
Factors Affecting Financial Literacy among Undergraduate Students
of Accounting Education in the Faculty of Economics of
Universitas Negeri Medan
Rini Herliani
1
, Andri Zainal
1
and Roza Thohiri
1
1
Faculty of Economics, Universitas Negeri Medan, Medan -Indonesia
Keywords:
Investment knowledge of financial education, financial experience, income and family-heritage,
demographics, logistic regression test
Abstract:
The aim of the research is to explore financial literacy related-aspects among students in the
Accounting Education department of Faculty of Economics at Universitas Negeri Medan
(UNIMED). The bottom line of this study is that a good financial management requires a good
financial knowledge in place. This research aims to help students in developing a complete
understanding and knowledge of financial literacy toward implementing the knowledge into their
daily personal finance management. The data was analyzed using the logistic regression test
indicating that there is a significant effect of financial education, financial, income, experience and
family-heritage and demographics on the knowledge investment. Cox and Snell R-Square is 0.706
(70,6%) and Nagelkerke R-Square is 0.a indicating that financial education, financial, income,
experience and family-heritage and demographics are good predictors for knowledge investment
among students in the Accounting Education department of Faculty of Economics at UNIMED.
1 INTRODUCTION
Financial intelligence is one of the important aspects
in today's life. Financial intelligence is the
intelligence in managing personal assets (Widyawati,
2012). Individuals must have the knowledge and
skills to manage their personal financial resources
effectively for their welfare. A person's knowledge
and understanding in managing his personal finances
is called financial literacy. Remund (2010) describes
five domains of financial literacy, namely 1)
knowledge of financial concepts 2) ability to
communicate about finance 3) ability to manage
personal finance 4) ability in making financial
decisions 5) confidence in making future financial
planning.
Financial literacy is closely related to individual
welfare. Financial knowledge and skills in managing
personal finance are very important in everyday life.
Yushita (2010) explained that financial literacy is a
basic need for everyone to avoid financial problems.
Financial difficulties occur not just a function of mere
income (low income). Financial difficulties can also
arise if there are errors in financial management
(missmanagement) such as credit card use errors and
lack of financial planning. Financial limitations can
cause stress, and low self-confidence.
Having financial literacy is a vital thing to get a
prosperous life. With the right financial management
which is certainly supported by good financial
literacy, the expected standard of living can increase,
this applies to every level of income, because no
matter how high a person's income level, without
proper financial management, financial security will
be difficult to achieve. Not only that, in understanding
the risk and profit figures associated with financial
products, the minimum level of financial literation
has become a necessity. Individuals who have
financial literacy can make effective use of financial
products and services so that individuals will not be
easily deceived by people who sell financial products
that are not suitable for that individual. Financial
knowledge is very important for an individual, so that
they are not wrong in making their financial
120
Herliani, R., Zainal, A. and Thohiri, R.
Factors Affecting Financial Literacy among Undergraduate Students of Accounting Education in the Faculty of Economics of Universitas Negeri Medan.
DOI: 10.5220/0009496401200126
In Proceedings of the 1st Unimed International Conference on Economics Education and Social Science (UNICEES 2018), pages 120-126
ISBN: 978-989-758-432-9
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

decisions. The level of a person's financial literacy
can be seen from how well the individual is able to
utilize financial resources, determine the source of
spending, manage soul risk, manage assets owned,
and prepare for future financial security if it is not
working (Ergun, 2018; Sari et al. , 2017).
For most students, college is the first time they
manage their own finances without supervision from
parents (Sabri et al. 2008). As students, they undergo
a financial transition period, from being tied to
parents to individuals who have the freedom to make
personal decisions regarding their finances. Students
must be able to independently manage their finances
well and must also be able to be responsible for the
decisions they have made. However, some studies
indicate students who have low knowledge of
financial literacy will make wrong decisions in their
finances (see: Ergun, 2018; Hospido et al., 2015;
Luhrmann et al., 2014; Chen and Volpe, 1988).
