
The Implementation of Project-based Learning using ICT
in Mathematical Proficiency Improvement of High School Students in
the Region of North Maluku at 3T
In H. Abdullah, Karman La Nani, Ikram Hamid, and Ariyanti Jalal
Mathematics Education Study Program, Faculty of Teacher Training and Education, Universitas Khairun
ikram_hm21@yahoo.co.id ; anthy.nyong@yahoo.com
Keywords: Teaching materials, Mathematical proficiency of students, ICT-Based Project Learning.
Abstract: The purpose of this study is to produce ICT-based project materials and project-based instruments to
improve the mathematical proficiency of high school students in 3T areas in mathematics learning. This
experimental research applies ICT-assisted PBP to improve students 'mathematical skills, beginning with
the development of quality teaching materials and instruments to measure the improvement of students'
mathematical skills through ICT-assisted project-based learning (ICT-assisted PBP). This research develops
ICT-assisted based project-based mathematics teaching materials, test instruments for students'
mathematical skills, observation sheets of teacher and student activities, to be applied in order to improve
the quality of mathematics learning and the quality of regional education 3T. Data analysis techniques use
qualitative and quantitative analysis to express the quality of teaching materials, instruments of students
'mathematical skills tests, and observation sheets of teacher and student activities to measure the
improvement of students' mathematical skills abilities. The results of advance validation, content validation
and empirical validation are limited, that the instructional materials for PBP-based statistical materials with
ICT, students' mathematical proficiency test instruments, and guidelines for observing the activities of
teachers and students are suitable to be used as tools and research instruments to improve the mathematical
proficiency of high school students.
1 INTRODUCTION
The advancement of technology and information
which is increasingly globalized today, encourages
all Indonesian people to try to get information in
abundance, quickly and easily from various sources
and various parts of the world. Likewise for the
community in the 3T area (leading, outermost and
disadvantaged) in preparing themselves to anticipate
the advances in technology, communication and
information (ICT). Anticipating the progress of ICT,
people in the 3T area are required to have the ability
to obtain, select, manage, and follow up on the
progress of ICT to be used in a dynamic,
challenging, and full of competition, especially for
the sake of improving the quality of education and
the quality of the learning process.
The development of the quality of education in
the 3T area in North Maluku requires special
attention from the government, in order to increase
human resources (HR) in anticipating the emergence
of ICT. This fact is in accordance with Luthfiyah
Nurlaela's experience in the book’ Berbagi di Ujung
Negeri [Sharing in the Nation Corner] (2013), that
the problems related to human resources in the 3T
area are a lack of educators (teachers), teacher
distribution is not balanced, mismatch between the
qualifications of educators and the field being
taught. This condition leads to the quality of
education in the 3T area is still below the standard
when compared with other regions nationally.
The creation of reliable human resources for the
3T area, it is necessary to increase the skills of
students as future generations through the
development of quality education in the learning
process in every field of science. Mathematics as a
scientific discipline has important access to the
formation of quality human resources and the
formation of students' mindset skills and can be
284
Abdullah, I., La Nani, K., Hamid, I. and Jalal, A.
The Implementation of Project-based Learning using ICT in Mathematical Proficiency Improvement of High School Students in the Region of North Maluku at 3T in Mathematical Proficiency
Improvement of High School Students in the Region of North Maluku at 3T.
DOI: 10.5220/0008901002840292
In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Teaching and Learning (ICTL 2018), pages 284-292
ISBN: 978-989-758-439-8
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

measured from mathematical skills (Mathematical
Profession).
Mathematical skills which include:
understanding concepts, smooth procedures,
strategic competencies, adaptive reasoning, and
productive character are abilities that are intertwined
with one another. The five mathematical skills are
integrated with each other and are synergistically
balanced in the intellectual development of students.
The process of constructing it, the teacher must not
only emphasize on one or several skills, but must
pay attention to all aspects of mathematical skills.
According to Kilpatrick (2001) mathematical skills
have components that cannot be separated, namely:
(1) conceptual understanding; (2) procedural
smoothness; (3) strategic competence; (4) adaptive
reasoning; and (5) productive disposition. These five
components of mathematical skills are not separate
things, but intertwine into one skill that represents
different aspects of something complex.
Mathematical skills as described above can be
developed through mathematics learning activities.
Mathematics learning in schools according to the
Ministry of National Education (2014) aims to: (1)
train students 'ways of thinking and reasoning in
drawing conclusions, (2) developing students'
creative activities that involve imagination, intuition,
and discovery by developing divergent, original,
curious thoughts. make predictions and predictions,
and experiment, (3) develop problem-solving skills,
and (4) develop the ability to convey information
and communicate ideas. The creation of these
abilities, students must have mathematical skills in
conducting mathematics learning activities.
Improving mathematical skills in learning
mathematics, it is necessary to use innovative
learning models that involve collaborative student
activity in solving real problems, completing
meaningful tasks, constructing knowledge, in
connection with certain material to be studied. One
of the learning that creates this situation is ICT-
assisted project-based learning (ICT-assisted PBP).
According to La Nani (2015), ICT-assisted PBP
can be used as an alternative in learning introductory
statistics. PBP-assisted ICT implementation
provides opportunities for students to learn statistical
concepts from various sources, understand the
implementation of statistics in real life, increase
interaction activities between students, encourage
the creation of a dynamic and conducive learning
atmosphere, and improve mathematical skills. The
application of ICT-assisted PBP is expected to
provide opportunities for students to learn statistical
material from various sources, understand the
implementation of statistics in real life, increase
interaction activities between students, encourage
the creation of a dynamic and conducive learning
atmosphere, and improve students' mathematical
skills.
