
Effects of Cooperative Learning Model Type of Investigation Group
(Group Investigation) Student Learning Outcomes of the Course
Introduction to Accounting
Putri Kemala Dewi Lubis
1
, Dita Eka Pertiwi
1
and Deni Adriani
1
1
Department of Economics, Universitas Negeri Medan, Medan -Indonesia
Keywords: Cooperative learning model, Group Investigation, Accounting Learning Outcomes
Abstract: This study aims to improve student results in the first half of the course PengantarAkuntansi Prodi
Economic Education academic year 2018/2019 to implement cooperative learning model of Group
Investigation (GI). This type of research is true exprimental design with posttest design only control design,
the population used are all students of the first semester Economics Education Program 2018/2019 school
year. This study took two classes as samples taken using cluster random sampling technique that is class B
with the number of 35 students as control class and C class numbered 35 students as a class ekprimen. The
study was carried out as many as four meetings. The first meeting until the third were given treatment that is
experimental class with group investigation methods and classroom control by conventional methods. At the
fourth meeting, the two classes are conducted posttest to determine student results in learning introductory
accounting after being treated. The collection of data is done using an instrument such as test results of
student learning in teaching introductory accounting. The data obtained from the test are used to test the
research hypothesis by using t-test. From the analysis results obtained t = 4.083 and α = 0.05 was obtained
table = 2.032, which means t> t table is 4.083> 2.032. This shows that Ha received means that there are
significant group investigation model of the learning outcomes of students in introductory accounting
courses. 032 which means t> t table is 4.083> 2.032. This shows that Ha received means that there are
significant group investigation model of the learning outcomes of students in introductory accounting
courses. 032 which means t> t table is 4.083> 2.032. This shows that Ha received means that there are
significant group investigation model of the learning outcomes of students in introductory accounting
courses.
1 INTRODUCTION
During this lack of analytical skills of students in
terms of learning outcomes of students in the course
Introduction to Accounting more due to the
approach, methods or strategies which are used by
professors in the learning process is still traditional
and less to allow students to develop thought
patterns in accordance with their abilities.
Alternative solutions to address the problem of
accounting student learning activity that is less than
optimal is to apply the model of learning that
stimulates the growth of activity. The learning
model that can be applied is cooperative learning.
Cooperative learning model is a model of learning
by groups. According Miftahul Huda (2012) in
cooperative learning, students should be active
participants and through the group can build learning
communities help each other. Learning like this
requires more active among students to work
together to achieve group goals, to train students in
expressing their opinions or ask questions, and carry
out the tasks which it is responsible within the
group. Cooperative learning model that can be
selected to address the problem of lack of classroom
learning activities accounting in the first half Prodi
Ekonomia Education dalah type Group Investigation
(GI). According Miftahul Huda (2012), the Group
Investigation (GI) Students will be involved in
activities such as making a summary, hypotheses,
conclusions, and present a final report.
Implementation of cooperative learning model of
240
Lubis, P., Pertiwi, D. and Adriani, D.
Effects of Cooperative Learning Model Type of Investigation Group (Group Investigation) Student Learning Outcomes of the Course Introduction to Accounting.
DOI: 10.5220/0009495002400243
In Proceedings of the 1st Unimed International Conference on Economics Education and Social Science (UNICEES 2018), pages 240-243
ISBN: 978-989-758-432-9
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
Group Investigation (GI) in general is a lecturer in
designing a fairly broad scope of topics and then
divide it into sub-topics. conclusions, and present a
final report. Implementation of cooperative learning
model of Group Investigation (GI) in general is a
lecturer in designing a fairly broad scope of topics
and then divide it into sub-topics. conclusions, and
present a final report. Implementation of cooperative
learning model of Group Investigation (GI) in
general is a lecturer in designing a fairly broad scope
of topics and then divide it into sub-topics.
Implementation Group Investigation (GI) in the
study is expected to improve student learning
activities. Group Investigation (GI) require students
to actively seek information from various sources, so
that students not only rely on the lecturer as an
information resource. Through Group Investigation
(GI) Students are expected to be more active,
namely in terms of recorded material, cooperation
within the group, issued an opinion / bartanya,
answering questions, participation in preparing
reports and presentations, as well as enthusiastic
about learning.
2 THEORICAL FRAMEWORK
2.1 Type Group Investigation
Model Group Investigation by Slavin (2005) is a
cooperative planning students on what is required of
them. Members of the group take part in the
planning of various dimensions and demands of their
projects. Cooperative planning skills should be
introduced gradually into the classroom and trained
in a variety of situations before the class is carrying
out a full investigation project ". It is intended that
the Group Investigation will be successfully carried
out if each member of the group participate actively
participated from the beginning of the end sampat
activities, namely in terms of planning,
investigation, preparation of a report or presentation
of the results of investigations should be done to be
able to run smoothly.
2.2 Learning Outcomes
Nana Sudjana (2009) defines student learning
outcomes in is a change in behavior as a result of
learning in a broader sense include the areas of
cognitive, affective, and psychomotor.Learning
Outcomes are the abilities of the students after
receiving their learning experience. "From these
processes will lead to new experiences by students.
