
Relationship between Curiosity and Intrinsic Motivation
for Science Process Skills
Tuti Hardianti
1
, Lisa Ariyanti Pohan
2
, Julia Maulina
2
and Uswatun Hasanah
2
1
Physic Education, Universitas Islam Sumatera Utara, Jl. Sisingamangaraja. Teladan-Medan. Medan, Indonesia
2
Chemistry Education, Universitas Islam Sumatera Utara, Jl. Sisingamangaraja. Teladan-Medan. Medan, Indonesia
Keywords: Curiosity, Intrinsic-Motivation, Science Process Skills.
Abstract: This research aims to analyze (i) the initial curiosity, motivation, and science process skills of students (ii)
the relationship between curiosity and science process skills; (iii) the relationship between intrinsic
motivation and science process skills; and (iv) the relationship between curiosity and intrinsic motivation
toward science process skills.The subject in this study is students of 7th grade An-Nizam Junior High
School Medan. This type of research is quantitative descriptive. Data about the curiosity, intrinsic
motivation and science process skills were collected by test and nontest instruments. This research was
analyzed by using linear regression. The results showed that the intrinsic motivation and curiosity of An-
Nizam students are already in the high category but students' science process skills are still low. There is no
significant relationship between curiosity and science process skills (0.478 > 0.05), intrinsic motivation
and science process skills (0.910 > 0.05) and curiosity and intrinsic motivation toward science process skills
(0.673> 0.05).
1 INTRODUCTION
Education is essentially a conscious effort to develop
personality and abilities within and outside the
school(Law of the Republic of Indonesia Number 20
of 2003 concerning the National Education System).
Education plays an important role in improving the
quality of human resources that support the progress
of development.
Students are resources that have the
fundamentals of potential that need to be developed
through education. All students basically want to
succeed in the learning process, but to achieve good
results, students find barriers that lead to failure in
achieving learning goals. Therefore, to achieve the
desired learning results, it is necessary to see some
factors that students have.
According to Ahmadi(Ahmadi,2005), the factors
that influence learning can be classified into two
parts, namely internal and external factors. Internal
factors are those that come from students.The
following are included in the internal factors such as
intelligence, physical factors or physiological
factors, attitudes, interests, talents, and intelligence.
While external factors cover social and
environmental factors nonsocial.In addition, Slameto
(Slameto,2013) states that external factors that can
affect learning are the family environment, school
environment, and community environment. Internal
and external factors significantly influence student’s
achievement. One of the most influential factors is
the curiosity and motivation factor.
The curiosity and motivation of a student is an
internal factor affecting the learning process in the
classroom. The curiosity is the initial asset for
students in the learning process. The curiosity will
encourage students to fulfill their motivation. In
order to fulfill his curiosity, the students will go into
the process of searching. The curiosity is a character
that comes from the processing of the mind (Samani,
dkk, 2012, p. 25). The curiosity makes students
more sensitive in observing the various phenomena
or events around them, and will open up challenging
new worlds and attract them to learn more deeply.
Sulistyowati (Sulistyowati,2012, p. 74) argues that
curiosity is the attitude and action that always try to
know more deeply and wider than what is learned,
seen, and heard.
Mustari (Mustari,2011, p. 109) argues that to
develop curiosity in children, the freedom of the
child itself must exist to perform and serve his
curiosity. One cannot simply rebuke somebody else
Hardianti, T., Pohan, L., Maulina, J. and Hasanah, U.
Relationship between Curiosity and Intrinsic Motivation for Science Process Skills.
DOI: 10.5220/0008893007230727
In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Multidisciplinary Research (ICMR 2018) - , pages 723-727
ISBN: 978-989-758-437-4
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
723

who does not know or is lazy when asked or asking.
Findings from the psychology of curiosity can be
profitably employed to guide teaching practice, in a
range of educational contexts, to motivate students
to seek information (Pluck and Johnson,2011, p. 29).
In addition to curiosity, the intrinsic motivation
of a student is also an important factor in learning.
Motivation is a dominant factor in influencing the
learning process. Motivation is the main factor
driving someone to do something. Therefore,
motivation is a factor that influences student to
involveactively in learning. Motivation is a complex
part of human psychology and behavior that
influences how individuals choose to invest their
time, how much energy they exert in any given task,
how they think and feel about the task, and how long
they persist at the task (Bakar, 2014). The
motivation of students in science learning is a point
as supporting conditions to the central dogma of
academic performance and critical thinking in
school science. Moreover, motivation refers to
reasons that underlie behavior that is characterized
by the students’ interests, willingness, and volition
(Beal and Stevens, 2011).According to Ryan and
Deci (Ryan and Deci,2000), intrinsic motivation is
defined as doing an activity for its inherent
satisfaction rather than for some separable
consequence. When intrinsically motivated, a person
is moved to act for the external challenge, pressures
or rewards.
