
Analysis the Effect of Dual Monetary Policy Instrument on Index
Industrial Productial in Indonesia
Mutiara Shifa
1
, Dede Ruslan
1
and Fitrawaty
1
1
Faculty of Economics, Universitas Negeri Medan, Medan, Indonesia
Keywords: Conventional Monetary Policy, Islamic Monetary Policy, Industrial Production Index (IPI), VAR/VECM.
Abstract: This study aimed to analyse instrument of monetary policy in affecting economic growth in Indonesia that
measure using Industrial Production Index (IPI). Since Indonesia has a dual finance system and this research
is meant to compare the effectiveness both system as a instrument of monetary policy through interest rate
channel, this research will be written in two models as in conventional model and sharia model. Using VAR
research and conducted by Impulse Response Function (IRF) and Forecast Error Variance Decomposition
Test. The IRF Test showed that on the conventional model, the responses of IPI to the shock of SBI and
PUAB is positive and permanent, so do the response of IPI to the shock of SBIS and PUAS is positive and
permanent. Fluctuation on the mechanism of sharia monetary policy subside faster than the conventional
monetary. And for the result of FEVD test, conventional model give a positive contribution in the sense of
raising economic growth, where in this research is measured by IPI, amounted to 37,51%, while the sharia
model give a positive contribution to IPI, amounted 7.14%. Therefore, we can conclude that in Indonesia,
mechanism of monetary transmission through interest rate channel using conventional model can be said
better than sharia model in the term of raising economic growth.
1 INTRODUCTION
The function and role of the Bank-owned Indonesia
as the central bank in support of the development of
the financial markets and the economy of a country.
According to Warjiyo and Solikin (2003), this is due
to the policies implemented by the central bank can
affect the development of interest rates, credit
amount, and the amount of money in circulation,
which will affect not only the development of
financial markets, but also economic growth,
inflation, and welfare of society as a whole. This is
called policy with monetary policy. The development
of the financial markets and the economy is that
macroeconomic stability is among other things
reflected by price stability (low inflation rate),
improving the development of real output (economic
growth), as well as sufficient breadth field/job
opportunities available.
Periodically, every year the Government set an
economic growth target and announced through the
State income and Expenditure Budget (APBN). Then
the target will be evaluated during the one year later
along with the turn of the year in which data on the
realization of economic growth that year was also
presented. The Government can just change the target
figures for economic growth in the middle period to
take place when the economic growth target proved
difficult to achieve on the State of the economy in the
period of walking. This is the same as the decision
changes the target figures for economic growth in the
last four years. The economic growth target set by the
Government for the period of 2010-2015 each year
amounted to 6.3%, 6.8%, 5.5%, and 5.1% by year
calculation base used is the year 2010, as can be seen
on the graph 1 below.
Source: Ministry of Finance.
Figure 1: Comparison of targets and the realization of
economic growth (Base Year 2010).
In the year 2013 the growth economy Indonesia
amounting to 5.78%. This figure is far lower than the
target which was already decided after roughly 6.8%.
398
Shifa, M., Ruslan, D. and Fitrawaty, .
Analysis the Effect of Dual Monetary Policy Instrument on Index Industr ial Productial in Indonesia.
DOI: 10.5220/0009494203980406
In Proceedings of the 1st Unimed International Conference on Economics Education and Social Science (UNICEES 2018), pages 398-406
ISBN: 978-989-758-432-9
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

In later years, Indonesia's economic growth was
increasingly debased i.e. 5.02% figure is treading in
the year 2014 and 4.73% in 2015. Indonesia's
economic growth rate by the year 2015 is the lowest
figure for six years, where this is the first time for
Indonesia stepped on the numbers below 5% since
2009. Later, in the year 2016 economic growth back
step on number 5% i.e. 5.02%. However, this figure
is still below the target of economic growth of 5.2%
in 2016.
The index of industrial production or IPI number
index that describes the development of the
production sector of manufacturing industry in early
as well as of data series that are longer and complete
because its nature is designed to periodically
monthly. Ordinary dipakain this index as a proxy for
the activities of the economy or the national income
primarily due to unavailability of real gross domestic
product or gross national Product as measured by the
monthly basic.
The Government is using monetary policy in
controlling and influencing the development of real
output (economic growth) that where data can be
reflected through IPI. In this case, the tool used by the
Government of one is the transmission mechanism of
monetary policy and its instruments are used. The
transmission of monetary policy basically shows the
interaction between central banks, banking, and other
financial institutions, as well as the perpetrators of
real sector of economy. The interaction between the
central bank and banking can be seen on the
interactions in financial markets. Interaction through
financial markets occurs because on the one hand the
central bank conducts monetary control through
financial transactions conducted with banking. On the
other hand, the financial transaction banking to
portfolio investment. These interactions will be
influential on the development of short term interest
rates as interest rates PUAB and SBI(Warjiyo,
2004:6-20).