Students have complex financial problems because
most students have no income and are still dependent
on parents. Problems can occur due to delays in
money from parents or it could also be because a
monthly allowance that runs out prematurely is
caused by unexpected needs or because of poor
financial management (Homan, 2015).
The conditions described in the previous
paragraph cause students to be required to have high
financial literacy. Especially, for students who live in
large cities, where the most consumptive behavior
occurs. This is due to the large number of shopping
centers that influence students to spend money
without thinking about the benefits of goods
purchased. They mostly buy goods only for pleasure,
not based on needs caused by poor financial
understanding.
In the local context in several regions in
Indonesia, Nababan and Sadila's (2012) research
found that the level of financial literacy of Faculty of
Economics undergraduate students from 2008 to
2011 was 56.61% which indicated that the level of
financial literacy was in the category low. The study
conducted by Krisna et al. (2010) revealed the
majority of students at the University of Education in
Indonesia had moderate financial literacy levels
(63%), and only 7% had a high level of financial
literacy, while the rest (30%) entered into groups that
had a low level of financial literacy.
The high and low level of students' financial
literacy is influenced by several factors, both external
and internal factors, including family financial
education, financial learning in universities and peer
interaction (Widyawati, 2012). In addition, financial
literacy is also influenced by demographic factors.
Demography is a description of a person's
background so that it can affect their financial literacy
(Mandell, 2008). Demographic factors according to
Kewon (2011) include age, gender, family status,
migration status, level of education, type of work,
place of residence and regional. Nidar and Bestari
(2012) mention demographic factors that influence
financial literacy include the level of education of
parents, pocket money, education level, faculty,
parental income and insurance. Whereas Ariani and
Susanti (2015) stated that demographic factors
suitable for student characteristics were GPA (Grade
Point Average), gender, place of residence, ATM
usage and work experience. Of the several
demographic factors above, the most appropriate for
the characteristics of students at Medan State
University (UNIMED) are gender, ethnicity, parent
income, residence, ownership of savings accounts
and level of education (having attended financial
seminars).
UNIMED is one of the state universities that is
quite attractive to high school / vocational high school
students or the equivalent who want to go to college,
especially for those who want to become a teacher
and professional in the field of work that is relevant
to accounting science. This high interest caused
UNIMED students not only to come from Medan but
also from outside Medan. Thus, UNIMED students
have diversity such as gender, ethnicity, parental
income, as well as differences in residence between
students as long as they are studying in college.
Savings ownership is also one of the factors that is
included because the average student must have a
savings account, especially for students who live far
from parents, they must have a savings account.
Currently the UNIMED Student Identity Card (KTM)
has been integrated with a savings account of one
bank that cooperates with UNIMED which can be
used by students as a debit card - although based on
the initial Questions and Answers to some
respondents, it indicates that the KTM has not been
used optimally by students concerned. In addition to
the above factors, the experience of financial
education is also a factor that influences financial
literacy, because the experience of students who have
attended financial seminars both in high school (high
school / vocational high school) or when in college
must have differences about their financial literacy
knowledge.
Factors Affecting Financial Literacy among Undergraduate Students of Accounting Education in the Faculty of Economics of Universitas
Negeri Medan
121

2 THEORICAL FRAMEWORK
A person's financial literacy is influenced by several
factors. Ansong and Gyensare (2012) found that
financial literacy was influenced by several factors,
namely: 1) Age 2) Work experience 3) Mother
education 4) Departments.Margaretha and Pambudhi
(2015) found an influence on factor 1) Gender 2)
GPA 3) Parent's income on the level of financial
literacy. Shaari et al. (2013), stating that 1) Age, 2)
Spending habit, 4) Gender, 5) Faculty, 6) Year of
entering college has an effect on financial literacy.
Nababan and Sadalia (2012) found an influence
between factor 1) Gender 2) Stambuk 3) Place of
residence 4) GPA affects financial literacy.
Gender (gender) is a biological difference
experienced by each individual from birth. Gender is
defined as the difference between men and women in
terms of value and behavior. This difference in values
and behavior is the beginning of an indication that
men and women have non-identical literacy.