Based on the above background, the main
problem of this research is, "how is the
implementation of ICT-assisted project-based
learning (PBP Assisted by ICT) to improve the
mathematical skills of students in the 3T area of
North Maluku?" In detail the research problems are
described in the following questions: (1) What is the
achievement and improvement of the mathematical
skills of high school students in 3T areas in North
Maluku through the implementation of ICT-assisted
PBP? (2) How is the effectiveness of PBP
implementation assisted by ICT in improving the
mathematical skills of high school students in 3T
areas in North Maluku? (3) Does the implementation
of PBP Assisted by ICT improve the mathematical
skills of high school students in 3T areas in North
Maluku?
Based on its content, school mathematics
learning is expected to form students' mathematical
skills. The low quality of learning and mathematical
skills of students in learning mathematics, especially
students in South Halmahera district, Morotai island
district and Taliabu district as 3T areas in North
Maluku. South Halmahera Regency, Morotai Islands
and Taliabu as 3T areas in North Maluku have geo-
political and geo-economic potential that can be
developed as catalysts for development and as a
gateway to Pacific axis competition, it is necessary
to prepare human resources through improving
mathematical skills so that the creation of quality
human resources, education and learning, as well as
the quality of mathematics learning.
2 THEORY STUDY
2.1 Mathematical Proficiency
Mathematical skills are the ability to understand
concepts, proficiency in using procedures,
mathematical problem solving, logical thinking
capacity, consisting of five strands with one another
must be established synergistically. Therefore the
mathematical skills themselves are not easily
observed. The formulation of mathematical skills is
as follows: (1) Conceptual Understanding, namely
the ability that includes concepts, operations and
relationships or connections in mathematics.
Understanding a concept in mathematics correctly
The Implementation of Project-based Learning using ICT in Mathematical Proficiency Improvement of High School Students in the Region
of North Maluku at 3T in Mathematical Proficiency Improvement of High School Students in the Region of North Maluku at 3T
285

will result in the use of mathematical operations in
various ways it can be done, or students will later
have the ability to use the concept associated with
various circumstances when they encounter
problems related to the concept in different
circumstances. (2) Procedural Fluency, namely the
students' skill in using procedures in a flexible,
accurate, efficient and appropriate manner. (3)
Strategic Competence, namely the student's ability
or ability to formulate, present, and solve
mathematical problems. (4) Adaptive Reasoning
(Adaptive Reasoning) is the ability of students to
think logically about the relationship between
concepts and situations, estimate, reflect, explain
and conclude with validity / validity and ultimately
can justify what they do. (5) Productive Disposition
is a habit that tends to see mathematics as something
that is reasonable, useful, and valuable along with
the belief in perseverance and its success in
mathematics.
The five mathematical skills must be intertwined
with each other and run in a balanced manner, as
teachers cannot only emphasize on one or several
skills. The five mathematical skills are interrelated
so that they are not easily observed in a simple way.
A student who has mastered these five abilities must
be seen as a whole, for example a high school
student who studies trigonometry. Knowing whether
these five mathematical skills are already present in
the student, cannot be easily observed at that time,
because it must be seen when the student uses
trigonometric concepts to solve problems in other
fields, using algorithms, strategies, trigonometric
concept procedures on different problems and
different times too, so that in the end it was able to
use the concept to justify the results of the work
which would lead to a sense of trust in mathematics.
2.2 Regional Education Concern 3T
The Presidential Regulation states that
disadvantaged regions are regencies whose regions
and communities are less developed than other
regions on a national scale. An area is designated as
a Disadvantaged Region based on the criteria of the
community's economy, human resources, facilities
and infrastructure, regional financial capacity,
accessibility and regional characteristics. The
criteria for underdevelopment as intended are
measured based on indicators and sub-indicators.
Provisions concerning indicators and sub-indicators
as referred to are regulated by a Ministerial
Regulation which organizes governmental affairs in
the development of underdeveloped regions, "read
Article 2 Paragraph (2.3) of the Presidential
Regulation.
According to the Presidential Regulation
(Perpres), the Government determines Regions Left
behind every 5 years nationally based on criteria,
indicators, and sub-indicators of regional
underdevelopment. Determination of Disadvantaged
Areas as intended is based on the Minister's proposal
by involving relevant ministries / institutions and
local governments. The establishment, expansion
and merger of regencies; or efforts to overcome
extraordinary circumstances, conditions of conflict,
or natural disasters, according to this Presidential
Regulation, the President can establish a new
Disadvantaged Region. This regulation also affirms,
that the Minister who carries out government affairs
in the field of underdeveloped regional development
by involving other relevant ministries / institutions
to evaluate the Disadvantaged Regions every 1 year.
Evaluation as referred to in paragraph (1) is
carried out using the calculation method: a.
composite index; b. interval value; c. interval; and /
or d. the percentage of underdeveloped villages in
the district. This Presidential Regulation comes into
force on the date of promulgation, "reads Article 8
of the Presidential Regulation Number 131 of 2015
which was promulgated by the Minister of Law and
Human Rights Yasonna H. Laoly on November 9,
2015.
