
Exploring Students' Perceptions and Experiences in using
Authentic Assessment at Subsidized Pre-service Teacher Profession
Education Program of English Language Education Study Program
of Universitas Khairun
Sutaryo
1
and Nurprihatina Hasan
2
1
English Language Education Study Program, Faculty of Teachers Training and Education, Universitas Khairun,
Ternate, Indonesia.
2
English Literature Study Program, Faculty of Culture Science, Universitas Khairun, Ternate, Indonesia.
Keywords: Authentic assessment, Productive skills, Qualitative research, Thematic analysis.
Abstract: Authentic assessment has been recommended to use in teaching and learning of English based on
Curriculum 2013 in Indonesian high schools. This is in line with the principle of the teaching and learning
of English which is mainly activity-based. Authentic assessment is particularly used when high school
teachers want to assess English speaking and writing skills of their students. This article presents part of the
research which is to explore views and experiences of the students of Program Pendidikan Profesi Guru
Prajabatan Bersubsidi [Subsidized Pre-Service Teacher Profession Education Program] at Universitas
Khairun concerning the use of authentic assessment during their teaching practicum. This is qualitative
research with a case study involving 11 students of ‘Program Pendidikan Profesi Guru Prajabatan
Bersubsidi [Subsidized Pre-service Teacher Profession Education Program] of English Language Education
Study Program at Universitas Khairun. Semi-structured interviews were used to collect data from the
respondents. The data obtained were analyzed using Miles and Huberman’s thematic analysis. Findings
from the data analysis were then discussed.
1 INTRODUCTION
Education is an important and strategic pillar in
nation building including Indonesia and because it is
part of the nation's component. In Indonesia, the
meaning of education is embodied in the 1945
Constitution Chapter XIII on Education and Culture
article 31 along with several related laws and
regulations. For example, Law Number 20 of 2003
which regulates the national education system,
especially in article 3, National education,
performance and character and dignified civilization
of the country in order to educate the nation's life,
aims to develop potential students to become
believers and fear God Almighty, noble, healthy,
knowledgeable, capable, creative, independent, and
a democratic and responsible citizen. Furthermore,
Law number 20 of 2003 also states that the system
of implementing national education which is a
united part of achieving national education goals,
among others, resources, society, curriculum,
students, education staff, and educators in all units,
types, and levels of education.
Teachers as professionals at the elementary and
secondary education units and act as learning agents
function to improve the quality of national education
must fulfil academic qualifications, have a number
of competencies and educator certificates. Law
number 14 of 2005 concerning Teachers and
Lecturers clearly emphasizes that a teacher must
have a minimum education qualification of Bachelor
(S1) or Diploma (D) IV. Law No. 14 of 2005 also
underlines that teachers must have several aspects,
namely social, pedagogic and professional
competence that is produced through professional
education. This means that being a professional
teacher, he or she has to have an S1 or D IV
academic education plus professional education.
This is in line with the issuance of Permenristekdikti
[Minister of Research, Technology, and Higher
Sutaryo, . and Hasan, N.
Exploring Students’ Perceptions and Experiences in using Authentic Assessment at Subsidized Pre-service Teacher Profession Education Program (SPTPEP) of English Language Education
Study Program of Uni.
DOI: 10.5220/0008898601470159
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Teaching and Learning (ICTL 2018), pages 147-159
ISBN: 978-989-758-439-8
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
147

Education Affairs Regulation] Number 55 of 2017
concerning Teacher Education Standards. Thus, it is
expected that the birth of quality generation can be
generated through education with teachers who meet
academic requirements, have several competencies,
and educator certificates.
Efforts to obtain a number of teacher
competencies are carried out through the Teacher
Professional Education Program (PPG).
Permenristekdikti Number 55 of 2017 concerning
Teacher Education Standards explains that PPG is
an educational program held after an undergraduate
or applied bachelor program to obtain an educator
certificate in early childhood education in the
formal, basic, and/or secondary education pathways.
The implementation of the PPG program is
implemented in a number of Education Personnel
Education Institutions (LPTK) that meets the
requirements. The PPG program consists of PPG in
both pre-service (Prajabatan) and in-service (Dalam
Jabatan). PPG Prajabatan itself consists of regular,
subsidized and independent.
Khairun University as one of the LPTK colleges
in Indonesia has been given the mandate to hold a
PPG 'Prajabatan' program with 44 other LPTK
colleges as well as the Menristekdikti Decree
Number 280 / M / KPT / 2017. The first class of the
PPG program entrusted by the Ministry of Research
and Technology is the PPG Subsidized English
Language Study Program which will last for one
year starting in even semester 2017/2018 by
applying the PPG curriculum recommended by
Kemenristekdikti with 38 credits, consisting of 22
credits in the first semester and 16 credits second
semester (Kemeristekdikti, 2017). Unlike learning in
undergraduate education programs, the learning
system of the PPG Subsidized Pre-service Study
Program in English in the first semester emphasizes
more on the pattern of a workplace.
To determine someone who participates in the
PPG Program to achieve graduate competency
standards that have been formulated in learning
outcomes, an assessment must be conducted.
Permenristekdikti Number 55 of 2017 concerning
Teacher Education Standards Article 21 paragraph
(1) states that the Standard of assessment as referred
to in Article 17 letter d is a minimum criterion
regarding the assessment of student learning
processes and outcomes in order to fulfil the
learning achievements of graduates of the PPG
Program. Furthermore, paragraph (2) states that the
assessment of the process and student learning
outcomes as referred to in paragraph (1) includes:
(a) assessment of the process and product of the
development of learning devices; (b) the process and
products of the Field Experience Program (PPL); (c)
competency test; and (d) assessment of community
life in dormitories / other facilities. The assessment
must be in accordance with the Process and Result
Assessment Guidelines compiled by
Kemenristekdikti [Ministry of Research,
Technology, and Higher Education Affairs] (2017)
and Kemendikbud [Ministry of Education and
Culture Affairs] (2015) as guidelines for Khairun
University as the organizer of the PPG Program for
Subsidized English Studies, instructor lecturers,
tutors, and students. Particularly related to the
assessment of points: (a) assessment of the process
and product development of learning tools carried
out during the workshop and (b) assessment of PPL
processes and products carried out during PPL, the
assessment is more focused on using authentic
assessments to measure pedagogical and
professional competencies.
