
Limitation in Conventional Oedometer Consolidation Test for Deep
Layered Soil
Adhya Nanda Kumara, Widjojo Adi Prakoso and Tommy Ilyas
Department of Civil Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, Universitas Indonesia, Depok, Indonesia
Keywords: Oedometer, Consolidation, Preconsolidation, Geotechnical, Soil Test, Terzaghi.
Abstract: Consolidation test for soil is a very common test to find compression parameter in geotechnical
investigation. Terzaghi invented the theory of consolidation in 1925 and the test became geotechnical
standard in 1945. Since then, the theory and mechanical in this test has no meaningful improvement,
whereas due to the rise in numbers of high-rise buildings, the foundation depth requirements are increasing.
In consolidation test, deeper foundation means higher pressure required to find the preconsolidation
pressure (pc). Meanwhile, the conventional equipment is still very popularly used in commercial
geotechnical laboratories causing the result from consolidation less accurate. This paper will discuss the
impact in consolidation test using conventional equipment for deep- layered soil and how to improve the
result of consolidation test.
1 INTRODUCTION
Consolidation test is one of the most common and
important test in geotechnical investigation. Its
purpose is to find the compression parameter from
soil, so that soil engineer can predict soil settlement
caused by the additional load from the construction
or structure. The theories of consolidation was
proposed by Terzaghi in 1925 and by 1945 this test
has become standard test in geotechnical society
(Head, 1998).
When the theory of consolidation was developed,
geotechnical world was still very young and
complex computer computations were still in early
stage, so like any other theory in its time, Terzaghi
developed the theory of consolidation with some
assumptions to simplify the mathematical
calculations. He developed testing apparatus called
Oedometer that only allowed the soil specimens to
move in one direction or also known as One-
Dimension Test (1D). But due to its simplicity and
accuracy, Terzaghi’s consolidation testing method
can easily be accepted in geotechnical society and
largely used in geotechnical practices all over the
world.
The oedometer consolidation apparatus works by
molding an undisturbed soil specimen inside a thin-
steel ring (1-inch) to confine the soil, then the soil
will be loaded with loading mechanism to simulate
the overburdened soil pressure. The steel ring is then
placed inside a watertight steel cell filled with water
to fully saturate the soil. By applying some load to
the soil with loading mechanism and monitoring the
deformation of the soil using a dial gauge, soil
settlement or consolidation could be observed from
this test. Later, the load will be added step by step to
observe the soil behavior to different loads, therefore
the apparatus is known as Incremental Loading (IL)
apparatus.
As technology development increases,
consolidation test was also developed further, but
the basic concept is still using the same principle.
Additional data acquisition and automatic loading
mechanism using step-motor or pneumatic pressure
only to simplify and automate the testing, but the
main concept is still based on Terzaghi’s theory of
consolidation. There are several new developments
in consolidation testing such as Constant Rate Strain
(CRS) and rowe cell, but they are not as popular as
Terzaghi’s Oedometer and not widely accepted in
geotechnical community.
When the apparatus become world standard, the
load requirement was not high. Back then, the final
set load for incremental loading is 800 kPa for
normal range of soil, and it could be extended to
1600 and 3200 kPa for stiff or overconsolidated
clays. These pressure equal to weight set of 64kg as
Kumara, A., Prakoso, W. and Ilyas, T.
Limitation in Conventional Oedometer Consolidation Test for Deep Layered Soil.
DOI: 10.5220/0009007601450150
In Proceedings of the 7th Engineering International Conference on Education, Concept and Application on Green Technology (EIC 2018), pages 145-150
ISBN: 978-989-758-411-4
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
145

standard weight when someone purchase the normal
oedometer equipment.
With the development of high-rise buildings,
deeper foundation is required, so the geotechnical
investigation which used to be only 20-30m depth, is
now required to be deeper to 50-80m, some even
requires more than 100m depth. With this additional
depth, it means the load requirement for the
geotechnical test also increases (BS1377:5, 1990).