Research conducted by Chen and Volpe (1998)
explains that men have a higher financial literacy than
women. The research was conducted by conducting a
survey at the University with a sample of 924
students. Krishna et al. (2010) in his study found that
women better understand financial literacy than men.
Bhushan and Medury (2013) conducted research in
India with 516 respondents, in his study found that
there were significant differences between male and
female respondents. who already have a salary in
terms of financial literacy.
Furthermore, Keown (2011) found that people
who live alone have higher levels of personal
financial literacy than those who live with their
spouses or parents. This is because people who live
alone have responsibility for their daily financial
transactions and financial decisions. others.
The study conducted by Shults (2012) found that
there was a significant difference between the value
of students who had savings accounts and no.
Students who have savings accounts even for various
reasons and needs mark their trust in banking
institutions. The need for combined financial
understanding will make them have a savings
account. While students who do not have a savings
account can be caused by the lack of need to make
savings and lack of understanding about finance.
Ownership of a savings account is the first step to
achieving financial security, so that someone who
understands finance will have a savings account even
if they do not have an urgent need for ownership of a
savings account, because the person is not only
thinking about this moment but also thinking about
his long-term plan.
Associated with parents, Nidar and Bestari
(2012) found that income from parents is a significant
factor in the level of financial literacy in West Java
students. Keown (2011) explains that there is a
relationship between the income of parents and
financial knowledge. This shows that parents with
higher household income tend to have higher levels
of financial literacy because they use financial
instruments and services more often.
On the other hand, learning is essentially the
conscious effort of teachers to teach their students
(directing students' interactions with other learning
resources) in order to achieve the expected goals
(Trianto, 2009: 17). Learning in higher education
plays an important role in the process of student
financial literacy. The related research is the result of
Jhonson (2007) research which states that financial
education has a very important role for students to
have the ability to understand, assess, and act in their
financial interests. Furthermore Gutter (2008) in his
research stated that financial education had a positive
and significant effect on knowledge and financial
attitudes
3 RESEARCH METHOD
The research method used in this study is a
descriptive case study using a combination of
quantitative and qualitative data from the
questionnaire adopted from previous research
conducted by T-Zu Chin Peng Martina, Suzanne
Bartholomae, Jonathan J.Fox, and Garrett Cravener
(2007) . Questionnaires were distributed to find out
whether educational experience has an effect on
investment knowledge for UNIMED Accounting
Education students and how the differences and
influence of investment knowledge on financial
education, financial experience, income and
inheritance and demography.
There are 19 statement items that must be filled by
respondents in the Yes and No columns. The
questionnaire also includes the identity of the
respondent, such as Name, Nim, Class, Stambuk,
Gender and Tribe.
The population in the study were all students of
Accounting Education Department in Faculty of
Economics of UNIMED from batches 2014-2017
who were actively attending lectures in the 2017/2018
school year in the even semester. Sampling was
carried out by purposive sampling technique that is
by selecting a sample purposively. The total sample
UNICEES 2018 - Unimed International Conference on Economics Education and Social Science
122

in this study is 120 respondents consisting of 30
respondents from each generation.