This research concentrates the instruments of
monetary policy interest rate channel. This is because
the channel of interest rates further stressed the
importance of this aspect of prices in financial
markets against a wide range of economic activity in
the real sector. The most important features in the
transmission mechanism of monetary policy path of
interest rates is on the emphasis of real interest rates
that affect the decisions of economic actors spending
(consumption and investment), so that although the
nominal interest rate is from any zero monetary
policy will still be used effectively through changes
in the price level. In this regard, monetary policy is
the central bank will have an effect on the
development of a wide range of interest rates in the
financial sector and will further influence on the level
of real output.
As a solution of the conventional monetary
system containing usury, Islam introduced Islamic
monetary system, i.e. the monetary system based on
Islamic sharia principles. Based on Bank Indonesia
Regulation No. 10/36/PBI/2008, to achieve the final
objective, Bank Indonesia can do control based on
sharia principles. Sharia's own monetary policy
prohibits the use of usury or interest in its execution,
because in addition to indeed is haraam, monetary
Islam considers interest usury or very risky against
the economic crisis and prone to instability.
In principle, monetary policy and the purpose of
islam is not much different from the conventional
monetary, that is, to achieve full employment
conditions in which all sectors of the production can
be used optimally, guarantee the stability of exchange
rates and prices (supervision inflation) and an
instrument of redistribution of wealth where wealth
synergize between monetary and real sector. In
achieving the goal, economic instruments have Sharia
moter monetary control is not much different from the
conventional instruments of monetary control.
In addition, to link the Islamic economic and
monetary policy, monetary economic system of
Sharia also has an Islamic monetary policy
transmission one of its channels is channel modifying
interest rates interest rate pass-through use the policy
rate pass-through, where interest rates used are
changed using the yield level. Some short term money
market instruments used were the SBIS and PUAS.
SBIS is a form of modification of Bank Indonesia
Certificates or SBI, SBI interest rates where replaced
by the level of berakadkan yields the SBIS were.
While PUAB is a form of modification of the PUAS
in which the instruments used in Indonesia is the
Mudharabah Interbank investment certificates
(SIMA).
SBI interest rates, interest rate PUAB O/N, yields
SBIS and SIMA are often used as an instrument of
short-term interest rates to monetary control in
achieving the target of the end of which one is
economic growth (real output developments) that can
Industrial production index using diliat. Here is the
data rates of SBI, PUAB O/N, yields SBIS, SIMA,
and the IPI 2013-2016 year.
Analysis the Effect of Dual Monetary Policy Instrument on Index Industrial Productial in Indonesia
399

Table 1: SBI Rate, Equivalent data Rate SBIS, PUAB O/N
Rate, Equivalent Rate PUAS, and IPI 2013-2016 Period (in
billion, and Percent).
Years
Position SBI
PUAB
O/N Rate
Position
SBIS
Eq
Rate
PUAS
IPI
2013
1,011,470
4.95
53,581
5.21
11489
2014
1,121,632
5,92
74,484
6.4
12036
2015
732,367
6.11
96,919
6.08
12609
2016
1,004,143
4.81
101,647
5
13114
Source: Bank Indonesia and the Central Bureau of statistics.
Table 1 above shows the trend of the fluctuation
in the position of SBI, SBI's position in 2013 is
Rp1,011,470 billion which then in 2014 rising to,632
billion Rp1,121. Then in the year 2015 positioning
SBI decline i.e. amounting Rp732,367 billion and
then menigkat again in 2015 i.e. Rp1,004 of,143
billion. While interest rates PUAB O/N tend to
increase from a year 2013-2015 but later experienced
a decline in the year 2016, where in the year 2013 the
figure stepped on 4.95% in 2014 rising at a rate of
5.92%. In the year 2015 back rising at 6.11%, then in
the year 2016 decline be 4.81%. While the rate of
yield SATISFIED investment certificates represented
by the Mudharabah Interbank tend to decline, where
in the year 2013 yield results are in Figure 5.21% then
in 2014 rising to 6.40% past year 2015 experience the
decline be 6.08% and then decreased until the year
2016 to reach 5.00%. IPI number syang index data
obtained from medium to large industrial production
with basic year 2010 issued on a monthly basis by the
Central Bureau of statistics, annual rataan
peningkataan experience each year, where in the year
2013 is at number 114.89, then in 2014 has increased
up to 120.36 on the numbers. And then in 2015 get
back on the numbers increased to 126.09, later in the
year 2016 continues to increase in numbers 131.14.