The Intrinsic motivation can be stronger if given
outside encouragement. In the learning process, if
the students perceive the task as something
interesting, relevant personally, meaningfully, and at
a level appropriate to the student's abilities, they
think they can succeed in completing the task. The
intrinsic motivation will also strengthen if the task is
connected to by the real world and students have
control over the task. Teachers support students'
intrinsic motivation by increasing their curiosity and
being sensitive to individual differences in
motivating students (Santrock, 2013).The function
of intrinsic motivation for students is to encourage
student learning behavior, influence student learning
achievement, build learning that is more meaningful
and motivate the achievement of student learning
goals.
The factors of curiosity and motivation are
equally important factors in achieving the expected
learning outcomes, one of which is the mastery of
science process skills. Scientific process skills are
the result of learning in the form of scientific work
skills. Abungu (Abungu,2014) states that process
skills are the centers for procurement of the
scientific knowledge that is useful for solving
problems in society. Therefore, the development and
improvement of students’ process skills become
matters of importance for the teacher to do for the
attainment of learning objectives.Scientific process
skills can also be interpreted as an insight or
development of intellectual, social, and physical
skills derived from the fundamental ability that in
principle exists in the learner (Dimyati and
Mudjiono, 2006, p. 138).When learners interact in
the world of science, they find their own research
through the question, hypothesis, prediction,
investigation, interpretation, and communication
stages and these are what are called science process
skills (Ash, 1998).Process skills could be developed
through direct experiences as learning experience
(Rustaman, 2005).
Rezba et al. (Rezba et al.2007) said that science
process skills could be divided into two groups,
namely the basic skills and the integrated skills. The
basic skills consist of the observation,
communication, classification, measurement,
temporary/tentative/initial conclusion (or inference),
and prediction skills. The integrated skills consist of
the variable identification, table making, graph
making, inter-variable relation description, data
elicitation and processing, investigation analysis,
hypothesis construction, variable operational
definition, and investigation and experiment design
skill.
All of the science process skills cannot be
instantly mastered by students. They takes a process
of habituation and practice.Creating and setting
learning habits that can grow process skills in