4 ANALYSIS
4.1 Validity and Reliability Tests of Financial
Literacy
Table 1: Validity and Reliability Tests of Financial
Literacy
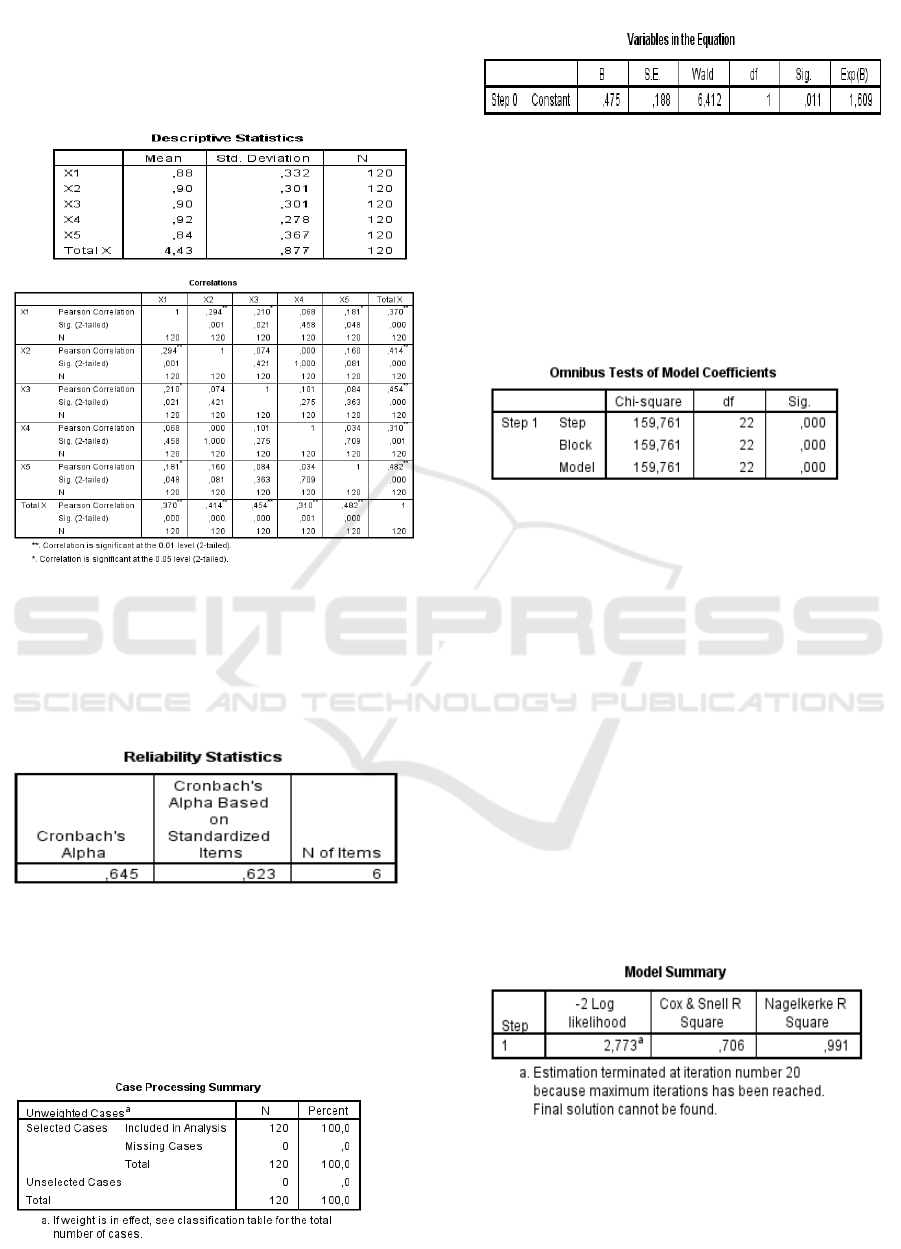
From the Descriptive Statistics table above, states that
all the data we provide to respondents is not lost / all
the questionnaires we gave back to us regarding
financial education. From the Correlation table above
states that all of our statements regarding financial
education are declared valid because in the far right
column the name "Total" is above 0.33.
Based on the table above, shows the value of
Cronbach's Alpha financial education variables worth
above 0.60. This shows that the research
questionnaire is reliable so it can be continued to
conduct research.
4.1.2 Validity and Reliability Tests of Financial
Experience
Table 2: Validity and Reliability Tests of Financial
Experience
From the Descriptive Statistics table above, states
that all the data we provide to the respondent is not
lost / all the questionnaires that we provide back to us
regarding financial experience. From the Correlation
table above states that all of our statements regarding
financial experience are declared valid because in the
rightmost column the name "Total" is above 0.33.
Based on the table above, shows the Cronbach
value "S Alpha financial education variables are
valued above 0.60. This shows that the research
questionnaire is reliable so it can be continued to
conduct research.
