
An Analysis of Transformational Leadership Influence toward
Employee Performance by using Psychological Empowerment
Mediation in East Java Regional Office of the Ministry of Law and
Human Rights
Leorisia Hardika Putra
Master of Management, Faculty of Economics and Business, Airlangga University, Surabaya, Indonesia
Keywords: Transformational Leadership, Employee Performance, Psychological Empowerment
Abstract: The success of an organization can be seen from the performance of its employee. Therefore improving the
employee’s performance is the most important thing for the company. By performing transformational
leadership in the company, it is expected that psychological empowerment can be shown in four cognitions
as a connection mediating variable between the transformational leadership and employee performance. This
study aims to analyze and to prove how the transformational leadership influences employee performance
mediated by psychological empowerment at the East Java Regional Office of the Ministry of Law and Human
Rights. The approach in this study uses a quantitative approach. The sample in this study are JFU (General
Functional Position), JFT (Specific Functional Positions), and Administrator Officers (Structural Officers)
divided into by 109 employees spreading in four divisions that is carried out by using the Proportionate
Stratified Random Sampling technique. The analysis technique used in this study is the Structural Equation
Model (SEM) approach by Partial Least Square (PLS) method. Results of SmartPLS path model analysis
confirm that Transformational leadership has a significant effect on employee performance, Transformational
leadership has a significant effect on employee performance with psychological empowerment as a mediating
variable.
1 INTRODUCTION
The success of an organization can be seen from the
performance of the employees. Gomes (2003) states
that the performance of an employee is basically the
work result of an employee for a certain period that is
compared to the possibilities, for example standards,
targets or performances that have been determined
and agreed in advance. Organizational leaders are
very aware of the difference in performance between
one employee and another under their supervision.
Even though employees work in the same place but
their quality is not the same.
A similar thing happened to organizations or
public services (bureaucracy) in the government. In
terms of service, bureaucratic organizations are
required to be adaptive institutions for development,
because bureaucracy should not be at that one point,
after all. In order to accelerate the achievement of
good governance, on December 21, 2010 the
government established Presidential Regulation
Number 81 of 2010 on the Grand Design of 2010-
2025 Bureaucratic Reform. The regulation is the
operationalization of the Grand Design of
Bureaucratic Reform as outlined in the Bureaucratic
Reform Road Map. Regulations were then gradually
enacted as an effort to implement bureaucratic
reforms, including Government Regulation Number
46 of 2011 on Work Performance Assessment of
Civil Servants to substitute the Work Performance
Assessment List (DP-3). In that new regulation, the
quality of employees can be measured and assessed
from several aspects including service orientation,
integrity, commitment, discipline, cooperation and
leadership.
As an organization that has a lot of contact with
community service, the Ministry of Law and Human
Putra, L.
An Analysis of Transformational Leadership Influence toward Employee Performance by using Psychological Empowerment Mediation in East Java Regional Office of the Ministry of Law and
Human Rights.
DOI: 10.5220/0009492206710677
In Proceedings of the 1st Unimed International Conference on Economics Education and Social Science (UNICEES 2018), pages 671-677
ISBN: 978-989-758-432-9
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
671

Rights is required to maintain service quality and
integrity in order to maintain the status of Corruption-
Free Zone (Wilayah Bebas Korupsi) and Clean and
Serving Bureaucracy Zone (Wilayah Birokrasi Bersih
dan Melayani) from the Ministry of Empowerment of
State Apparatus and Bureaucracy Reform, which has
been achieved since 2016. Several complaints in
public service must of course be minimized because
it can disrupt the objectives of the organization that is
oriented to excellent service. Since the existence of
“E-LAPOR” application in 2015, there were 242
complaints entered the system where the complaints
can also be seen and connected with the system
General Secretary of each Ministry. Meanwhile, for
the first semester of 2018 there have been 60
complaints, where Immigration service received the
most complaints, 55, then Correctional with 4
complaints, and legal services contribute to one
complaint. Moreover, according to recent data in the
third quarter, there were 8 complaints entering the
system (according to the office’s Public Relations
data ), and of course this is a boomerang if the report
/ public complaint is not immediately followed up.