SBI, PUAB O/N, SBIS and SIMA as instruments
of short-term interest rates in the monetary policy
transmission mechanism is already widely used by
previous studies. Such as research conducted by Aam
Selamet with the result that the relationship of SBI,
SBIS, PUAB, and with the banking financing PUAS
is negative and the pattern of relationship banking
financing and inflation also negatively. Then research
other Aam Slamet with Yulizar Sanrego have results
that conventional monetary instruments contribute
more than the monetary instruments. Later, Irfan
Ayuniyyah Qurroh research Syauqi Beik, Laily
Arsyianti Dwi and have the results that total and the
return of Sharia financing has a positive relationship
with the IPI.
Against the background of the research above,
there are any formula problem that will be raised in
this research are as is how significant an influence and
comparison between conventional monetary policy
variables and Sharia line interest rates affect the IPI.
2 THEORICAL FRAMEWORK
The theory Keynes mentioned that, the interest rate is
determined by the supply and demand for money,
according to this theory there are three motifs, why
would someone be willing to hold cash, i.e.
transaction motives, just in case and speculation.
Three motives which are the source of any such
request for money that is termed Liquidity preference
(Mankiw,2003), requests the money according to the
theories of Keynes based on the conception that
generally people want him remains illiquid for meet
three of these motifs. The theory Keynes stressed the
existence of a direct relationship between people's
willingness to pay the price of money (interest rates)
with a request for money for the purpose of
speculation, in this case a huge demand when interest
rate is low and small requests If the high interest.
According to Kasmir (2007:37-40) are the main
factors that influence the determination of the
seriousness of the great interest rates generally can be
explained as follows, namely: Needs funds, profit
Target is desirable, Quality Assurance, the wisdom of
the Government, Period of time, the reputation of the
company, the products are competitive, good
relations, competitors.
2.1 Conventional Monetary Policy
Monetary policy is primarily a policy that aims to
achieve internal balance (high economic growth,
price stability, equitable development) and external
balance (the balance of the balance of payments) as
well as macroeconomic goal, namely maintaining
economic stabilization can be measured by
employment, price stability and a balanced
international balance of payments. If stability in the
troubled economy activity, then monetary policy can
be used to restore the (stabilization actions). The
influence of monetary policy is first felt by the
banking sector, which is then transferred to the real
sector.
2.2 Islamic Monetary Policy
Based on the concept of Islam, money is the property
of the Community (public goods) (Arif,2010).
Hoarding of money or activities that are not
productive money will result in the amount of money
UNICEES 2018 - Unimed International Conference on Economics Education and Social Science
400

in circulation is reduced, so that the process of the
economy will be hampered. On the other hand,
stacking the money or property will push human
nature of greed and lazy, and imposes against the
continuity of the economy.
In addition, the money that is not utilized in the
productive sector (idle assets) will be reduced due to
the existence of the obligation of zakat must be
issued. Therefore, the money must be spun (u.s.
money flow concept) in order to give rise to the
economic prosperity of the community. Like the
theory of the economic system of Islam, Islamic
financial instruments does not recognize interest rates
and implement a system of profit and loss (profit and
loss sharing). Big nothingness of customer profit
Islamic banking is determined by his little big profit
earned from bank financing and investment activities
conducted in the real sector, so that the monetary
sector has a dependency on the real sector. If
investment and production in the real sector is doing
well, then returns on the monetary sector will increase
as well (Huda,2008)
Islamic monetary management rationale was
the creation of the stability of money demand and
ordered him to an important objective that is
productive activities. So, every instrument that
leads to instability and allocating funding sources
that are not productive, would be abandoned. aim
to ensure that monetary expansion, but quite able
to generate adequate growth and can produce an
equitable prosperity for the community. The rate of
growth of the intended nature of sustainability,
must be realistic and include the medium term and
the long term.
2.3
Instruments of Monetary Policy
Conventional monetary policy instruments
according to Bank Indonesia consists of: discount
rate (Discount Rate), Compulsory Minimum Giro
(Statutory Reserve Requirment), an appeal to the
Moral (Moral Suasion), open market operations
(Open Market Operation). In its open market
operations, BI can do the buying and selling of
securities that Bank Indonesia's certificate there is
(SBI).
Islamic monetary policy Instrument according
to Karim (2002:203-204) are: certificates of
Wadiah Bank Indonesia (SWBI) or currently
known as Certificate Bank Indonesia Sharia
(SBIS), current Mandatory Minimum (Statutory
Reserve Requirment) and mudharabah interbank
investment certificates (certificate IMA) Sharia.
Based on the problem and research objectives,
then the hypothesis in this study include:
1. Allegedly there is influence and significant
among variables of conventional monetary
policy interest rate path with IPI in Indonesia.
2. Allegedly there is influence significant
between the variable and the monetary policy
interest rate IPI line Sharia in Indonesia.
