, data Xi obtained orders
ascending the convert to be Zi raw number using the
equation 5 below
.
S
xx
Zi
i
(5)
Xi, in the equation above, is the score obtained
by student i, x is the average score, and S is
ICMR 2018 - International Conference on Multidisciplinary Research
580

deviation standard. The chance of F(Zi) = P (Z < Zi)
is obtained using deviation standard list.
Furthermore, proportion is stated using S(Zi) which
is obtained using the equation 6 below
.
n
ZwhichZZnumberofZ
ZiS
in
,...,
)(
21
(6)
By counting the deviation of F(Zi) – S(Zi) with
absolute price, which is the greatest price among the
the absolute prices, the deviation obtained is called
Lo. After obtaining Lo and Ltable on the real rate α
= 0,05, the two values is compared. The criteria is if
Lo<Ltable, the sample comes from the population
which normally distributed. And if Lo>Ltable, the
sample comes from unpopulation which normally
distributed.
Homogeneity test aims to know whether two
samples have homogeneous variance or not. F-test is
done to test the homogeneity as the equation 7
below
.
2
2
2
1
S
S
F
(7)
F, in the equation 7 above, is data group
variance, S1
2
is the variance of achievement of
experiment class students, S2
2
is the variance of
achievement of control class students. If Fcount
obtained is lower than Ftable, the two data groups
have homogeneous variance, vice versa.
Hypothesis test is done using t-test as the
equation 8 below
.
𝑡
S
(8)
1
X
, in the equation above, is the average score
of experiment class. is the average score of
control class. S is joining deviation standard. n1 is
the number of students of experiment class. n2 is the
number of students of control class. Test criteria is
that Ho is accepted if t> t(1-α) at 0,05 and Ho is
rejected if t has other prices.
Ttable
is obtained from
distribution list of t with degree of freedom (DoF) =
(n1+n2-2) and chance (1-α)
.
3 RESULT AND DISCUSSION
The research had been conducted on 15 January to 5
March 2013 in SMP N 24 Padang and obtained data
of learning outcomes on IPA Physics of Grade VIII
students. The assessment of learning outcome was
reviewed for three aspects those are cognitive,
affective and psychomotor. The data of cognitive
aspect was obtained through written test in the form
of 20 objective questions. Post test was done to the
two sample classes in the end of research.
Meanwhile, data of affective and psychomotor
aspects were obtained along learning process
through affective and psychomotor assessment
format.
Data of Physics learning outcomes on cognitive,
affective, and psychomotor aspects can be seen at
the Table 4 below
.
Table 4: The Average Score of Sample Classes on
Cognitive, Affective and Psychomotor Aspects
.
Class
Average Score (
x
)
Cognitive Affective
Psycho
moto
r
Experiment
70,5 77,93 77,13
Control
62,58 70,45 72,96
Table 4 above shows that the average scores of
experiment class on cognitive, affective, and
psychomotor aspects are higher than control class.
Statistic analysis of equation test of two averages
is needed to know whether the difference of Physics
learning outcome of the students on the three aspects
has meaning or not.
At cognitive aspect, the result of normality test
using Lilefors test at sample class was obtained as
the following table
.
Table 5: The Result of Normality Test of Sample Class at
Cognitive Aspect.
Class N
L
0
L
t
Experiment 30 0,05 0,1214 0,161
Control 29 0,05 0,1349 0,161
Table 5 above shows that L
0
<Lt which means
that the data of the two sample classes comes from
population which normally distributed. Moreover,
homogeneity test is done.
Homogeneity test is done using F test. The result
obtained is as in the Table 6 below
.
