
Factors Affecting the Increasing of Agricultural Extension
Professionalism in Batubara Regency, Indonesia
Nurliana Haharap
1
, Ameilia Zuliyanti Siregar
2
and Kennedy
1
1
College of Agriculture Extension Medan (STPP Medan), Jl. Binjai Km 10 Medan, Sumatera Utara
2
Department of Agrotechnology, Universitas Sumatera Utara, Jl. Dr A.Sofyan No 3 Medan, 20155, Sumatera Utara
Keywords: Factors, Professionalism, Extension, Agricultural, Batubara
Abstract: This research was conducted in Batu Bara Regency on March 10 to May 16 2015 purposively with an area
of paddy fields reaching ± 19 thousand Ha, productivity of 5.2 tons / Ha. The collected data research will
done using by distributing questionnaires, tests, structured interviews. The result calculated of agricultural
extension workers with a Bachelor of Education background of 15 people (48%) and SPP/ SMK 14 people
(45%), while the Diploma is 2 people (7%). Then the age distribution of extension respondents was
dominated by extension workers aged between 36-40 years (35%) and 30-35 years old (32%), then each age
between 41-45 years (13%), aged between 46 -50 and aged between 51-55 years each of 3 people (10%).
The most dominant tenure tenure is 45% with tenure ranging from 6-10 years, then each extension period
between 1-5 years is 11 people (36%), tenure between 16- 20 years as many as 2 people (6%), the service
period between 21-25 years is 3 people (10%) and the service period between 26-30 years is one person
(3%). The most dominant respondent income level is 2-3 million as many as 19 people (61%), then each
level of income between 1-2 million instructors is 5 people (16%), the income level of the instructor
between 3- 4 million as many as 2 people (7%) and income levels of instructors between 4-5 million as
many as 5 people (16%). The income earned by an instructor will influence in meeting the needs of his life
and his family. It is expected that reliable extension workers supported by technical competence, ethics and
moral commitment as well as deep responsibility for their work can be realized in the future.
1 INTRODUCTION
The development of agricultural extension is
currently dominated by Field Agricultural Extension
Officers from the Government and Private
Agricultural Extension which are aggressively
distributed by the producer of production facilities.
Although there are nuances of business in carrying
out their duties, these private extension agents
contribute greatly to the application of technology to
farmers. This Private Agricultural Extension is
considered to be more professional in carrying out
its duties because it is burdened with measurable and
clear targets and if it cannot perform its duties
properly it will be automatically displaced by other
instructors who are considered more professional.
The private extension work mechanism has not been
implemented by extension officers who are civil
servants (PNS) or THL-TBPP extension officers.
Agricultural extension agents currently available,
related to the internal conditions of extension
workers still do not have sufficient knowledge,
attitudes and skills, where there are still limited
skills and skills possessed by extension workers.
Imagine that most of the extension workers are
graduates of SPMA or equivalent education and they
are now working for decades and most of the age of
instructors are willing to enter retirement which will
have an impact on the number of extension workers,
while technology continues to grow along with the
increasing needs and quality of life.
There is still a lack of adequate facilities in
supporting his career duties, especially in field
mobilization and obtaining opportunities in
capturing information quickly, the low linkage of
counseling with aspects of assessment, so that
extension workers cannot freely develop themselves
towards professionalism as qualified instructors.
Haharap, N., Siregar, A. and Kennedy, .
Factors Affecting the Increasing of Agricultural Extension Professionalism in Batubara Regency, Indonesia.
DOI: 10.5220/0009495303550361
In Proceedings of the 1st Unimed International Conference on Economics Education and Social Science (UNICEES 2018), pages 355-361
ISBN: 978-989-758-432-9
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
355

Associated with extension agents as agents of
change in carrying out their duties in the field often
collide with the attitude of the community towards
the innovations delivered. Some communities
welcome a change by actively knowing and learning
innovation and up to the stage of adoption of
innovations delivered, but there are also those who
oppose changes made by extension agents.