As stated above, the Subsidized Pre-Service PPG
Program for the English Language Education Study
Program is the first PPG program held at Khairun
University. In addition, the implementation of this
PPG program constitutes the first experience by
lecturers, tutors, students, and PPG Program
administrators at Khairun University. This study
aims to know the students' perceptions and
experiences in using authentic assessment at the
Subsidized Pre-Service PPG Program of the English
Language Education Study Program of Khairun
University during teaching practicum (PPL) in
partner schools.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
2.1 Teachers and Teacher
Professionalism
In article 1 point 1 of the Law of the Republic of
Indonesia (RI) Number 14 of 2005 concerning
Teachers and Lecturers, it is stated that teachers are
professional educators with the main task of
educating, teaching, guiding, directing, training,
assessing, and evaluating students in education early
childhood at formal education, basic education, and
secondary education. Furthermore, Article 4
underlines the position of the teacher as a
professional who functions to enhance the dignity
and role of the teacher as an agent of learning that
serves to improve the quality of national education.
From the two articles in the Act, it is clear that the
teacher has an honourable and strategic duty and
ICTL 2018 - The 1st International Conference on Teaching and Learning
148

position because the teacher is the front guard to
prepare a quality national generation for the progress
of the nation, especially through formal education,
both primary and secondary education. The
affirmation of the two articles in the Law which
underline the teacher as a professional also suggests
that the teacher must have a number of
requirements.
The requirements of teachers as professionals are
to fulfil academic qualifications, have a number of
competencies and educator certificates as stated in
Article 8-11 of the Republic of Indonesia Law
Number 14 of 2005 concerning Teachers and
Lecturers. In terms of fulfilling academic
qualifications, article 9 of the Law clearly confirms
that teachers must have a minimum education
qualification of Bachelor (S1) or Diploma (D) IV.
Furthermore, Article 10 of Law Number 14 of 2005
also underlines that teachers must have a number of
competencies, namely personal, social, pedagogical
and professional competencies obtained through
professional education. Meanwhile, to obtain an
educator certificate, the teacher must attend
professional education. This means that the
requirement to become a professional teacher
besides having to have an S1 or D IV academic
qualification must also be added with professional
education in order to have a number of competencies
mentioned above. This was reinforced by the
issuance of Permenristekdikti Number 55 of 2017
concerning Teacher Education Standards that efforts
to realize the creation of professional teachers with a
number of competencies mentioned above are
carried out through the Teacher Professional
Education (PPG) program.
2.2 Teacher Competency Standards
As stated earlier, Republic of Indonesia Law
Number 14 of 2005 concerning Teachers and
Lecturers mandated that in addition to fulfilling
academic qualifications and a number of the
requirements above, teachers must have a number of
competencies namely pedagogical, personality,
social and professional competencies obtained
through professional education. The Government
Regulation (PP) of the Republic of Indonesia
Number 74 of 2008 further contains in detail the
understanding and examples of the said
competencies.
Pedagogic competence is defined as the ability of
teachers in the management of learning of students
as stated in article 3 paragraph 4 of the PP, which at
least includes:
a). understanding of insight or educational
foundation;
b). understanding of students;
c). development of a curriculum or syllabus;
d). learning design;
e). the implementation of learning that is
educational and dialogical;
f). utilization of learning technology;
g). evaluation of learning outcomes; and
h). development of students to actualize the various
potentials they have.
Meanwhile, personality competencies as
contained in article 3 paragraph 5 of PP Number 74
of 2008 include a). believe and fear; b). noble; c).
wise and prudent; d). democratic; e). steady; f).
authoritative; g). stable; h). adult; i). honest; j).
sportsmanship; k). be an example for students and
society; l). objectively evaluating one's own
performance; and m). develop yourself
independently and sustainably.
Furthermore, social competence as stated in
article 3 paragraph 6 of PP No. 74 of 2008 is
interpreted as the teacher's ability as part of the
community which at least includes the competence
to:
a). communicate verbally, write and/or gesture
politely;
b). use functional communication and information
technology;
c). get along effectively with students, fellow
educators, energy education, the leadership of the
education unit, parents or guardians of students;
d). get along politely with the surrounding
community by heeding the norms as a well
applicable value system, and
e). apply the principle of true brotherhood and a
spirit of togetherness.
Finally, professional competence as stated in
article 3 paragraph 7 of PP No. 74 of 2008 is defined
as the ability of teachers to master knowledge in the
fields of science, technology, and/or arts and culture
which at least includes the mastery as the following
example:
a). subject matter broadly and deeply in accordance
with the standards of the unit program content
education, subjects, and/or group of subjects to be
taught; and
b). relevant concepts and methods of scientific
discipline, technology, or arts, which conceptually
overshadow or are coherent with the educational
unit program, subjects, and/or group of subjects to
be taught.
As mandated in article 10 of the Republic of
Indonesia Law Number 14 of 2005 and article 3
Exploring Students’ Perceptions and Experiences in using Authentic Assessment at Subsidized Pre-service Teacher Profession Education
Program (SPTPEP) of English Language Education Study Program of Uni
149

paragraph 2 of PP RI Number 74 of 2008 which was
amended by PP RI Number 19 of 2017, the four
competencies (pedagogic, personality, social, and
professional) mentioned above are obtained through
education profession. The issuance of
Permenristekdikti Number 55 of 2017 concerning
Teacher Education Standards explains that what is
meant by professional education is Teacher
Professional Education (PPG). So, the four teacher
competencies are obtained through the PPG program
with various fields of studies including the field of
English Language Education.
2.3 Teacher Professional Education
Program (PPG)
Permenristekdikti Number 55 of 2017 concerning
Teacher Education Standards explains that PPG is
an educational program held after an undergraduate
or applied bachelor program to obtain an educator
certificate in early childhood education in the
formal, basic, and/or secondary education pathways.
The implementation of the PPG program is
implemented in a number of Education Personnel
Education Institutions (LPTK) that meets the
requirements. The PPG program consists of PPG in
Pre-Service (Prajabatan) and In-Service (Dalam
Jabatan) programs. PPG Prajabatan itself consists of
regular, subsidized and independent. Khairun
University as one of the LPTK colleges in Indonesia
has been given the mandate to hold a PPG
Prajabatan program with 44 other LPTK colleges as
stated in the Menristekdikti Decree Number 280 / M
/ KPT / 2017.