In addition to service, accountability and
structuring HR is also a very important thing to assess
employee performance in supporting performance
achievements because inside of it there is a part of
employee performance targets that will support it,
including commitment, cooperation and leadership
factors. The work plan should be carried out
according to the schedule, that is, at the time of the
initial preparation of the activities, the
implementation must be given more attention,
because there are still many activities carried out after
the second semester. In fact, in evaluating the
achievement of good performance, the work calendar
that has been prepared is really in accordance with the
target to be achieved. The activities compiled in the
first semester should be carried out in the first
semester as well, otherwise they will reduce the
quality of output from the performance achievements
that has been prepared at the beginning of the year.
The fact is that there are still many activities that have
been boosted at the end of the year with the aim that
the budget absorption achieved gets good percentage
in accordance with the performance target. This must
be evaluated so that the work plan and work calendar
are in accordance with the performance targets so that
the output produced in the performance achievement
is truly high quality.
To realize the quality of public services and the
achievement of performance in accordance with the
target and work calendar and HR arrangement in an
organization contained in 8 (eight) areas of change,
surely the role of the leader has a considerable
contribution. The role of leadership is very strategic
and important in an organization as one of the success
determinants to achieve the mission, vision and goals
of an organization. Therefore, the challenge in
developing a clear organizational strategy mainly lies
in the organization on the one hand and depends on
leadership (Porter, 1996).
The right leadership style in moving and directing
all potential employees to realize organizational
stability and increasing productivity oriented to
organizational goals is transformational leadership
because it describes a process where leaders bring
significant positive changes to individuals, groups,
teams and organizations (Avolio, et al., 1990).
Transformational leadership is described as a
leadership style that motivates employees by giving
individual attention to each follower (Bass, 1985).
Transformational leadership is also able to provide a
positive example to subordinates. Positive behavior
can be in the form of taking risks together and
instilling a sense of pride in their subordinates and
always motivating their employees to perform higher
than the expected.
However, the goal or success of an organization
is not only from a transformational leader, it also
requires employees as driving forces as well as targets
for change. Transformational leadership must be able
to give more freedom to employees who lack the
freedom to be more creative and innovative and to be
involved in making organizational decisions.
Previously, creative and proactive culture in
bureaucratic organizations was less developed and
employees were merely technical implementers who
were in the lowest structure of bureaucracy and
worked after orders/dispositions from superiors.
To realize competency, employees need to be
more empowered to develop their existing potential
and provide other ways of working, which is by
giving empowerment to employees (Lovelock and
Wirtz, 2010). Empowerment is a time when
organizations equip employees with autonomy or
power to make decisions when they face everyday’s
life in the work environment (Haas, 2010). With the
provision of empowerment, of course, employees are
expected to be able to improve their abilities,
knowledge, creativity and quality of work.
Employees can be motivated, motivated to believe in
their ability to do the tasks given to succeed.
Employees must be able to make decisions and
employees must be able to think correctly and quickly
when facing problems that occur right away.
Empowerment is part of the process and also the
organizational context. Empowerment not only
UNICEES 2018 - Unimed International Conference on Economics Education and Social Science
672
includes increasing individual motivation and
delegation from top to bottom. Liden and Wayne
Sparrowe, 2010) describes empowerment as intrinsic
motivation, job design, collaborative decision
making, social learning theory, and self management.
Empowerment is referred to as psychological
empowerment. Itself is a state of mind where an
employee can master his feelings for the work done,
must be aware of the tasks of the work being done,
with a large level of responsibility for both work
results for the individual and the overall progress of
the organization and perceived justice in terms of
wages based on individual and group performance
(Melhem, 2006). Psychological empowerment is
divided into four variables, namely, competence,
meaningfulness, self-determination, and impact
(Spreitzer, 1995).