With the increase in load requirement to simulate
the overburden pressure, this gives new challenges
for geotechnical testings, especially in laboratories.
The equipments being used in the laboratories also
needed to be checked for its specifications, since
most laboratory equipments has their limitations.
These laboratory equipment limitations never
became a problem for geotechnical laboratories in
Indonesia, since typically in Indonesia the soil
consist of soft soil, but now with the increase in load
requirement, it becomes a new challenge for
geotechnical laboratories in Indonesia.
This paper will discuss about the background
theory of load requirement for the consolidation test.
Then, then this paper will discuss equipment
limitations and what might happen when the soil
tested with less than load requirement. At the end,
we will discuss how to increase test accuracy in
consolidation testing.
2 PRECONDOLIDATE
PRESSURE
In 1920, Terzaghi introduced principle of effective
stress, where he demonstrate an apparatus filled with
water and on the bottom filled with cohesive soil
(Figure 1), by measuring the height of water (hw)
and unit weight of water, pressure applied to the soil
by the water could be measured. This principle is
called neutral stress (Terzaghi, 1943).
Figure 1: Terzaghi’s apparatus to simulate neutral stress.
With the same principle, this principle also
applied to the soil specimen beneath the earth, but
for the soil, there are overburden soil above the soil
specimen, so that by measuring the soil depth and
unit weight of overburden soil, pressure applied to
the soil specimen could be achieved. This pressure
known as total stress.
The difference between pressure caused by
overburden soil (total stress) and the pressure caused
by water (neutral stress) is known as effective stress.
This effective stress is a very important principle in
geotechnical testing, because soil deformation is not
affected by total stress, but only by effective stress
(Budhu, 2010).
Soil has a unique characteristic, where the soil
could maintain memory of the past maximum
effective stress (Budhu, 2010). This is known as soil
loading history and this value could be determined
from the consolidation test. In consolidation test, the
past maximum vertical effective stress that soil has
experienced is known as preconsolidation pressure
(ASTM D653-03, 2003). If the preconsolidation
pressure is less than the overburden effective stress,
it is known as normally consolidated soil, if the
preconsolidation pressure is more than the
overburden effective pressure, it is known as
overconsolidated soil.
According to ASTM D2435 (2011), to find
preconsolidation pressure the final pressure should
be minimum four times the preconsolidated
pressure. This means that the loading requirement is
four times the overburden effective stress from soil
specimen (ASTM D2435-11, 2011).
For example, to perform consolidation test for
soil with 77m-depth, the overburden effective
pressure would be around 600 kPa. The final
pressure for the consolidation test should be around
2400 kPa. Now, if the soil specimen taken from
140m-depth, the overburden effective pressure
would be around 1050 kPa, and the final pressure for
consolidation test should be minimum 4200 kPa.
What would happened if the final pressure is less
than four times the overburden pressure? For
example, this test was conducted for 139.5-meter-
depth soil specimen. The test was conducted in
Japan up to 10240 kPa. As discussed before, for
140m-depth specimen, final pressure required is
4200 kPa, so the final pressure for this test is more
than four times the overburden pressure. As shown
from Figure 2, the preconsolidation pressure of the
sample is 1900 kPa, which shown that the soil is
overconsolidated soil.
If the test stops at 2560 kPa which is more than
overburden pressure, but it does not reach four times
EIC 2018 - The 7th Engineering International Conference (EIC), Engineering International Conference on Education, Concept and
Application on Green Technology
146

Figure 2: Consolidation result of Stress vs Void Ratio Graph for soil specimen with 139.5m-depth. (Data from Pondasi
Kisocon tested in Japan).
Figure 4: Maximum weight set up to 128 kg (2560 kPa).
And not possible to add more weight.
Figure 5: Counterweight to prevent equipment from
tilting.
the overburden pressure, the preconsolidation
pressure is only 750 kPa as Figure 3 shows and the
soil becomes normally consolidated. This would
make an error in the result of the consolidation test.
Another difference is in Compression Index
Value (Cc), where if the final load is properly set up
the Cc value is around 0.52, but if the final load only
stops at 2560 kPa the Cc becomes 0.78. Not only
Compression Index, Recompression Index (Cr) will
also be different.
