
Factor-Factor Affecting Labor Demand Food Beverages and Tobacco
Industry of North Sumatra Province
Elida Madona Siburian
1
, Muhammad Fitri Rahmadana
1
and Indra Maipita
1
1
Department of Economics, Faculty of Economics, State University of Medan, North Sumatra, 20219, Indonesia
Keywords: Labor Demand Food Beverages and Tobacco Industry, Investment Industry Sector, Number of Large and
Medium Manufacturing, Minimum Wage of Regency/City, Gross Regional and Domestic Product
Abstract: Labor demand in North Sumatra during the period 2012 to 2016 showed a fluctuating condition. The aim of
this research is to analyze the factors that affecting labor demand food beverages and tobacco industry at the
regency/city in North Sumatra Province using panel data. With independent variables Investment Industry
Sector, Industry Number, Minimum Wage for regency/city and Gross Regional Domestic Product while the
dependent variable is Labor Demand. Data obtained the Central Statistics Agency (BPS) of North Sumatra
Province during 2012-2016. The method used Panel Least Square (PLS) with Random Effect Model
(REM). The result show that Investment Industry Sector has positively effect the labor demand as 21,88%
and significant, Industry Number has positively effect the Labor Demand as 48,48% and significant,
Minimum Wage of regency/city has negatively effect the Labor Demand as 13,14% and significant and
Gross Regional Domestic Product has positively effect the Labor Demand as 34,51% and significant at the
Labor Demand in North Sumatra Province.
1 INTRODUCTION
Improving community welfare is one of the main
goals of economic development in developing
countries. One of the important problems faced by
developing countries is high population growth. The
high population growth affects the increase in the
workforce. This condition will be a problem if it is
not balanced with employment. One indicator used
to assess the success of a country's economic
development is seen from the employment
opportunities created by economic development
activities (Freter, 2014). One sector that plays an
important role in economic development is the
industrial sector. This sector has several advantages,
such as absorbing a large workforce and creating
high added value. The industrial sector is believed to
be a sector that can lead other sectors in an economy
towards progress
In Indonesia, the industrial sector is prepared to
be able to become a leading sector that is able to
become a motor that drives the progress of other
sectors. Thus the industrial sector is expected to be
able to provide employment so that it can absorb the
large number of workers in Indonesia. In the
Province of North Sumatra from 2014-2016 the
contribution of the manufacturing industry to the
GRDP of North Sumatra Province each year has
increased. Where each year the contribution of the
Processing Industry to North Sumatra GRDP always
increases in 2015 by 0.13 percent from 2014 and in
2016 by 0.28 percent. While the lowest contribution
is from the water supply sector, recycling waste
management where in 2015 only increased by 0.01
percent from 2014 and in 2016 did not experience an
increase from the previous year.
In the Province of North Sumatra the Processing
Industry is divided into 9 groups namely (1) Food,
beverages and tobacco industries; (2) Manufacture
of textiles, apparel and leather; (3) Timber industry,
household; (4) Paper industry, printing and
publishing; (5) Chemical, coal, rubber and plastic
Siburian, E., Rahmadana, M. and Maipita, I.
Factor-Factor Affecting Labor Demand Food Beverages and Tobacco Industry of North Sumatra Province.
DOI: 10.5220/0009500304350441
In Proceedings of the 1st Unimed International Conference on Economics Education and Social Science (UNICEES 2018), pages 435-441
ISBN: 978-989-758-432-9
Copyright
c
2020 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
435

industries; (6) Industries of non-metallic minerals
except oil and coal; (7) Base metal industry; (8)
Manufacture of metal goods, machinery and
equipment; (9) Other processing industries. (BPS
North Sumatra, 2017). Of the 9 industrial groups, the
growth of the number of industries each year from
2013-2016 fluctuated, the highest growth was
achieved by the food, beverage and tobacco
industries. The role of growth in the 9 industrial
groups will have an impact on the number of
workers used.
Absorption of labor in 9 industrial groups each
year fluctuates. The highest absorption of labor is in
the food, beverage and tobacco industry sectors
where the number of workers employed in 2016 is
89,782 people. While the lowest was in other
processing industries, which amounted to 2,655
people. So that it can be concluded that the role of
the food, beverage and tobacco industry sector is
able to spur regional economic growth and the
development of the industrial sector in North
Sumatra Province. The growth and development of
the industrial sector promises to broaden
employment opportunities. On the other hand, the
government wants to optimize the role of the food,
beverage and tobacco industries in North Sumatra
province in contributing to the demand for labor so
that there needs to be an in-depth study of the factors
that affect labor demand in the food, beverage and
tobacco industries.