Based on Programme BKP3 in Batu Bara
Regency The condition of agricultural extension
workers in Batu Bara District at this time the number
of agricultural extension workers was 103 people,
consisting of 49 PNS extension workers and THL-
TBPP extension workers 54 people with 151
villages/states assisted extension agents. with the
village/states, the WKPP extension workers have
built up to two villages. Since the enactment of the
certification of extensionists in 2010 to make
extension workers as professionals who have
Indonesian national work competency standards
(SKKNI) extension workers in Batu Bara District
until now only two people have followed.
Furthermore, since 2012 as many as 12 people have
attended the official education of the Ministry of
Agriculture's Medan STPP to make extension
workers who have qualified technicians and
analysts, equivalent to level 6 in the Indonesian
National Qualification Framework (KKNI). Based
on the information obtained by extension workers
who have participated in skilled basic training as
much as ± 8 people and basic expert training ± 2
people. While for education and training programs,
it was felt that the programs of BKP3 Batu Bara
Regency were still lacking and from other parties,
resulting in weak levels of competency and capacity
of extension agents related to their level of
professionalism.
In addition to the problems of planning,
institutions, manpower, programs, management and
financing that are constraints for field instructors and
the demands to provide quality services that are only
obtained from the prime performance process as a
symbol of instructor professionalism, the internal
factors of agricultural extension agents also have a
very direct influence on professionalism of
instructors which is manifested by personality and
ability in dizziness increase in competence, included
of availabilty of instructor. Therefore it is necessary
to examine the influence of the internal factors of
agricultural extension agents to increase the
professionalism of extension agents in the Batu Bara
Regency of North Sumatra Province.
Benefit of research such as:
1. Taking into account the various problems that
exist, the main purpose of this study is to
determine the influence of the instructor's
internal factors on improving the
professionalism of the Agriculture Extension
and specifically the objectives of this study are:
2. To find out the influence of the education level
of instructors on improving the professionalism
of extension workers?
3. To find out the influence of the age, level of
income, the number of extension workers of the
instructor on improving the professionalism of
the instructor?
Hypothesis
Based on the formulation of the problem there is a
hypothesis that is:
H0: There is no influence of the internal factors
of instructors (education (X1), age (X2), experience
(X3), income (X4) and the number of dependents
(X5)} on the improvement of professionalism of the
instructor (Y).
H1: There is an influence of the internal factors
of the instructor (education (X1), age (X2),
experience (X3), income (X4) and the number of
dependents (X5)} on the improvement of
professionalism of the instructor (Y).
2 METHODS
Location and Time of Research
The assessment was carried out in Batu Bara
Regency on March 10 to May 16, 2015. Batu Bara
Regency was a potential area for increasing food
production, especially rice with an area of paddy
fields reaching ± 19 thousand Ha with a productivity
of 5,2 tons/ha, so that reliable extension workers are
needed which are supported by technical
competence, ethics and moral commitment as well
as deep responsibility for their work.
Type of Assessment
This type of assessment is quantitative assessment
with survey methods, where the type of problem
formulation is causal associative. According to
(Sugiyono, 2008) explains that quantitative survey
assessment is a method used to obtain data from
locations that have been determined (not artificial)
but researchers do treatment in data collection by
distributing questionnaires, tests, structured
interviews. Clause associative is a causal
relationship, namely the independent variable (X)
affects the dependent variable (Y).
Operational Limitation
Education (X1) is that the education achieved by
extension agents in formal education institutions
based on the latest diploma possessed and the effect
UNICEES 2018 - Unimed International Conference on Economics Education and Social Science
356
on professional work productivity is measured using
an ordinal scale on four scales with criteria strongly
agree, agree, disagree and strongly disagree.
Age (X2), that is the age of the instructor at the
time the assessment is stated in years and the effect
on professional work productivity is measured using
an ordinal scale on four scales with the critics
strongly agree, agree, disagree and strongly disagree.