learners will not be easy.Habits are only possible
through persistent processes, and sacrifices
accompanied by ongoing training for consistent
repetition.It is so difficult to build positive habits
because every habit must be driven by an
understanding of knowledge and capable of benefit
from the behavior.
Therefore, the factor from within the student is
an important part to assist the process of habituation,
such as curiosity and intrinsic motivation of student
so that the student process skills can be mastered
properly.
This study was conducted to see the early interest
and intrinsic motivation as well as its relationship
with students' science process skills because
basically the success or failure of learning depends
not only on external but also internal factors; both
factors are equally important.
ICMR 2018 - International Conference on Multidisciplinary Research
724
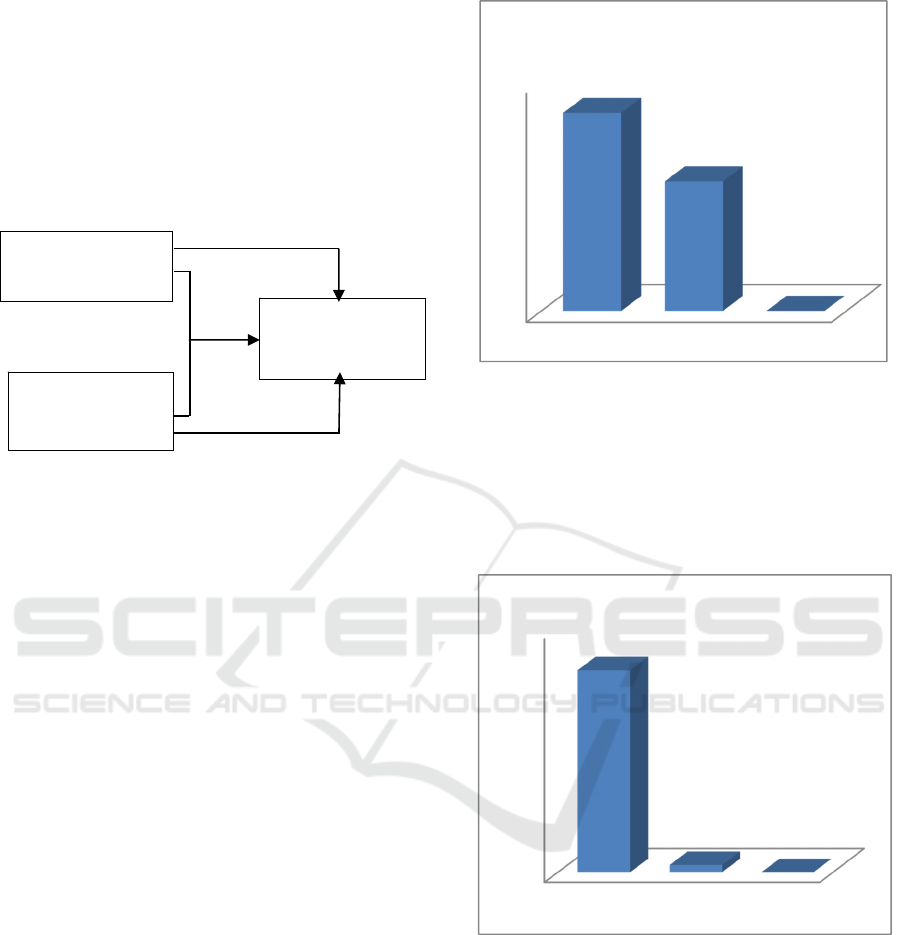
2 METHODS
The method of research in this study is quantitative
descriptive. This method provides a description of
the variables to be studied and investigate the
relationship between variables, among them is the
relationship between the variables of curiosity and
intrinsic motivation with sains process skills.
Figure 1: Design of research method.
The study was conducted at AN-Nizam junior
high school Medan. The subjects of the study were
students of 7th grades. The Technique of collecting
the data was done by a technique of test and nontest.
Science process skills are using test instrument for
data collection, while nontest technique is using
instrument in the form of the question to reveal data
about curiosity and intrinsic motivation.
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
3.1 Results
Based on the data analysis obtained, the results ca be
described as the following:
a. Curiosity (X1)
The curiosity obtained from the questionnaire is
shown in Figure2.
Based on Figure 2, it can be seen that students
who have high curiosity are 52, medium curiousity
34, and low curiousity 0. It indicates that the
curiosity of An-Nizam's students in this initial study
is essentially excellent.
Figure 2: The curiosity students with high, medium, and
low criteria.
b. Intrinsic Motivation (X2)
The curiosity obtained from the questionnaire is
shown in the Figure 3..
Figure 3: The intrinsic motivation students with high,
medium and low criteria.
Based on Figure 3, it can be seen that the
students who havehigh intrinsic motivation are 83,
medium intrinsic motivation3, and low intrinsic
motivation 0. It indicates that the intrinsic
motivation of An-nizam's students in this initial
study is essentially excellent.
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
High Medium Low
52
34
0
0
20
40
60
80
100
High Medium Low
83
3
0
Curiosity
Intrinsic