According to Simanjuntak (1985) and Hani
Handoko (1985), Demand for labor in the small
industrial sector is influenced by internal and
external factors of each of its business units.
Internally influenced by output values, wage rates,
labor productivity, capital (technology), and other
non-wage expenditures. While externally is
influenced by the level of economic growth,
inflation, unemployment and interest rates. Based on
the research of Afrida (2003) that the high and low
absorption of labor by the economic sector depends
on several factors such as output value, wage level,
education level (labor quality), working capital and
the number of industries. In line with the results of
the study of Esti R (2003) that the factors that
influence labor demand are industrial output,
working capital (investment), wage level and the
number of industries used by the sector. Based on
the results of previous research the author tried to
examine the factors that influence labor demand,
namely: industrial investment, number of industries,
wage level and GRDP.
2 THEORICAL FRAMEWORK
2.1 Effects of Investment Industrial Sector on
Labor Demand
In Keynes's macro theory, to decide whether an
investment will be carried out or not depends on the
comparison between the amount of expected profit
(expressed in percentage per unit time) on the one
hand and the cost of using funds / interest rates on
the other. This expected level of profit is called the
Marginal Efficiency of Capital / MEC (Boediono,
1986). In summary this concept can be described, if
the expected profit (MEC) is greater than the interest
rate, then the investment is carried out. If the MEC
is smaller than the interest rate, then the investment
should not be carried out and if the MEC = the
interest rate, then the investment may be carried out
and may not be in accordance with the decision of
the owner of the capital.
From the description above it is known that the
level of investment desired by investors is
determined by two things, namely the interest rate
that applies the MEC or investment function. This
MEC function / investment function shows the
relationship between the prevailing interest rate and
the level of investment expenditure desired by
investors.
Through the investment function curve there are
three things that need to be underlined about this
investment function, that is, first, the function has a
negative slope which means that the lower the
interest rate, the greater the investment expenditure
desired or planned by investors.
Second, in reality this investment function is
difficult to obtain because its position is very labile
and easily changed in a short period of time. The
volatility of the investment function can be
understood, because its position is very dependent
on the MEC values of the existing projects and that
the MEC is the profit expected by investors. Because
it is based on future expectations / expectations (if
on the basis of subjective calculations) where the
MEC of a project may change from day to day and
sensitive to changes in the socio-economic
conditions of a country. The existence of political
turmoil in an area, rumors of a devaluation, the issue
of foreign exchange control, and restrictions on
imports for example will directly be able to change
the subjective judgment of investors in a project. So
many factors influence the MEC, so the position of
investment functions will be very easy to change.
The volatility of the investment function is a
theoretical and Keynesian explanation of the fact
that in reality investment expenditure (I) shows
UNICEES 2018 - Unimed International Conference on Economics Education and Social Science
436

unpredictable up and down fluctuations over time.
This instability is a characteristic that distinguishes
investment from other aggregate demand elements
(C, G).
Third, what needs to be emphasized is the
relationship between Keynes's investment theory and
reality, especially regarding the issue of the
availability of investment funds. Keynesian theory is
based on the assumption that at the prevailing
interest rate, every investor can get any funds to
finance projects that are considered profitable to
implement. What limits the amount you want to
invest is only an assessment of MEC projects that
are open to him. In reality the opposite is often the
case with so many profitable projects, MEC rises but
it is difficult to obtain credit from banks for
example, resulting in realized investments being
smaller than the desired level of investment
(Boediono, 1986).
2.2 Effect of the Number of Large and Medium
Regency/City on Labor Demand
A company or industrial business is a unit (unit) of a
business that carries out economic activities, aimed
at producing goods or services. Squire in Kemala
(2006) argues that in general, the growth of business
units in a production sector in an area will increase
the number of workers.
Matz (1990) said, to determine the size of adding
or reducing the amount of labor carried out by
employers, then:
1) Employers will need a certain amount of money
to be obtained with the additional company, as
well as labor. If the number of outputs produced
by a larger number of companies will produce a
large output as well, so the more number of
companies that stand, the more likely there will
be an increase in production output.
