
The Civil Servants’ Intention to Be Whistle Blowers of Corruption
Cases in Government Sector
Badingatus Solikhah
1
, Agus Wahyudin
1
and Agung Yulianto
1
1
Faculty of Economics, Universitas Negeri Semarang, Semarang-Indonesia
Keywords: Whistle-blowing Intention, Attitudes, Organizational Commitment, Prosocial Theory.
Abstract: This study aims to describe the intentions of civil servant in Central Java Indonesia to do whistle-blowing.
This paper also examined the relationship of attitudes toward whistleblowing and organizational
commitment toward whistleblowing intention. The respondents within this study were 200 government civil
servants working on Audit Board of the Republic Indonesia Representative of Central Java Province and
Inspectorate of Central Java Province. This paper using closed questionnaire to collect the data. The
questionnaire developed from previous study using scale 1-5 and 135 questionnaires were analyzed using
IBM SPSS 21. The respondents were willing to become whistle-blowers in the event of fraud cases they
found out. The research findings indicated that the attitude and organizational commitment gave a positive
influence on whistle-blowing intentions. It can be concluded that in the formation of intentions to do
whistle-blowing influenced factor inside oneself to form the intention and required the existence of self-
control from various limitations.
1 INTRODUCTION
Over the past few decades, issues regarding whistle-
blowing have become a global concern since they
are proven effective for detecting fraud in
organizations. The whistle-blowing system, which is
effective, transparent and responsible, is highly
expected to overcome employee reluctance to report
suspected violations and to increase employee
participation in reporting suspected violations. Park
et al. (2008) suggested that whistle-blowing is a
means to report any violations to individuals or
organizations considered to have an authority to put
an end to them and there may be considerable
variation in the actual way in which employees can
become whistle-blowers. Referring to the Indonesian
ACFE report in 2016, the highest fraud prevention
method as much as 20.6% was the whistle-blowing
system method.
Most previous studies (Tavakoli et. al, 2003)
agreed that whistle-blowing is an internal
organizational structure that is significant to strive
against company mistakes and questionable actions
(Kaplan & Schultz, 2007). Near and Miceli (1995)
declared that fraud not disclosed to anyone will put
their organization in danger. Whistle-blowing
requires collective efforts within an organization
since it is effective in combating fraud as long as all
members of the organization actively participate.
Whistle-blowing is able to increase the effectiveness
and efficiency of the organization and therefore, can
be considered a mitigating factor to prevent
unexpected negative occurrence (Ahmad et.al, 2012;
Kaplan & Schultz, 2007; Winardi, 2013).
Thus whistle-blowing is a notable way to prevent
and deter any frauds, losses and misuses (Hwang
et.al, 2008). For the significance of the whistle-
blowing, a method is necessary to encourage the
effectiveness of fraudulent disclosures that occur
within the organization. The Sarbanes-Oxley Act
2002, Section 302 and 806, are specifically designed
to encourage whistle-blowing and provide protection
from retaliation for employees who disclose fraud or
who become whistle-blowers within the
organization.
In fact, being a whistle-blower is not an
effortless matter. Anyone who comes from an
internal organization will generally face an ethical
dilemma in deciding whether to report it or leave it
hidden. Some people view the whistle-blower as a
traitor violating the norms of organizational loyalty,
yet others view the whistle-blower as a heroic
protector of values which considered more important
Solikhah, B., Wahyudin, A. and Yulianto, A.
The Civil Servants’ Intention to Be Whistle Blowers of Corruption Cases in Government Sector.
DOI: 10.5220/0009498709630967
In Proceedings of the 1st Unimed International Conference on Economics Education and Social Science (UNICEES 2018), pages 963-967
ISBN: 978-989-758-432-9
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
963

than loyalty to the organization. A person may be a
whistle-blower in order to get attention, fame,
promotion, and retainer for his whistle, even though
the organization may designate a whistle-blowing as
a mechanism to expose and control organizational
errors (Rothschild, 1999 and Hwang et al., 2008).