1
X
2
X
1
n
2
n
2
X
The Effect of Guided Discovery Learning Strategy using Students’ Worksheet (LKS) to the Learning Outcomes on IPA Physics of Grade
VIII Students in SMP N 24 Padang
581
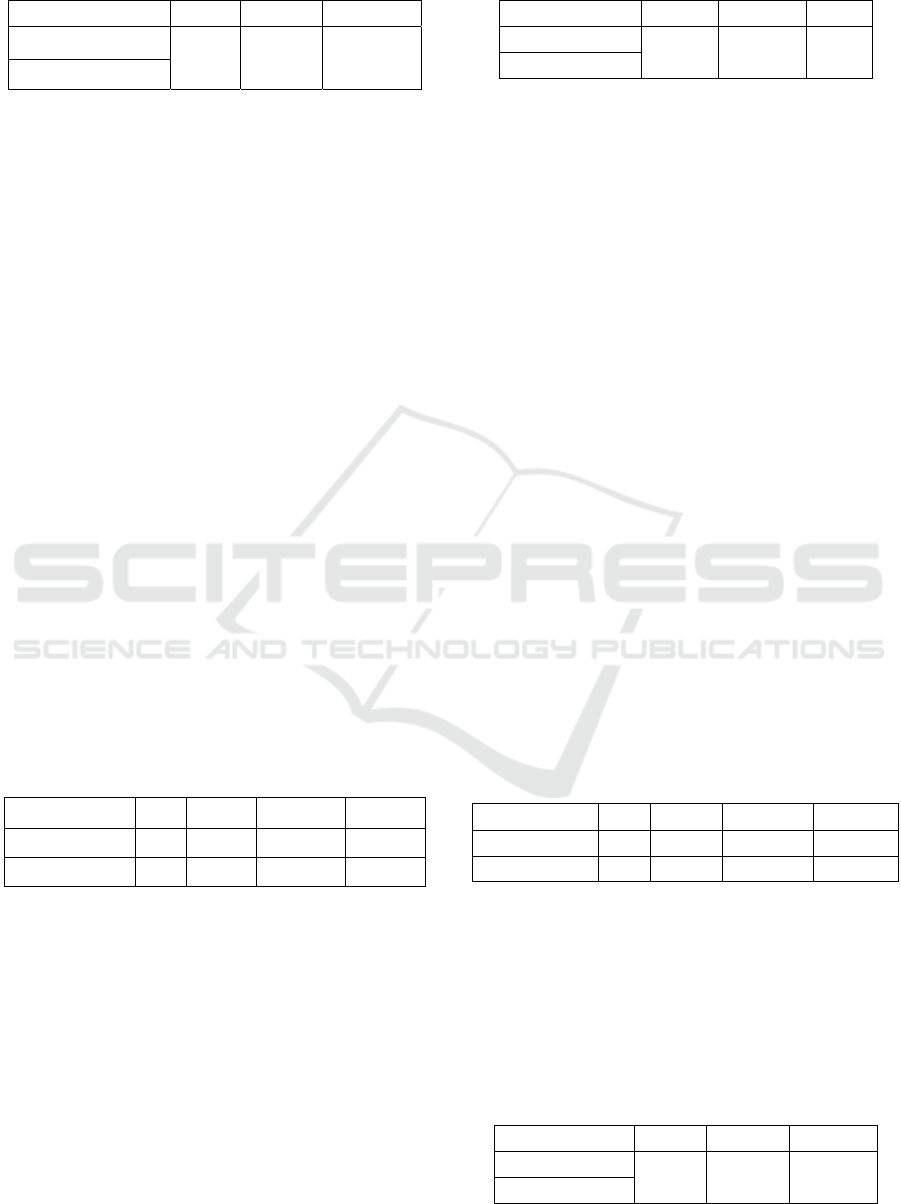
Table 6: The Result of Homogeneity Test of Sample
Classes at Cognitive Aspect.
Class
F
count
F
table
Experiment
0.05 1,125 1,87
Control
Table 6 above shows that F
count
< F
table
which
means that learning outcomes of students at each
experiment class and control class have
homogeneous variance.
Based on normality test and homogeneity test
done for experiment class and control class, it is
obtained that the data of learning outcomes of the
two classes are normally distributed and have
homogeneous variance. T-test is done to test the
hypothesis.