2) The output value of a region estimates that
production will increase with the increase in the
number of companies producing the same goods.
By increasing the number of companies, it is
expected to increase the number of production,
so that the increase in the number of workers will
also increase because labor is needed in the
production process. Lestari (2011) argues that
the more the number of companies or business
units that stand, the more there will be an
increase in labor force, meaning that if a business
unit of an industry is added, then the demand for
labor will also increase.
2.3 Effect of Minimum Wages of Regency/City
on Labor Demand
Wages are an income as a reward from employers to
workers or workers for a job or service that has been
or has been done. Simanjuntak, (2001) says that
wages for employers can be seen as a burden
because the greater the wages paid to employees, the
smaller the proportion of profits for employers.
According to Kuncoro, 2002 (in Fitria, 2014), the
quantity of labor demanded will decrease as a result
of wage increases. If the wage level rises while the
prices of other inputs remain, then the price of labor
is relatively more expensive than other inputs. This
situation encourages employers to reduce the use of
labor that is relatively expensive with other inputs
whose relative prices are cheaper in order to
maintain maximum profits. Siringo-ringo (2012),
Providing wages is a reward / remuneration from the
company to its workers for the achievements and
services contributed in production activities. The
Effect of Minimum Wages on Labor Demand
Wages are an income as a reward from
employers to workers or workers for a job or service
that has been or has been done. Simanjuntak, (2001)
says that wages for employers can be seen as a
burden because the greater the wages paid to
employees, the smaller the proportion of profits for
employers.
2.4 Effect of GRDP on Labor Demand
The increase in GRDP is one of the most important
indicators in assessing the performance of an
economy, especially to carry out an analysis of the
results of economic development that has been
carried out by a country or region. The increase in
GRDP will drive other sectors so that from the
production side it will require a production
workforce. A general view states that increasing
GRDP is positively correlated with labor. Todaro
(2000) says that population growth and labor force
growth (which occurs after population growth) are
traditionally considered as one of the positive factors
that spur economic growth (GRDP). A larger
number of labor means that it will increase the
number of productive labor, while greater population
growth means increasing the size of its domestic
market.
Factor-Factor Affecting Labor Demand Food Beverages and Tobacco Industry of North Sumatra Province
437
3 RESEARCH METHOD
This study uses secondary data with time series data
types during the period 2014-2016. With the data
used sourced from the Central Statistics Agency.
The data required include the number of industrial
sector investments in rupiah units, the number of
food, beverage and tobacco industries in company
units, district / city minimum wages in rupiah units,
and the GRDP of constant prices in rupiah units in
North Sumatra Province.
The data analysis method used in this study is
quantitative with a panel data analysis model or
pooled data. Panel data is a combination of time
series data and time data (cross section). To
overcome the intercorrelations between the
independent variables which ultimately can lead to
the inappropriate regression estimation, the panel
data method is more appropriate to use. The data
used in this study are in the form of time series data
from 2014 to 2016 and a cross section consisting of
25 districts and 8 cities in North Sumatra Province.
The function model of the equation in this study are:
JTKMMT = 𝛽
+ 𝛽
INVSI
+ 𝛽
NLMM
+𝛽
MWRC
+ 𝛽
GRDP + ε
..(3.1)
4 ANALYSIS
4.1 Selection of models in data processing
In panel data processing, it is necessary to select the
most appropriate model between Common Effect
estimation models, Fixed Effect estimation models
and Random Effect estimation models. To choose
between the three estimation models there are
several tests that can be done, including:
4.1.1 Chow Test (F-statistical test)
This test is used to determine the most
appropriate model to be used between the Common
Effect estimation model or the Fixed Effect
estimation model, with the hypothesis:
H0: choose to use the CommonEffect
estimation model.
H1: choose to use the fixed effect
estimation model.
This hypothesis test can be done by comparing
F-statistics with F-tables. If F-statistics > F-table
then H0 is rejected which means the most
appropriate model to use is the Fixed Effect Model
and can also be done by considering the probability
value (Prob.) For F-statistics. If the value of the
Prob. F-statistic < 0.05 (determined at the beginning
as the level of significance or alpha) then the chosen
model is Fixed Effect Model, but if > 0.05 then the
chosen model is the Common Effect Model.
