
Information Technology Utilization in Environmentally Friendly
Higher Education
Leon Andretti Abdillah
1*
, Arif Ainur Rofiq
2
, and Dian Eka Indriani
3
1
Department of Information Systems, Universitas Bina Darma, Jalan Ahmad Yani, Palembang, Indonesia
2
Department of Islam Guidance and Counseling, UIN Sunan Ampel Surabaya, Jalan Ahmad Yani, Surabaya, Indonesia
3
Pancasila and Civic Culture Education, STKIP PGRI Bangkalan, Jalan Soekarno Hatta, Bangkalan, Indonesia
Keywords: DropBox, Higher Education, Information Technology, WordPress
Abstract: The awareness of an environmentally friendly learning process has been of concern lately. IT offers some
applications that are able to provide better green education environments in higher education sectors. This
research involves top social information technology applications, DropBox and WordPress. DropBox is the
most popular cloud storage in the world. Meanwhile, WordPress is a top content management systems at the
moment. This research examines the utilization of those two applications in student assignments and
presentations. The study observed 150 sophomore students in computer science faculty. The results show that
the use of DropBox and WordPress in higher education learning activities is able to significantly reduce paper
and ink usage. The combination of those two applications create a very handy and comfortable environment
for students in higer education. This strategy reduces the consumption of papers and inks and is accepted well
by most of the students.
1 INTRODUCTION
The development of information technology (IT) can
be used for various purposes. In the field of
government, IT has been used to cut bureaucracy and
complicated procedures. In the business field, IT has
been widely used as a virtual media for sellers and
buyers to conduct online transactions or online
shopping. The trend of using information technology
such as the internet has also experienced a significant
increase in transportation sector, such as online ride
sharing. From those examples, the authors would like
to define the term of “IT utilization” as involving IT
applications in daily activities. In this article, we
involved some IT applications for education field.
According to the Internet World Stats, Asia
continent is a region that has the biggest number of
internet users (Internet World Stats, 2018b) followed
by Europe, Africa, Latin America/Carribean, North
America, Middle East, and Oceania/Australia. In
Asia, 48.7% of the population are internet users
(Table 1) or almost half of the population.
From those data, Indonesia ranks number 5 after
China, India, the United States, and Brazil.
Indonesian internet users per December 2017 (Table
2) are 143,260,000 users (Internet World Stats,
2018a).
Table 1: World Internet Usage and Population Statistics.
World Regions
Internet Users
Internet
Users
%
Africa
453,329,534
10.9 %
Asia
2,023,630,194
48.7 %
Europe
704,833,752
17.0 %
Latin America / Caribbean
437,001,277
10.5 %
Middle East
164,037,259
3.9 %
North America
345,660,847
8.3 %
Oceania / Australia
28,439,277
0.7 %
WORLD TOTAL
4,156,932,140
100.0
%
In the early 2018 period, it was known that
internet users in all over the world reached more than
4 (four) billion people (Kemp, 2018) or equal to 53%
(more than half world population). The number of
university students enrolled in Kemenristekdikti in
2017 totaled 6,924,511 students (Ristekdikti, 2018).
Learning activities at college campus that have been
carried out conventionally involve the provision of
teaching materials, daily examinations, midterms,
350
Abdillah, L., Rofiq, A. and Indriani, D.
Information Technology Utilization in Environmentally Friendly Higher Education.
DOI: 10.5220/0008908303500355
In Proceedings of the Built Environment, Science and Technology International Conference (BEST ICON 2018), pages 350-355
ISBN: 978-989-758-414-5
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
semester exams, and work assignments (both
individual and group assignments). With that number
of students, a significant amount of paper and ink are
used for the printing needs of these student
assignments.
Table 2: Top 20 Countries With Highest Number of Internet
Users - December 31, 2017.
No
Country or Region
Internet Users 31
Dec 2017
1
China
772,000,000
2
India
462,124,989
3
United States
312,322,257
4
Brazil
149,057,635
5
Indonesia
143,260,000
6
Japan
118,626,672
7
Russia
109,552,842
8
Nigeria
98,391,456
9
Mexico
85,000,000
10
Bangladesh
80,483,000
11
Germany
79,127,551
12
Philippines
67,000,000
13
Vietnam
64,000,000
14
United Kingdom
63,061,419
15
France
60,421,689
16
Thailand
57,000,000
17
Iran
56,700,000
18
Turkey
56,000,000
19
Italy
54,798,299
20
Egypt
48,211,493
Furthermore, people will continue the trend of
reducing their need to rely on costly hardware and
infrastructure by placing files and applications in the
cloud (Drake, 2018). Cloud storage will reduce the
cost for investment in hardware and infrastructure.