The initial class of the PPG program entrusted by
the Ministry of Research and Technology to Khairun
University is the Subsidized Pre-Service PPG
program of the English Language Education Study
Program which will last for one year starting in even
semester 2017/2018 by applying the PPG curriculum
recommended by Kemeristekdikti. Starting in July
2018, Khairun University is also entrusted by the
Ministry of Research, Technology and Higher
Education to hold an online or online PPG in the
Subsidized Study Program for Primary School
Teacher Education (PGSD).
Specifically, the Subsidized Pre-Service PPG
program of the English Language Education Study
Program applies the English PPG Curriculum from
Kemenristekdikti with 38 SKS, consisting of 22
SKS in the first semester and 16 SKS in the second
semester (Kemeristekdikti, 2017). Unlike learning in
undergraduate education programs, the learning
system of the Subsidized Pre-Service PPG program
of the English Language Education Study Program
in the first semester emphasizes the workshop
pattern and the teaching practicum/ field experience
program (PPL) in the second semester. In the PPG
curriculum in the English Language Education
Study Program there is a profile description of
professional English teachers, namely "English
Educators who are able to plan and implement
collaborative and sustainable learning that have four
competencies namely professional, pedagogical,
social, and personality competencies", in line with
what is mandated in the Republic of Indonesia Law
Number 14 of 2005 concerning Indonesian Teachers
and Lecturers and PP Number 74 of 2008
concerning Teachers. There are ten workshops in the
Subsidized Pre-Service PPG program of the English
Language Education Study Program so that PPG
graduates could achieve the learning outcomes of
the three aspects (attitudes, knowledge, and skills),
which include Workshops to PPG, Prota and
Prosem, Preparation of SMP Learning Instruments
(Class VII, VIII, IX), High School (Class X, XI,
XII) and Vocational School, and Preparation of
Classroom Action Research (CAR). To find out the
extent to which the implementation of the PPG
program runs well and achieve the learning
outcomes set forth in the PPG curriculum so that the
profiles of professional teachers can be realized, it is
necessary to conduct a series of assessments.
2.4 Assessment and Authentic
Assessment
There are several definitions of assessment. Nitko
and Brookhart (2011: 3) suggest: "Assessment is a
process for obtaining information for making a
particular educational decision", which can be
interpreted that assessment is a process of gathering
information to make an educated decision. Nitko and
Brookhart (2011) further suggest that when it is
associated with students' learning, then the
assessment used in the management of learning
consists of two assessments used to gather
information in student-related decision making
which includes:
a). management of learning;
b). placement of students in a program;
c). student grouping;
d). counselling and directing students;
e). student selection; and
f). determining the graduation of students from a
program using formative assessment and summative
assessment (Nitko & Brookhart, 2011; Brown &
Abewickrama, 2010). Furthermore, it is said that
ICTL 2018 - The 1st International Conference on Teaching and Learning
150

formative assessment aims to plan learning
activities, place students in the learning process,
monitor student progress in learning, diagnose
student learning difficulties, and provide feedback or
feedback on how students improve their learning.
Formative assessment is often also called assessment
for learning. Assessment for learning is carried out
during the learning process and is usually used as a
basis for improving the teaching and learning
process. With assessment for learning,
teachers/educators can provide feedback on the
learning process of students and monitor their
learning progress. Assessment for learning can also
be used by teachers/educators to improve
performance in facilitating students (Airasian, 2005;
Butler & McMunn, 2006; McDonald, 2013; Nitko &
Brookhart, 2011; Pellegrino et al., 2001). Various
forms of formative assessment, such as assignments
and quizzes, are examples of assessment for
learning.
While summative assessment aims to report to
students and parents about the achievement of
learning, and report to the teacher concerned about
the effectiveness of the learning done, and of course
to give grades to students related to their learning
outcomes. Summative assessment is often referred
to as assessment of learning (the final assessment of
learning to find out the achievement of learning.
Assessment of learning is an assessment carried out
after the learning process is complete. The learning
process is completed does not always occur at the
end of the year or at the end the students complete a
certain level. Teacher or educator education
conducts assessments that are intended to provide
recognition of the achievement of learning outcomes
after the learning process is complete (Airasian,
2005; Butler & McMunn, 2006; McDonald, 2013;
Nitko & Brookhart, 2011), meaning that the
educator conducts an assessment of learning. In the
Indonesian context, National Exams,
school/madrasah examinations, and various forms of
summative assessment are an assessment of
learning.
Assessment as learning has a function similar to
assessment for learning, which functions as a
formative and is implemented during the learning
process. The difference is that as learning
assessment involves students actively in the
assessment activities. Students are given the
experience to learn to be an appraiser for
themselves. Self-assessment and peer assessment are
examples of assessment as learning. In an
assessment, students can also be involved in
formulating assessment procedures, criteria, or
rubrics/assessment guidelines so that they know
exactly what must be done in order to obtain
maximum learning outcomes (Bloxham & Boyd,
2007).
Of the two assessment objectives (formative and
summative) in three forms, namely assessment of
learning, assessment for learning and assessment as
learning, the assessment of learning outcomes by the
teacher/educator is not only focused on results, but
also on the learning process. Learners can be
involved in the process of assessing themselves as a
means to practice self-assessment.
From the form, the assessment can be done both
formally and informally, both through tests and non-
tests. The various forms of tests that exist such as
the form of the test is true-false, multiple choice,
matching, filling out, and description. These various
forms of assessment tests are often called standard
assessment or conventional assessment and are often
criticized by various parties because the assessment
of this form of test only emphasizes cognitive or
knowledge aspects. Even if it is still used, it is
recommended that the use of an assessment of this
form of test should be directed at directing students
to the ability to think critically at a high level (higher
order thinking skills). Whereas the non-test
evaluation forms include performance appraisal
using a rubric, portfolio, journals, conferences,
interviews, and observations of Nitko & Brookhart,
2011). Assessments of non-test forms such as these
are often called alternatives in assessment or
performance assessment or authentic assessment
(Nitko & Brookhart, 2011; Brown &
Abeywickrama, 2010). The term alternatives in
assessment and authentic assessment are not
automatically exchanged for their use because of
different intentions. Alternatives in the assessment
are called because this assessment is the opposite of
the standard assessment (use of a test in the form of
a test). While authentic assessment means an
immediate meaningful assessment for students in the
learning process.