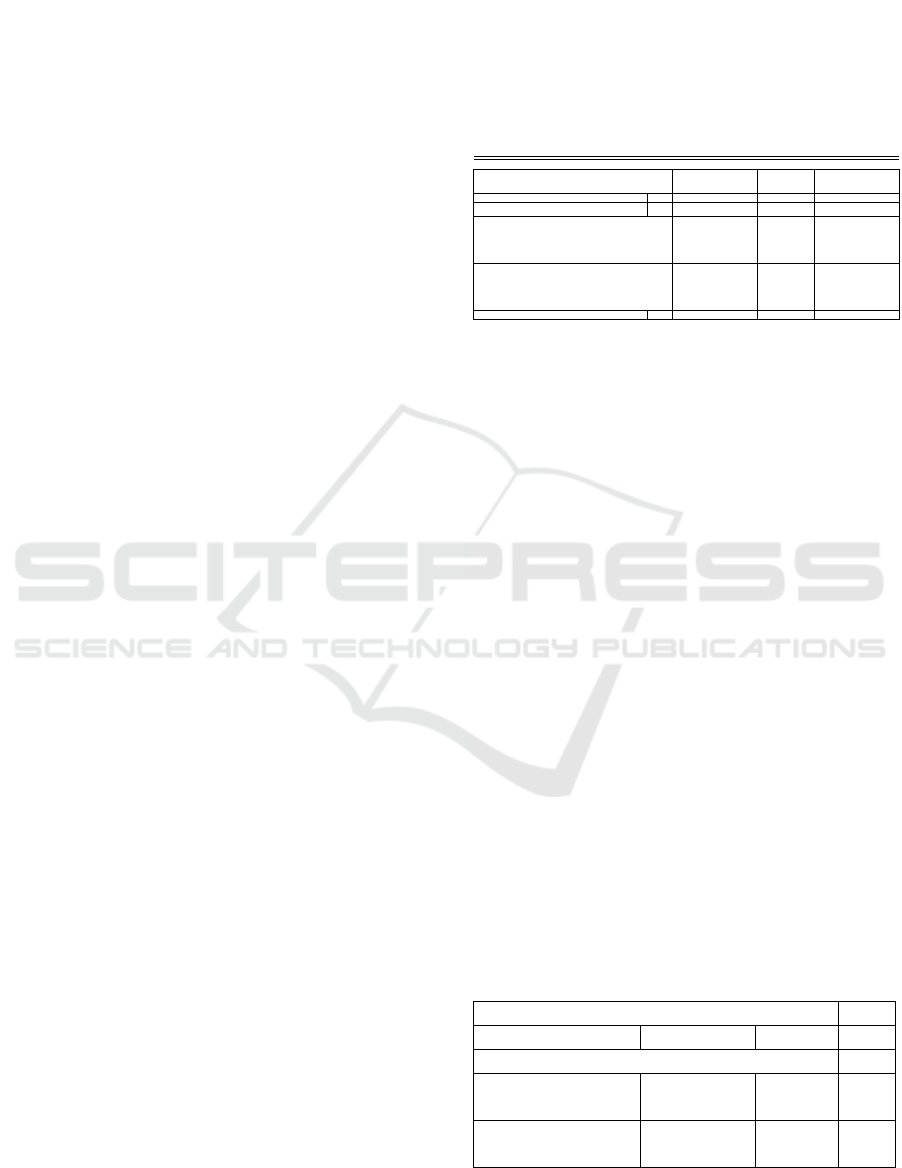
Table 1
Chow Test Results
Redundant Fixed Effects Tests
Equation: FEM
Test cross-section fixed effects
Effects Tes
t
Statistic d.f. Prob.
Cross-section F 9.508492
(32,62
) 0.0000
Cross-sectionChi-square
175.8478
72 32 0.0000
From Table 1, the F-statistic value is 9.508492
with the F-table value in df (32.62) α = 5% is
1.51520 so that the F-statistic value > F-table with a
probability of 0.0000 (< 0.05), so H1 statistics are
accepted and reject H0, according to the results of
this estimation the right model used is the estimation
model Fixed Effect Model.
4.1.2 Hausman Test
This Hausman test is used to select the model that
will be used between the Fixed Effect estimation
model or the Random Effect estimation model, with
the following hypothesis test:
H0: choose to use the Random Effect
estimation model.