3 RESEARCH METHOD
To analyze and manipulate data in this study, the test
will use Vector Autoregressive (VAR). VAR
describes the relationship of causality between the
variables in a model including intersep. This method
was developed by Sims in 1980 (Sugianto, Hermain
Harahap, and 2015; Ascarya 2009) that assumes that
all the variables in the model are endogenous,
meaning that it is specified in the model, so this
method is called by the ateoritis model (unfounded
theory).
VAR is a model of a-priori against economic
theory, however it is very useful in determining the
level of eksogenitas a variable economy in an
economic system in which occurs the
interdependence between variables in the economy.
The VAR model is mathematically can be written
(Ramadan and Beik, 2013; P, 2003) as follows:
Z
t
:
vector of endogenous variables as much as t
X
t
:
vector of endogenous variables as much as t
A
i
dan B:
matrix-matrix coefficients of
the will being estimated
t
:
vector of residual-residual that is contemporary berkolerasi but
not berkolerasi with the values of their own lag nor berkolerasi
with the rest of the variables in the right-hand side of the above
equation.
The first phase is done in process data time series
is to test the stasioneritas or the unit root test.
Stationary data will have a tendency to approach the
average value and fluctuated around the average
value or have a constant variety. If the data is
stationary, then the selected methods are methods of
VAR and if not stationary then the VECM using the
method. (Ramadan and Beik, 2013).
VAR estimation is very sensitive to the length of
the lag are used. Determination of lag (order) to be
used in the VAR model can be determined based on
the criteria of Akaike Information Criterion (AIC),
Schwaz Information Criterion (SC), or Hannan
Analysis the Effect of Dual Monetary Policy Instrument on Index Industrial Productial in Indonesia
401
Quinnon (HQ). In addition the optimal lag length
testing is very useful for relieving the problem of
autocorrelation in the VAR system, so that the
optimal lag with use expected to no longer appear
problem of auto correlation (Nugroho, 2009;
Hasanah 2011).
If the phenomenon of stasioneritas is at the level
of the first difference, then the testing needs to be
done to look at the possibility of Granger. The
concept of Granger was basically to see long-term
balance between variables observed. Sometimes an
individual data is not stationary, but when connected
in linear data becomes stationary. This is then called
terkointegrasi that such data. (Rusydiana, 2009).
Forecast Error Variance Decomposition (FEVD)
is another method of dynamical systems by using
VAR. In response to the presence of innovation
demonstrates the effect of a policy (shock)
endogenous variable against other variables.
Variance decomposition is used to compile an
estimate of error variance of a variable, that is, how
big is the difference between a variation before and
after the shock, the shock that comes from either
myself or the shock of the other variables to see the
influence of relative variables research on other
variables.
4 ANALYSIS
This research uses the Augmented Dickey-Fuller test
(ADF) to test the stasioneritas of each variable.
Stasioneritas ADF test results are then compared with
critical values McKinon on degree of significance of
5%.
Table 2: Stationerity Test ADF Method.
Variable
Level
Prob.
ADF
t-statistic
ADF
p-value
5%
LNIPI
0.7322
-1.036381
-2.928142
LNSBI
0.2238
-2.158510
-2.926622
LNPUAB
0.5529
-1.442889
-2.928142
LNSBIS
0.7539
-0.977155
-2.925169
LNPUAS
0.1840
-2.275281
-2.926622
1
st
difference
LNIPI
0.0000
-7.902248
-2.928142
LNSBI
0.0012
-4.319495
-2.926622
LNPUAB
0.0000
-6.961848
-2.928142
LNSBIS
0.0000
-6.535199
-2.926622
LNPUAS
0.0000
-9.213325
-2.926622
Source: the Data that have been processed.
The result of the stationary test made the sixth
data variables are shown from the above table that
looks at the level of the level, all variables have the
value of the probability of more than 0. Because of
those reasons, then performed a test of integration at
the level of the first difference. At the level of the first
difference, it can be seen that all variables have values
less than 0.05 probability of ADF so that it is said that
all the variables are stationary and do not occur in the
root level of the unit is the first difference.
4.1 The Optimum Lag Test
Following are the results of the test the optimum lag
(lag length) Conventional Models prepared from data
variables are used i.e. variable IPI, SBIS, and PUAB
(conventional).
Table 3: Result the Optimum Lag of conventional Models.
Lag
LR
FPE
AIC
SC
HQ
0
NA
1.04e-07
1.300969
-7.444375*
-7.521937*
1
20.04045*
9.45e-08*
-7.662502*
-7.171004
-7.481253
Source: The Data that have been processed.
As seen from the above table, the data States that
in this study, the lag criteria suggested by SC and HQ
is the lag to-0. But when viewed from the criteria of
LR, FPE, and AIC, the lag suggested to use is the lag.