From this exercise, the decision for final pressure
in consolidation testing is very important.
3 EQUIPMENT LIMITATIONS
To understand how difficult it is to increase load
pressure for deeper soil, we need to understand the
equipment specifications. Every equipment was
made with its specifications and limitations. If we
over-specify the equipment, there must be some
accuracy that being compromised.
Equipment specifications also depend on the year
that equipment was made. As discussed before, in
the old days load requirement is not as high as it is
as today, so most of old equipments were not
designed for very high load. This is one of the issue
in geotechnical practices in Indonesia, because most
geotechnical testing were done using very old
equipment. For example, the equipment that the
writer uses daily only have maximum weight up to
1280 kPa. We manage to add up to 2560 kPa by
0.400
0.500
0.600
0.700
0.800
0.900
1.000
100.00 1000.00 10000.00 100000.00
DB2‐139.5m (final:10240kPa)
pc‐a:1900
Limitation in Conventional Oedometer Consolidation Test for Deep Layered Soil
147

borrowing the weight set from other equipment. The
equipment itself is not possible to be added to more
than 2560 kPa, since there is no more room to add
more weight (Figure 4). The CRS consolidation
machine that the writer faces daily has load cell only
up to 2000 lbf or 2800 kPa, but after using it for
testing several samples with 2500 kPa, the motor
starts to break down. The equipment from the
university that the writer uses also only have weight
set up to 32 kg (1000 kPa). Since the equipment
from university was made from original ELE,
according to the specification, the equipment has
maximum load up to 8800 kPa, but in reality to set
up 8800 kPa is not easy because when such a high
load being used on the apparatus, the whole
apparatus needs to be counterweighted to prevent the
equipment from tilting (Figure 5).
As discussed before, to test 77m soil sample,
minimum load for consolidation test is around 2400
kPa and for 140m depth, the minimum load is 4200
kPa. Meanwhile if the equipment maximum capacity
is only up to 2560 kPa, the equipment is only accurate
up to 70-80m depth and not suitable to be used for
more than 80m depth. This is the reason why some
geotechnical companies send their sample to Japan
only for consolidation testing. The example above
was tested in Japan with load up to 10.000 kPa.
The quality-made of the equipment also affecting
the accuracy of the test. According to ASTM
D2435-03 the loading device shall have precision of
+/- 0.5% of applied load. With this precision, the
quality of equipment can make a difference
especially when the equipment is being pushed up to
its limit. To compare between equipments, the writer
compares consolidation results between several
different equipments which are available (Figure 6).
For information, the CRS consolidation machine
was made in America, Oedometer E4 was made in
Japan, and Oedometer B3 was made in Singapore.
These equipments also have different models, while
CRS and Oedometer E4 has typical vertical load
frame, meanwhile the Oedometer B3 is typical ELE-
type consolidation machine with yoke and beam
mechanism. Shown in Figure 6, the CRS and
Oedometer E4 give similar results, where
Oedometer B3 gives a completely different result.
At lower stress, Oedometer B3 still gives similar
result as the rest up to 500 kPa, where the line start
to separate from the other equipments.
Oedometer B3 also shows higher strain result
where it could happen due to soil starts to creep out
from the oedometer ring. This creep phenomenon
are quite common happening in Oedometer with
yoke and beam model.
When checking the equipment manufacturer’s
website, the specification from the equipment varies,
but the latest equipment already prepared for higher
load as specified in Table 1 where the latest trend of
equipment has maximum load capacity above 5000
kPa.
Figure 6: Graph of comparison between different equipments.