H1: choose to use the FixedEffect
estimation model.
The Hausman test can be done by comparing
Chi-Square statistics with Chi-Square tables. If Chi-
Square statistics > Chi-Square table then H0 is
rejected which means the most appropriate model to
use is the Fixed Effect Model and can also be done
by considering the probability value (Prob.) For Chi-
Square statistics. If the value of the Prob. Chi-
Square statistic < 0.05 (determined at the beginning
as a significance level or alpha), the chosen model is
Fixed Effect Model, but if > 0.05 then the selected
model is Random Effect Model.
Table 2: Hausman Test Results
Correlated Random Effects - Hausman Tes
t
Equation: REM
Test cross-section random effects
Test Summar
y
Chi-Sq.
Statistic
Chi-Sq.
d.f. Prob.
Cross-section
rando
m
9.157344 4
0.
0673
UNICEES 2018 - Unimed International Conference on Economics Education and Social Science
438
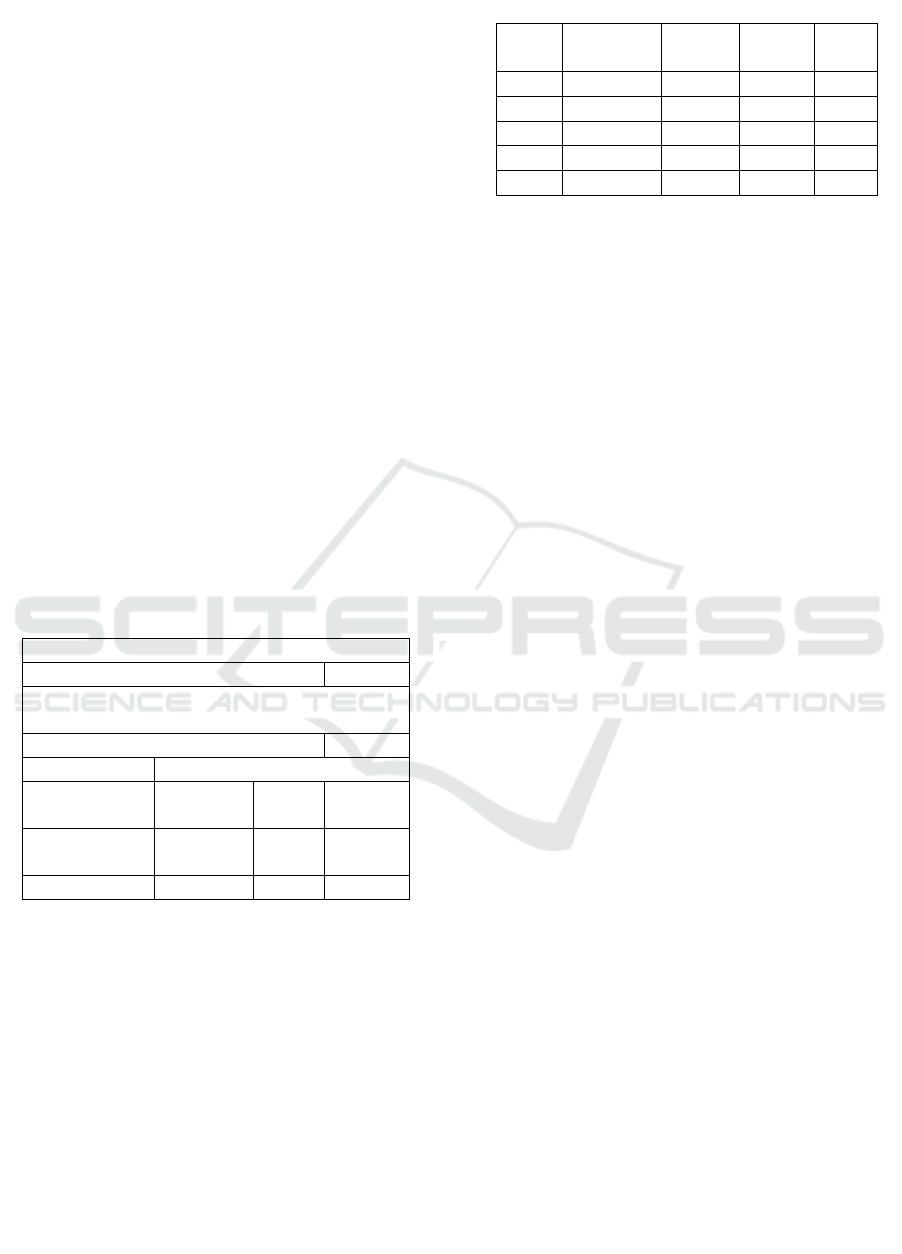
From Table 2 the statistical Chi-Square value is
9.157344 with the Chi-Square table at df (4) α = 5%
is 7.815 so the Chi-Square value is statistical > Chi-
Square table with a probability of 0.0673 ( > 0.05)
then H0 is accepted and H1 is rejected so the panel
data model used is the Random Effect Model.