North Maluku Province is an archipelago which
results in differences in culture, customs and quality
of education in each region. In addition to the lack of
education in North Maluku, especially in remote
areas, there is no quality learning that is relevant to
environmental conditions, student needs and subject
matter. Education services in North Maluku
Province have not yet been felt evenly, resulting in
low quality of education from years of exposure,
especially in the 3T (frontier, outermost, and
disadvantaged) regions. This inequality of education
has become a complex problem as if it is difficult to
solve, if it is not immediately resolved by the
provincial government of North Maluku and share
stakeholders in each district of the city.
Addressing the problem of education in the
province of North Maluku, especially in the 3T area
requires the care of the government, both local
government and central government in conducting
scientific studies and research, especially the
implementation of effective and efficient learning to
be able to prepare quality generations so that they
can compete nationally. That is, it is necessary to
carry out learning that is relevant to environmental
conditions (local wisdom), student needs, and
ICTL 2018 - The 1st International Conference on Teaching and Learning
286

efficient learning media to encourage student
learning motivation is expected to improve the
quality of mathematics learning. The process of
learning mathematics that is adjusted to
environmental conditions, readiness of students, and
the use of relevant learning media is expected to
motivate students in improving the quality of
learning.
Its relevance to environmental conditions, the
readiness of students in learning and their suitability
with the subject matter of mathematics need to be
applied ICT-assisted project-based learning (PBP
assisted by ICT). PBP-assisted ICT activities that are
student-centered are expected to be able to deliver
students' abilities in learning mathematics.
According to La Nani, K (2015), the application of
ICT-assisted PBP by using an authentic structured
problem type project provides an opportunity for
students to learn the concept of statistics from
various sources, understand the implementation of
statistics in real life or other fields of science,
increase the interaction activity between students,
the interaction of students with relevant experts or
sources, encourages the creation of a dynamic and
conducive learning atmosphere, and enhances
students' reasoning and communication skills.
2.3 Learning Based on ICT- Assisted
Projects
Operationally, the implementation of ICT-assisted
PBP encourages the growth of creativity,
independence, responsibility, confidence, critical
thinking and analytical competence. PBP's Focus on
ICT Assistance lies in mathematical objects,
including: facts, concepts, principles, and skills,
involving students in investigating problem solving
and meaningful task activities, providing
opportunities for students to work autonomously
constructing their knowledge, and culminating in
producing real products ( Thomas, 2000)
PBP Assisted by ICT is a learning model that uses
contextual learning, where students play an active
role in solving problems, making decisions,
presenting, and making report documents. ICT
Assisted PBP designed to be used in complex
problems in carrying out investigations has the
potential to be very large to make learning
experiences more interesting and meaningful for
students. Through PBP Assisted with ICT, students
become active in learning, and the instructor
functions as a facilitator to provide facilities and
evaluate projects on statistical problems related to
daily life.
Santyasa (2006) presents four characteristics of
PBP, namely: content, conditions, activities, and
results. Content characteristics are: (1) complex
problems, (2) students find relationships between
ideas proposed, (3) students face ill-defined
problems, and (4) raise questions that tend to
question real-world problems. The characteristics of
the condition are prioritizing student autonomy.
Activity characteristics are conducting collaborative
group investigations. Garfield and Change (Ying
Cui, et al, 2010) that project learning, authentic
assignments, and criticism are alternative
approaches that can help instructors to gain better
student understanding of mathematical skills.
Therefore, developing ICT-assisted project-
based teaching materials that are authentic and
contextual are expected to guide students in
conducting direct investigations in order to obtain
data, then further processing, presenting, analyzing,
interpreting, drawing conclusions, and presentations.
As a result, students can utilize concepts,
procedures, and processes based on mathematical
rules to improve mathematical skills. The
development of project-based teaching materials to
support school mathematics teaching using ICT-
assisted PBP in this study seeks to: (1) involve
students in complex problems, real-world problems
that are meaningful, and required to use
investigations, research planning skills, critical
thinking and the ability to solve problems when
completing a project; (2) students can learn, apply
the skills and knowledge they have in a variety of
contexts when working on mathematical problem
projects with the help of ICT, to then be revealed
when collaborating, or when discussing.
ICT-assisted project-based learning in this study
is intended to improve the mathematical proficiency
of high school students in 3T areas in North Maluku.
The steps for implementing Learning Based on ICT
Assisted Projects (La Nani, 2015) are as listed in
Table 2 below.