Experience (X3), that is the length of the
instructor working up to the present, expressed in
years and the effect on professional work
productivity is measured using an ordinal scale on
four scales with the critics strongly agree, agree,
disagree and strongly disagree.
Revenue (X4), namely compensation received
for one month and its effect on professional work
productivity is measured using an ordinal scale on
four scales with criteria strongly agree, agree,
disagree and strongly disagree.
The number of dependents (X5), namely the
number of family members who are the
responsibility of the instructor at this time and their
influence on the productivity of professional work,
are measured using an ordinal scale on four scales
with very agree, agree, disagree and strongly
disagree.
Professionalism as an individual who works in
accordance with moral and ethical standards that are
determined by employment as an agricultural
extension agent. Requirements that must be
possessed by a professional instructor, include:
Variable measurement is arranged to facilitate
assessment to compile questionnaire instruments
from each study variable. Measurement of variables,
indicators, criteria and scores is presented in Table
1.
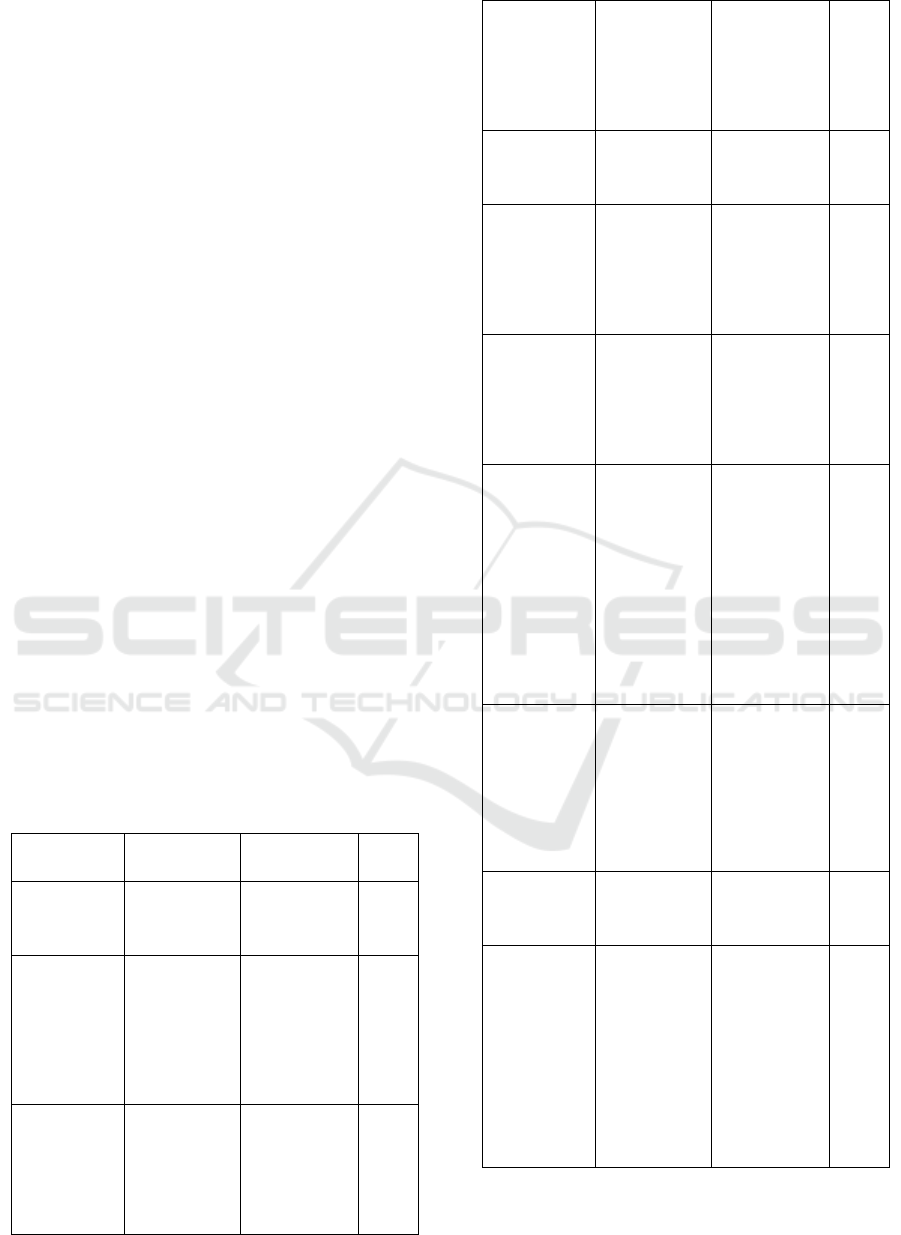
Table 1: Variable Measurement, Indicators, Criteria
and Scores
Variabel
Indicator
Criteria
Score
Education
(X1)
Formal
education
based on the
last diploma
S2
S1
DIII
SLTA
4
3
2
1
Age (X2)
The age of the
instructor at
the time of the
assessment
30 – 35 year
old
36 – 41 year
old
42 – 47 year
old
48 – 52 year
old
4
3
2
1
Experiences
(X3)
The duration
of the
extension
agent is
functional
22 – 27 year
old
15 – 21year
old
8 – 14 year
old
1 – 7 year old
4
3
2
1
Salary (X4)
Compensation
received by
the instructor
for 1 month
>4 juta million
3 juta – 4
million
2 juta- 3
million
<2 million
4
3
2
1
The number
of dependents
(X5)
The burden of
the number of
family
dependents
Total 0-1
Total 2
Total 3
Total >4
4
3
2
1
a. Institutional
understandi
ng of
counseling
Function
Very
understanding
Understand
Don’t
inderstand
Very not
understood
4
3
2