According to Sukmanada Kassim (2010), the length
of the lag that is used must be long enough to limit the
dynamics of the system. However, the length of the
lag also should not be too long. The conventional
model for this, since three of the five criteria
suggested to use 1 lag, then lag lag is used to-1.
Following are the results of the test the optimum lag
(lag length) Model of Sharia that are processed from
the data of the variables used i.e. variable IPI, SBIS,
and satisfied.
Table 4: Results Lag Optimum Model of Sharia.
Lag
LR
FPE
AIC
SC
HQ
0
NA*
4.63e-08*
-8.374261*
-8.251387*
-8.328949*
1
11.521
5
5.25e-08
-8.251082
-7.759584
-8.069833
Source: The Data that have been processed.
As seen from the above table, the data States that
in this study, the lag criteria suggested by LR, FPE,
AIC, SC, and HQ is the lag to-0. Because the five
criteria suggested lag lag 0 is used, then the lag lag is
used to-0. Lag 0 results obtained by these Islamic
monetary instruments can happen considering
transactions SBIS and PUAS is the kind of spot
transactions settlement was the slowest in two days,
UNICEES 2018 - Unimed International Conference on Economics Education and Social Science
402

allowing a relationship both these variables do not
have lag.
4.2 Test the Granger Johannsen
After knowing the value of optimal lag, Granger test
done next to analyze long-term relationship
antarvariabel. Following are the results of the test of
a conventional Model Johansen Granger.
Table 5: Test Conventional Model Granger.
Hypotesis
Trace
Statisitc
0.05
Critical Value
Prob.
Conclusion
None
115.1736
29.79707
0.0000
Countegrated
At most 1
61.01620
15.49471
0.0000
Countegrated
At most 2
14.52600
3.841466
0.0001
Countegrated
Source: The Data that have been processed.
Test results from the above it can be concluded
that there is a Conventional Model at Granger. It can
be seen from Statistics Trace values greater than the
value of the 0.05 Critical Value, and is seen also from
the probability value smaller than 0.05. In addition,
the results of the above tests can also be inferred that
there is a linear equation is long term contained in the
model, including variables IPI, SBI, and PUAB.
These test results also show that analysis of the
Conventional Model is used for the analysis of the
VECM. After learning the results of Conventional
Models, Granger test next would be presented o
Granger Sharia Model test data.
Table 6: Granger Test Model of Sharia.
Hypotesis
Trace
Statisitc
0.05
Critical
Value
Prob.
Conclusion
None
129.8704
29.79707
0.0000
Cointegrated
At most 1
75.63557
15.49471
0.0000
Cointegrated
At most 2
30.24998
3.841466
0.0000
Cointegrated
Source: The Data that have been processed.
Test results from the above it can be concluded
that there exists a Granger on the Model. It can be
seen from Statistics Trace values greater than the
value of the 0.05 Critical Value, and is seen also from
the probability value smaller than 0.05. In addition,
the results of the above tests can also be inferred that
there are two long-term linear equations contained in
models, between variables IPI, SBIS, and satisfied.
The results of this test also proves that the analysis is
used to Model the sharia is the analysis of the VECM.
After the known existence of Granger's next test
then the process is done using methods of error
correction. If there is a difference in the degree of
integration of the antarvariabel test, the testing was
done simultaneously (jointly) between long term
equations with equation error correction, having in
mind that in a variable occurs Granger. Following are
the results of the estimation of the conventional
Model of the VECM.
Table 7: VECM estimation of short term and long term
Conventional Model.
Variable
Coef.
t-stat
Short Term
CointEq1
-1.758884
-7.82460
DDLNPUAB(-1)
-0.030082
-1.44460
DDLNSBI(-1)
-0.007983
-0.30626
Long Term
DLNPUAB(-1)
-0.028445
-0.86480
DLNSBI(-1)
0.005043
0.27146
Source: The Data that have been processed.
Based on the test results of the VECM on top, on
a short term analysis, both variables significantly to
IPI, is it seen from the second t-statistic value of
variable on smaller than -1.67943. On its influence on
IPI, the existence of a mechanism of adjustment of
sound long term short term indicated by error Granger
is negative (CointEq1-1.758884). While in the long
run, these two variables are significantly to IPI, these
views of the value of the t-statistic greater than
PUAB-1.67943 and t-statistics of SBI are smaller
than at 1.67943. Then occurred the following is an
analysis of the VECM to Islamic Model.
Table 8: VECM estimation of short term and long term
Islamic Model.
Variable
Coef.
T-stat
Short Term
CointEq1
-0.291197
-2.60881
Long Term
LNPUAS(-1)
-0.438058
-9.24157
LNSBIS(-1)
-0.104447
-1.82001
Source: processed data.