From the results of the Chow Test and Hausman
Test different results were obtained then continued
with the Lagrange Multiplier Test.
4.1.3 Lagrange Multiplier Test
The Lagrange Multiplier Test is used to select the
model that will be used between the Random Effect
estimation model or the Common Effect estimation
model, with the following hypothesis test:
H0: choose to use the Common Effect
estimation model.
H1: choose to use the Random Effect
estimation model.
If the LM value is greater than the critical value
of Chi-Squares then H0 is rejected which means that
the right model for panel data regression is Random
Effect Model and vice versa, if the LM value is
smaller than the critical Chi-Squares value then the
null hypothesis is accepted which means the model
the right for panel data regression is the Common
Effect Model.
Table 3: Lagrange Multiplier Test Results
La
g
ran
g
e Multiplier Tests for Random Effects
N
ull h
y
potheses: No effects
Alternative hypotheses: Two-sided (Breusch-
Pa
g
an) and one-side
d
(all others) alternatives
Test H
y
pothesis
Cross-
section Time Both
Breusch-Pa
g
an 47.26726
0.41381
4 47.68107
(0.0004) (0.5200) (0.0000)
In Table 3 it can be seen that the value of the
Prob. Breusch-Pagan cross-section is 0.0004 ( <
0.05) so that H1 is statistically accepted and H0 is
rejected. Then the model used is the estimation
model of Random Effect.
4.2 Hypotesis Result
4.2.1 T-Test (Partial Test)
T-Test aims to determine the effect of the
independent variables of industrial sector
investment, number of industries, regency / city
minimum wages and GRDP in North Sumatra
Province.
Table 4: T-Statistical Result
Varia Coefficien
t
Std.
Erro
r
t-
Statistic Prob.
C 0.8850 1.2648 0.6997 0.4858
INVSI 0.1811 0.0831 2.1882 0.0311
N
LMM 0.7235 0.1493 4.8485 0.0000
MWRC -0.2470 0.1879 -1.3148 0.0191
GRDP 0.6282 0.1820 3.4513 0.0008
Table 4. is the result of testing the independent
variables, Investment Industry Sector, Number of
Large and Medium Manufacturing, Minimum Wage
of Regency/City, Gross Regional and Domestic
Product partially towards the demand labor in North
Sumatra Province in 2014 - 2016. This study uses α
= 5% or α = 0.05 .
If written in an equation, the result is:
JTKMMT
it
= 0,885050 + 0.181931INVS
it
+
0.724135JIMMT
it
-0,247051UMK
it
+
0.628250PDRB
it
+ ɛ
it
From these equations can be concluded as follows:
1. Constants of 0.885050 which means that if the
Investment variable, the number of industries,
MSEs and GRDP is zero, meaning that there is
no increase or decrease then the amount of labor
demand in North Sumatra Province is 0.885050.
2. Investment Variables have a t-statistic of
2.188233 and probability shows a value of
0.0311 which is smaller than the confidence level
α = 5% (0.0311 < 0.05) then this can prove that
the investment variable in the industrial sector
has a significant effect on the demand of North
Sumatra Province workers means H1 is accepted
and H0 is rejected. The investment variable
coefficient is 0.181931, which means that every
increase in investment by 1 percent will increase
labor demand by 0.181931 percent with the
assumption that number of large and medium
manufacturing, minimum wage of regency/city
and GRDP is considered to be zero, meaning
there is no increase or decrease. This is in line
with the opinion of Sukirno (2000) which states
that investment or investment can develop
businesses or add business units, with business
development will require a lot of labor. Thus the
addition of capital can reduce the problem of
unemployment. Also in line with the results of
Erviyanti's (2013) study that increasing
investment will also increase the amount of
employment.