The results of t-test obtain that t
count
= 2,51 and
t
table
= 1,67. The acceptance of Null Hypothesis (Ho)
criteria is if t
count
<t
table
. It is obtained that t
count
= 2,51
is on the outside area of acceptance Ho. The result
shows that there is a significant difference on the
learning outcome of students in experiment class and
control clas. It is proved with the average score of
students in experiment class is higher than control
class. It can be concluded that there is a significant
influence of the implementation of Guided
Discovery Strategy using LKS on the learning
outcomes on IPA Physics of VIII students in SMP
N 24 Padang at cognitive aspect.
At the affective aspect, the result of normality
test using Liliefors test for sample class is obtained
as table 7 below
.
Table 7: The Result of Normality Test of Sample Classes
at Affective Aspect
.
Class N
L
0
L
t
Experiment 30 0,05 0,1376 0,161
Control 29 0,05 0,1286 0,161
Table 7 above shows that L
0
<Lt so that the data
of the two sample classes comes from the population
which is normally distributed. Furthermore,
Homogeneity test is done.
Homogeneity test is done using F test. Table 8
below shows the result of homogeneity test
.
Table 8: The Result of Homogeneity Test of Sample
Classes at Affective Aspect.
Class
F
hitung
F
Tabel
Experiment
0.05 1,705 1,85
Control
Table 8 above shows that Fcount < Ftable which
means that learning outcomes of the students of
experiment class and control class have
homogeneous variance.
Based on normality test and homogeneity test
done on experiment class and control class, it is
obtained that learning outcomes of the students of
the two sample classes are normally distributed and
have homogeneous variance. T-test is used to test the
hypothesis.
The result of t-test obtains that t
count
= 7,69 and
ttable
= 1,67. The acceptance ofnull hypothesis (Ho)
criteria is t
count
<t
table
. The result shows that t
count
=
7,69 is at the outside of the acceptance area of Ho.
The result shows that there is a significant difference
of learning outcome of students at experimental
class and control class which is proved with the
average score of students at experimental class is
highger that control class. By that significant
difference, it can be concluded that there is a
significant influence of the implementation of
Guided Discovery Strategy using LKS on the
learning outcomes on IPA Physics of VIII Students
in SMP N 24 Padang at affective aspect.
At psychomotor aspect, the result of normality
test using Liliefors test to the sample classes is
shown in table 9 below
.
Table 9: The Result of Normality Test of Sample Classes
at Psychomotor Aspect.
Class N
L
0
L
t
Experiment 30 0,05 0,1197 0,161
Control 29 0,05 0,1465 0,161
Table 9 shows that L
0
< Lt which means that data
of the two sample classes comes from the population
which is normally distributed. Furthermore,
homogeneity test is done.
Homogeneity test is done using F test. The result
of the test is shown in Table 10 below
.
Table 10: The Result of Homogeneity Test of Sample
Classes at Psychomotor Aspect.
Class
F
hitung
F
Tabel
Ecxeriment
0.05 1,034 1,85
Control
ICMR 2018 - International Conference on Multidisciplinary Research
582

Table 10 shows that F
count
< F
table
which means
that learning outcomes of the students at experiment
class and control class have homogeneous variance.
Based on normality and homogeneity done for
experiment class and control class, it is obtained that
learning outcome of students at experiment class and
control class is normally distributed and have
homogeneous variance. T-test is implemented to test
the hypothesis.
The result of t-test shows that t
count
= 4,27 and
t
table
= 1,67. The acceptance criteria of null
hypothesis (Ho) is t
count
<t
table
. The result shows that
t
count
= 4,27 is out of the acceptance area of Ho. It
means that there is a significant difference to the
learning outcome of the students at experiment class
and control class which the average score of the
students at experiment class is higher than those at
control class. For that reason, it can be concluded
that there is significant effect of the implementation
of Guided Discovery Strategy using LKS on the
learning outcomes on IPA Physics of Grade VIII
students in SMP N 24 Pada at psychomotor aspect.