Factors Affecting Financial Literacy among Undergraduate Students of Accounting Education in the Faculty of Economics of Universitas
Negeri Medan
123
4.1.3. Validity and Reliability Tests of Income and
Family-Heritage
Table 3: Validity and Reliability Tests of Income and
Family-Heritage
From the Descriptive Statistics table above, states
that all data we provide to respondents is not lost / all
questionnaires that we provide back to us regarding
income and inheritance. From the Correlation table
above states that all of our statements regarding
income and inheritance are declared valid because in
the rightmost column the name "Total" is above 0.33.
Based on the table above, shows the Cronbach value
"S Alpha variable income and inheritance value
above 0.60. This shows that the research
questionnaire is reliable so it can be continued to
conduct research.
4.2. Logistic Regression Analysis
The criteria for the data above are: if the value of
S.E> 0.05 means the model is able to explain the data.
If the value of S.E <0.05 means that the model is
unable to explain the data. Based on the table above,
the value of S.E is 0.188 (> 0.05), this means that it is
unable to provide an explanation of the data, so the
Omnibus Test Of Model Coefficents table is needed
as follows:
The criteria: If the results of the Chi Square test
value> Chi Square table test value then Ho is rejected
and if the results of the Chi Square test value <Chi
Square table value test then accept Ho. Chi-Square
Value 159,761> Chi-Square Table on degree of
freedom 22 is 33,924 or with a significance of 0,05 so
reject Ho. Which states that the addition of
independent variables can have a real influence on the
model or in other words the model is declared FIT.
(the model simply explains the data).
So the answer to the hypothesis of the
simultaneous effect of the independent variable on the
dependent variable is to accept H1 and reject H0 or
that means there is a significant influence between
simultaneous financial education, educational
experience, income and inheritance, demography on
investment knowledge because the value of P-value
Chi-Square is 0,000 <Alpha 0.05 or Chi-Square value
count 159.761> Chi Square table 33.924.
From the table above, it can be seen that the
model by entering independent variables (financial
education, financial experience, income and
inheritance, and demographics) on the dependent
variable (knowledge of investment) turns out to have
UNICEES 2018 - Unimed International Conference on Economics Education and Social Science
124
changed in the interpretation of parameters (-2 log
likelihood) of 2,773. The R-Sqaure value of 0.706 or
70.6% (Cox & Snell) and 0.991 or 99.1%
(Nagelkerke). Nagelkerke R-Square values of 0.991
and Cox & Snell R Square are 0.706, which indicates
that the ability of the independent variable to explain
the dependent variable is 0.991 or 99.1%. This means
that there is another factor of 0.9% outside the model
that explains the independent variables.
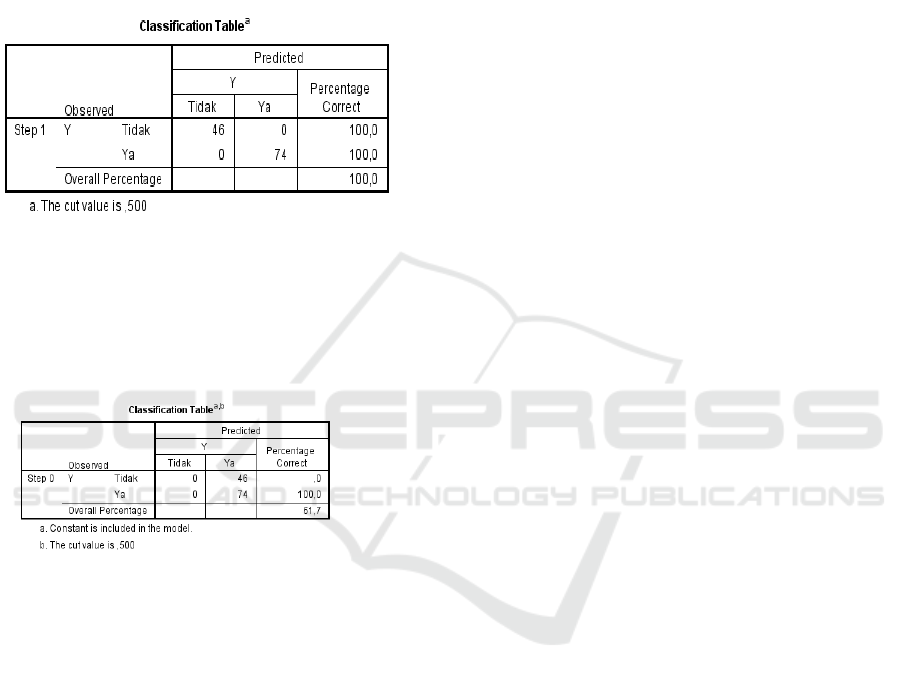
Based on the Classification Table table above,
there are 46 samples whose answers are "No". And
the number of samples whose answer is "Yes" is 74
people. In logistic regression interpretation with
SPSS: The table above gives an overall percentage
value of (46 + 74) / 120 x 100% = 100%. Which
means the accuracy of this research model is 100%.