The Implementation of Project-based Learning using ICT in Mathematical Proficiency Improvement of High School Students in the Region
of North Maluku at 3T in Mathematical Proficiency Improvement of High School Students in the Region of North Maluku at 3T
287
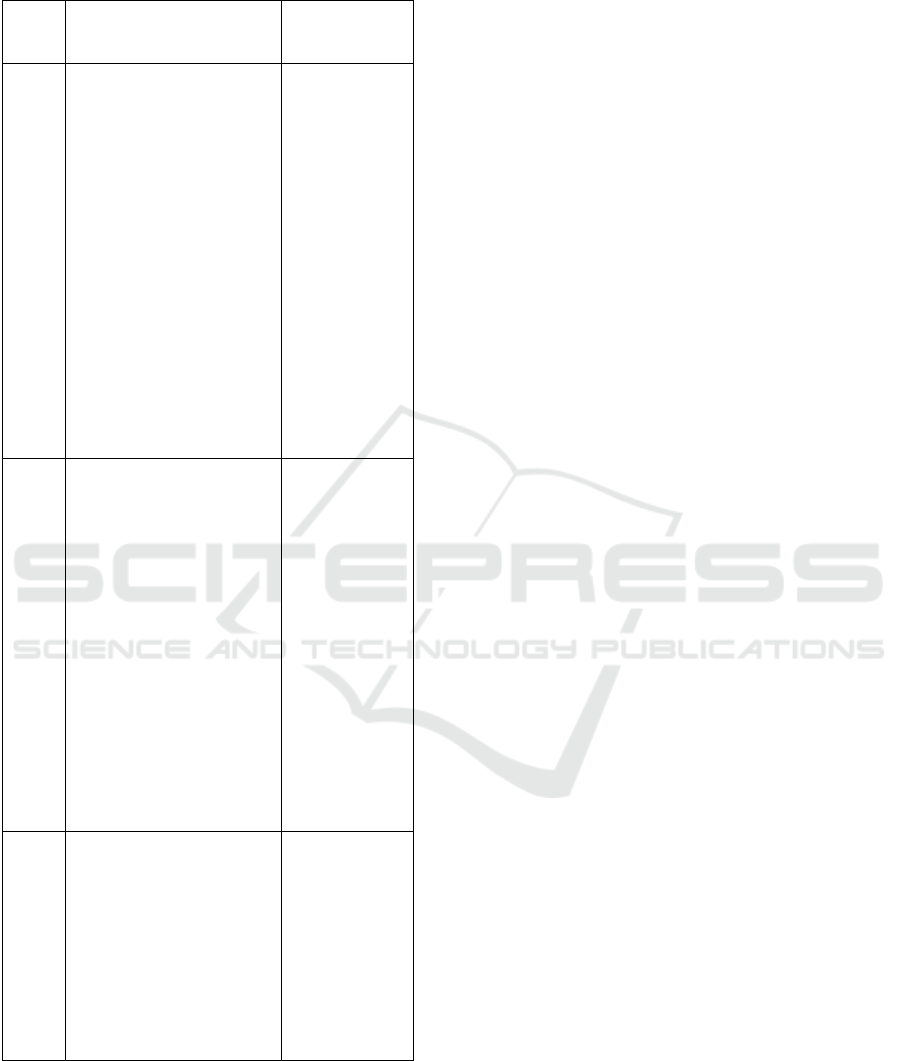
Table 1: Scenario for the Implementation of ICT-Assisted
PBP Activities.
Stage
Student Activity
Student
Activity
1. Planning
Formulate learning
objectives; determine the
topics to be discussed;
prepare the problem
project and the
instructions for the
investigation; design and
compile LKS and learning
resource needs; grouping
students in 5-6 people
with heterogeneous ability
levels; determine the
allocation of investigation
time; prepare guidelines
and practices for the use
of ICT; and designate
monitoring and evaluation
designs
Identify and
choose context
as a project
assignment;
prepare
everything that
will be needed
in the
investigation
and
investigation
of the problem
project; and
data collection
according to
the problem
project
provided.
2. Implementation
Monitor investigation and
data collection activities;
Direct the outline of the
subject matter; Guiding
and facilitating students in
collaborating; Providing
assistance to students or
groups seeking assistance
as needed; monitoring
student learning and
collaboration activities;
facilitate group
presentation activities and
discuss; together with
students draw conclusions
about the material being
studied.
Investigate or
think with
their abilities
based on
experience;
utilizing SPSS
software;
collaborate
with group
friends;
compile
reports; and
present and
discuss about
the results of
their activities
(in groups).
3. Evaluation
Evaluate the work of each
group; make conclusions
whether these activities
need to be improved or
not, which parts need
improvement, and which
parts can be developed.
Revise reports
based on class
discussion
results; Submit
reports on the
results of
project
activities (in
groups and
individuals).
3 RESEARCH METHODS
This study uses a modified development research
method from the development model of
Sukmadinata, et al (2006), consisting of four stages,
namely: (1) preliminary study, (2) product
development model teaching materials and
instruments and assessment rubric, (3) test products,
and (4) the application of ICT-assisted project-based
learning. Activities in the preliminary study are:
literature study, field survey, drafting of teaching
materials, drafting instruments and assessment
rubrics, and testing of research instruments. The
literature study was partially carried out until the
completion of this proposal, but in principle it will
always be re-analyzed and continued to meet the
research needs. Library search through journals,
textbooks, and research relevant to the problems
developed. Field survey activities, carried out
through documentation studies, direct observation,
and interviews. Data collected in the form of student
learning outcomes and teacher perceptions of the
learning process that has been practiced. Preparation
of draft teaching materials, draft instruments and
assessment rubrics, as well as instrument testing as
the last activity in the preliminary study.
The development of draft teaching materials and
research instruments through several stages: (1)
analyzing competency standards, basic competencies
and indicators of high school mathematics lessons
according to the applicable curriculum (2013
curriculum); (2) compile a concept map based on SK
and KD; (3) compile a matrix of test grid design and
classify it based on indicators that will be developed
as items; (4) write down the item and its settlement;
and (5) determining the scoring rubric or guidelines.