Based on the test results of the VECM on top,
both variables are PUAS or SBI has no effect against
the IPI. In addition, in the long run, these two
variables are not significant effect on IPI, it is seen
from a t-statistic value each smaller than-1.67943. It
is typical of the VECM VAR/test in which not all lag
significantly in each equation.
Analysis the Effect of Dual Monetary Policy Instrument on Index Industrial Productial in Indonesia
403

Figure 2: Impulse Response of industrial production index
(IPI) Conventional Models.
From the picture above, can be parsed results IRF
on variables in the Conventional Model is as follows:
1. DLNIPI response against the shock
DLNPUAB fluctuate until the thirteenth
month and began converging on the fourteenth
period. One month lag time required for
DLNIPI to respond to the shock DLNPUAB.
This positive response indicates when interest
rates rise, the PUAB it would be followed by
a rise in the level of the IPI.
2. DLNIPI response against the shock DLNSBI
fluctuate until the twelfth month and began
converging on the thirteenth period. One
month lag time required for DLNIPI to
respond to the shock DLNSBI. This positive
response indicates when the number of
positions the SBI is increasing, it will be
followed by a rise in the level of the IPI. Then,
here are the results of the IRF on variables in
the Model.
Figure 3: Impulse Response of industrial production index
(IPI) Model of Sharia.
From the above image obtained results IRF on
variables in the Model of Sharia is as follows:
1)
Response DLNIPI DLNSBIS surprise against
fluctuating funds sixth month and began
converging on the seventh period. A one
month grace period required for DLNIPI to
respond to the shock DLNSBIS. This positive
response indicates when the number of
positions the SBIS increases, it will be
followed by a rise in the level of the IPI.
DLNIPI response against the shock DLNPUAS
fluctuate until the fifth month and start converging on
the sixth period. One month lag time required for
DLNIPI to respond to the shock DLNPUAS. This
positive response indicates when the yield rate
increasing, it will be followed by a rise in the level of
the IPI.
The picture IRF that is approaching the point of
balance (equilibrium) indicates that a response is
variable due to the longer shocks will progressively
disappear, so the shocks are not left a permanent
influence against the variable. The response variable
of monetary policy interest rates to conventional line
the longer this increasingly stable indicating response
was the longer responya are increasingly
disappearing. The following is the conclusion from
the test results IRF for Conventional Models and
models of Sharia.
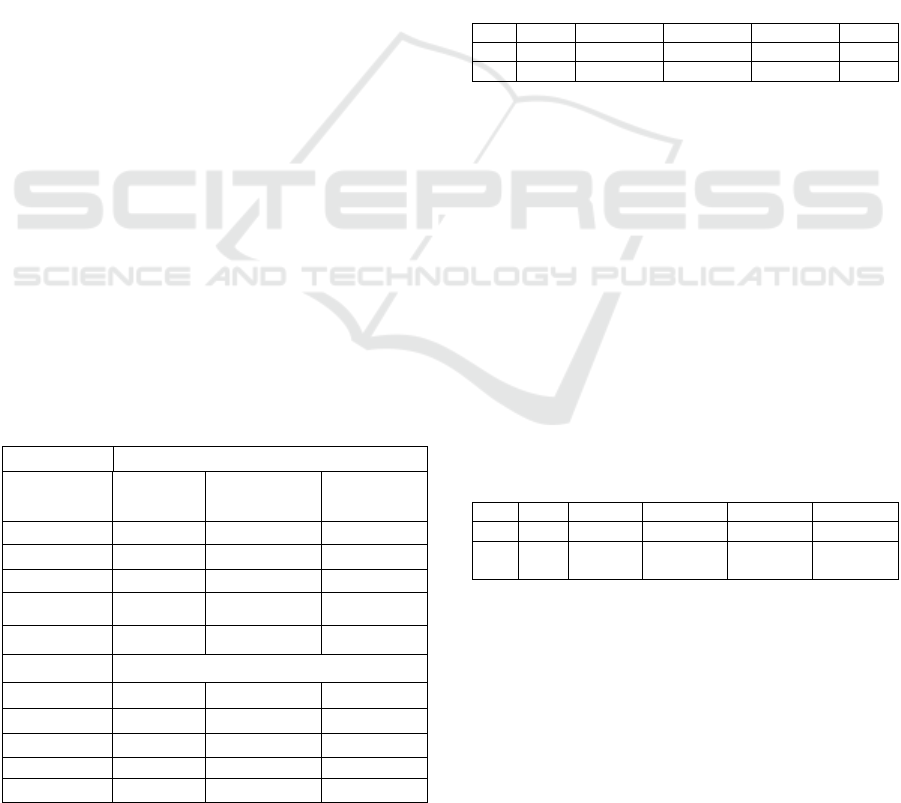
Table 9: The response Variable Against the increase of one
standard deviation of the IPI.