These conflicting views often make candidates for
whistle-blowers in a dilemma of uncertainty
determine attitudes that can ultimately distort the
interests of whistle-blowing (Bagustianto &
Nurkholis, 2015).
The objectives of this study was to examine
whether individual factors that consisting of
organizational attitudes and commitment influence
the auditor's intention to do whistle-blowing. This
study was conducted on government auditors who
worked for the Indonesian Financial Audit Agency
(BPK) representative of Central Java Province and
Inspectorate of Central Java Province. The
respondents were selected in government auditors
with the idea that they have already known the
systematic whistle-blowing and fraudulent reporting
system applied at their workplace.
2 THEORICAL FRAMEWORK
Pro-social Organizational Behavior Theory
Brief and Motowidlo (1986) suggested that pro-
social behavior is behavior carried out by members
of an organization, directed at individuals, groups, or
organizations with whom they interact when playing
their organizational roles in order to promote the
welfare of individuals, groups or organizations
targeted. Brief and Motowidlo (1986) mentioned
whistle-blowing as either the 13 forms of pro-social
organizational behavior. The relation of pro-social
theory with the intention of whistle-blowing is that
sometimes members of an organization see an urgent
need for change, for instance, due to certain orders,
procedures or policies that may be unethical, illegal,
or cause harm to the organization in long term, but
cannot suggest or bring change directly. If done with
sincere intention to help the organization, this is also
a pro-social behavior (Brief & Motowidlo, 1986).
This is in accordance with the opinion of Dozier and
Miceli (1985) which stated that whistle-blowing
behavior can be viewed as pro-social behavior since
in general these behaviors will provide benefits to
other people (or organizations) besides being useful
for the whistle-blowers themselves so that whistle-
blowing can be said to be pro-social behaviour.
Development of Hypotheses
Attitude against whistle-blowing
Park and Blenkinsopp (2009) stated that someone
develops his attitude based on his belief on the
behavior which was being considered connecting
that behavior with the certain consequences. The
first step in the process of making pro-social
decision is focal member (individual who will be
observed) consider whether focalactivity is
wrongdoing or not (Greenberger et al., 1987 in
Manafe, 2015). The attitude toward a behavior refers
to the extent to which a person has evaluation or
favorable judgment or unfavorable judgment to the
certain behavior (Ajzen, 1991, Solikhah, 2014).
Winardi (2013) stated that an employee more tends
to be whistle-blower if he believes that whistle-
blower brings positive results and the results is
important to be evaluated. For example, the results
of whistle-blowing could prevent serious damage on
the organization and help to eradicate a corruption.
If employee assumes that whistle-blower is as
corrective steps for organization, which could save
organization, it means this attitude bring positive
effect. The previous research done by Park and
Blenkinsopp (2009), Winardi (2013), Bagustianto
and Nurkholis (2015) stated that an attitude brings
positive effect to the intention whistle-blowing. So
that the hypothesis is
H
1
: The attitudes supportive against the whistle-
blowing system will bring positive effect to
intention of whistle-blowing.
The Commitment of Organization
Mowday et al. (1979) define the commitment of
organization is as relative power of identification
and individual involvement in an organization. This
component of organizational commitment show the
disposition of pro-social behavior, is individuals
committed to the organization will be willing to give
something of themselves to contribute to the welfare
of the organization (Brief and Motowidlo, 1986). In
Myers's book, (2012:196) the norm of social
responsibility is the belief that someone must help
those who need help regarding reciprocity, this is
corresponding with the principle of the commitment
of organization. For whom has high organizational
commitment will always be actively involved and
contribute to the organization, so that they have
more sense of belonging to the organization, then
they will do anything to protect their organization,
then that commitment bring positive effect to
intention of whistle-blowing. The previous research
result done by Napitupulu (2016) and Bagustianto
and Nurkholis (2015) stated that the organizational
UNICEES 2018 - Unimed International Conference on Economics Education and Social Science
964
commitment has a positive effect on whistle-
blowing intentions, thus, the hypothesis proposed:
H
2
: The Commitment of an Organization bring
positive effect N whistle-blowing intention.