The draft of ICT-assisted project-based
mathematics teaching materials and the
mathematical skills instruments developed before
being tested are validated to the expert team. The
team of experts as validators of teaching materials
and instruments are people who are experts in their
fields (mathematics, mathematics education,
research and education evaluation, etc.). Expert
validation aims to get corrections as input regarding
improvements to draft teaching materials and
instruments and the results of their validation.
Validation tests include content and face validation,
which is intended to examine: readability, linguistic
structure and conformity of concepts to competency
standards (SK), basic competencies (KD), material
indicators, and students' mathematical skills
indicators developed.
ICTL 2018 - The 1st International Conference on Teaching and Learning
288

The draft of ICT-assisted project-based
mathematics teaching materials and revised
mathematical skills instruments from the results of
expert validation, followed by a limited trial of
students in several high schools in Ternate City and
South Halmahera Regency. The results of expert
validation analysis and limited trials are then
analyzed to be refined. Indicators of achievement of
ICT-based mathematics teaching projects,
instruments of mathematical skills, and measurable
validation and testing results include: (1) Content
and face validation results, obtained quality
readability of sentences or sentence meanings,
linguistic structure, conformity of concepts in
teaching materials and instruments against
competency standards, basic competencies, and
mathematical material indicators, as well as valid
and reliable student mathematical skills indicators.
Besides the validity and reliability, also obtained the
significance of similarity of validity and reliability
by several expert validators known through Q-
Cochran test statistics. (2) The results of empirical
validation through limited and widespread trials,
obtained the quality of the items that meet the
requirements: validity, reliability, level of difficulty,
and differentiation in good qualifications. (3) The
compilation of ICT-assisted project-based
mathematics teaching materials and students'
mathematical skills instruments that qualify as a
measuring tool to be applied in mathematics learning
and measure the mathematical skills of high school
students.
4 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Analysis of Advance Validation Results and Content
of Research Instruments. Before being used, the
project-based teaching materials that are prepared
are reviewed or assessed by 5 (five) validators to
determine their suitability with the learning
objectives and indicators of the mathematical
proficiency of the students studied. Validators who
are trusted to examine the validity of the
instructional material in question are 2 (two)
lecturers of mathematics education, and 3 (three)
high school mathematics teachers who teach in the
3T area in North Maluku who hold an undergraduate
degree. Suitability of teaching materials includes
aspects: (1) clarity in terms of language or editorial;
(2) the language used is standard; and (3)
authenticity of interesting topic topics to be
discussed; (4) suitability of the material with the
topic of the problem given; (5) compliance with
indicators of achievement of learning outcomes; (6)
suitability in fostering students' mathematical
proficiency as measured; and (7) the level of
difficulty for high school students.
Data from the validation of teaching materials by
the validators were analyzed descriptively and
inferentially using Q-Cochran test statistics to
determine the validity uniformity by the validators
on the suitability of teaching materials. Project-
based statistical introductory teaching materials are
prepared for 6 (six) face-to-face meetings. The
results of the conformity analysis of ICT-assisted
project-based instruments are described below.
Advance Validation Results of Mathematical
Proficiency Instrument for Students with Statistical
Material. The frequency of valid and invalid
administration of the five validators is shown in
Table 2 below.
Table 2: Frequency of Valid and Invalid Giving
Instruments by Validator.
Validator
Frequenc
y
of Validit
y
Valid (%) Invalid (%)
I8
(
80
)
2
(
20
)
II 8
(
80
)
2
(
20
)
III 9
(
90
)
1
(
10
)
IV 8(80) 2(20)
V 10(100) 0
Total 86.00 14.00
Based on table 2 above, there is one validator stating
that teaching materials (LKPD) meet the
requirements of face validity, three validators say 8
items of questions fulfil the validity requirements
and 2 items of questions are invalid, and one
validator states 9 items of valid items and 3 items of
questions not valid, and one validator states 9 valid
items and 1 invalid item. Overall, six validators who
examined the face validity of 10 items about
students' mathematical proficiency instruments can
be said that 86.00% were declared valid and 14.00%
were invalid. Question items that are declared
invalid will be revised according to the validator's
advice and adjusted to the student's mathematical
proficiency indicators.
Knowing the face validity of mathematical
proficiency instruments students used Q-Cochran
test statistics. The null hypothesis (H0) tested is that
the validators give the same or uniform assessment.
Test criteria: accept H0 if the value is Asymp. Sig
Q-Cochran is more than the significance level α =
5%. The results of the Q-Cochran test of the validity
of the face of the instrument of statistical reasoning
ability as described in Table 3.