0.00
5.00
10.00
15.00
20.00
25.00
10 100 1000 10000
STRAIN(%)
STRESS(kPa)
CONSOLIDATIONAT48MDEPTH
OEDOE4 CRS‐effectivestress OEDOB3
EIC 2018 - The 7th Engineering International Conference (EIC), Engineering International Conference on Education, Concept and
Application on Green Technology
148
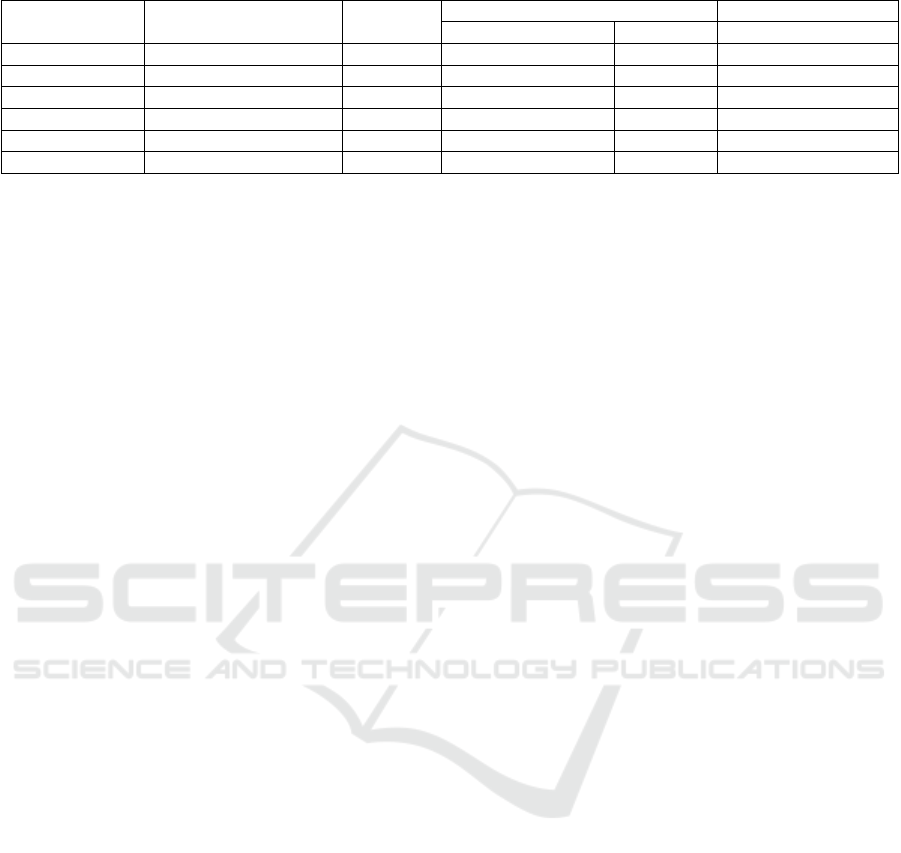
Table 1: Maximum equipment specification.
Band Type
Maximum
Load
Load Applied on Sample
D: 6.35 cm/ 2.5 inch D: 5 cm Note
Hogentogler Geostar Consolidometer 8.9 kN 2800 kPa 4500 kPa Since 1991
GCTS CRS-10 10 kN 3150 kPa 5000 kPa
Controls Group ACE-Ems 20 kN 6300 kPa 10000 kPa
Conrols Group Oedometer 18 kN 5700 kPa 9000 kPa 168 kg weight (11:1)
VJ Tech ACONS 15 kN 4800 kPa 8000 kPa
ELE Oedometer 12.5 kN 4000 kPa 6400 kPa 128 kg weight (10:1)
For note in Table 1, these are maximum
specifications for the equipment, where some
equipments need extra modifications to reach these
limits. For example, for ELE oedometer the standard
weight is set only up to 64kg. Extra weight set needs
to be purchased separately, and a special table is
needed to prevent the equipment from tilting.
4 IMPROVING THE
CONSOLIDATION TEST
RESULT
As discussed before, incorrect use of final load could
lead to inaccuracy in consolidation test result, so the
decision to determine correct final load is very
important in consolidation testing. There are several
methods that could be applied to current equipment
to increase load.