3 RESEARCH METHOD
Sample
The samples of this research were civil servants
working in the Inspectorate of Central Java Province
and representative of BPK Central Java Province.
Both agencies were selected because the system
reporting of whistle-blowing was already presented
in those institutions /organizations. The sampling
technique used is Non-Probability, while in selecting
the sample the method used was purposive sampling
with the criteria ‘the employee has at least on year
working experience’. It was with the consideration
that respondents who have work at least one year
have proper knowledge, have understood to the
working environment, and have perception and
consideration of the comprehensive to whistle-
blowing intention. The research data was collected
through conducting 200 questionnaires. There were
135 questionnaires were returned (response rate
72%).
Table 1 describes about definition variable,
indicator or the way of measurement.
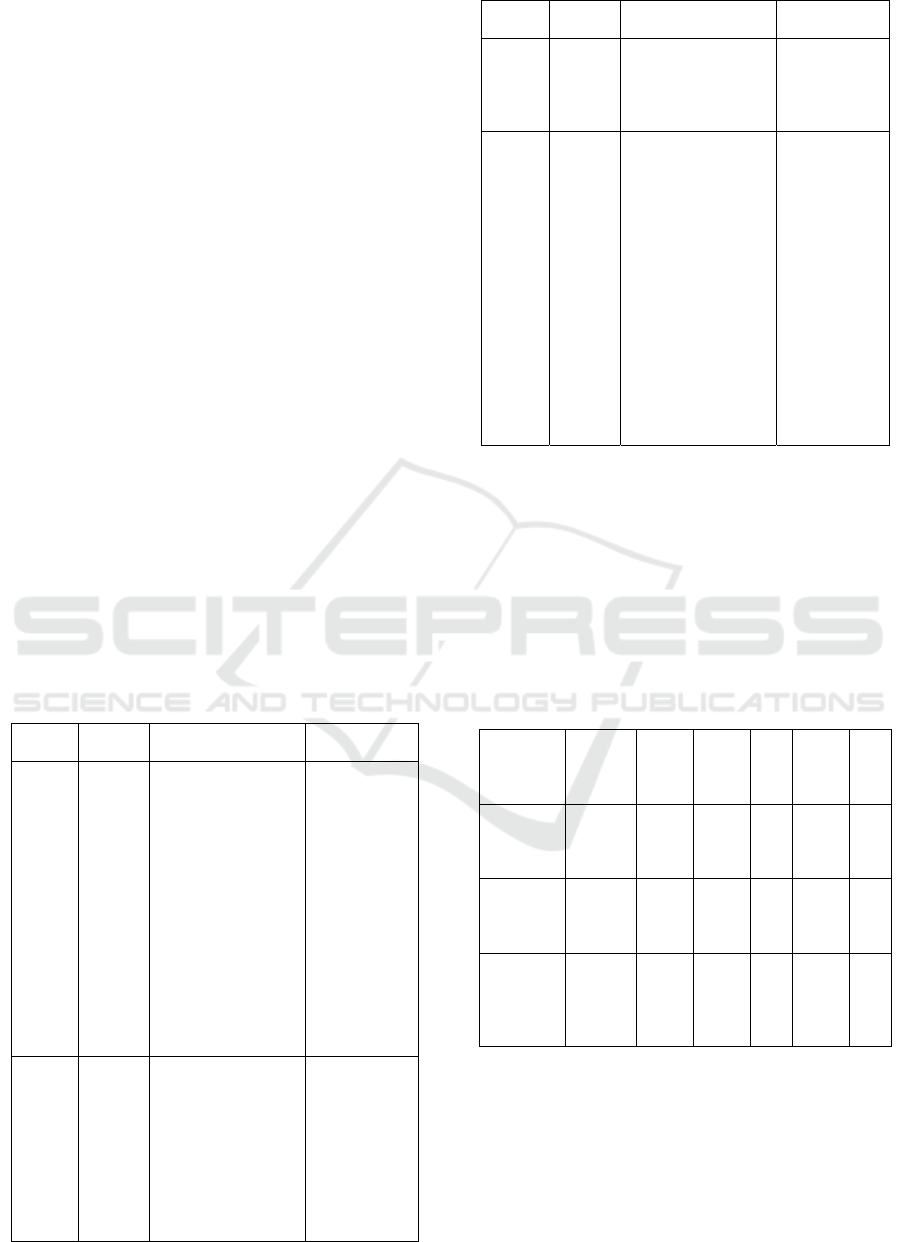
Table 1: The Variable Deskreption.