The Implementation of Project-based Learning using ICT in Mathematical Proficiency Improvement of High School Students in the Region
of North Maluku at 3T in Mathematical Proficiency Improvement of High School Students in the Region of North Maluku at 3T
289
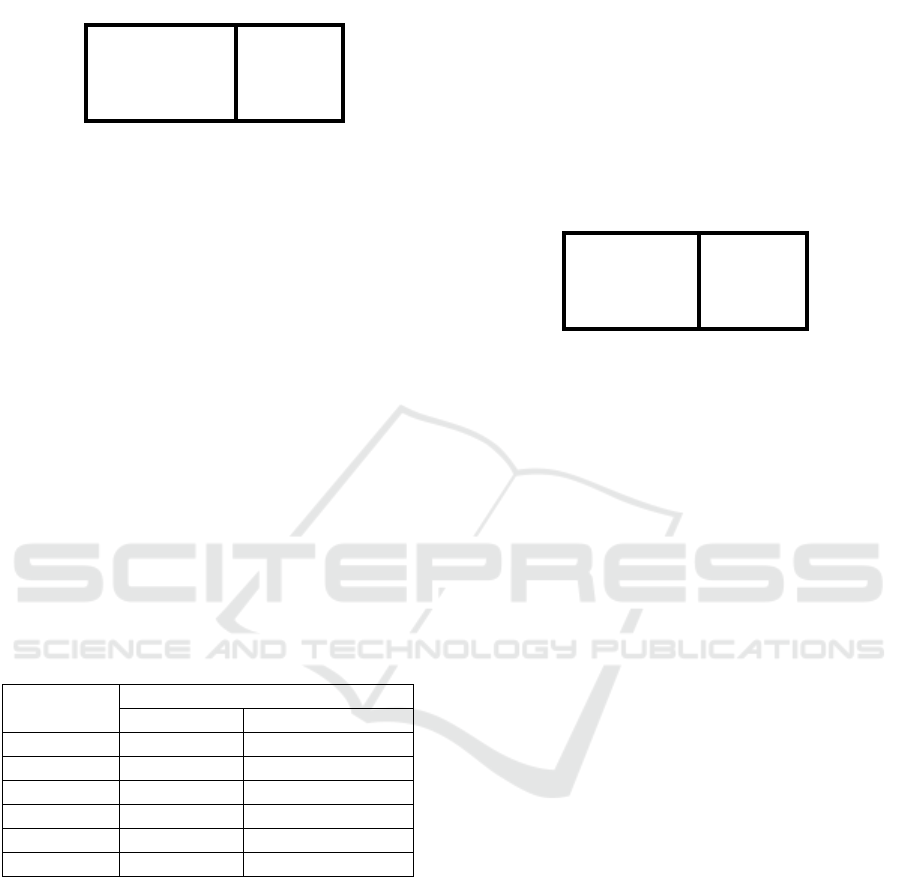
Table 3: Advance Validity Test Instrument Statistic
Reasoning Ability.
N
10
Cochran's Q 5.789
a
df 5
As
y
mp. Si
g
. .327
a. 1 is treated as a success.
Output data in the Test Statistics table
obtained Cochran's value Q = 3.467 with Asymp.
Sig 0.327 is greater than the significance level α =
5%. This shows that 10 students' mathematical
proficiency instruments were rated uniformly by the
validators. This shows that students' mathematical
proficiency instruments are declared to meet the
requirements of face validity with minor
improvements.
Validation Results of Students' Content of
Mathematical Proficiency Instrument Statistical
Material. In the validity, the contents of all
validators do not provide corrections to students'
mathematical proficiency instruments. This shows
that the instrument has fulfilled aspects related to the
material, indicators of achievement, and the
mathematical proficiency of the students to be
achieved. Quantitatively, the frequency of
instrument validity by five validators can be shown
in Table 4 below.
Table 4: Frequency of Validity of Instrument Content by
Validator.
Validator
Frequenc
y
of Validit
y
Valid (%) Invalid(%)
I 8 (80) 2 (20)
II 8(80) 2(20)
III 10(100) 0
IV 9(90) 1(10)
V 10(100) 0
Total 90, 00 10, 00
Based on table 4 above, there are two validators
stating that 10 items of questions fulfill the
requirements of content validity, two validators say
8 items of questions fulfill the requirements of
validity (valid) and 2 items of questions are invalid,
and one validator states 9 items of valid items and 1
item of question invalid. Overall, of the five
validators who examined the content validity of the
10 items about students' mathematical proficiency
instruments that 90.00% were declared valid and
10.00% were invalid.
Knowing that the mathematical proficiency
instrument of students fulfilled the requirements for
content validity, the Q-Cochran test statistics were
used. The null hypothesis (H0) tested is that the
validators give the same rating. Test criteria: accept
H0 if the value is Asymp. Sig Q-Cochran is more
than the significance level α = 5%. The results of the
Q-Cochran test validity of the content of students'
mathematical proficiency instruments as described
in Table 5.
Table 5: Validity Test Results of Students' Mathematical
Proficiency Instruments.
N
10
Cochran's Q 9.815
a
df 5
As
y
mp. Si
g
. .081
a. 1 is treated as a success.
Output data in Test Statistics table obtained
Cochran's-Q value = 9.815 with Asymp. Sig = 0.081
is greater than the significance level α = 5%. This
shows that 10 students' mathematical proficiency
instruments were rated uniformly by the validators.
Furthermore, the comment of one of the validators
that the aspect of indicators and indicators of the
measured questions contained synchronization and
operational verbs had indicated the validity of an
instrument. Thus the instrument of statistical
reasoning ability can be stated to fulfill the
requirements of content validity.
4.1 Analysis of Research Instrument
Test Results
After the instrument meets the face validity and
content validation by expert validators, the research
instrument of students' mathematical proficiency
tests is conducted a trial (try out) before being
applied to the research subjects to determine
reliability, validity, level of difficulty (TK) and
differentiation (DP) of the instrument. The trial of
this research instrument was applied to high school
students in Ternate City (not sample classes) who
had studied and experienced the learning process of
statistical material. Data from the results of the
research instrument trial (attached), the description
below.