1
b. Technology
Apserpsion
Technical
suitability
Economic
suitability
Social-cultural
suitability
Very suitable
Corresponding
It is not in
accordance
Very
inppropriate
4
3
2
1
c. Ability to
explain
program
objectives
Benefits of
program
objectives
How to
achieve
program goals
Relationship
of program
objectives
Skills to
convey
program
objectives
Very capable
Able
Unable
Very unable
4
3
2
1
d. Ability to
organized
Organization
function
Organization
principal
Organization
techniquen
Integration
with
programme
Always
Often
Rarely
Never
4
3
2
1
e. Skills
linking
counseling
principles
Do
Consequences
Asossiation
Always
Often
Rarely
Never
4
3
2
1
f. Research
skills
Identification
of problems
Determine the
main activities
Detailing
alternative
solutions
Choose
alternative
problem
solving
Evaluate.
Always
Often
Rarely
Never
4
3
2
1
Source: Data Analysis (2015)
Factors Affecting the Increasing of Agricultural Extension Professionalism in Batubara Regency, Indonesia
357

Data Collection
The data used in this study are primary data and
secondary data collected using: Interview, which is a
method of collecting data about the identity of
respondents, by asking questions directly to
respondents using a prepared questionnaire.
Recording, which is a method of collecting data
about the respondent's identity and supporting data
by citing and recording sources of information from
respondents, libraries, as well as from the relevant
agencies that are related to the assessment, such as:
Agriculture Service; Food Security Agency and
Counseling Implementation (BKP3); and the Central
Statistics Agency (BPS) .
(Prasetyo and Jannah, 2005) states that there are
various ways that can be done to obtain data with
questionnaires, namely: (1) telephone interviews; (2)
the questionnaire system posted; (3) the
questionnaire is completed by the respondent; and
(4) through direct interviews. Furthermore, Sekaran
(1992) in (Prasetyo and Jannah, 2005) defines
questionnaires as a list of questions that measure
variables, relationships between existing variables,
or also the experience or opinions of respondents.