Varia
ble
Definit
ions
Indicators/Measure
ment
Reference
Whistl
e-
blowin
g
Report
the erro
r to the
trusted
individ
ual or
organiz
ation th
at has
power
to stop
it.
1. Report an error
with complete
identity.
2. The
anonymously
report
3. Report to the
internal
organization.
4. Report to the
external
organization.
The
measurement uses
likert scale 1-5
Park &
Blenkin-sopp,
(2009)
Attitud
e
The
individ
ual
attitude
toward
how
many h
e
approv
es or n
1. The confidence
behavior
2. Evaluation of
Importance
The
measurement uses
likert scale 1-5
Park &
Blenkin-sopp,
(2009)
Varia
ble
Definit
ions
Indicators/Measure
ment
Reference
ot appr
ove a
certain
behavi
or.
The
commi
tment
of
organi
zation
How
far the
involve
ment of
an
employ
ee to
the
organiz
ation.
1. Strong
confidence and
acceptance
goals and value
organization,
2. The
willingness for
exert
considerable eff
ort on nae of
organization,
and
3. loyalty.
The measurement
uses likert scale
1-5
Mowday
et al.
(1979)
4 ANALYSIS
Findings of Descriptive Statistical Analysis
Analysis statistics descriptive used for describing the
existing variables in the research seen from
minimum and maximum value and mean. The
analysis of statistics descriptive could be seen in
table 2 the results of analysis descriptive statistics:
Table 2: The results of analysis descriptive statistics.
Variable
Numb
er of
Respo
ndent
Min Max
M
ea
n
St.
Devi
ation
Ca
teg
or
y
Intention
of
Whistle-
blowing
135 1 5
3.4
2
0.76
It
ca
n
be
Attitude
toward
Whistle-
blowing
135 1 5
3.9
7
0.53
Ap
pr
ov
ed
The
commitm
ent of
organizati
on
135 2 5
3.6
1
0.56
Hi
gh
The findings of descriptive statistics showed that
the intention of the whistle-blowing variable fell into
the possible category. This means that research
respondents were willing to become whistle-blowers
in the event of fraud cases they found out. The
attitude variable towards the whistle-blowing was in
the agreed category in which the respondent's
organizational commitment variable got a high
The Civil Servants’ Intention to Be Whistle Blowers of Corruption Cases in Government Sector
965

category and the retaliation view variable is also
included in the fairly high category. The status of
offenders belonged to the quite powerful category;
the ethical environment was in the high category
while the ethnic groups included in a possible
category.
Findings of Hypothesis Test
All variables in this study passed the classic
assumption test. Classical assumption test shows that
the data is normal which is expressed with a
significance value of 0.537 or above 0.05.
Multicollinearity test shows that tolerance value is
more than 0.10 and VIF value is less than 10, so
there is no correlation between independent
variables and the regression model. Therefore, it
does not occur multicollinearity. The
heteroscedasticity test using the glejser test shows
that the significance is above 0.05 and the variable
does not occur with heteroscedasticity so that all
variables pass the classical assumption test.
The Result of Multiple Linear Regression is
shown in the table 3.