Consequently, the existence of psychological
empowerment driven by a transformational
leadership is expected to produce performance
accountability implemented in the employee
performance and improve the quality of public
services oriented to excellent service so that the goals
of an organization towards change can be realized,
especially in East Java Regional Office of Law and
Human Rights Ministry.
2 THEORICAL FRAMEWORK
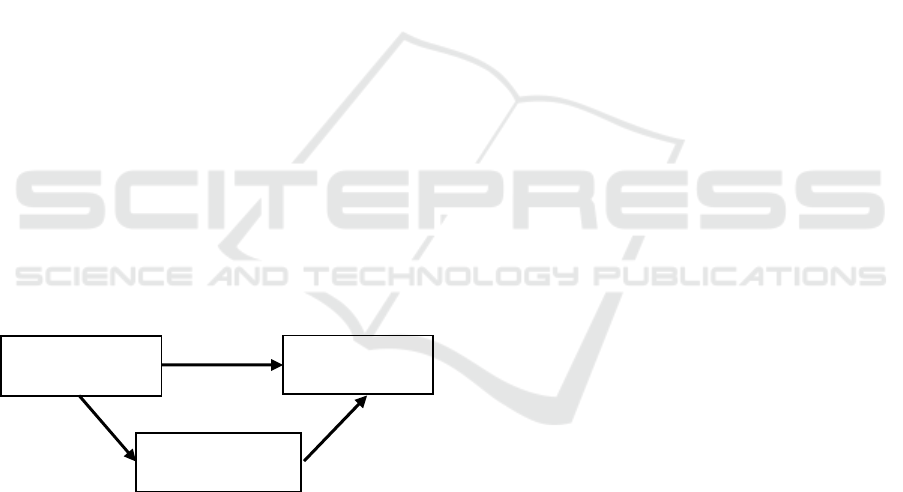
2.1 Analysis Model
Figure 1: Analysis Model
2.2 Transformational Leadership
According to Yammarino and Bass (1990),
transformational leaders must be able to persuade
their subordinates to carry out their duties beyond
their own interests for a larger organization interest.
Yammarino and Bass (1990) also state that
transformational leaders articulate a realistic vision of
the organization's future, stimulate subordinates in an
intellectual manner, and pay attention to the
differences possessed by their subordinates. Tichy
and Devanna (1990) state that the existence of
transformational leaders has a transformation effect
both at the organizational level and at the individual
level.
Bass and Avolio (1994) suggest that
transformational leadership has four dimensions.
They called it "the Four I's". They are:
1. Idealized Influence or Charisma
2. Inspirational Motivation
3. Intellectual Stimulation
4. Individualized Consideration
2.3 Psychological Empowerment
According to Yukl (2005, 129), empowerment is
very important in the context of leadership because
delegating responsibility for more important tasks
will not give authority if people lack the skills and
knowledge needed to successfully carry out the task
and feel worried about failure. Therefore, in each
empowerment there must be an understanding of
psychological empowerment, which according to
Spreitzer (in Yukl, 2005: 129) includes four elements,
including:
1. Meaning. The content and the consequences of
work are consistent with one's values and
idealism.
2. Self determination. The person has the ability
to determine how and when the work is
completed.
3. Competence. The person has high confidence
about being able to do the job effectively.
4. Impact. The person believes that it is very
possible to have an important impact on the
work and work environment.
2.4 Employee Performance
According to Gibson et al. (1996) employee
performance is a measure that can be used to
determine the comparison of task implementation
result, responsibilities given by the organization in a
certain period and relatively can be used to measure
work performance or organizational performance.
Mathis and Jackson (2006) define that performance is
basically what employees do and do not do.