Motivation
ScienceProcess
Skills
Relationship between Curiosity and Intrinsic Motivation for Science Process Skills
725
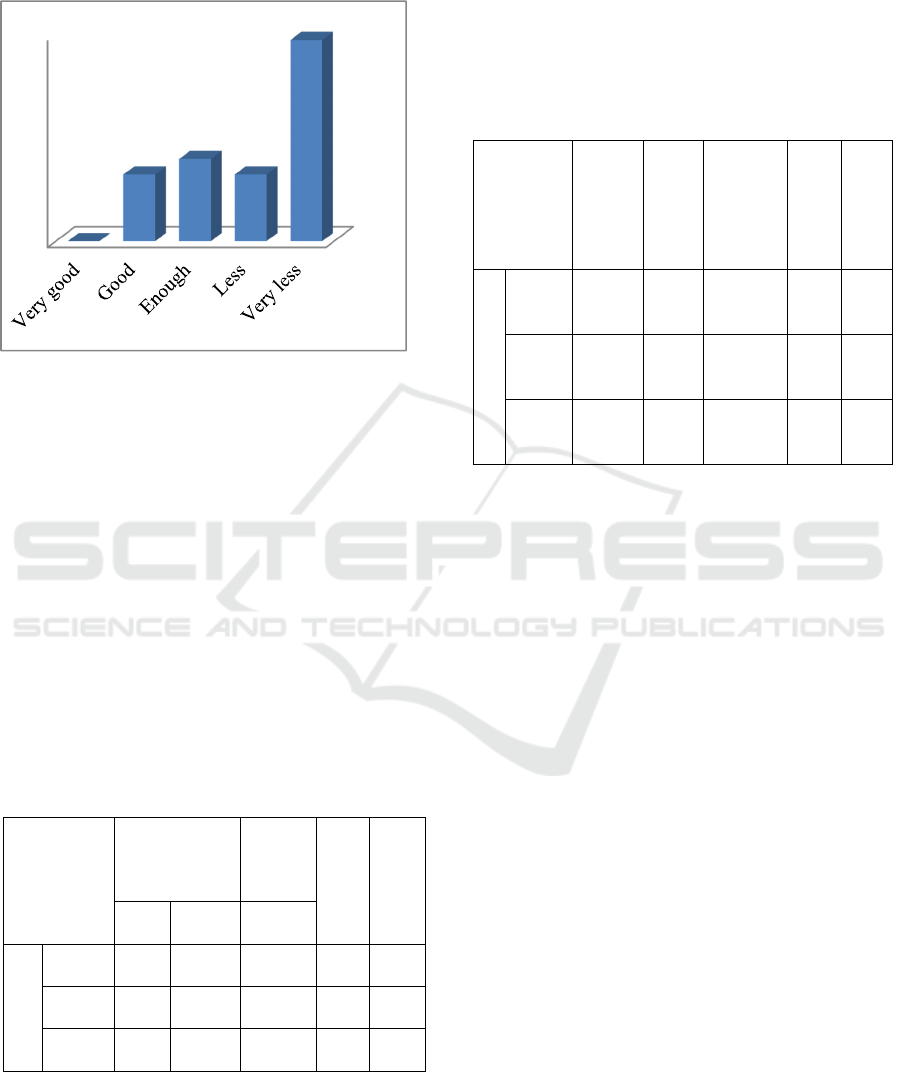
c. Science Process Skills (Y)
The sains process skills obtained test is shown in
Figure 4.
Figure 4: The science process skills students with some
criteria.
Based on figure 4, it can be seen that students
who have science process skill with a very good
category are 0. Students who have good category are
13 and enough category 16. Students who have a
low category are 39. This indicates that science
process skills of An-nizam's students in the initial
study were low.
The results obtained were to find out the linear
relationship of curiosity (X1) and intrinsic
motivation (X2) towards scientific process skills (Y)
by conducting a linear regression test. The results of
the analysis with the SPSS assistance program for
several variables can be seen in Table 1 and Table 2.
Table 1:Table of Significance of Curiosity and
Intrinsic Motivation.
Model Unstandardize
d Coefficients
Standa
rdized
Coeffi
cients
t Sig.
B Std.
Error
Beta
1 (Const
ant)
22.8 26.54
.85 .393
Curios
ity
.262 .367 .092 .71 .478
Motiv
ation
.027 .237 .015 .11 .910
Table 1 shows the significant value for the
curiosity of 0.478 (p> 0.05) so that the hypothesis is
rejected. It means that the curiosity variables have
no significant effect on the science process skills.
Furthermore, for intrinsic motivation variables, the
above data shows a significant value of 0.910
(p>0.05); therefore, the hypothesis is rejected. It
means that intrinsic motivation variables also have
no effect on the science process skill.
Table 2: Table of Significance of Curiosity and
Intrinsic Motivation toward Science Process Skills.
Model Sum
of
Squar
es
df Mean
Square
F Sig.
1 Regre
ssion
405.6
61
2 202.830 .398 .67
3
a
Resid
ual
39720
.882
78 509.242
Total 40126
.543
80
Table 2 shows the significant value of 0.673 (p>
0.05). It can be concluded that the hypothesis is
rejected. It means that the variables of curiosity and
intrinsic motivation have no significant effect
simultaneously on the science process skills.
3.2 Discussion
Based on the results, it has been found that the
motivation and curiosity of the students in this initial
study are in the high category. This can give a good
influence in the learning process because the success
or failure of a learning can be influenced by factors
from within the students. As revealed by Syah
(2006), there are several factors that affect the
learning achievement of internal factors and external
factors. Internal factors consist of physical and
psychological aspects (talents, attitudes, habits,
interests, motivation, and intelligence); External
factors consist of the social environment and
nonsocial environment.