Before being used for assessment data, first a
trial was conducted on the questionnaire to obtain
valid and reliable instruments using validity and
reliability tests. This validity and reliability test will
be carried out to 15 respondents outside the study
sample but still within the study population.
Data Analysis Technique
To determine the influence of the instructor's
internal factors on improving the professionalism of
the instructor used regression analysis with the help
of SPSS 18 for Windows. According to Levin and
Rubin (1998) in (Sarwono, 2012), regression is used
to determine the properties and strength of the
relationship between two variables and predict the
value of a variable that is not yet known based on
past observations of these variables and other
variables. This linear regression analysis is widely
used to test the effect of the independent variable
(X) on the dependent variable (Y).
Multiple linear regression equations, namely:
Y=α+β_1 X_1+β_2 X_2+β_3 x_3 + β_4 x_4 + β_5
x_5 + u_i
Information:
Y = Variables Professionalism
X_1 = Education Variables
X_2 = Age Variable
x_3 = Experience Variable
x_4 = Revenue Variable
x_5 = Variable Amount of Dependent
α = Constants
β = Regression Coefficient
u_i = Error or error
R2 values range from 0-1 and if the results
obtained are close to 1, the model is said to be good.
The coefficient of determination is formulated as
follows:
R2 = or (5)
Information:
Y ’= The results of estimating the value of the
dependent variable
Y = Average value of the dependent variable
Yi = value of observation
R2 = Coefficient of Determination
F test is used to determine the level of influence
of all independent variables together on the
dependent variable or to find out whether the
independent variable (X) has an effect on
independent variables (Y).
Ftable = (k-1), (n-k): α (6)
Information
R2 = coefficient of determination
k = Number of regression coefficients
n = Number of samples
α = Critical value
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Characteristics of Respondents
Characteristics of agricultural extension agents in
Batu Bara District who are respondents in this study,
including the level of education, age, experience,
income and the number of dependents of agricultural
extension agents, can be described in detail as
follows:
Education
The level of education of agricultural extension
workers which is used as a variable in the
assessment of the influence of the instructor's
internal factors on improving the professionalism of
extension workers (Anoraga, 1998) and (Anoraga,
1998), especially in Batu Bara Regency is presented
in Table 2.
Table 2: Distribution of Respondents by Education
Level in Batu Bara Regency
Number
Education
level
Total
Respondents
(individual)
Percentages
(%)
1
SPP/SMK
14
45
2
Diploma
2
7
3
Strata 1
15
8
UNICEES 2018 - Unimed International Conference on Economics Education and Social Science
358

Total
31
100
Sources: Analysis of Primer Data(2015
Based on Table 2, the distribution of formal
education level of agricultural extension is
dominated by agricultural extension workers with a
Bachelor of Education background of 15 people
(48%) and SPP/ SMK 14 people (45%), while the
Diploma is 2 people (7%). The level of formal
education will show different levels of knowledge in
carrying out tasks, so that a high level of education
is able to think more advanced and have a broader
view and adapt more quickly to all the changes in
technology that are developing. This is in line with
the opinion of that the higher the level of education
of a person, there is a tendency for higher
knowledge, attitudes and skills, efficient work and
more and more know ways and techniques to work
better and more profitable. According to
(Mardikanto, 2009) the level of education of
instructors will greatly affect the ability or mastery
of the material provided, the skills to choose
counseling methods and effective communication
techniques with (the community). Likewise what
Pauline (2006) said in Rosni and Suprijanto (2010)
that a person's formal education has a positive
influence on its performance.
Age
The age of agricultural extension workers in Batu
Bara Regency varied between 31 years to 52 years,
the more complete the distribution of respondents
according to the age of field agricultural extension
officers in Batu Bara District is presented in Table 3.