3. Variable number of large and medium
manufacturing has a t-statistic of 4.848522 and
probability shows a value of 0.000 which is
smaller than the level of confidence α = 5%
Factor-Factor Affecting Labor Demand Food Beverages and Tobacco Industry of North Sumatra Province
439

(0.000 < 0.05) so this can prove that the variable
number of large and medium manufacturing has
a significant effect on the demand for Sumatra
Province labor North which means H1 is
accepted and H0 is rejected. The number of large
and medium manufacturing coefficients is
0.724130, which means that each increase in the
number of industries by 1 percent will increase
labor demand by 0.724130 percent with the
assumption that the investment variable,
minimum wage of regency/city and GRDP are
considered to be zero, meaning there is no
increase or decrease.
Minimum wage of regency/city variable has a t-
statistic of -1.314806 and probability shows a
value of 0.0191 which is smaller than the
confidence level α = 5% (0.0191 < 0.05) so this
can prove that Minimum wage of regency/city
variables have a significant effect on the demand
for labor in North Sumatra Province which
means H1 is accepted and H0 is rejected. The
Minimum wage of regency/city variable
coefficient is -0.247051, which means that every
increase in Minimum wage of regency/city of 1
percent will reduce labor demand by -0.247051
percent assuming the investment industry sector
variable, number of large and medium
manufacturing and GRDP are considered to be
zero, meaning there is no increase or decrease.
This is in line with the opinion of Kuncoro
(2001) that the quantity of labor demanded will
decrease as a result of rising wages. It is also in
line with Ehrenberg's (1998) research stating that
if there is an increase in the average wage level,
it will be followed by a decrease in the number
of workers requested.
4. GRDP variable has a t-statistic of 3.451348 and
probability shows a value of 0.0008 which is
smaller than the level of confidence α = 5%
(0.0008 < 0.05) then this can prove that the
GRDP variable has a significant effect on the
demand of North Sumatra Province workers
means H1 is accepted and H0 is rejected. The
GRDP variable coefficient is 0.628250, which
means that every increase in GRDP of 1 percent
will increase labor demand by 0.628250 percent
with the assumption that the investment industry
sector variable, number of large and medium
manufacturing and minimum wage of
regency/city is considered to be zero, meaning
that there is no increase or decrease. This is in
line with the opinion of Todaro (2000) which
states that population growth and labor force
growth are traditionally considered as one of the
positive factors that spur economic growth
(GRDP).
4.2.2 F-Statistics Test
To test whether the independent variable has a
simultaneous effect on the dependent variable, the F-
test is used by looking at probability and F-statistics.
The hypothesis is as follows:
H1: Investment industry sector, number of large and
medium manufacturing, Minimum wage of
regency/city, and GRDP together have a
significant effect on the demand labor in the
North Sumatra Province for the period 2014-
2016.
H0 : Investment industry sector, number of large and
medium manufacturing, Minimum wage of
regency/city, and GRDP does not affect the
demand for labor in the Province of North
Sumatra for the period 2014-2016.
The F-statistic Result value is 64,887 with a
probability of 0.0000 which means it is smaller than
α = 5%. The probability value of F-Statistics is
smaller than α = 5%, then H1 is accepted and H0 is
rejected so it can be concluded that together the :
Investment industry sector, number of large and
medium manufacturing, Minimum wage of
regency/city, and GRDP have a significant effect of
64,887 on the demand for provincial labor North
Sumatra 2014-2016 period.
4.2.3 Determination Coefficient Test Results (R2)
According to Gujarati and Porter (2012), the
coefficient of determination (R2) is used to measure
the goodness of fit of a regression line. This value
shows how much influence the independent
variables together can provide an explanation of the
dependent variable, where the coefficient of
determination (R2) is between 0 to 1 (0 ≤R2 ≤1).
The smaller R2 approaches 0, meaning that the
smaller the influence of the independent variable on
the dependent variable. Conversely, if R2
approaches 1, it indicates the stronger influence of
independent variables on the dependent variable.
Based on the results of the panel data analysis of
R Square the determination coefficient is 0.734. This
means that 73 percent of the demand labor in 33
(thirty three) regencies / cities in the Province of
North Sumatra in the 2014-2016 period can be
explained by Investment industry sector, number of
large and medium manufacturing, Minimum wage of
regency/city, and GRDP. While the remaining 27
percent is explained by other variables not examined
in this study.