Classification Table The table is a contingency
table that should occur or also called the expectation
frequency based on empirical data on the dependent
variable, where the number of samples that have the
dependent variable category that answers No (code 0)
is 46 people and those who answer Yes (code 1) are
74 people. The number of samples is 120 people. So
that the overall percentage value before the
independent variable is included in the model is:
74/120 = 61.66%. (rounded up to 61.7%).
5 RESULTS
The purpose of this study was to analyze the influence
of financial education, financial / investment
experience, income, family inheritance and
demographics on investment knowledge in students
in accounting education study programs at the Faculty
of Economics UNIMED. The results reveal that
financial education has a significant influence with
overall financial knowledge. These results are in line
with Chon and Volpe (1998) concluding that financial
education is strongly influenced by financial
knowledge.
Furthermore, when tested based on financial
experience, we found that there was a significant
relationship after learning about financial education.
Students who have experience in managing finances
will have more knowledge in investing. These results
are in line with Chon and Volpe (1998) concluding
that financial education is strongly influenced by
financial knowledge. For variable financial
experience, we found that there were no demographic
differences after learning about financial education.
This is in line with the study of Mandell (2004)
concluding that financial experience has a significant
influence on financial knowledge.
Regarding income and inheritance factors, we
find that there is a significant influence on investment
knowledge. This is in line with the research of
Huddleston (1999) also concluded that income and
inheritance also have a positive impact on one's
knowledge in investing. We found that there was no
significant demographic effect after learning about
financial education. This is in line with the research
of Hayhoe, Leach, Turner, Bruin and Lawrence
(2000). In particular, to answer the purpose of
research on whether students of Unimed Accounting
education study program have implemented financial
education they have learned in real life, we conclude
that students of accounting education study program
Unimed have applied it in their daily lives.
6 CONCLUSIONS
Based on the results of the research, analysis and
discussion, conclusions taken, it can be given advice,
which is suggested to the campus to develop financial
education for students. One of them is by making
seminars on finance for students and making several
courses that discuss finance. Thus, students'
knowledge of UNIMED Accounting Education on
finance will also increase. The higher financial
knowledge a person has, the more likely he or she will
be more understanding and smarter in financial
management.
REFERENCES
ANZ Bank (2011). Adult financial literacy in
Australia. Executive summary of the results
from 2011 ANZ Survey.
Factors Affecting Financial Literacy among Undergraduate Students of Accounting Education in the Faculty of Economics of Universitas
Negeri Medan
125

Ariani, N. A. dan Susanti. (2015). Pengaruh Faktor
Demografi Terhadap Financial Literacy
Mahasiswa Fakultas Ekonomi Universitas
Negeri Surabaya Angkatan 2012. Jurnal
Mahasiswa Teknologi Pendidikan, 3(2).
Ayu Krishna, dkk. (2010). Analisis Literasi keuangan
di Kalangan Mahasiswa dan Faktor-Faktor yang
Mempengaruhinya. Proceeding of The 4th
International Confeeence on Teacher
Education; Join Conference UPI & UPSI: 552-
560
Bhushan, P., & Medury, Y. (2013). Financial literacy
and its determinants. International Journal of
Engineering, Business and Enterprise Applica-
tions (IJEBEA), 4(2), 155–160.