Table 3: Distribution of Respondents by Age in Batu
Bara Regency
Num
ber
Education
level
Total
Respondents
(individual)
Percenta
ges (%)
1
30-35
10
32
2
36-40
11
35
3
41-45
14
13
4
46-50
3
10
5
51-55
3
10
Total
31
100
Sources: Analysis of Primer Data (2015)
Based on Table 3, the age distribution of
extension respondents was dominated by extension
workers aged between 36-40 years (35%) and 30-35
years old (32%), then each age between 41-45 years
(13%), aged between 46 -50 and aged between 51-
55 years each of 3 people (10%). When viewed from
the age level of the respondents, it can be said that
90% are of productive age, who still have physical
strength and high enthusiasm to carry out the tasks
for which they are responsible. At a young age, it is
usually more enthusiasm to attend education and
training (diklat) to increase competence as an
instructor who is proud of his profession.
According to (Rivai and Sagala, 2011) there is a
widespread belief that productivity has fallen along
with the age of a person. Whereas in the opinion of
Beth (1998) in Rosni and Suprijanto (Rivai and
Sagala, 2011) and (Sugiyono, 2008) who say that
older age can reduce performance, especially in
work that uses cognitive abilities, perceptual and
memory.
Experience
Experience is the period of service of an agricultural
instructor who has been counted since he began
serving as a functional extension worker. The
assignment period describes the time span
experienced by the instructor in situations and
circumstances that are influenced by internal and
external conditions of the instructor. Based on data
obtained by the respondent's working period varies
from 1 year to 27 years, more complete distribution
of respondents according to experience in Batu Bara
Regency is presented in Table 4.
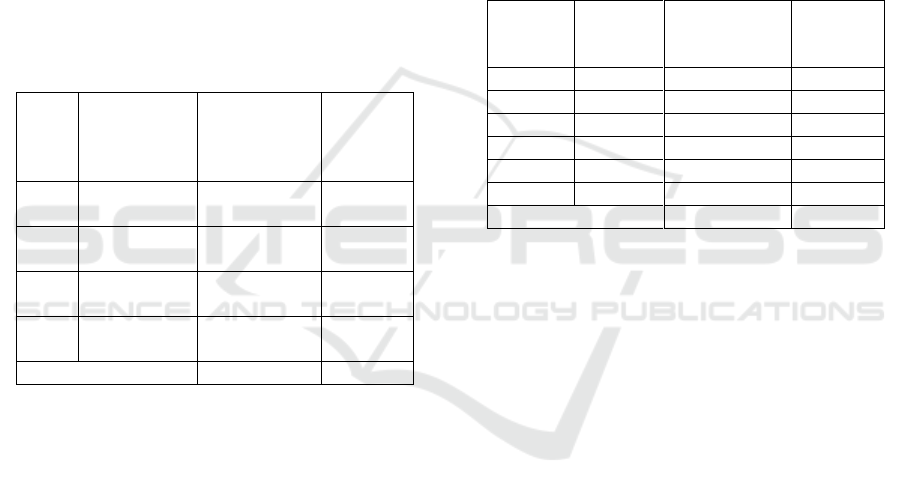
Table 4: Experiences work of respondents in Batu
Bara Regency
Numbe
r
Experience
s of work
(years old)
Total
Respondent
s
(individual)
Percent
ages
(%)
1
1-5
11
36
2
6-10
14
45
3
11-15
0
0
4
16-20
2
6
5
21-25
3
10
6
26-30
1
3
Total
31
100
Sources: Analysis of Primer Data (2015)
Based on Table 4, it can be concluded that the
most dominant tenure tenure is 45% with tenure
ranging from 6-10 years, then each extension period
between 1-5 years is 11 people (36%), tenure
between 16- 20 years as many as 2 people (6%), the
service period between 21-25 years is 3 people
(10%) and the service period between 26-30 years is
one person (3%). Overall, the respondent's tenure is
still relatively low. A low task period indicates that
the instructor does not have enough experience in
mastering the field of work as an instructor.