The first method is by adding the weight set to
increase the load for the test. Most of geotechnical
practices, usually has more than 1 consolidation
equipment. To increase the load, it is very easy to
add more weight by borrowing weight set from the
other equipments since the weight set from the same
equipment usually already calibrated and compatible
with each other. Buying another weight set from
manufacture also possible to add more load. But this
method only applicable up to equipment
specification. Making weight set is also possible, but
each weight needs to be calibrated.
Second method is by increasing the beam ratio.
For beam and yoke type of equipment, usually the
beam ratio could be change from 10:1 to 11:1, which
will increase the load applied on the sample.
The third solution is by decreasing sample
diameter could increase the load applied to the
sample. The standard sample diameter usually 2.5
inch (6.35 cm). According to ASTM, minimum
sample diameter is 5 cm. By decreasing the sample
diameter could increase the load applied to the
sample. Table 1 shows comparison between samples
diameter 6.35 cm to 5 cm, where the load could
increase quite significantly. Changing sample from
6.35cm to 5 cm is not as easy as changing the ring,
since most oedometer ring is set with its oedometer
cell. So to change the sample size, the whole
oedometer cell needs to be replaced as well. This
becomes a problem for old equipment where the
oedometer cell with 5 cm diameter is not available.
Last method is by purchasing higher capacity
consolidation machine. Of course, purchasing new
equipment with higher capacity will solve this
problem, but with such low fee for consolidation
testing in Indonesia, not everybody is able to
purchase expensive equipment from well-known
equipment manufacturer. It is not a secret that some
geotechnical practices has equipments made in
Indonesia, which is not a problem for low capacity,
but by pushing the equipment above its limit would
not give a good and accurate result.
5 CONCLUSIONS
In consolidation testing for deep soil, to determine
final load is very important to get a reliable and
accurate data. According to ASTM D2435-03, to
calculate preconsolidation pressure, the final load
should be minimum four times effective overburden
pressure, which for deep soil sample would be very
high pressure. When the final load does not meet
four time the effective overburden, the
preconsolidation pressure (pc), compression index
(Cc), and Recompression Index (Cr) would not be
accurate and could lead the overconsolidated soil to
be normal consolidated soil.
To be able to achieve this high load,
consolidation apparatus needs to be checked for its
specification since the old model apparatus usually
does not have capability for high-pressure testing.
Checking for available weight set, diameter of
oedometer ring, and beam ratio would show the
equipment capability. Some model of consolidation
apparatus could have high load pressure with some
modification like changing the beam ratio, adding
weight set, and reduce the oedometer ring size.
Limitation in Conventional Oedometer Consolidation Test for Deep Layered Soil
149

Purchasing a new equipment need to check
equipment capability, although most new
equipments are capable to have high load pressure,
but not all equipments have similar specifications.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
Acknowledgments and gratitude to all the parties
who have assisted and supported the research of this
paper, especially to research grant from PITTA
Universitas Indonesia with Contract No.
2548/UN2.R3.1/HKP.05.00/2018, PT. Pondasi
Kisocon Raya (Mr. Y. P. Chandra), and PT
SOFOCO (Mr. Benny Kumara).
REFERENCES
ASTM D653-03, 2003. Standard Terminology Relating to
Soil, Rock, and Contained Fluids, ASTM
International. West Conshohocken: PA.
ASTM D2435/D2435M-11, 2011. “Standard Test
Methods for One-Dimensional Consolidation
Properties of Soils Using Incremental Loading.”
ASTM International. West Conshohocken: PA.
Budhu, M., 2010. Soil Mechanic and Foundations, Wiley,
USA.
BS 1377-2:1990, 1990. Methods of test for soils for civil
engineering purposes. Compressibility, permeability
and durability tests, British Standard Institution.
London, UK.
Head, K. H., 1994. Manual of Soil Laboratory Testing:
Volume 2: Permeability, Shear Strength and
Compressibility Tests, Chichester: Wiley.
Terzaghi, K., 1943. Theoretical Soil Mechanics, USA:
John Wiley & Sons.
EIC 2018 - The 7th Engineering International Conference (EIC), Engineering International Conference on Education, Concept and
Application on Green Technology
150