4.2 Validity and Reliability of Student
Mathematical Proficiency Tests
The process of calculating item validity and
reliability of students' mathematical proficiency test
questions using SPSS for Windows version 20
ICTL 2018 - The 1st International Conference on Teaching and Learning
290
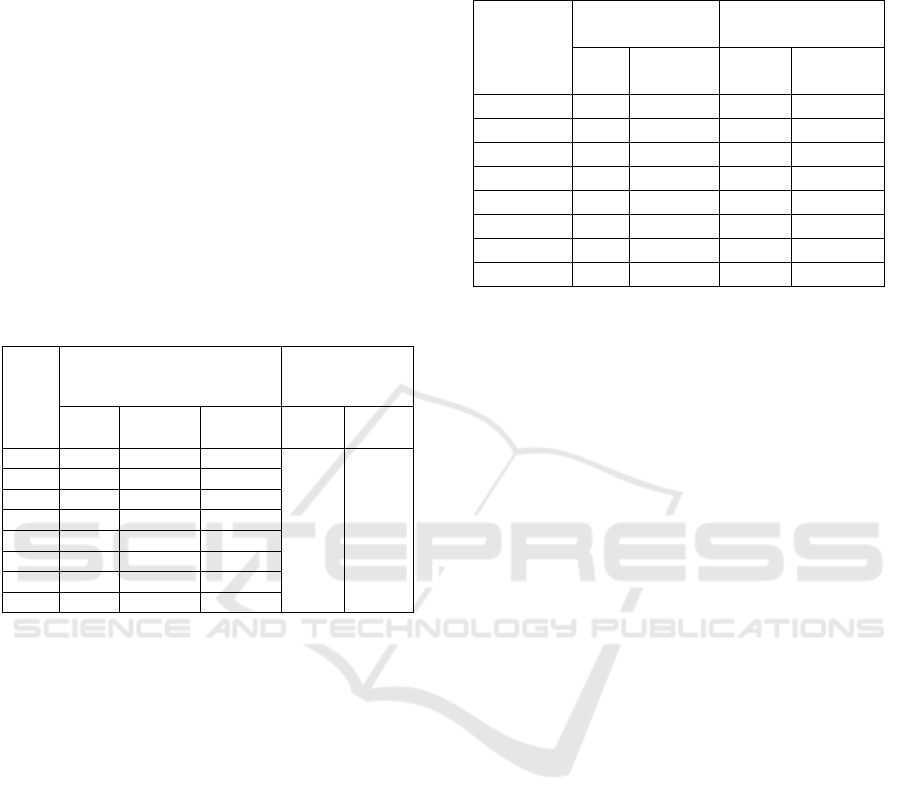
software. Test the validity of the items using the
rough number product moment correlation formula
that correlates the score of each item with the total
score. While the reliability test questions using the
Cronbach-Alpha formula. The null hypothesis (H0)
tested is that there is no significant positive
correlation between item item scores and total score.
Test criteria, accept H0 if r count <r table. At the
significant level α = 5% and n = 26 obtained r table
= 0.317. (Usman H., and Akbar S.P., 2011).
Calculation of item validity and reliability of
students' mathematical proficiency tests are
presented in Table 6 below.
Table 6: Validity and Reliability of Students'
Mathematical Proficiency Tests for 15 High School
Students.
Ques
tion
Num
ber
Question Item Validity
Problem
Reliability
𝑟
Interpret
ation
Criteria
𝑟
Interpr
etation
1a 0.784 High Valid
0.695 High
1b 0.414 Mediun Valid
2a 0.583 Mediun Valid
2b 0.699 High Valid
3a 0.455 Mediun Valid
3b 0.595 Mediun Valid
4 0.497 Mediun Valid
5 0.404 Mediun Valid
Description of table 6 shows that the reliability
coefficient is large r
11
= 0.695. According to
Guilford (Suherman, 2003), an instrument with a
reliability coefficient of 0.60 ≤ r_11 <0.80 is a
classification in the high category. Furthermore, the
validity of item questions in Table 4.5 based on
Guilford (Suherman, 2003) classification shows that:
there are two items of questions (1a, & 2b) in high
interpretation and six items of questions (1b, 2a, 3a,
3b, 4, and 5) in the interpretation of moderate
validity. These results provide an illustration that
students' mathematical proficiency instruments
compiled by the research team are declared valid
and reliable, so that they can be used to measure the
mathematical proficiency of high school students in
the 3T Region in North Maluku. Level of Difficulty
and Distinction of Students' Mathematical
Proficiency Test Calculation of the level of difficulty
and distinguishing power is done manually using
Microsoft Excel, the calculation results are described
in the following table 7.
Table 7: Levels of Difficulties and Differences in
Students' Mathematical Proficiency Tests Trial Results to
15 Students.
Question
Item
Difficulty
Differential
Powe
r
Ind
ex
Interpre
tation
Index Interpret
ation
1a 0.43 Mediu
m
0.25 Enou
g
h
1b 0.44 Mediu
m
0.31 Enou
g
h
2a 0.39 Mediu
m
0.32 Enou
g
h
2b 0.38 Mediu
m
0.25 Enou
g
h
3a 0.42 Mediu
m
0.33 Enou
g
h
3b 0.32 Mediu
m
0.25 Enou
g
h
40.51Mediu
m
0.44 Good,
50.34Mediu
m
0.27 Enou
g
h
The results of the calculation of TK and DP tests
of statistical reasoning ability in Table 7 after
adjusting to the classification (Suherman, 2003)
indicate that: eight items in the interpretation as a
problem with moderate difficulty; (2) there is one
item (number 4) in a good interpretation of power
(DP), and seven other items in the interpretation of
DP are sufficient. This shows that the students'
mathematical proficiency test items are considered
to have fulfilled the characteristics that are sufficient
enough to be used in the study.