Experienced extension workers will be more flexible
Factors Affecting the Increasing of Agricultural Extension Professionalism in Batubara Regency, Indonesia
359
and easy to carry out counseling activities with key
actors and are better able to solve problems often
encountered in their work. According to Rosni &
Suprijanto (2010) and Harahap (2013), the longer
the tenure of the instructor will be to master the
work area that is his responsibility, so that the more
mature and more productive workers and together
with the ability to work determine their
performance. In line with this according to
(Sarwono, 2012) and (Abdi, 2008), someone who
has been in a job for a long time will have better
abilities than those with lower levels of seniority.
Income
Respondent's income is financial compensation for a
month. Distribution of respondents according to
income in Batu Bara Regency is presented in Table
5.
Table 5: Distribution of Respondents by Income
Level in Batu Bara Regency
Num
ber
Experience
s of work
(years old)
Total
Respondent
s
(individual)
Percenta
ges (%)
1
1,0-1.9
million
5
16
2
2.0-2.9
million
19
61
3
3.0-3.9
million
2
7
4
4.0-4.9
million
5
16
Total
31
100
Sources: Analysis of Primer Data (2015)
Based on Table 5, the most dominant respondent
income level is 2-3 million as many as 19 people
(61%), then each level of income between 1-2
million instructors is 5 people (16%), the income
level of the instructor between 3- 4 million as many
as 2 people (7%) and income levels of instructors
between 4-5 million as many as 5 people (16%). The
income earned by an instructor will influence in
meeting the needs of his life and his family. The
need to live not only includes primary needs but
secondary needs. Per capita income below the
standard of living would result in the opportunity for
the population to achieve a high level of education
and perfect health to be increasingly difficult to
achieve. This condition will affect a person's
performance at work, which is below standard
(Mangkuprawiro, 2009; Mangkuprawiro & Sjafri
(2002); Slamet, 1992). A professional instructor
must be able to provide maximum service to farmers
as beneficiaries of their extension activities. How an
instructor can provide this if his needs are not met
properly, so that the income earned is very
influential to be able to work professionally who
loves his profession as a field agriculture instructor
The Number of Dependents
The number of agricultural extension counseling
family respondents varied between those who did
not have dependents alias single until the number of
dependents amounted to 5 people. Distribution of
respondents according to the number of family
dependents in Batu Bara Regency is presented in
Table 6.
Table 6: Distribution of Respondents According to
Number of Family Dependents in Batu Bara District
Number
Total
individu
Total
Respondents
(individual)
Percenta
ges (%)
1
0
2
6
2
1
4
13
3
2
7
23
4
3
12
39
5
4
4
13
6
5
2
6
Total
31
100
Sources: Analysis of Primer Data (2015)
Based on Table 6, respondent's family
dependents were dominated by extension workers
who had a total of 3 dependents as many as 12
respondents (39%). Overall respondents who have a
dependency of 0-4 people are 29 respondents (94%),
this indicates that the number of family dependents
carried out by respondents who are the responsibility
of their life is still classified as medium. According
to Ilyas (1987), Hanafie (2010) and Sarwono
(2013), the number of family dependents ranges
from 3-4 people classified as moderate and more
than 5 people classified as large. The number of
dependents can affect someone to be able to work
better because if the number of dependents they
carry is relatively large, it will also require a large
enough cost of living, of course he will try to fulfill
them. If the income earned as an instructor cannot
meet his needs and his family, of course, he will
seek other income, this will certainly have an impact
on his work which always provides the best service
for institutions/institutional extension agents and
farmers/groups as beneficiaries of activities
counseling.