Table 3: The Result of Multiple Linear Regression
Model Unstandardized
Coefficients
Standardi
zed
Coefficien
ts
t Sig. Concl
usion
B Std. Error Beta
(Constant)
13.808 5.377 2.568 .011
Attitude
.574 .101 .494 5.661 .000 Accep
ted
Commitm
ent Org.
.158 .056 .214 2.799 .006 Accep
ted
Dependent Variable: Whistle-blowing Intention
The results coefficient of determination test
shows that the amount of Adjusted R Square is
0.387 which means that 38.7% variable variation
from whistle-blowing intentions can be explained by
variable attitudes, organizational commitment,
retaliation views, offender status, ethical
environment, and ethnicity, while the remaining
62.3% explained by other variables outside the
model.
5 RESULTS
H
1
which stated that a supportive attitude towards
the whistle-blowing system would have a positive
effect on whistle-blowing intentions received. The
employee agreed to the benefits of whistle-blowing
and he agreed that the results after reporting became
an important matter. For instance, it could prevent
the loss of the organization and eradicate corruption.
As a state civil servant, he must also carry out his
obligations as a servant of the state, which were
protecting and maintaining the reputation of his
organization so that he could fulfil the public's desire
to make a clean organization, if he did a whistle-
blowing, and then makes a better organization.
This result was in accordance with the theory of
pro-social behaviour. The steps in the process of
making pro-social decisions were related to whistle-
blowing, which was to consider whether the whistle-
blowing is wrong. In the theory of planned of
behaviour proposed by Ajzen (1991), either
predictor in shaping intention is attitude. Attitude
towards whistle-blowing refers to the extent to
which a person has a favourable evaluation or
assessment of the attitude towards the question. The
results of this study were consistent with the
research of Park and Blenkinsopp (2009), Winardi
(2013), and Bagustianto and Nurkholis (2015) which
stated that attitudes had a significant positive effect
on the intention to do whistle-blowing.
H
2
was accepted which means that organizational
commitment has a positive effect on whistle-
blowing intentions. Employees had similarities with
the values applied in the organization, and they
would be glad and proud to be part of the
organization, so that they easily approved the
policies set by the organization. Employees were
also willing to work on a variety of tasks and will try
hard so that the organization could achieve its
objectives because it has a high level of concern for
how the organization is going. As well as employees
felt their current organization is the best
organization, so they would be pleased and fortunate
to be able to work at the BPK or Inspectorate.
This result was supported by pro-social
behaviour theory and the concept of organizational
commitment, that whistle-blowing is a positive
social behaviour that can provide benefits to the
organization in the form of protecting the
organization from the dangers of fraud (fraud). Brief
and Motowidlo (1986) mention one of the
antecedents of pro-social theory namely
organizational commitment. This component of
organizational commitment showed the disposition
of pro-social behaviour, which were individuals
committed to the organization would be willing to
contribute to the welfare of the organization.
Employees who had high organizational
commitment tent to have a sense of ownership and
had high loyalty and when the values existing in the
organization were inherent in the employees so that
the organization was a part of themselves, so that
UNICEES 2018 - Unimed International Conference on Economics Education and Social Science
966

they had high responsibilities to protect the
organization either by doing whistle-blowing. This
results were in line with the research conducted by
Napitupulu (2016) and Bagustianto and Nurkholis
(2015) which stated that organizational commitment
had a positive effect on the intention to do whistle-
blowing.
6 CONCLUSIONS
A total of 135 civil servants working at the Audit
Board of the Republic Indonesia Representative of
Central Java Province and Inspectorate of Central
Java Province responded that they had the intention
to become whistleblowers if they knew that fraud
had occurred in their workplace which caused losses
to the state. The conclusions from this study are;
partially attitudes towards whistle-blowing, and
organizational commitment, have a positive effect
on whistle-blowing intentions. It can be concluded
that in the formation of intentions to conduct
whistleblowing influenced factor from within
oneself to form the intention and required the
existence of self-control from various limitations.
REFERENCES
ACFE. (2016). Report to the Nations on Occupational
Fraud and Abuse 2016 Global Fraud Study. USA.