Employee performance influences how much they
contribute to the organization, including output
quantity, output quality, output period, workplace
attendance, and cooperative attitude.
Based on Government Regulation Number 46 of
2011 on the Assessment of Civil Servants, there are
several aspects to assess employee performance
behavior, which are:
1. Service orientation
2. Integrity
3. Commitment
4. Discipline
Transformational
Leadership (X)
Employee
Performance (Y)
Psychological
Empowerment (Z)
H1
H2
An Analysis of Transformational Leadership Influence toward Employee Performance by using Psychological Empowerment Mediation in
East Java Regional Office of the Ministry of Law and Human Rights
673

5. Cooperation
6. Quantity (target output)
7. Quality (target quality)
8. Time (target time)
9. Cost (target cost)
3 RESEARCH METHOD
Population is a generalization area consisting of
objects or subjects that have certain quantities and
characteristics set by researchers to be studied and
then drawn a conclusion (Sugiyono, 2009).T he
population of the object of this research are all
employees of East Java Regional Office of Ministry
of Law and Human Rights, amounting to 150 people.
Samples are part of the number and characteristics
possessed by the population (Sugiyono, 2009). In this
study the samples were employees of East Java
Regional Office of Ministry of Law and Human
Rights with the sampling technique uses the Slovin
formula result is 109 people.
This research was conducted by randomly
distributing questionnaires on JFU (General
Functional Position), JFT (Specific Functional
Position), and Administrator Officers (Structural
Officers) which is divided into 4 (four) different
divisions, so that in taking samples from each division
it is carried out by using Proportionate Stratified
Random Sampling technique. According to Sugiyono
(2009) Proportionate Stratified Random Sampling is
taking sample from members of the population
randomly and proportionally structured. This
sampling is carried out if the members of the
population are heterogeneous and divided into groups
according to similar characteristics or certain
conditions.
Table 1: Samples by Division
No. Division Σ
Employee
Σ
Sample
1 Administratio
n
48 35
2 Legal and Human Rights
Services
59 43
3 Immigratio
n
18 13
4 Correctional 25 18
Total 150 109
Source : HRD
Table 2: Samples by Position
No. Position Σ Officer Σ Sample
Structural Position (administrator/Supervisory)
1. Echelon II.b 4 2
2. Echelon III 9 7
3. Echelon IV 18 13
Functional Position
1. Specific Functional 42 31
2. General Functional 77 56
Total 150 109
Source : HRD
4 RESULT AND DISCUSSION
Table 3 shows that the number of 109 respondents
who are Administrator/Supervisory officials is 20.18
percent, JFT are 28.44 percent and JFU or commonly
called dominating staff is 51.37 percent with 60
respondents or as many as 55, 1 percent of male have
a little more than female 49 respondents or 44.9
percent. For ages, respondents were in the range of 24
years to 58 years, which was dominated by
respondents aged between 36 years and 45 years
(40.36 percent). For the education taken by
respondents, doctor is 1.83 percent, as many as 74
respondents who dominated the most undergraduate
education with a percentage of 67.88 percent, then
master's program 27.52 percent and diploma
education at 1.83 percent.
Table 3: Profile of the Respondent
Profile Total Percentage
Number of Samples 109 100%
Position :
Supervisory Officer
Specific Functional
General Functional
22
31
56
20,18 %
28,44 %
51,37 %
Gender :
Male
Female
60
49
55,1 %
44,9 %
Age :
≤ 25 year
26 – 35 year
36 – 45 year
> 45 yea
r
7
32
44
26
6,42 %
29,35 %
40,36 %
23,85 %
Education :
Diploma
Bachelor
Master
Doctor
3
74
30
2
2,75 %
67,88 %
27,52 %
1,83 %
Source : Data processed, 2018
Figure 2 below, Inner model testing done to see
the coefficient of determination, predictive relevance,
UNICEES 2018 - Unimed International Conference on Economics Education and Social Science
674

goodness of fit, estimation of path coefficients and
parameter coefficients. After knowing the significant
relationship between variables, it can be concluded
the hypothesis related to transformational leadership,
psychological empowerment, and employee
performance in East Java Regional Office of Law and
Human Rights Ministry. Hypothesis testing is done
by bootstrapping method.