UNICEES 2018 - Unimed International Conference on Economics Education and Social Science
360

4 CONCLUSIONS
The level of formal education has a significant effect
on enhancing the professionalism of extension
workers, therefore for extension workers with high
school education are given the widest motivation
and opportunity and full support by the local
government through BKP3 as the Counseling
Implementing Body to continue higher education
level as an effort to improve the quality of human
resources extension agent. For the government to
further improve the welfare of extension workers
through providing direct and indirect financial
compensation that is sufficient so that it raises
motivation to run the profession professionally
Furthermore, further research / study needs to be
carried out by examining broader variables and in-
depth theoretical studies in finding other variables
which are thought to have a significant effect on the
professionalism of extension workers. The variables
are work culture, competence, motivation and
facilities and infrastructure.
REFERENCES
Abdi, U. R. (2008) ‘Metode Penelitian Sosial dan
Ekonomi dan Aplikasi’, Bandung: Alfabeta.
Anoraga, P. (1998) Psikologi kerja. PT Rineka Cipta.
Mardikanto, T. (2009) ‘Agricultural Extension System’,
Agribusiness Development Center and Social
Forestry.
Prasetyo, B. and Jannah, L. M. (2005) Metode Penelitian
Kuantitatif: teori dan aplikasi. RajaGrafindo
Persada.
Rivai, V. and Sagala, E. J. (2011) ‘Human Resource
Management For Companies’. Jakarta: PT Raja
Grafindo Persada.
Sarwono, J. (2012) ‘Path Analysis: teori, aplikasi,
prosedur analisis untuk riset skripsi’. Tesis Dan
Disertasi (Menggunakan SPSS). Jakarta: PT Elex
Media Komputindo.
Sugiyono (2008) Metode penelitian
pendidikan:(pendekatan kuantitatif, kualitatif dan
R & D). Alfabeta.
Anoraga, P, (1998), Work psychology, Jakarta: Rineka
Cipta.
Anoraga, P & Sri Suyati, (2001), Organizational behavior,
Jakarta: Publisher.
Hanafie R, (2010), Introduction to agricultural economics,
Yogyakarta: ANDI
Harahap N, (2013), Social assessment methodology,
Medan: Medan STTP.
Ilyas Y, (1987), Performance: assessment and research
theory, Jakarta: PT Gramedia Pustaka Utama.
Mangkuprawiro, T, & Sjafri, B, (2009), Business,
management and human resources, Bogor: IPB-
Press.
Mangkuprawiro T, Sjafri, B, (2002), Strategic HR
management, Third print, Jakarta: PT Ghalia
Indonesia.
Mardikanto T, (2009), Agricultural extension systems,
Surakarta: UNS Press.
Prasetyo B & Jannah Lina Miftahul, (2005), Quantitative
assessment methods: theories and applications,
Jakarta: PT Rajagrafindo Persada.
Nababan, (2013), "Correlation of the Characteristics of
PNS Agricultural Extension to Extension Success in
Sunggal and Kutalimbaru Districts, Deli Serdang
District", Thesis. Medan: USU.
Rianse U & Abdi, (2008), Social and economic
assessment methodology theory and application,
Bandung: Alfha Beta.
Riduwan, (2003), Measurement scale of assessment
variables, Bandung: CV. Alfabeta.
Rosni M, & Suprijanto, (2010), ‘Development of a
determinant factor model for improving the
performance of field Agriculture Extension in South
Kalimantan Province with a structural equation
modeling approach’, Agroscintiae Journal, vol.17,
no 1, pp. 21.
Rivai, V & Ella Jauvani Sagala, (2012), Human resource
management for companies, Jakarta: Rajagrafindo
Persada.
Sarwono, J, (2013), 12 Effective SPSS skills for thesis
research, Jakarta: PT Elex Media Komputindo.
Slamet, Margono, (1992). Perspective of the knowledge of
welcoming development in era taking off. Edited by:
Aida V., Prabowo T., and Wahyudi R. Jakarta:
Library of National Self-help Development.
Sugiyono, (2008), Business assessment method, Bandung:
Alfabeta
Factors Affecting the Increasing of Agricultural Extension Professionalism in Batubara Regency, Indonesia
361