5 CONCLUSION
Based on the description of the results and
discussion described above, the development of
ICT-assisted project-based statistical material
teaching materials and research instruments to
measure the improvement of students' mathematical
skills can be concluded as follows:
1. Teaching materials (LKPD) ICT-assisted
project-based statistical materials that are
expected to motivate student learning, create
collaboration of individual students in
cooperative groups, shape ICT utilization skills
(SPSS software) as learning aids, and enhance
students' mathematical skills. On teaching
material materials, statistical materials prepared
based on the project by the weighers provide the
same or uniform assessment of the seven aspects
of the assessment of the teaching material. Thus
it can be said that the instructional material of
statistical material compiled based on ICT-
assisted projects is fulfilling the requirements of
face validity and content so that it is considered
The Implementation of Project-based Learning using ICT in Mathematical Proficiency Improvement of High School Students in the Region
of North Maluku at 3T in Mathematical Proficiency Improvement of High School Students in the Region of North Maluku at 3T
291

feasible to be applied in the learning of statistical
material.
2. Developing a quality statistical test instrument to
be able to measure the improvement of students'
mathematical skills in learning statistical
material that meets the requirements of validity,
meets reliability, has a good level of difficulty,
and has a strong distinguishing power. The
results of expert validation and the results of the
trial showed that the instrument of statistical
reasoning ability after going through several
trials and revisions was stated to have fulfilled
the requirements of validity, reliability in high
categories, good level of difficulty, and strong
differentiation so that it could be used as a
research instrument. The results of expert
validation and the results of the trial showed that
the instrument of statistical communication
ability after going through the trial and revision
showed that there were 8 (eight items that met
the validity requirements.
REFERENCES
Baran M. dan Maskan A. 2010. The effect of project-
based learning on pre-service physics teachers’
electrostatic achievements. Dicle University, Faculty
of Education, Department of Science and Mathematic
Education, Sivas, Turkey. Cypriot Journal of
Educational Sciences 5 (2010) 243-257.
Kilpatrick, J., Swafford, J., & Findell, B. 2001. Adding it
up: Helping children learn mathematics. Washington,
DC: National Academy Press.
Kusumah, S.Y. 2011. “Aplikasi Teknologi Informasi dan
Komunikasi dalam Pembelajaran Matematika untuk
Meningkatkan Kemampuan Matematis Siswa”.
Makalah disajikan dalam Kegiatan Pelatihan Aplikasi
Teknologi dan Komunikasi dalam Pembelajaran
Matematika, 16 Desember 2011.
Kusumah, S.Y. 2012. “Aplikasi Teknologi Informasi dan
Komunikasi dalam Pembelajaran Matematika untuk
Meningkatkan Kemampuan Berpikir Matematis
Siswa”. Makalah Disajikan dalam Seminar Nasional
Pendidikan Kerjasama Ikatan Alumni Pendidikan
Matematika dan Himpunan Mahasiswa Matematika,
FKIP Universitas Sriwijaya, Palembang 26 Mei 2012.
La Nani, K. 2015 Kemampuan Panalaran Statistis,
Komunikasi Statistis dan Academic Help-Seeking
Mahasiswa dalam Pembelajaran berbasis Proyek
Berbantuan ICT. SPS.UPI, Disertasi. Tidak
Diterbitkan.
La Nani, K. 2016 Pembelajaran Berbasis Proyek
Berbantuan ICT. Bandung: Pustaka Ramadhan.
Peraturan Presiden Number 131 2015 tentang Penetapan
Daerah 3T (terdepan, terluar, dan tertinggal) di
Indonesia.
Santyasa, W.I.2006. Pembelajaran Inovatif: Model
Kolaboratif, Basis Proyek, dan Orientasi NOS.
Makalah Disajikan dalam Seminar Di Sekolah
Menengah Atas (SMA) Negeri 2 Semarapura Tanggal
27 Desember 2006,di Semarapura.
Santyasa, & Sukadi. 2007. Model-model Pembelajaran
Inovatif. Materi Pelatihan Sertifikasi Guru di Provinsi
Bali, Undiksha.
Sukmadinata, et al. 2006. Metode Penelitian Pendidikan.
Bandung: PT. Remaja Rosdakarya.
Sumarmo, U. 2012, Pengukuran dan Evaluasi dalam
Pembelajaran Matematika. Handout Mata Kuliah
Evaluasi dalam Pembelajaran Matematika. Tidak
dipublikasikan.
Thomas, J.W. 2000. A Review of Research On Project-
Based Learning. Supported by The Autodesk
Foundation 111 McInnis Parkway San Rafael,
California.(0nline).(http:/www.autodesk.com/foundati
on.[17 November 2012].
Widjajanti B.J. 2011. Mengembangkan Kecakapan
Matematis Calon Guru Matematika Melalui Strategi
Perkuliahan Kolaboratif Berbasis Masalah. Prosiding
Seminar Nasional Penelitian, Pendidikan dan
Penerapan MIPA, Fakultas MIPA, Universitas Negeri
Yogyakarta.
ICTL 2018 - The 1st International Conference on Teaching and Learning
292