Cloud computing is viewed as a method for achieving
efficiency and cost saving through the use of IT
infrastructures (Waddington et al., 2013).
This paper discusses the role of IT in supporting
environmentaly friendly higher education.
Environmentally friendly higher education is
everyday behavior that is applied or carried out at a
university that has a positive impact on the
environment and does not damage the environment.
The involvement of popular social information
technology in lectures gained a very good response
from the learners (Abdillah et al., 2018). The
researcher involved 2 (two) famous applications.
Those applications are DropBox and WordPress.
One of the most popular cloud repository is
DropBox. Research showed that DropBox is
currently the most popular provider (Drago et al.,
2012) of cloud-based storage systems. The second
application is WordPress. WordPress is a free
installation resource which has many useful plug-ins,
comment spam-fighting features, and user-friendly
interface (Hong, 2008). Furthermore, bloggers can
customize WordPress template and script according
to their interest.
The combination of those two applications creates
a very handy and comfortable enrivonment for
students in higher education. With the use of no cost,
high level of popularity, and ease of use, the two top
applications can represent the use of IT or “IT
utilization”, especially in higher education.
Some previous studies have been reported in the
fields of IT and higher education, such as: 1) Social
network in blended learning (de Jorge Moreno, 2012,
Abdillah, 2016a), 2) Students learning center and
course management system (Dougiamas and Taylor,
2003, Abdillah, 2013), 3) Managing information and
knowledge sharing (Abdillah, 2014), 3) Enriching
course materials by using innovative learning
resource for college students (Burke and Snyder,
2008, Abdillah, 2017).
The next section of this paper is research method
(section II) followed by results and discussions
(section III). The last section is conclusion, which is
section IV.
2 RESEARCH METHODS
In the research method section, the authors describe
the college students participants, the course subject,
and the learning activities.
2.1 College Students Respondents
The respondents of this study were students at level 3
(three), fifth and sixth semester students.Those
students were those who have taken elective courses.
The elective courses taken will be the basic material
for student research activities which then become the
main theme or topic of their thesis. Total students
participating in the study were 150 students who took
three courses.
From a number of elective courses available, the
subjects that get the highest grades will be prioritized
as the student thesis research theme. If there are
several elective courses that get the same grades, then
the students will consult more closely with their
academic advisers.
2.2 Course Subjects
The author involved 3 (tree) subjects in information
systems study program. Those course subjects are: 1)
Information Technology Utilization in Environmentally Friendly Higher Education
351
Customer Relationship Management (CRM), 2)
Supply Chain Management (SCM), and 3) Systems
Analysis and Design (SA&D). All courses are taught
for 16 (sixteen) meetings in about 4 (four) months.
CRM and SCM courses have a weight of 2 (two)
credits while SA&D courses have a weight of 4 (four)
credits.
The content of CRM (Anderson and Kerr, 2002,
Lindstrand et al., 2006, Buttle, 2009, Abdillah,
2018a) is as follows: 1) Introduction, 2) Basic
Concept of CRM, 3) The Customer Service/Sales
Profile, 4) Managing Your Customer Service/Sales
Profile, 5) Choosing Your CRM Strategy, 6)
Managing and Sharing Customer Data, 7) Tools for
Capturing Customer Information, 8) Service-Level
Agreements, 9) E-Commerce: Customer
Relationships on the Internet, 10) Managing
Relationships Through Conflict, 11) Fighting
Complacency: The “Seven-Year Itch” in Customer
Relationships, 12) Resetting Your CRM Strategy, 13)
Presentations, and 14) Final Exam.
SCM course consists of (Simchi-Levi et al., 1999,
Firdaus et al., 2015, Abdillah, 2018b): 1)
Introduction, 2) Basic Concepts, 3) The Role of
Purchasing in an Organization, 4) Creating &
Managing Supplier Relationships, 5) Strategic
Sourcing For Successful SCM, 6) Demand
Forecasting & Collaborative Planning, Forecasting,
& Replenishment, 7) Inventory Management, 8)
Transportation Management, 9) Vendor
Management, 10) Warehouse Management, 11)
Cross Docking, 12) Third Party Logistics (3PLs), 13)
IT in Supply Chain, 14) Presentations, and 15) Final
Exam.