Learning Physics which implements guided
discovery strategi from the observation at
experiment class obtains that the students are active
and have desire to solve the problem given by the
teacher. Student’s activity in finding the concept and
also the principle makes the students active to find
the solution of the problem from source book and to
do exercise or try out. According to Bruner in
Oemar (Bruner in Oemar, 2011, p. 117), “student’s
discovery on the concept and also on the principle
gives them stimulus to study through their own
active involvement”. Suherman (Suherman, 2003, p.
214) states that this learning makes the students
active in learning activity and trains the students to
study more themselves.
Using LKS as the aids in the implementation of
Guided Discovery Strategy will make the students
more active and more directed than the students at
control class who do not use LKS. This is in line
with Depdiknas (Depdiknas, 2004, p. 23) which
states that LKS supports the students in developing
and finding concept based on the description of
observation result of the data obtained in the
experiment activity.
The implementation of Guided Discovery
Strategy using LKS effects the student’s
competency achievement on IPA Physics. It is
proved by the average score of students at
experiment class which is higher than those at
control class. This result shows that students who
implement this strategy in their learning process
many of them will reach the KKM set. So, the
implementation of Guided Discovery Strategy using
LKS can increase students’ learning outcome on IPA
Physics
.
4 CONCLUSION
The research result shows that learning outcomes of
students at experiment class with average score 70,5
at cognitive aspect, 77,93 at affective aspect, and
77,13 at psychomotor aspect are higher than those at
control class with average score 62,58 at cognitive
aspect, 70,45 at affective aspect, and 72,96 at
psychomotor aspect. Hypothesis is tested using t-
test. T-test result shows that t
count
= 2,51 at cognitive
aspect, t
count
= 7,69 at affective aspect, and t
count
=
4,27 at psychomotor aspect, and t
table
= 1,67 at 0,05,
which means that t
count
>t
table
so that Ho is rejected.
The results show that there is significant difference
on the learning outcomes of the students at
experiment class and control class. For that, it can be
concluced that there is a significant effect of the
implemention of Guided Discovery Strategy using
LKS to the learning outcomes on IPA Physics of
VIII students in SMP N 24 Padang.
The implementation of Guided Discovery
Strategy using LKS will assist the teachers in
increasing students involvement in learning process.
In the strategy students are let finding the solution of
the problem themselves or experiencing themselves.
Teacher only guides and gives instruction. Guided
Discovery Strategy using LKS can be used as an
alternative strategy to solve the problem in learning
Physics in the class.
REFERENCES
Arikunto, S., 2009. Dasar-Dasar Evaluasi
Pendidikan.rev.ed. Jakarta: Bumi Aksara.
Depdiknas.2008. Panduan PenyusunanKurikulum Tingkat
Satuan Pendidikan JenjangPendidikan dasar dan
menengah. Jakarta: BSNP.
Hamalik, O., 2011. Kurikulum dan pembelajaran. Jakarta:
Bumi Aksara.
Roestiyah. 2008. Strategi Belajar Mengajar.Jakarta:
Rineka Cipta.
Suherman, E., 2003. Strategi Pembelajaran Matematika
Kontemporer.Bandung: UPI.
Sudjana, N. 2002. Penilaian Hasil Proses Belajar
Mengajar. Bandung: Remaja RosdaKarya.
Sugiyono. 2010. Metode Penelitian Kuantitatif Kualitatif
dan R & D. Bandung: Alfabeta.
Suryosubroto. 1997. Proses Belajar Mengajar di Sekolah.
Jakarta: Rineka Cipta.
The Effect of Guided Discovery Learning Strategy using Students’ Worksheet (LKS) to the Learning Outcomes on IPA Physics of Grade
VIII Students in SMP N 24 Padang
583