Figure 2: Inner Model
Source : Data processed, PLS 3
Table 4: R Square
R
Square
R Square
Adjusted
Employee Performance 0.357 0.345
Psychological
Empowermen
t
0.404 0.398
Source : Data processed, PLS 3
The R-Square value above, each of which has
been multiplied by 100 percent, produces a
coefficient of determination from employee
performance of 35.7 percent. This value indicates that
employee performance can be explained by
transformational leadership, while the remaining 64.3
percent is explained by other variables outside the
analysis model. The coefficient of determination from
psychological empowerment produces a value of 40.4
percent, where the value shows that psychological
empowerment can be explained by transformational
leadership, employee performance, while the
remaining 59.6 percent is explained by other
variables outside the analysis model.
Table 5: Test the Direct Hypothesis
Orgnl
Sample
(O)
Sample
Mean
(M)
St.
dev
t-
stat
p-
value
Psychological
Empowerment
Employee
Performance
0.315 0.293 0.130 2.424 0.016
Transformationa
l Leadeship
Employee
Performance
0.345 0.357 0.093 3.699 0.000
Transformationa
l Leadeship
Psychological
Empowerment
0.635 0.639 0.129 4.924 0.000
Source : Data processed, PLS 3
Hypothesis 1 states that Transformational
Leadership has significant effect on Employee
Performance.
An Analysis of Transformational Leadership Influence toward Employee Performance by using Psychological Empowerment Mediation in
East Java Regional Office of the Ministry of Law and Human Rights
675

The calculation resulted from SMARTPLS 3.0
software shows the path coefficient value of
Transformational Leadership on Employee
Performance has significant influence with T-
Statistics more than 1.96, which is 3.699. This means
that hypothesis 1 suggesting that Transformational
Leadership has significant effect on Employee
Performance in East Java Regional Office of
Kemenkumham is supported.
Hypothesis 2 states Transformational Leadership
has significant effect on Employee Performance with
Psychological Empowerment as mediating variable.
The calculation resulted from SMARTPLS 3.0
software shows the path coefficient value of
Transformational Leadership on Employee
Performance has significant influence with T-
Statistics more than 1.96, which is 3.699. The path
variable of Transformational Leadership with
Psychological Empowerment has significant
influence with T-Statistics more than 1.96, which is
4.924. Meanwhile the Psychological Empowerment
variable with Employee Performance has a
significant influence with T-Statistics more than 1.96,
which is 2.424. Thus it can be said that
Transformational Leadership has a significant effect
on Employee Performance and also when
Transformational Leadership towards Employee
Performance through Psychological Empowerment
produces significant value because the T-Statistics
value is more than 1.96. Because all variables have a
significant influence both Transformational
Leadership on Employee Performance,
Transformational Leadership has a significant effect
on Psycchological Empowerment and Psychological
Empowerment has a significant effect on Employee
Performance. It is concluded that the hypothesis is
proven or the second hypothesis is supported.
5 CONCLUSIONS
Based on the analysis and the discussion, it can be
concluded that:
1. Transformational leadership has significant
influence on employee performance.
2. Transformational leadership has significant
influence on employee performance with
psychological empowerment as a mediating
variable.
The result of this study indicates that the
Transformational Leadership variable with the
mediation of Psychological Empowerment has
significantly influenced the performance of
employees and therefore suggests the government
especially the East Java Regional Office of Law and
Human Rights Ministry:
1. To pay special attention to the
Transformational Leadership applied so far, as
well as the Psychological Empowerment
factors. If the two variables are noticed, it will
improve Employee Performance.