Meanwhile, for SA&D (Whitten and Bentley,
2007, Kendall and Kendall, 2011, Dennis et al.,
2012a, Dennis et al., 2012b, Abdillah, 2016b), the
lessons are: 1) Part One Planning Phase (The Systems
Analyst and Information Systems Development,
Project Selection and Management), 2) Part Two
Analysis Phase (Requirements Determination, Use
Case Analysis, Process Modeling, Data Modeling), 3)
Part Three Design Phase (Moving Into Design,
Architecture Design, User Interface Design, Program
Design, Data Storage Design), and 4) Part Four
Implementation Phase (Moving Into Implementation,
Transition To The New System, The Movement To
Objects).
2.3 Learning Activities
This study applies a blended learning approach that
combines the process of conventional learning (face
to face) activities with electronic based learning.
Out of sixteen meetings, more than half were
face-to-face meetings. There are 2 (two) meetings
that are indeed allocated for e-learning activities. if
there is a lecture schedule during the national holiday
period, then the schedule will be held with an e-
learning approach.
In conventional learning, students will study
together with students in certain classes (around 20-
40 students). In each class, a number of groups will
be created. Each group will consist of 4 (four) to 8
(eight) students who will discuss a particular theme.
The theme will be given in the early conventional
meeting by the lecturer.
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSIONS
The results and discussion section explain the results
obtained after the research was completed. This
section consists of 1) Characteristics of student
respondents, 2) Use of blogs, 3) Use of cloud
repositories, 4) Evaluation of blog usage, and 5)
Evaluation of cloud repository usage
3.1 College Students Characateristics
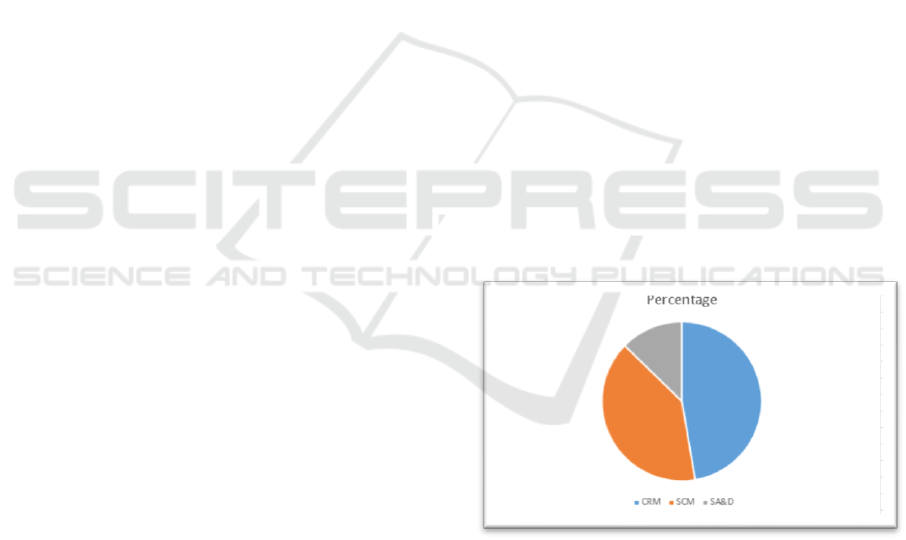
From the 150 students, 47.33% of them were taking
CRM course subject, 40% are taking SCM course
subject, and the rest of them or equal to 12.7% are
taking SA&D course subject.
Figure 1: Lecturer Blog Page.
Meanwhile, most of the college participants were
dominated by male students by 56% or 84 students,
while female students amounted to 44% or 66
students.
BEST ICON 2018 - Built Environment, Science and Technology International Conference 2018
352

Figure 2: Lecturer Blog Page.
3.2 Blog
The use of blogs in learning provides alternatives that
are cheap and fast. Blogs are generally offered free or
without fees. Blogs also have templates that can be
selected according to the needs and desires of the
lecturers or students. Furthermore, blogs can be
combined with both social media and the cloud
repository.
Figure 3: Lecturer Course List Blog Page.
Lecturers can utilize blog media for lecture
materials, group lists, as well as a list of students who
take certain courses. If needed, the lecturer can also
add links that are considered useful or related to the
course.
Meanwhile, students will work on weekly group
assignments. Each task will be made into a post on
the blog or in cloud storage. Every student who joined
a flow group posted the assignment on their
respective blogs.
3.3 Cloud Repository
During the lecture, there were a number of
assignments given to students. In the conventional
lecture system, these tasks will be collected in the
form of volumes of papers. In this study, the authors
utilized cloud storage media. Placing files in the cloud
has many benefits (Mitroff, 2016). Almost all popular
cloud repositories at the moment provide some free
storage, paying for extra space, and the most
important thing is the ability to synchronize between
devices. Files stored in the cloud can be accessed
anywhere and anytime as long as there is an internet
connection.