Following are the results from the test of Variance
Decomposition on a Conventional Model.
Table 10: The Test Results of The Forecast Error Variance
Decomposition of Industrial Production Index (IPI)
Conventional Models.
The table above presents the test results of
Variance Decomposition, in which any variables and
how big the variables affect variables industrial
production Index (IPI) in the Groove of conventional
monetary policy. In the first period to see that IPI
could be explained by the PUAB of 0% to during the
IPI could be explained PUAB of 36.79%. Next on the
UNICEES 2018 - Unimed International Conference on Economics Education and Social Science
404

first period look that IPI could be explained by the
SBI of 0% to during the IPI could be explained SBI
of 0.77%.
For IPI, can explain the period 100% of IPI and
declining influence on late period amounted to
62.44%. So on a Conventional Model, variable IPI as
an indicator of economic growth was largely
influenced by the PUAB variable of 36.79%. These
results indicate that the influence of a variable
throughout the period PUAB and SBI against IPI will
be even greater. This happens because the IPI get
direct influence from all the variables such as the
proposed instrument and the conventional monetary
effect on the monetary transmission. In addition, test
results from the FEVD known PUAB (36.74%) and
SBI (0.77%) positive contributions of 37.51%. Then
here is the variance decomposition test results on the
Islamic Model.
Table 11: The test results of the Forecast Error Variance
Decomposition Indexes of industrial production in
Indonesia.
The table above presents the test results of
Variance Decomposition, in which any variables and
how big the variables affect variables industrial
production Index (IPI) in the Groove of monetary
policy. In the first period to see that IPI could be
explained by PUAS amounting to 0% until the end of
the period of IPI could be explained PUAS of 6.74%.
Next on the first period look that IPI could be
explained by the SBIS registration 0% until the end
of the period of IPI could be explained SBIS of
0.40%.
The test results of both FEVD well on
conventional monetary policy as well as monetary
policy of Sharia can be said that conventional
monetary policy path of interest rates contributed the
increase in the production of industrial output bigger
than monetary policy Sharia, i.e. the interest rate path
of 37.51%, and Islamic monetary policy interest rates
line accounts for the production of industrial output
amounted to 7.14%. So it can be said that
conventional monetary policy interest rate path have
instruments that leih instrument than monetary policy
interest in the path of Sharia influenced the
production of the output of the industry.
5 RESULTS
Economic growth is one of the final target of monetary
policy in Indonesia, which is one of the charge
indicators will be seen using the industrial production
Index (IPI). The end goal can be reached through
several lines using monetary policy, one of which is
the monetary policy interest rate path.
This study discusses the transmission mechanism
of monetary policy conventional and syariah track
interest rates in affecting economic growth reflected
industrial production index (IPI). Based on the testing
that has been done on conventional models by using
the variable position of the SBI interest rates and
PUAB, the results obtained are saying that these
variables have a positive affect toward the IPI and
permanent, where the increase in the number of both
the variables affect the increase of IPI 37.51%.
6 CONCLUSIONS
VECM estimation of the results it can be concluded
that:
a.
Both in the short and long term, PUAB and SBI
significant effect on IPI.
1) In the short term, as the independent
variable of the transmission mechanism of
monetary policy,SBI and PUAS no effect
on IPI.
2) As for the long term, PUAS and SBIS no
significant effect on IPI.
b.
On the results of the test Impulse Response
Function (IRF) on the transmission mechanism
of monetary policy path of interest rates,
showed that:
1) The Conventional Model.
- Shock (shock), SBI respond positively
and permanently, which means that
variable of SBI influenced the increase
of economic growth (IPI)
- Shock (shock) PUAB respond
positively and permanently, which
means the PUAB affect the increase of
economic growth (IPI)
2) The Model Syariah.
- Shock SBIS respond positively and
permanently, which means that variable
of SBI decrease increase in economic
Analysis the Effect of Dual Monetary Policy Instrument on Index Industrial Productial in Indonesia
405

growth (IPI)
- Shock PUAS respond positively and
permanently, which means that the
variable PUAB influenced the increase
of economic growth (IPI)
In a test of Variance Decomposition variables a
transition mechanism of conventional models of
monetary policy against the IPI, it can be concluded
that the conventional variables include SBI (0.77%)
and PUAB (36.74%) that provides a positive
contribution against the IPI of 37.51%. Whereas in a
test of Variance Decomposition variables
transmission mechanisms of monetary policy against
the Islamic model of IPI, it can be inferred that Sharia
variables include SBIS (0.40%) and content (6.74%)
that provides a positive contribution against the IPI of
7.14%. So it can be said, based on results of test of
VECM in this study, the flow of transmission
mechanism of monetary policy through interest rates
to conventional models of the line better than any line
of transmission mechanism of monetary policy
through the tribal line model Sharia in affect IPI as
one indicator of economic growth.