UNICEES 2018 - Unimed International Conference on Economics Education and Social Science
440

5 RESULTS
Based on the results of the analysis that has been
carried out regarding the factors that affect the
demand for labor in the food, beverage and tobacco
industries in the Sumatran province, the following
conclusions are obtained:
a. Investment Industry Sector has a positive and
significant effect on the demand labor in North
Sumatra Province. This means that the increase
in investment in the industrial sector causes
demand for labor in the food, beverage and
tobacco industries to also increase.
b. The number of large and medium manufacturing
has a positive and significant effect on the
demand labor in North Sumatra Province. This
means that the increasing number of industries
causes the demand labor food, beverage and
tobacco industries to also increase.
c. Minimum Wages of regencycity have an effect
on negatively influencing the demand for labor
in North Sumatra Province. This means that the
increase in minimum wages causes the labor
demand food, beverage and tobacco industries to
decline and vice versa.
d. GRDP has a positive and significant effect on the
demand labor in North Sumatra Province. This
means that increasing GRDP causes the demand
labor food, beverage and tobacco industries will
also increase.
6 CONCLUSIONS
Based on the results of the testing and the following
discussion some suggestions were made regarding
the results of the study:
a. Private investment as a source of development
funding needs to be increased by increasing the
provision of facilities to encourage private
investment. The facilities in question are: clear
regional regulations on investment, ease of
investment, providing clear and accurate
information about investment opportunities,
making maps of regional potential, establishing
integrated service units in the regions to facilitate
the service of making business licenses and no
less important conducive climate for private
investment such as security.
b. District / city governments in North Sumatra
Province are expected to continue to increase
minimum wage of regency/city so that the
community can meet their needs.
c. In addition to investment, the number of large
and medium manufacturing, minimum wage of
regency/city and GRDP there are other factors
related to labor demand such as credit interest
rates, real GRDP, industrial output values and
others that might be used as additional variables
for further research.
REFERENCES
Afrida BR., (2003), Ekonomi Sumber Daya
Manusia. Jakarta: Ghalia Indonesia.
Boediono. (1986). Teori Pertumbuhan Ekonomi.
Balai penerbit Fakultas Ekonomi, UGM.
Yogyakarta.
Central Bureau of Statistics (BPS). North Sumatra in
Numbers. Year 2001 - 2017.
Fitria Riyan, Parapita. (2014). Effect of production
value and wage level on employment in the
food and beverage manufacturing industry in
Semarang district. Vol 1 no 1.
Freter, Pieter N. De. (2007). Analysis of the Effect
of Investment on Economic Development in
the Papua Province. Management Application
Journal. Vol. 5 No. 1.
Hani Handoko, (1985), Personnel and Human
Resource Management, Liberty, Yogyakarta.
Kemala, Eva Sari. (2006). Pengaruh Investasi dan
Upah Terhadap Kesempatan Kerja Pada
Industri Besar dan Menengah di Provinsi
Sumatera Selatan. Kajian Ekonomi, Vol. 5 No.
2, 2006.
Kuncoro Haryono, (2001), "Profit Sharing System
and Absorption Stability of Labor", Media
Economy, Volume 7, Number 2 pp. 165-168.
Lestari Sucitrawati. (2011). Effect of Inflation,
Investment, and Wage Levels on
Unemployment Rate in Bali Province. Bali:
Faculty of Economics, Udayana University.
Matz, Hanmen Usry. (1990). Akuntansi Biaya
Perencanaan dan Pengendalian l. Jakarta:
Erlangga.
Simanjuntak, Payaman J. (2001) Pengantar Ekonomi
Sumber Daya Manusia, Jakarta: Lembaga
Penerbit Fakultas Universitas Indonesia.
Simanjuntak, Payaman J. 1985. Pengantar Ekonomi
Sumber Daya Manusia. Jakarta: Penerbit FE
UI.
Sukirno, Sadono. (2000). Pengantar Teori Mikro
Ekonomi. Jakarta: PT. Raja Grafindo Persada.
Todaro, Michael P. 2000. Pembangunan Ekonomi di
Dunia Keriga. Erlangga Jakarta.
Factor-Factor Affecting Labor Demand Food Beverages and Tobacco Industry of North Sumatra Province
441