Chen, H., & Volpe, R. P. (1998). An analysis of fi-
nancial literacy among college students. Finan-
cial Services Review, 7(1), 107–128.
Herliani, R. (2012). Pengaruh Anggaran Biaya
Terhadap Efisiensi Biaya Operasional Pada
Asuransi Jiwa Bersama Bumiputera 1912
Medan. Jurnal Mediasi, 4(01).
Homan, Hery Syaerul. (2015). Comparative Study of
Student Financial Literacy and Its Demographic
Factors. First International Conference on
Economics and Banking, 106-111.
Hospido, L., Villanueva, E., & Zamarro, G. (2015).
Finance for all: The impact of financial literacy
training in compulsory secondary education in
Spain. Banco de Espana. Documentos de
Trabajo N.8 1502. Retrieved from
https://pdfs.semanticscholar.org/f393/345ed297
828c34b9e283e28319514dac43d1.pdf
Keown, Leslie Anne. (2011). The Financial
Knowledge of Canadians. Canadian Social
Trends, 91.
Lusardi, A., & Mitchell, O. S. (2014). The Economic
importance of financial literacy: Theory and
Evidence. Journal of Economic Literature,
American Economic Association, 52(1), 5–44.
Nababan, D., & Sadila, I. (2012). Analisis personal
financial literacy dan financial behavior
mahasiswa strata I fakultas ekonomi
Universitas Sumatera Utara.
Nidar, S.R., & Bestari, S. (2012). Personal literacy
among university students (case study at
Padjajaran University students, Bandung,
Indonesia. World Journal of Social Sciesnce,
2(4), 162-171.
Otoritas Jasa Keuangan. (2014). Strategi Nasional
Literasi Keuangan. Jakarta: direktorat literasi
dan Edukasi.
Remud, D.L. (2010). Financial literacy explicated:
The case for a clear definition in an increasingly
compex economy. The Journal Of Consumer
Affairs, 4(2), 276-295.
Sabri, M. F., Othman, M.A., Masud, J., Paim, L.,
MacDonald, M., & Hira, T. K. (2008) Financial
behavior and problems among college students
in Malaysia: Research and education
implication. Consumer Interest Annual, 54, 166-
170.
Sagala, G. H., Zainal, A., & Effiyanti, T. (2017).
Attitude Toward Computer-Based Statistics
Among Pre-Service Teacher Candidates.
Proceedings of MAC 2017. MAC Prague
consulting
Sari, R. C., & Fatimah, P. R. (2017). Bringing
Voluntary Financial Education in Emerging
Economy: Role of Financial Socialization
During Elementary Years. The Asia-Pacific
Education Researcher, 26(3-4), 183-192.
Thohiri, R. (2016). Pengaruh Modernisasi Pajak
Terhadap Tingkat Kepatuhan Wajib Pajak di
KPP Pratama Medan Kota. Jurnal Manajemen
Perpajakan. Volume 5: No.2 Desember.
Thohiri, R. (2016). Pengaruh Kecerdasan Emosional
Terhadap Tingkat Pemahaman Perpajakan
Dengan Kepercayaan Diri Sebagai Variabel
Moderating. Bina Akuntansi IBBI. Volume 20:
No.1, Januari.
Widyawati, I. (2012). Faktor-faktor yang
mempengaruhi literasi finansial mahasiswa
fakultas ekonomi dan bisnis Universitas
Brawijaya. Jurnal Akuntansi dan Pendidikan
1(1), 89-99.
Yushita, A.N., (2017). Pentingnya Literasi Keuangan
Bagi Pengelolaan Keuangan Pribadi. Jurnal
Nominal IV(1).Yeni, Putri Anggraeni. (2017).
Pengaruh Pengetahuan Keuangan dan
Pendidikan Keuangan di Keluarga Terhadap
Pengelolaan Keuangan Mahasiswa di
Surabaya. Jurnal Program Studi Manajemen.
Sekolah Tinggi Ilmu Ekonomi Perbanas
UNICEES 2018 - Unimed International Conference on Economics Education and Social Science
126