According to Nitko and Brookhart (2011: 246),
performance assessments or authentic assessments:
(a) requires students to create a product or
demonstrate a process or both, and (b) clearly define
criteria to evaluate the qualities of students' work. A
performance assessment requires students to do
something about their knowledge, such as making
something, producing a report, or demonstrating a
process. So authentic assessment is used to assess
the process and learning outcomes of students and
their use emphasizes more on skill aspects. Nitko
and Brookhart (2011) also underline that authentic
Exploring Students’ Perceptions and Experiences in using Authentic Assessment at Subsidized Pre-service Teacher Profession Education
Program (SPTPEP) of English Language Education Study Program of Uni
151

assessment must have two things, namely (1)
question or performance task itself and (2)
assessment rubric. In other words, authentic
assessment aims to assess students' abilities related
to the real world, namely how students apply their
knowledge and skills to real tasks using accurate
measurements so that they can describe the abilities
of students as a whole.
3.5 Authentic Assessment at the
Subsidized Pre-Service PPG
Program for the English language
Education Study Program of
Khairun University
To determine whether PPG students who take part in
the PPG Program, including the Subsidized Pre-
Service PPG Program at Khairun University, can
achieve graduate competency standards that have
been formulated in learning outcomes or not, an
assessment must be conducted. Permenristekdikti
Number 55 of 2017 concerning Teacher Education
Standards Article 21 paragraph (1) states that the
Standard of assessment as referred to in Article 17
letter d is a minimum criterion regarding the
assessment of student learning processes and
outcomes in order to fulfil the learning achievements
of graduates of the PPG Program. Furthermore,
paragraph (2) states that the assessment of the
learning process and results of the PPG students as
referred to in paragraph (1) includes: (a) assessment
of the process and product of the development of
learning devices; (b) the process and products of the
Teaching Practicum/ Field Experience Program
(PPL); (c) competency test; and (d) assessment of
community life in dormitories / other facilities. The
assessment must follow the Process and Product
Assessment Guide prepared by Kemenristekdikti
(2017) guidelines for Khairun University as the
organizer of the Subsidized Pre-Service PPG
Program in English Language Education Study
Program, instructor lecturers, tutors, and students
must follow Kemenristekdikti’s assessment
guidelines (2015) for tutors and students in assessing
students in learning English in middle and high
school / vocational school. Particularly related to the
assessment of the points: (a) the assessment of the
process and product development of learning tools
carried out during the workshop and (b) the
assessment of PPL processes and products carried
out during PPL, the assessment emphasizes on using
authentic assessment to measure the pedagogical and
professional competence of the PPG students.
In the Process and Product Assessment Guide
(Kemenristekdikti, 2017), the assessment of the PPG
learning process and product is carried out using the
benchmark reference (PAP). PAP is intended to
obtain an overview of the level of mastery of student
mastery level. Referring to the Government
Regulation of the Republic of Indonesia Number 74
of 2008 which was updated by Number 19 of 2017
concerning Teachers Article 15 paragraph (4) which
states that teacher professional allowances are given
to teachers who fulfil several requirements,
including having a minimum value of performance
appraisal, the graduation limit (passing grade) the
learning outcomes of the PPG program are set at 76
(with Good criteria). Students who have not reached
the graduation limit (benchmark) are given the
opportunity to take the re-examination.
In addition, the Assessment Guide also
emphasizes that the assessment of PPG students
must also follow the principles such as: Valid
(Accurate assessment requires accurate data;
Objective (Assessment is carried out as is; not
influenced by the subjectivity factor of the assessor,
so the assessment results illustrate appropriately
mastery of competence by students) Fair
(Assessment is not profitable or detrimental to
certain students because it is influenced by the
background of students, such as social status,
economy, religion, ethnicity, etc.); Systematic
(Assessment is done in a structured, planned
manner), and follow standard procedures);
Accountable (Assessment must produce accountable
decisions from the side of the process, instruments,
and personnel who carry out the assessment);
Sustainability (Assessment is carried out throughout
the learning process; Goal-oriented (Assessment is
carried out in an integrated and comprehensive way
to measure the success of the learning process as a
benchmark for achieving goals; Integrated
(Assessment is one component of the learning
system which includes planning, implementing, and
evaluating learning; and Open (Assessment must be
conducted openly, meaning the assessment process
to be carried out and the assessment criteria to be
used can be accessed by stakeholders, as a reference
in following the assessment process, a number of
these principles have become commonplace or
generally accepted in the implementation of the
assessment).
In assessing the process and product of
workshops on the development of learning tools and
evaluating PPL processes and products which
include assessments of pedagogic and professional
competencies, the following components, sub-
ICTL 2018 - The 1st International Conference on Teaching and Learning
152

components, indicators, data collection techniques
and forms of assessment instruments are in
accordance with the Ministry of Research,
Technology and Process Assessment Guide (2017)
as the following:
a. The workshop process includes:
1) Mastery of subject matter material to determine
mastery of knowledge such as a) factual; b)
conceptual; c) procedural; d) metacognitive and this
is done through written tests.
2) Mastery of scientific methods such as a)
observing; b) asking; c) collect information; d)
processing information; e) communicating; f)
curiosity; g) objective; and h) critical and this is
done through written tests.
3) Mastery of scientific attitudes such as a)
skepticism; b) open attitude; and c) academic
honesty and this is done through the Questionnaire /
Questionnaire Technique.
4) Mastery of the foundation of educational science
such as a) Theory of child development; and b)
Learning and learning theory and this is done
through written tests.
5) Performance in carrying out workshop such as a)
ability to initiate ideas/activities; b) ability to enrich
ideas/activities; c) Level of Participation in
conducting workshops; d). Combined capabilities in
workshops; e) Ability in presenting the concept of
learning instruments (Attitudes in presentation
activities, functions of communicating material,
Mastery of presentation material) and this is done
through Observation.
6) Peer teaching abilities such as a)
behaviour/appearance in peer teaching; b) Mastery
of material; and c) Pedagogic abilities are carried out
through observation
b. Workshop Products include:
1) Learning instruments (completeness of learning
instruments and instruments quality) are carried out
through documents.
2) Classroom Action Research (PTK) proposals
(complete components of PTK proposals and
Quality of PTK proposals) are carried out through
documents content analysis.
c. The PPL process includes:
1) Teacher competency in implementing PPL such
as a) Pedagogical competency; b) Professional
competence; c) social competence; and d)
Personality competencies carried out through
observation.