The realization of his own learning outcomes are
skills that have been mastered by students, so that
the learning outcomes is the ability of students
receiving learning experience which looked at
changes in behavior.
2.3 Framework for Thinking
This study uses a model of cooperative learning
Group Investigation. Implementation of cooperative
learning model of Group Investigation in general is a
lecturer in designing a pretty broad scope of topics
and then divide it into sub-topics. The class is
divided into groups of 5-6 students. These groups
can be formed based on shared interests, or
familiarity. Students are given the freedom to form
their own group. Each group chooses a topic and
then conduct an investigation on the topic. As part of
the investigation, students seeking information from
various sources that offer a variety of ideas,
opinions, data or solutions related to the topic being
studied. Results of investigation of students then
made a report and presented to the class. Lecturer in
this study serve as resource persons and facilitators.
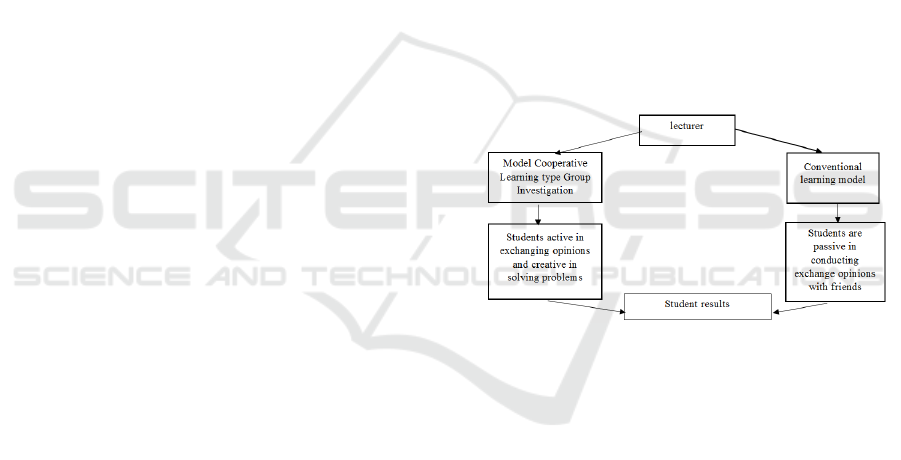
Based on the above, it can be described as follows
frameworks.
Figure 1: Worldview
2.4 Research Hypothesis
According Arikunto (2010) hypothesis comes from
two fragments word "hypo", which means "under"
and "Thesa" which means "truth". The hypothesis in
this study there, namely:
H0 = No influence of the model group investigation
on learning outcomes in the course Introduction to
Accounting students of the first semester of the
academic year 2018/2019 Prodi Pendeko.
Ha = There is the influence of the model group
investigation on learning outcomes in introductory
accounting courses students Prodi Pendeko the first
half of the academic year 2018/2019.
3 RESEARCH METHOD
This study uses a true experimental research
(research that truly). In this design researchers can
Effects of Cooperative Learning Model Type of Investigation Group (Group Investigation) Student Learning Outcomes of the Course
Introduction to Accounting
241

control all external variables that influence the
course of the experiment. The main characteristic of
true experimental is that the sample used for the
experiment as well as a randomly selected control
group of a given population. The study design used
is by using the Posttest only Control Design (Design
Control Post-test) (Sugiyono, 2013).
3.1 Operational Definition of Variables
a. Cooperative Learning Model Group
InvestigationGroup Investigation is one type of
cooperative learning model. The class is divided
into groups of 5-6 students. teaching methods
that focus on problem solving in groups.
Learners acquire information, analyze
information, provide ideas and jointly solve the
problem.
b. Learning outcomes Introduction to Accounting
courses obtained by students after a group
investigation methods applied in the form of a
written test where the ability were measured
students' cognitive abilities such as knowledge
(C1), comprehension (C2), and application
(C3).
3.2 Data Analysis Techniques
This study using inferential statistical analysis
techniquesto test the hypothesis. Before performing
hypothesis testing requirements that must be met is
to perform the test requirements of normality and
homogeneity.
4 ANALYSIS
a. Normality test
Normality test is performed to determine whether
the sample studied normal distribution or not.
Normality test results can diihat in Table 1:
Table 1: Test Normality
Eksperim
ent
Control
N 35 35
Normal
Parameters a,
b
mean 77.6286 67.7143
Std.
deviatio
n
9.29606 11.40839
Most
A
bsolute .217 .224
Extreme
Differences
positive .127 .098
negative -.217 -.224
Kolmogorov-Smirnov Z 1285 1,326
A
symp. Sig. (2-tailed) .073 .059
According to the table can be seen from the
Kolmogorov - Sminornov, the significant value of
0.073 for class experiments and to control class
significance value of 0.059. Because of the
significant value for all the variables is greater than
0.05, it can be concluded that the data on class
variables and class Control Experiments normal
distribution.
b. Homogeneity test
Homogeneity test is used to determine whether the
study group have the same variance or not. If both
groups have the same variance then the group is said
to be homogeneous. Homogeneity test results are
shown in Table 2:
Table 2: Test Homogeneity
Test of homogeneity of Variances
Eksperiment
Levene
Statistic
DF1 DF2 S
ig.