REFERENCES
Ascarya. (2002). Instrumen-instrumen Pengendalian
Moneter. Jakarta: Pusat Pendidikan dan Studi
Kebanksentralan (PPSK) BI.
Ascarya. (2012). Alur Transmisi dan Efektifitas Kebijakan
Moneter Ganda di Indonesia. Jakarta: Pusat Pendidikan
dan Studi Kebanksentralan (PPSK) BI.
Ascarya. (2014). Monetary Policy Transmission
Mechanism under Dual Financial System in Indonesia:
Interest-Profit Channel. Malaysia: The International
Islamic University Malaysia.
Ayuniyyah Qurroh, Irfan Syauqi Beik, dan Laily Dwi
Arsyianti. (2013) Dynamic Analysis of Islamic Bank
and Monetary Instrument towards Real Output and
Inflation in Indonesia. Hannover: Proceding of Sharia
Economics Conference.
Chapra, M. Umer. (2000) Sistem Moneter Islam. Jakarta:
Gema Insani Pres.
Ginting, Ramlan et al. (2013) Likuiditas Rupiah Operasi
Moneter, Operasi Moneter Syariah dan Sertifikat Bank
Indonesia Syariah. Jakarta: Pusat Pendidikan dan Studi
Kebanksentralan (PPSK) B,.
Hasanah, Dini. (2011). Analisis Efektivitas Jalur
Pembiayaan Dalam Mekanisme Transmisi Kebijakan
Moneter Di Indonesia Dengan Metode VAR/VECM.
Bahan-Bahan Terpilih dan Hasil Riset Terbaik. Medan:
FRPS.
Natsir, M. (2008) Peranan Jalur Suku Bunga Dalam
Mekanisme Transmisi Kebijakan Moneter di Indonesia.
Jurnal Ekonomi.
Pratama, Yogi Citra. (2013). Effectiveness of Conventional
and Syariah Monetary Policy Transmission. Bogor:
Tazkia University College of Islamic Economics Vol.
8.1:79-96.
Rusydiana, Aam Slamet. (2009). Mekanisme Transmisi
Syariah Pada Sistem Moneter Ganda di Indonesia.
Bogor: Tazkia University College of Islamic
Economics.
Sanrego, Yulizar D dan Aam Slamet Rusydiana. (2013).
Transmission Mechanism in Dual Monetary System:
Comparison Between Shariah and Conventional
Monetary System. Bogor: Tazkia University College of
Islamic Economics.
Setiawan, Rifky Yudi dan Karsinah. (2016). Mekanisme
Transmisi Kebijakan Moneter Konvensional dan
Syariah dalam Memengaruhi Inflasi dan Pertumbuhan
Ekonomi di Indonesia. Semarang: Economics
Development Analysis Journal.
Simorangkir, Iskandar. (2014). Pengantar
Kebanksentralan: Teori dan Praktik di Indonesia.
Jakarta: Rajawali Pers.
Sri Herianingrum dan Imrojan Syapriatma. (2016) “Dual
Monetary System and Macroeconomic Performance in
Indonesia”. Jakarta: Al-Iqtishad Vol. 8, No. 1:65-80.
Sugianto, Hendra Hermain, dan Nurlela Harahap. (2015)
“Mekanisme Transmisi Kebijakan Moneter Melalui
Sistem Moneter Syariah”. Sumatera Utara: Human
Falah Vol. 2, No. 1:50-75.
Sugiyono, F.X. (2004). “Instrumen Pengendalian Moneter:
Operasi Pasar Terbuka”.Jakarta: Pusat Pendidikan dan
Studi Kebanksentralan (PPSK) BI.
Susamto, Akhmad Akbar dan Malik Cahyadin. (2008)
“Praktik Ekonomi Islami di Indonesia dan Implikasinya
terhadap Perekonomian”. Jurnal Ekonomi Syariah
MUAMALAH Vol. 5.
Warjiyo, Perry dan Solikin. (2003) “Kebijakan Moneter di
Indonesia”. Jakarta: Pusat Pendidikan dan Studi
Kebanksentralan (PPSK) BI.
Warjiyo, Perry. (2004) “Mekanisme Transmisi Kebijakan
Moneter di Indonesia”. Jakarta: Pusat Pendidikan dan
Studi Kebanksentralan (PPSK) BI.
Zein, Aliman Syahuri. (2015) “Apa dan Bagaimana:
Mekanisme Transmisi Kebijakan Moneter Syariah di
Indonesia”. Padangsimpuan: At-Tijaroh Vol. 1, No.
1:91-122.
UNICEES 2018 - Unimed International Conference on Economics Education and Social Science
406