2) Ability to carry out PTK such as a) Accuracy in
carrying out the stages/cycle of PTK; and b) the
quality of the PTK stage report is carried out
through observation
3). School management skills such as a)
Participation in building school culture; b) the
ability to foster co-curricular and/or extra-curricular
activities; and c) Using administrative tasks as a
teacher is done through observation with anecdotal
records
d. PPL products include:
1) PPL reports such as a) Completeness of the
components of the PPL report, and b) Reports on the
quality of PPL through document content analysis.
2) PTK reports such as a) Completeness of
components of PTK reports, and b) The quality of
the PTK report is done through document content
Analysis.
From the assessment of (a), the process and
product development of learning instrument during
the workshop and (b) PPL processes and products
that measure pedagogical and professional
competencies, the assessment using the Observation
Sheet and the Document Analysis Sheet is an
example of some assessment techniques in authentic
assessment. This is because in addition to measuring
the skill aspect also because the Observation Sheet
and document content Analysis Sheet are in the form
of Rubrics in which there is coverage that is
assessed so that it reflects all aspects assessed.
Authentic assessments that use this rubric are carried
out by instructor lecturers and in part by tutor
teachers.
Meanwhile, assessments to measure social
competence and personality competence include:
1. Personality Competence, including:
a). Obeying religious teachings and legal norms such
as: Carrying out religious teachings (worship); Stay
away from religious prohibitions, and Obedience to
legal norms and regulations is carried out using
questionnaire techniques/ questionnaires and
observations.
b). Honest such as: Do not lie and can be trusted by
using questionnaire techniques / questionnaires and
observations
c). Responsible such an Acting in harmony with
what is said, Keeping promises, Sacrificing for
others, and Active participation in activities carried
out through questionnaire techniques / Questionnaire
and Observation
d). Polite/polite such as: Do not like to hurt others,
Respect others, Respect others, Speak well is done
by using the technique questionnaire / Questionnaire
/ and Observation.
e). Independent such as: Not dependent on others,
Not easily influenced by others, and having
principles is done through questionnaire techniques /
Questionnaire and Observation.
Exploring Students’ Perceptions and Experiences in using Authentic Assessment at Subsidized Pre-service Teacher Profession Education
Program (SPTPEP) of English Language Education Study Program of Uni
153

f). Creative such as: Having initiative, producing
unique works and having ideas is done by using
questionnaire techniques / Questionnaire and
Observation.
g). Disciplines such as: Acting in accordance with
the provisions, Appreciating time, and Keeping time
is done through Questionnaire / Questionnaire
techniques and Observation.
2. Social competencies, including:
a). Able to work together such as: Sharing work,
Various ideas (Can give and receive ideas), Can
accept the truth of others, Participate actively carried
out through questionnaire / Questionnaire
Techniques.
b). Leadership spirit such as: Can manage other
people, Can be arranged by others, Loyal both as a
leader and member, and has an initiative carried out
using the technique questionnaire / Questionnaire.
c). Inclusive and Tolerant such as: Respecting
differences, Empathy, Not acting discriminatory,
Acting objectively through questionnaire /
Questionnaire techniques.
d). Care like: responsiveness and helpfulness is done
through questionnaire techniques.
e). Possessing communication skills in the
community such as Polite and Effective/productive
through questionnaire / Questionnaire techniques.
In implementing PPL, PPG students also conduct
an assessment of their students to assess the
achievement of their English learning outcomes. In
the Assessment Guidelines published by the
Ministry of Education and Culture (2015), several
examples of authentic assessments are used that use
the rubric in learning English in middle and high
schools. The authentic assessment used to assess
English learning processes and products are such as
in assessing speaking and writing skills. In assessing
these two skills accompanied by a rubric in which
aspects are assessed. An authentic assessment
conducted by PPG students while implementing PPL
is the focus of this research.
Research related to assessment has been carried
out. In the Indonesian context, for example, Sutaryo
(2016) conducted research on assessment involving
a number of college officials, lecturers and more
than 800 students at a university. This research was
to find out their perceptions and experiences in the
use of summative and formative assessments, and
especially how to use assessment of learning,
assessment for learning, and assessment as learning
conducted at a tertiary institution. This was research
with case study design and used mixed methods
because it used data collection techniques commonly
used in quantitative research such as questionnaires /
closed questionnaires and commonly used in
qualitative research such as semi-structured
interviews. The findings showed that the application
of assessment of learning is more dominant than
assessment for learning and assessment as learning.
The respondents actually strongly agreed the need to
use assessment for learning and assessment as
learning but still lack knowledge about this
including how to use it.
Research on authentic assessment in learning
English has been done by Sa'idah, Yulistianti, and
Farida (2017) in learning Indonesian. The study
aimed to determine the effectiveness of applying the
three authentic assessments, namely project
appraisal, performance assessment, and portfolio
assessment. The research method used was
experimental research with a sample of three classes
subjected to three different authentic assessment
treatments. The research sample was class X MA
Darul Ulum Purwogondo Jepara with random
sampling. The research was preceded by a data
requirement test, namely homogeneity test with the
results of p-value 0.163 which showed that the
samples taken were identical because more than sig
0.05. The results of the study indicated that there are
differences in the average value of the three
authentic assessment applications with p-value 0.00.
Among the three assessment, the most effective is
the assessment of the project with the mean
difference showing a value of 3.371. Therefore
authentic assessments are very effective in learning
to improve students' scientific performance.
When compared with this research, Sutaryo
(2016) conducted a study more on how the
assessment of learning, assessment for learning and
assessment as learning were carried out both at the
perspectives and experiences level of the related
parties in higher education. Meanwhile, the research
conducted by Sa'idah, Yulistianti, and Farida (2017)
focused on the effectiveness of the use of authentic
judgments in Indonesian language learning by
involving students at the MA level.
This study focuses on the use of authentic
assessments in the Subsidized Pre-Service PPG
Program for the English Language Education Study
Program, especially on the skills aspect by involving
PPG students to see how their views and experiences
in using authentic judgments.
ICTL 2018 - The 1st International Conference on Teaching and Learning
154

3 RESEARCH METHOD
3.1 Method and Design
This study used a qualitative research method
(Creswell, 2014) with a case study research design.
This research is qualitative research because the
researchers want to know in detail the phenomena
being studied rather than trying to associate between
two or more variables. This study used a qualitative
method because it is characterized by data collection
techniques that primarily used interview according
to the research problem as suggested by Bloch
(2004), Creswell (2012), and deVaus (2014). In
addition, the data obtained from interviews and
observations were in the form of text (words) and
not in numbers, and analyzed to look for
descriptions of themes that arise through text
analysis rather than statistical analysis. Creswell
(2012) states that in qualitative research "at each
stage of the research process: exploring a problem
and developing a detailed understanding of a central
phenomenon; ... collecting data based on words ...;
analyzing the data for description and themes using
text analysis.