1,481 7 23
.
223
Based on the table it can be seen a significance of
0.223. Due to the significance greater than 0.05, it
can be concluded that the class Experiment and kels
control have the same variance. Figures levene
Statistics show the smaller the value, the greater
homogeneity.
c. Hypothesis testing
To prove the hypothesis that has been formulated
and to get a conclusion the results of the test data
will be analyzed using t-test. T-test results are shown
in Table 3:
Table 3: Test -t
Based on Table 3 can be seen the value of t count
equal to 4.083 while t-table value of 2.032. Based on
the decision-making criteria if t count> t-table then
Hα H0 is accepted and rejected. Value t count> t-
table (4.083> 2.032) it can be concluded thatNo
influence of the model group investigation on
learning outcomes in subjects introductory
UNICEES 2018 - Unimed International Conference on Economics Education and Social Science
242

accounting students of the first semester Prodi
Pendeko 2018/2019 academic year.
5 RESULTS
Based on significant if α = 0.05> Sig (2-tailed) then
Hα H0 is accepted and rejected. 2-tailed significant
value of 0.000 <0.05 then H0 is rejected and Hα
meaning that there is the influence of the model
group investigation on learning outcomes in subjects
introductory accounting students of the first
semester Prodi Pendeko 2018/2019 academic year.
This suggests that the cooperative learning model
type group investigation applied in the experimental
class in introductory accounting courses better than
conventional learning models that are applied in the
control class. The use of cooperative learning model
type group investigation can provide a positive
influence on learning hahsil introductory accounting
students Prodi Economic Education first semester of
the school year 2018/2019.
Model group investigation cooperative learning
is a method that involves students from the planning,
both in determining the topic as well as how to learn
through investigation. This method requires students
to have good skills in communication or in a group
process skills. (Group process skills).
6 CONCLUSIONS
Based on the results of research and discussion
paper entitled, "The Effect of Method Group
investigation against Student Learning Outcomes in
Mathematics Learning Class X High School
'Aisyiyah 1 Palembang". It can be concluded that the
learning outcomes of students who use group
investigation method is better than the results of
student learning without using group investigation.
Based on the results of the calculation of the t-test
that produces t = 4.083 and t table is 2.032 with
significance level α = 5%, in order to get t> t table,
then the conclusion is H0 rejected and Ha accepted,
meaning that there is the influence of the model
group investigation on learning outcomes in eyes
introductory college accounting students Prodi
Pendeko the first half of the academic year
2018/2019.
REFERENCES
Dimyati & Mudjiono. (2009). Teaching and Learning.
Jakarta: Rineka Reserved.
E. Mulyasa. (2006). Competency-Based Curriculum
Concepts, Characteristics, Implementation, and
Innovation. Bandung: Youth Rosdakarya.
Eko Putro Widoyoko. (2009). Evaluation of Learning
Program A Practical Guide For Prospective
Teachers and Educators. Yogyakarta: Student
Library.
Khusnul khotimah. (2009). Application of Cooperative
Learning Model Group Investigation in Improving
Student Learning Activities Class X Accounting
Expertise Program SMK 1 Bantul Year 2009/2010.
Essay. UNY.
Martinis Yamin. (2007). Students membelajarkan tips.
Jakarta: Echoes Press Persada Jakarta.
Masnur Muslich. (2011). PTK implement it Easy
(Classroom Action Research). Jakarta: Earth
Literacy.
Miftahul Huda. (2012). Cooperative Learning Methods,
Mechanical, Structural and Implementation Model.
Yogyakarta: Student Library.
Oemar Hamalik. (2011). Curriculum and Learning.
Jakarta: Earth Literacy.
Radno Harsanto. (2007). Dynamic Classroom
Management. Yogyakarta: Canisius.
Rianti Sri Sulistia Infantry. (2009). Implementation
Method Investigation Cooperative Group mode to
Improve Civics Activities and Student Achievement
SMA Negeri 2 Wonosari. Essay. UNY.
Rochiati Wiriaatmadja. (2009). Class Action Research
Methods. Bandung: Youth Rosdakarya.
Sardiman. (2011). Interaction & Learning Motivation.
Jakarta: Rajawali Pers.
Slavin, Robert. E. (2010). Cooperative Learning Theory,
Research and Practice. Bandung: Nusa Media.
Sugiyono. (2009). Educational Research Methods
Quantitative Approach, Qualitative and R & D.
Bandung: Alfabeta.
Suharsimi Arikunto, Suhardjono, and Supardi. 2009).
Classroom action research. Jakarta: Earth Literacy.
Trianto. (2010). Designing Innovative Learning Model
Progressive Concepts, Policy, and Implementation in
Education Unit Level Curriculum (SBC). Jakarta:
Kencana Prenada Media Group.
Effects of Cooperative Learning Model Type of Investigation Group (Group Investigation) Student Learning Outcomes of the Course
Introduction to Accounting
243