In weekly assignment, some of the assignments
will be posted in the blog, and some others will be
stored in the cloud repository and the URL will be
linked into blog. Cloud services provide 3 (three)
main services (Fikri et al., 2015): 1) Software as a
Service (SaaS), 2) Platform as a Service (PaaS), and
3) Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS). This study
employing DropBox is close to SaaS.
3.4 Blog Usage Evaluation
During the exam, the lecturer will provide a
questionnaire regarding the involvement of blogs and
cloud repositories. Lecturers can use blogs as a
medium to place lecture materials that will be given
to students. Based on the questionnaires distributed,
it is known that most of the students really like and
like to get lecture materials through blogs (figure 4).
Figure 4: Student responses in getting lecture material
through a blog.
Blogs can also be used to view the tasks from the
group assignments. Each assignment will be grouped
together and collected individually in the form of a
blog post. Based on the questionnaires distributed, it
is known that the majority of students are very fond
and like to work on lecture assignments through blogs
(figure 5).
Figure 5: The response of students working on college
assignments through blogs.
Information Technology Utilization in Environmentally Friendly Higher Education
353

3.5 Evaluation DropBox Usage
Cloud repository is also used by students to store
lecture tasks. A number of operating systems have
provided cloud storage service. Apple has an iOS
platform providing iCloud, Google with Android has
Google Drive, and Microsoft Windows provides
OneDrive.
Figure 6: Students responses in storing their assignment in
DropBox.
All cloud repositories must be accessed with an
email affiliated with them. For this study, the authors
prefer to use DropBox which can run on all platforms.
DropBox provides huge storage media up to 10 (ten)
TB for free. Based on the questionnaires distributed,
it is known that most of the students really like and
like keeping their college assignments using
DropBox (figure 6). In addition, it is known that most
students also like and like to receive lecture materials
from lecturers through DropBox (figure 7).
Figure 7: Students responses in getting their lecture
materials by using DropBox.
4 CONCLUSIONS
Based on the results of the research. The following
conclusions can be drawn: 1) The application used is
an application that is free or does not require specific
costs, such as software costs, hardware costs, and
maintenance fees, 2) The use of WordPress and
DropBox in the learning process greatly minimizes
the use of paper and ink, and 3) Most students really
like to receive lecture materials and work on their
lecture tasks through Blog (WordPress) and Cloud
Repository (DropBox).
REFERENCES
Abdillah, L. A. 2013. Students learning center strategy
based on e-learning and blogs. In: Seminar
Nasional Sains dan Teknologi Ke-4 (SNST2013),
19 June 2013 Fakultas Teknik Universitas Wahid
Hasyim Semarang Fakultas Teknik Universitas
Wahid Hasyim Semarang: Fakultas Teknik
Universitas Wahid Hasyim Semarang F.3.15-20.
Abdillah, L. A. 2014. Managing information and
knowledge sharing cultures in higher educations
institutions. In: The 11th International Research
Conference on Quality, Innovation, and Knowledge
Management (QIK2014), 19-21 February 2014 The
Trans Luxury Hotel, Bandung, Indonesia.
Universitas Padjadjaran, Indonesia & Monash
University, Australia.
Abdillah, L. A. 2016a. Exploring Student's Blended
Learning Through Social Media. ComTech
(Computer, Mathematics and Engineering
Applications), 7, 245-254.
Abdillah, L. A. 2016b. Systems Analysis and Design.
Computer Science for Education [Online].
Available from:
http://blog.binadarma.ac.id/mleonaa/teaching/syste
ms-analysis-and-design/].
Abdillah, L. A. 2017. Enriching Information Technology
Course Materials by Using Youtube. In: The 5th
International Conference On Artificial Intelligence,
Computer Science and Information Technology
(AICSIT2017), July 31-August 1, 2017 2017
Bayview Beach Resort, Batu Ferringhi, Pulau
Pinang, Malaysia. WorldConferences.net @
KOKUIS, Koperasi Kolej Universiti Islam
Antarabangsa Selangor 75-82.
Abdillah, L. A. 2018a. Customer Relationship
Management. Computer Science and Information
Systems [Online]. Available from:
https://leonabdillah.wordpress.com/teaching/custo
mer-relationship-management/].
Abdillah, L. A. 2018b. Supply Chain Management.
Computer Science and Information Systems
[Online]. Available from:
https://leonabdillah.wordpress.com/supply-chain-
management/].
Abdillah, L. A., Sari, I. N. & Indriani, D. E. 2018. Computer
science students simulation in capturing tacit
knowledge by using NGT for reducing traffic jam.