The case study design was used because of
Khairun University where the Subsidized Pre-
Service PPG Program was held as the bounded
system (Creswell, 2012; Stake, 2005; Yin, 2003)
which means Khairun University is a system that is
bound or inseparable from the PPG program.
3.2 Subjects of the Research
This study involved a number of research subjects
consisting of all PPG students (11 people outside
one research member) at the Subsidized Pre-Service
PPG Program for the English language Education
Study Program 2018,
3.3 Sites and Time of the Research
The research was carried out at Teacher Training
and Education Faculty (FKIP) of Khairun
University, the location where the Subsidized Pre-
service PPG Program was held and in partner
schools (SMP Negeri 2 Ternate and SMA Negeri 4
Ternate) where PPG students carried out teaching
practicum (PPL). FKIP Khairun University is
located on Campus I, Akehuda Village, Jl. Bandara
Sultan Babullah, Ternate. SMP Negeri 2 and SMA
Negeri 4 are located in Dufa-Dufa Village. This
research was carried out for 3 (three) months starting
from August to October 2018.
3.4 Data Collection Technique
The data collection technique used in this study was
an interview. Interviews were conducted for 11
students of the Subsidized Pre-Service PPG program
at the English Language Education Study Program
of Khairun University. PPG students at Khairun
University were interviewed about their views and
experiences in using authentic assessments in
assessing their students learning of English at
partner schools during their teaching practicum
(PPL). Interview questions are as attached (See
Appendix 1). Interviews were conducted face-to-
face at agreed locations using good and correct
Indonesian. During the interview, each respondent's
answers were recorded using a recording device
prepared by the researchers for further transcripts as
needed. The interview question guideline as attached
used was more semi-structured because this
interview question guide could develop during the
interview process as long as it was still relevant to
the points being studied.
3.5 Data Analysis Technique
The technique used to analyze the data obtained
through interviews are thematic analysis. In this
case, interview data that have been transcribed as
needed were analyzed thematically using a
qualitative data analysis framework from Miles and
Huberman (1994), Seale (2004), Fielding (2008, and
Saldana (2013), who include "coding, categories,
and emerging themes." Especially, for interview data
were analyzed through the following stages:
a. The transcript of the interview was coded.
b. Coding from the PPG students was made with a
category and theme.
c. The themes emerged from interviews from the
respondent s were concluded. The themes of the
findings that emerged from both interview data
analysis were then compared. Furthermore, the
results of the findings were interpreted.
4 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
4.1 Results
Data analysis was carried out in line with the
research question so that it is easy to understand.
The results of the analysis of student interview data
from the Subsidized Pre-Service PPG Program of
the English language Education Study Program at
Khairun University showed similar perceptions and
Exploring Students’ Perceptions and Experiences in using Authentic Assessment at Subsidized Pre-service Teacher Profession Education
Program (SPTPEP) of English Language Education Study Program of Uni
155

a variety of experiences using authentic assessment
rubrics. All 11 students interviewed agreed that the
use of rubric helped teachers what aspects to be
assessed. Meanwhile, their experience of using
rubric depended on the class where they did PPL
and what topics they taught. For example, PPG
student 'H' stated that in its application, the rubric of
authentic assessment helped teachers assess aspects
that should be assessed for example in speaking
skills (speaking) and writing (writing). Respondent
H expressed: "Authentic assessment used by the
teacher in skills is quite helpful also for a teacher
because for the points, for example for speaking or
writing, there have included criteria or the weight of
each point assessed in each skill". The same thing
was expressed by the respondent S: "If there is an
authentic review there, what has been called in the
rubric, the evaluation also has points such as
speaking points which are assessed".
Meanwhile, the use of authentic assessments
depended on the basic competencies and topics
taught by PPG students. The respondent 'SBM used
rubric writing assessment to assess the ability of
their students in high school to write e-mails
according to basic competency 1 and making
Congratulation cards according to basic competency
2, as revealed by SBM in the following:
"If the speaking assessment rubric has been used
because it is related to PTK. So I took rubric ratings
from the high school curriculum guidebook for
2013. Then for my product I have a product if my
first KD is in the form of e-mail because it refers to
KD and if the 2nd KD is the product form the
congratulation card and is now KD 3 is in the
interim process for the daily journal which is a note
of the assessment of attitudes and knowledge and
skills I noted as information for the following
meeting. The condition of the students is changing
so that the results of the assessment note that the
notes are recorded and for the assessment using the
rubric, I will have already stayed in what the name
implies is summarized and finalized at the end of the
study".
In addition, respondent N used rubric assessment
speaking (speaking) to assess the ability of students
to do role play and not do it at one meeting:
"For speaking, indeed for one meeting not all turn to
speak, if there is a role play, so every meeting has a
pecan role play, some of them are judged. Then the
next turn in class also when the learning process
takes place is often given like a stimulus. English
from there is where the assessment process ".
In practice, it was also revealed that there were
difficulties in using authentic rubric assessments,
especially for speaking and writing. In assessing
speaking ability (speaking) for example, the
difficulty lies in determining the ability of a student
in a range of value scales as revealed by the
respondent H in the following:
"The difficulty is generally when we assess the
student whether the results given by the student
enter on a point or scale which sometimes makes the
teacher confused to enter the student's score or
student's results on the scale criteria which is on a
very good scale or good or which ones are good and
not good ".
In addition to the difficulty of determining the
scale is also a difficulty because the number of
students must be assessed, especially in speaking
ability (speaking) individually, including other
difficulties, for example in understanding the
indicators assessed as in terms of fluency in
assessing speaking skills of students. This was
revealed from interviews with respondents S:
"Yes, he meant the difficulty, sir, because the
students here are for example 40 people if judged
one by one, e ... very difficult, very difficult. So if we
judge like that usually at presentations or in
speaking assessment, that's difficult what are the
meanings, for example speaking, do not let us give
the wrong value, for example, the students, for
example, they are fluent but we are wrong to give
the scale, for example it is difficult, sir. "
Another difficulty is when assessing speaking
skills (speaking) in groups as expressed by the PPG
student respondent G: "Because students are also
having difficulties so their presentation is not how
they read what is made together. One is directly
wrong they are the same read, so it's not detailed ".