2. As government employees who serve to
provide services to the community, it is
necessary to devote their performance to the
maximum extent possible so public can be
served.
3. For future research, this research can be used
as an idea for future research development.
For another development, it is recommended
to add other variables that can affect employee
performance.
REFERENCES
Bass, B.M. (1985) Leadership and Performance Beyond
Expectations. New York: The Free Press.
Bass, M and Avolio, (1990) The Implication Of
Transactional And Transformational, Team And
Organization Development, Vol. 4, page 231-273.
Bass, B.M. & Avolio, B.J. (1994) Improving
Organizational Effectiveness through
Transformasional Leadership. Thousand Oaks: Sage.
Haas. (2010). “Employee Empowerment, Job Satisfaction,
and Organizational Commitment: An in-depth
Empirical Investigation”. Journal of Employee
Empowerment, Vol. 5, No. 3, page 325-344.
Liden, RC, Wayne, SJ & Sparrowe, RT. (2000) ”An
examination of the mediating role of psychological
empowerment on the relations between the job,
interpersonal relationships, and work outcomes‟.
Journal of applied psychology, vol. 85, no. 3, pp. 407.
Lovelock and Wirtz. (2010) “Understanding the Impact of
Employee Empowerment on Customer Oriented
Behavior”. Journal of Business Studies Quarterly, Vol.
6, No. 1, page 55-67.
Mathis, R.L. & J.H. Jackson. (2006) Human Resource
Management: Manajemen Sumber Daya Manusia.
Jakarta: Salemba Empat.
Melhem. (2006) “Understanding the Impact of Employee
Empowerment on Customer Oriented Behavior”.
Journal of Business Studies Quarterly, Vol. 6, No. 1,
page 55-67.
Porter, Michael E. (1996) Strategi Bersaing : Teknik
Menganalisis Industri dan Pesaing. Jakarta: Erlangga.
Sofyani, Hafiez, SE., M.Sc. (2016) Modul Praktik Partial
Least Square (PLS) Untuk Penelitian Akuntansi
Pendekatan Kuantitatif, Prodi Akuntansi Universitas
Muhammadiyah Yogyakarta.
UNICEES 2018 - Unimed International Conference on Economics Education and Social Science
676

Sugiyono. (2009) Metode Penelitian Kuantitatif, Kualitatif,
dan R&D. Bandung: Alfabeta
Spreitzer, G. M. (1995) Psycological Empowerment In The
Workplace: Dimensions, Measurements, And
Validation. Academy of Management Journal.
----------. 1996. Organisasi, Prilaku, Struktur, Proses.
Jakarta: Erlangga.
Tambun, Sihar, SE, M.Si, Ak. (2014) Workshop Metode
Penelitian Kuantitatif Metode “Structural Equation
Modeling” dan Interpretasi Hasil Penelitian Dengan
Menggunakan Program Smart PLS (Partial Least
Square) Intervening Variabel, Universitas Tujuhbelas
Agustus’45 Jakarta
Tichy, N.M. & Devanna, M.A. (1990) The
Transformational Leader, John Wiley & Sons. New
York : NY.
Yammarino, F.Y & Bass, B.M. (1990) Long Term
Forecasting or Transformational Leadership and Its
Effect Among Naval officers. Group and Organizational
Studies.
Yukl, Garry. (2005) Kepemimpinan dalam Organisasi.
Terjermahan Budi Suprianto. Edisi ke 5. Jakarta:
Penerbit PT. Indeks.
Presidential Regulation Number 81 of 2010 on the Grand
Design of 2010-2025 Bureaucratic Reform
Government Regulation Number 46 of 2011 on Work
Performance Assessment of Civil Servants to substitute
the Work Performance Assessment List (DP-3)
An Analysis of Transformational Leadership Influence toward Employee Performance by using Psychological Empowerment Mediation in
East Java Regional Office of the Ministry of Law and Human Rights
677