The high curiosity and high motivation in this
initial study were not in line with the value of
students' science process skills. This can be seen that
there is no significant relationship between the
curiosity and science process skills (0,478>
0,005),intrinsic motivation and science process skills
(0.910> 0.05) and curiosity and motivation toward
students' science process skills (0.673> 0.05). This is
0
10
20
30
40
0
13
16
13
39
ICMR 2018 - International Conference on Multidisciplinary Research
726

because the science process skills are still quite
foreign to the students so that they feel unfamiliar in
doing tests related to the science process skills. In
addition, students are still rarely given lessons that
can improve the science process skills, though
science process skills are skills that need to be
trained to start from the basic level. This is in
accordance with the claim proposed by Padilla &
Okey (1984) who state that science process skills
need to be strongly emphasized in elementary,
middle, and secondary science curricula and
classrooms.
The findings of this initial study suggest that
there should be still a need to familiarize learning
that can improve the science process skills. In
addition, the curiosity and high motivation of
students can be a positive thing for the
implementation of a good learning process in the
future.
4 CONCLUSION
Based on the foregoing results, the following are
concluded: (1) The intrinsic motivation and curiosity
of An-Nizam students are already in the high
categorybut students' science process skills are still
low, (2) There is no significant relationship between
curiosity andscience process skills, (3) There is no
significant relationship between intrinsic motivation
andscience process skills and (4) There is no
significant relationship between curiosity and
intrinsic motivation toward science process skills.
REFERENCES
Bakar, Ramli. 2014. The Effect of Learning Motivation on
Student’s Productive Competencies in Vocational
High School, West Sumatra. International Journal of
Asian Social Science, 2014, 4(6): 722-732.
Beal, C.R., & Stevens, R.H., 2011. Improving students’
problem solving in a web-based chemistry simulation
through embedded metacognitive messages.
Technology, Instrumentation,Cognition and Learning,
8(3), 255-271
Ryan, R., Deci, E., 2000. Intrinsic and extrinsic
motivations: classic definitions and new directions.
Contemp. Educ. Psychol. 25, 54–67.
Pluck,Graham & Johnson,Helen. 2011.Stimulating
Curiosity To Enhance Learning GESJ: Education
Science and Psychology, No.2(19)
Padilla, M. J., & Okey, J. R., 1984. The Effects of
Instruction on Integrated Science Process Skill
Achivement. Journal of Research in Science
Teaching, 21, 3, 277-287.
Tuana, H.L., Chin, C.C., & Shieh, S.H., 2005. The
development of a questionnaire to measure students’
motivation towards science learning. International
Journal of Science Education, 27(6), 639-654.
Syah, M. 2006. Psikologi Belajar. Jakarta: Raja Grafindo
Persada.
Samani,Muchlas., & Hariyanto. 2012. Pendidikan
karakter. Bandung: PT Remaja Rosdakarya.
Mustari, Mohamad. 2011.Nilai Karakter. Yogyakarta:
LaksBang PRESSindo.
Depdiknas., 2003. Undang-undang RI Nomor 20 Tahun
2003 Tentang Sistem Pendidikan Nasional. Bandung:
Citra Umbara.
Ahmadi, A. dan Prasetyo.,2005. Strategi Belajar
Mengajar. Bandung: Pustaka Setia.
Slameto., 2013. Belajar dan Faktor-Faktor yang
Mempengaruhinya Edisi Revisi.Jakarta: Rineka Cipta
Abungu, H. E., Mark 1.O., & Samuel, W., 2014. The
effect of Science process skills teaching approach on
secondary school students; Achievement in Chemistry
in nyando district, Kenya. Journal of Education and
Social Research, 4 (6), 559-371.
Ash, D., 1998. Inquiry thoughts, views, and strategies for
the K–5 classroom. Arlington: National Science
Foundation.
Rustaman, N. Y. 2005. Strategi belajar mengajar biologi.
Malang: UM Press
Dimyati & Mudjiono., 2009. Belajar dan Pembelajaran.
Jakarta: Rineka Cipta.
Santrock, J.W. 2013. Psikologi Pendidikan. Jakarta:
Kencana.
Rezba, R.J., Sprague, C.R., McDonnough, J.T., & Mat,
J.J., 2007Learning and Assessing Science Process
Skills. Dubuque: Kendall/ Hunt Publishing Company.
Relationship between Curiosity and Intrinsic Motivation for Science Process Skills
727