However, not everything is difficult in using the
assessment rubric even though it takes longer to
complete it and by modifying the assessment rubric
according to its designation as revealed by the PPG
student respondent SD:
"I rate per student so each student can get an
original verb or verb because our material happens
to be present continuous tense so they make
composing a continuous tense sentence based on the
verb that I give to get together and I see so I see
based on the rubric that I made ".
"If it's only writing at least 2 hours or 3 hours.
Because it really has to be seen all. So because now
maybe that seems like there are other classes that
have not been examined."
The results of interview data analysis with PPG
students revealed the need for training to equate
perceptions about rubric assessment in question,
including by maximizing the role of Subject
ICTL 2018 - The 1st International Conference on Teaching and Learning
156
Teachers' Consultation (MGMP) so that English
language teachers can share experiences in using
assessment rubrics especially for speaking
assessment and writing. Respondents of PPG H
students stated:
"I think it is very necessary to conduct training
especially for determining the scale of each aspect
so that we do not give a scale to certain points while
the aspects assessed by students are not appropriate.
So I think there needs to be training for teachers in
terms of assessing by using authentic assessment of
students ".
The same thing was conveyed by S (a PPG
student) about the need for training to use authentic
assessment rubrics:
"Yes if for example there is training that is very
helpful because here we can be trained how or there
may be suggestions from the instructor or we can if
we have training we can discuss with others how to
overcome this how to do an authentic assessment it
applies the authentic assessment especially to the
number of students then also how to assess by
following the scale in the rubric ".
"In my opinion, the training has been very helpful
then if for example if the others are right what is the
MGMP. Now in the English MGMP, it is very
helpful for example English teachers can share
discussing how the judgments are".
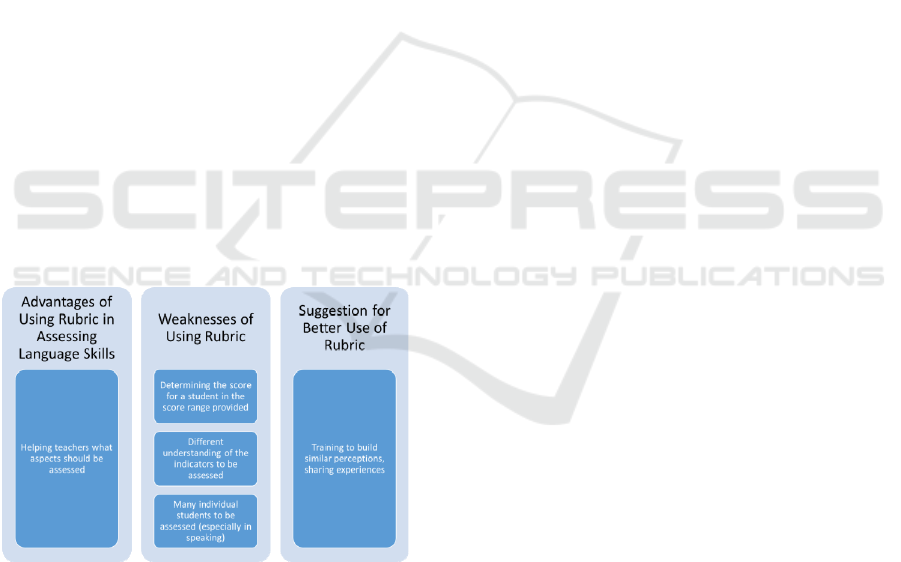
In general, the advantages, difficulties, and
suggestions for the use of authentic assessments can
be summarized in the following diagram:
Figure 1: Strengths, Difficulties, and Suggestions for
Using Authentic Assessment.
4.2 Discussion
The results of the data analysis on interviews with
the perceptions and experiences of the PPG students
in using authentic assessments in the Teacher
Professional Education Program (PPG) of the
English Language Education Study Program at
Khairun University are in line with Sa'idah,
Yulistianti, and Farida's research (2017) despite
using different research methods. This is because
authentic assessments are accompanied with rubrics
that allow people who judge to understand what
should be assessed or who are perceived to
understand what will be assessed so that the assessed
party shows their best performance based on the
indicators used in the rubric.
In rubric, there is a comment column that allows
the assessor to provide a good record of what funds
should be improved so that those who are considered
able to reflect so that they can show the best
performance in the future. This is in line with the
feedback function as a hallmark of assessment for
learning as stated by Bloxham & Boyd (2007) that
assessment for learning through the inclusion of
feedback in the form of comments and notes as a
form of formative assessment to improve
competency in the future.
Revealing the difficulties in using authentic
assessments and the advice that should be made is
valuable feedback for the implementation of the
PPG Program at Khairun University towards a better
approach, especially from the aspect of
implementing the assessment using authentic
assessment.
5 CONCLUSION AND
SUGGESTIONS
5.1 Conclusion
From the analysis and interpretation of the data
above, it can be summarized as follows. In the PPG
students' practice of using authentic assessments
during their PPL to assess their school students'
competency in the English language (mainly
speaking and writing), PPG students found that the
rubric assessment used was very helpful for
teachers. The difficulty lies in understanding the
indicators that are assessed, determining the ability
of students in a range of scales and many students
who must be assessed. That is why students see the
need for equal perception through training to make it
easier for them to understand well how to judge by
using authentic judgments better.
5.2 Suggestions
From the above conclusion, the following
suggestions can be put forward:
Exploring Students’ Perceptions and Experiences in using Authentic Assessment at Subsidized Pre-service Teacher Profession Education
Program (SPTPEP) of English Language Education Study Program of Uni
157

a. There should be a perceptual equalization session
conducted by the organizers of the Teacher
Professional Education Program (PPG), especially in
using authentic assessments to assess the products
and learning processes of PPG students both in the
workshop on the preparation of learning instruments
and during implementing PPL programs in partner
schools.
b. The perception similarity should involve all
parties related to PPG implementation, namely
instructor lecturers, tutors, including PPG managers
and PPG students.
c. It is a need to publish assessment guidelines using
authentic assessment as a guide for instructor
lecturers, tutors, PPG managers and PPG students in
carrying out authentic assessments.
ACKNOWLEDEGMENTS
In this opportunity, the researchers would like to
thank the Faculty of Teacher Training and Education
of Khairun University for the funding assistance so
that this research could be successfully conducted as
expected.