Ahmad, S. A., Smith, M., & Ismail, Z. (2012). Internal
whistle-blowing intentions: A study of demographic
and individual factors. Journal of Modern Accounting
and Auditing, 8(11), 1632.
Ajzen, I. (1991). The theory of planned behavior.
Organizational Behavior and Human Decision
Processes, 50(2), 179–211.
Bagustianto, R., & Nurkholis, N. (2015). Factors
Affecting the Interest of Civil Servants to Take
Whistle-Blowing Actions (Study of BPK RI Civil
Servants). EKUITAS (Jurnal Ekonomi Dan
Keuangan), 19(2), 276–295.
Brief, A. P., & Motowidlo, S. J. (1986). Prosocial
organizational behaviors. Academy of Management
Review, 11(4), 710–725.
Dozier, J. B., & Miceli, M. P. (1985). Potential predictors
of whistle-blowing: A prosocial behavior perspective.
Academy of Management Review, 10(4), 823–836.
Hwang, D., Staley, B., Te Chen, Y., & Lan, J. (2008).
Confucian culture and whistleblowing by
professional accountants: an exploratory study.
Managerial Auditing Journal, 23(5), 504–526.
https://doi.org/doi:10.1108/02686900810875316
Kaplan, S. E., & Schultz, J. J. (2007). Intentions to report
questionable acts: An examination of the influence of
anonymous reporting channel, internal audit quality,
and setting. Journal of Business Ethics, 71(2), 109–
124. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10551-006-0021-6
Manafe, M. W. N. (2015). Effects of Moral Reasoning,
Retaliation and Gender on the Trend of Internal
Whistleblowing. SUSUNAN REDAKSI JURNAL
WAHANA, 113.
Mowday, R. T., Steers, R. M., & Porter, L. W. (1979). The
measurement of organizational commitment. Journal
of Vocational Behavior, 14(2), 224–247.
Myers, D. G. (2012). Social Psychology, Issue 10.
Translator by Tusyani, A. Jakarta: Salemba
Humanika.
Napitupulu, G. B. (2016). Pengaruh Faktor
Organisasional, Faktor Individual, Dan Faktor
Demografi Terhadap Intensi Whistleblowing.
Simposium Nasional Akuntansi XIX Lampung.
Near, J. P., & Miceli, M. P. (1995). Near, Janet P Miceli,
Marcia P. The Academy of Management Review,
20(3), 679–708.
Park, H., & Blenkinsopp, J. (2009). Whistleblowing as
planned behavior–A survey of South Korean police
officers. Journal of Business Ethics,
85(4), 545–556.
Park, H., Blenkinsopp, J., Oktem, M. K., &
Omurgonulsen, U. (2008). Cultural orientation and
attitudes toward different forms of whistleblowing: A
comparison of South Korea, Turkey, and the UK.
Journal of Business Ethics, 82(4), 929–939.
Rothschild Miethe, Terance, J. (1999). Whistle-Blower
Disclosures and Management Retaliation. WORK
AND OCCUPATIONS, 26(1), 107–128.
Solikhah, B. (2014). An Application of Theory of Planned
Behavior towards CPA Career in Indonesia. Procedia
- Social and Behavioral Sciences, 164, 397–402.
https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbspro.2014.11
.094
Tavakoli, A. A., Keenan, J. P., & Crnjak-Karanovic, B.
(2003). Culture and Whistleblowing an Empirical
Study of Croatian and United States Managers
Utilizing Hofstede’s Cultural Dimensions. Journal of
Business Ethics, 43(1/2), 49–64.
https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1022959131133
Winardi, R. D. (2013). The Influence of Individual And
Situational Factors on Lower-Level Civil
Servants’whistle-Blowing Intention In Indonesia.
Journal of Indonesian Economy and Business: JIEB.,
28(3), 361.
The Civil Servants’ Intention to Be Whistle Blowers of Corruption Cases in Government Sector
967