International Journal of Engineering and
Technology(UAE), 7, 1463-1467.
Anderson, K. & Kerr, C. 2002. Customer Relationship
Management, McGraw-Hill.
Burke, S. C. & Snyder, S. L. 2008. YouTube: An
Innovative Learning Resource for College Health
BEST ICON 2018 - Built Environment, Science and Technology International Conference 2018
354

Education Courses. International Electronic
Journal of Health Education, 11, 39-46.
Buttle, F. 2009. Customer relationship management:
concepts and technologies, Routledge.
De Jorge Moreno, J. 2012. Using social network and
dropbox in blended learning: An application to
university education. Business, Management and
Education, 10, 220-231.
Dennis, A., Wixom, B. H. & Roth, R. M. 2012a. Systems
Analysis and Design, John Wiley and Sons.
Dennis, A., Wixom, B. H. & Tegarden, D. 2012b. Systems
analysis and design: An object-oriented approach
with UML, John Wiley & Sons.
Dougiamas, M. & Taylor, P. 2003. Moodle: Using learning
communities to create an open source course
management system. In: World Conference on
Educational Multimedia, Hypermedia and
Telecommunications (EDMEDIA) 2003, 2003
Chesapeake, VA, USA.
Drago, I., Mellia, M., M Munafo, M., Sperotto, A., Sadre,
R. & Pras, A. 2012. Inside dropbox: understanding
personal cloud storage services. In: Proceedings of
the 2012 Internet Measurement Conference, 2012.
ACM, 481-494.
Drake, N. 2018. The best cloud storage of 2018 [Online].
London: TechRadar. Available:
https://www.techradar.com/news/the-best-cloud-
storage [Accessed].
Fikri, Abdillah, L. A. & Apriyani, E. 2015. Perancangan
Teknologi Cloud untuk Penjualan Online Kain
Songket Palembang. In: Seminar Nasional Sistem
Informasi Indonesia ke-8 (SESINDO2015), 2015
Institut Teknologi Sepuluh Nopember (ITS),
Surabaya. Institut Teknologi Sepuluh Nopember
(ITS), Surabaya, 387-392.
Firdaus, O. M., Hartati, V., Prambudia, Y. & Saptadi, S.
2015. Supply Chain Management.
Hong, W. 2008. Exploring Educational Use of Blogs in US
Education. Online Submission, 5, 34-38.
Internet World Stats. 2018a. Internet Top 20 Countries -
Internet Users 2018 - Internet World Stats [Online].
Miniwatts Marketing Group. Available:
https://www.internetworldstats.com/top20.htm
[Accessed].
Internet World Stats. 2018b. World Internet Users Statistics
and 2018 World Population Stats [Online].
Miniwatts Marketing Group. Available:
https://www.internetworldstats.com/stats.htm
[Accessed].
Kemp, S. 2018. Digital in 2018: World’s internet users pass
the 4 billion mark. We are social [Online].
Available from:
https://wearesocial.com/sg/blog/2018/01/global-
digital-report-2018 [Accessed 29 January 2018].
Kendall, K. E. & Kendall, J. E. 2011. Systems analysis and
design, Upper Saddle River, New Jersey, Prentice-
Hall.
Lindstrand, A., Johanson, J. & Sharma, D. D. 2006.
Managing customer relationships on the Internet.
International Business & Management: Series
editor Pervez N. Ghauri.
Mitroff, S. 2016. OneDrive, Dropbox, Google Drive and
Box: Which cloud storage service is right for you?
[Online]. San Francisco, CA: CBS Interactive.
Available: https://www.cnet.com/how-to/onedrive-
dropbox-google-drive-and-box-which-cloud-
storage-service-is-right-for-you/ [Accessed].
Ristekdikti 2018. Buku Statistik Pendidikan Tinggi 2017,
Jakarta, Pangkalan Data Pendidikan Tinggi
(Pusdatin) Iptek Dikti, Setjen, Kemenristekdikti.
Simchi-Levi, D., Simchi-Levi, E. & Kaminsky, P. 1999.
Designing and managing the supply chain:
Concepts, strategies, and cases, McGraw-Hill New
York.
Waddington, S., Zhang, J., Knight, G., Jensen, J., Downing,
R. & Ketley, C. 2013. Cloud repositories for
research data–addressing the needs of researchers.
Journal of Cloud Computing: Advances, Systems
and Applications, 2, 13.
Whitten, J. L. & Bentley, L. 2007. Systems analysis and
design methods, McGraw-Hill Professional.
Information Technology Utilization in Environmentally Friendly Higher Education
355