REFERENCES
Brown, H. D., & Abeywickrama. 2010. Language
Assessment: Principles and Classroom Practices (2
nd
ed.). New York: Pearson.
Butler, S. M., & McMunn, N. D. 2006. A teacher's guide
to classroom assessment: Understanding and using
assessment to improve student learning San Fransisco,
CA: Jossey-Bass.
Chappuis, J., Stiggins, R. J., Chappuis, S., & Arter, J.
2012. Classroom assessment for student learning:
Doing it - using it well (2nd ed.). Boston: Pearson.
Creswell, J. W. 2012. Educational research: Planning,
conducting, and evaluating quantitative and
qualitative research (4th ed.). Boston: Pearson.
Creswell, J. W. 2014. Research design: Qualitative,
quantitative, and mixed methods approaches (4th ed.).
Thousand Oaks, California: SAGE Publications, Inc.
Direktorat Jenderal Pembelajaran Dan Kemahasiswaan
Kementerian Riset, Teknologi dan Pendidikan Tinggi.
2017. Pedoman Penyelenggaraan Pendidikan Profesi
Guru. Jakarta
Direktorat Pembelajaran, Direktorat Jenderal
Pembelajaran dan Kemahasiswaan, Kementerian
Riset, Teknologi, dan Pendidikan Tinggi. 2017.
Panduan Penilaian Proses dan Hasil Belajar
Mahasiswa Program Pendidikan Profesi Guru [Guide
to Assessment of Student Learning Process and
Outcomes of the Teacher Professional Education
Program]. Jakarta.
Kemeristekdikti. 2017. Kurikulum, RPS, dan Kompilasi
Bahan Belajar: Program PPG Bahasa Inggris
[Curriculum, Lesson Planning, and Compilation of
Learning Materials: PPG English Program]. Jakarta:
Kemenristekdikti
McDonald, M. 2013. The nurse educator's guide to
assessing learning outcomes: Jones & Bartlett
Publishers.
Nitko, A. J., & Brookhart, S. M. 2011. Educational
assessment of students (6th ed.). Boston, MA:
Pearson.
Pellegrino, J. W., Chudowsky, N., & Glaser, R. 2001.
Knowing what students know: The science and design
of educational assessment (J. W. Pellegrino, N.
Chudowsky & R. Glaser Eds.). Washington, DC:
National Academy Press.
Peraturan Pemerintah Republik Indonesia Nomor 19
Tahun 2017 Tentang Perubahan atas Peraturan
Pemerintah Nomor 74 Tahun 2008 tentang Guru
[Republic of Indonesia Government Regulation
Number 19 Year 2017 concerning Amendments to
Government Regulation Number 74 of 2008
concerning Teachers]
Peraturan Pemerintah Republik Indonesia Nomor 74
Tahun 2008 tentang Guru [Republic of Indonesia
Government Regulation Number 74 of 2008
concerning Teachers].
Permenristekdikti Nomor 55 tahun 2017 tentang Sistem
Pendidikan Guru [Permenristekdikti Number 55 of
2017 concerning the Teacher Education System]
Pusat Penilaian Pendidikan, Badan Penelitian dan
Pengembangan, Kementerian Pendidikan dan
Kebudayaan. 2015. Pedoman Teknis Penilaian Hasil
Belajar Berdasarkan Kurikulum 2013: Bahasa Inggris
Sekolah Menengah Pertama (SMP) [Technical
Guidelines for Assessing Learning Outcomes Based on
2013 Curriculum: English in Junior High Schools
(SMP)]. Jakarta.
Sa’idah, N., Yulistianti, H. D., dan Farida, Y. E. 2017.
Efektifitas Penerapan Penilaian Otentik Pembelajaran
Bahasa Indonesia untuk Peningkatan Kinerja Ilmiah
Siswa. Jurnal Refleksi Edukatika 8 (1) (2017) p-ISSN:
2087-9385 e-ISSN: 2528-696X
http://jurnal.umk.ac.id/index.php/RE
Saldana, J. 2013. The coding manual for qualitative
researchers. London: SAGE Publications, Inc.
Seale, C. 2004. Coding and analysing data. In C. Seale
(Ed.), Researching society and culture (2nd ed., pp.
305-323). London: SAGE Publications.
Stake, R. E. 2005. Qualitative case studies. In N. K.
Denzin & Y. S. Lincoln (Eds.), The Sage handbook of
qualitative research (3rd ed., pp. 443-466). Thousand
Oaks, California: SAGE Publications.
Stiggins, R. J., & Chappuis, J. 2012. An introduction to
student-involved assessment for learning. Boston,
MA: Pearson Education, Inc.
Sutaryo. 2016. Exploring Assessment Beliefs and
Practices in Large Classes in an Indonesian
ICTL 2018 - The 1st International Conference on Teaching and Learning
158

University. Unpublished Dissertation. Adelaide
Australia: Flinders University.
Undang Undang Nomor 14 tahun 2005 tentang Guru dan
Dosen [Law Number 14 of 2005 concerning Teachers
and Lecturers].
Undang Undang Nomor 20 tahun 2003 tentang Sistim
Pendidikan Nasional [Law Number 20 of 2003
concerning the National Education System]. .
Wylie, E. C., Gullickson, A. R., Cummings, K. E.,
Egelson, P. E., Noakes, L. A., Norman, K. M., &
Veeder, S. A. 2012. Improving formative assessment
practice to empower student learning. Moorabbin,
Victoria: Hawker Brownlow.
APPENDIX
Interview Guide: Interview Questions
1. Questions about respondents' perceptions or views
about authentic assessment.
a. What is your view of the authentic assessment
used in the PPG program at the Khairun
University's English Language Study Program?
b. What are the advantages and disadvantages
compared to other forms of assessment such as
tests?
c. What are your suggestions for the use of authentic
assessment assessments used in the PPG
program at the Khairun University English
Language Study Program?
2. Questions about the respondent's experience of
authentic assessment.
a. What is your experience about authentic
assessments used in the PPG program at the
Khairun University English Language Study
Program and at the School?
b. What are the advantages and disadvantages
compared to assessing other forms such as tests
and at school?
c. What are your suggestions for using authentic
assessment assessments used in the PPG
program at the Khairun University English
Language Study Program and at school?
Exploring Students’ Perceptions and Experiences in using Authentic Assessment at Subsidized Pre-service Teacher Profession Education
Program (SPTPEP) of English Language Education Study Program of Uni
159
